POM II - Malignant Skin Neoplasms - Exam 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
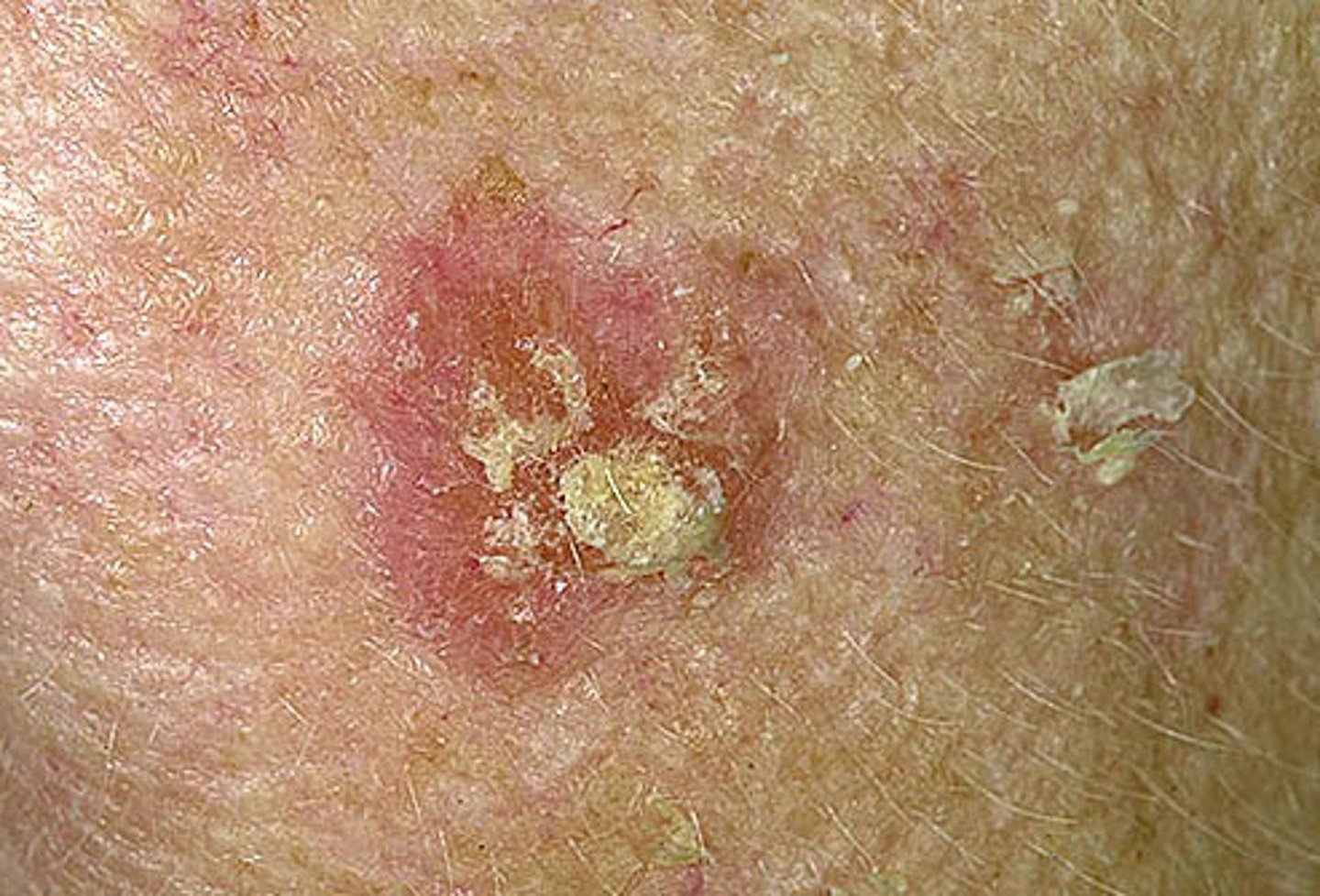
Actinic keratosis
UV light induced lesion considered precancerous (precursor of invasive SCC)
Actinic keratosis - Incidence
-1 per 1000 people per year
-higher in arkansas
Actinic keratosis - RF
-frequency increases with age and cumulative lifetime sun exposure
-proximity to equator and outdoor occupation can increase risks
-most common in caucasians
-more common in individuals who are immunosuppressed and in males
Actinic Keratosis - Presentation
-rough, scaly macules or patches on chronically sun-exposed skin (face, hands, ears, scalp, neck, chest, forearms, dorsal hands, shins, lips)
-feels like sandpaper
-SCC progression is around 10%
Actinic keratosis - Dx
-clinical dx
-biopsy if unsure
-prognosis is excellent if treated
Actinic keratosis - tx
-cryotherapy
-topicals: imiquimod or 5-FU, PDT tx
-prevention is best medicine - mineral SPF daily
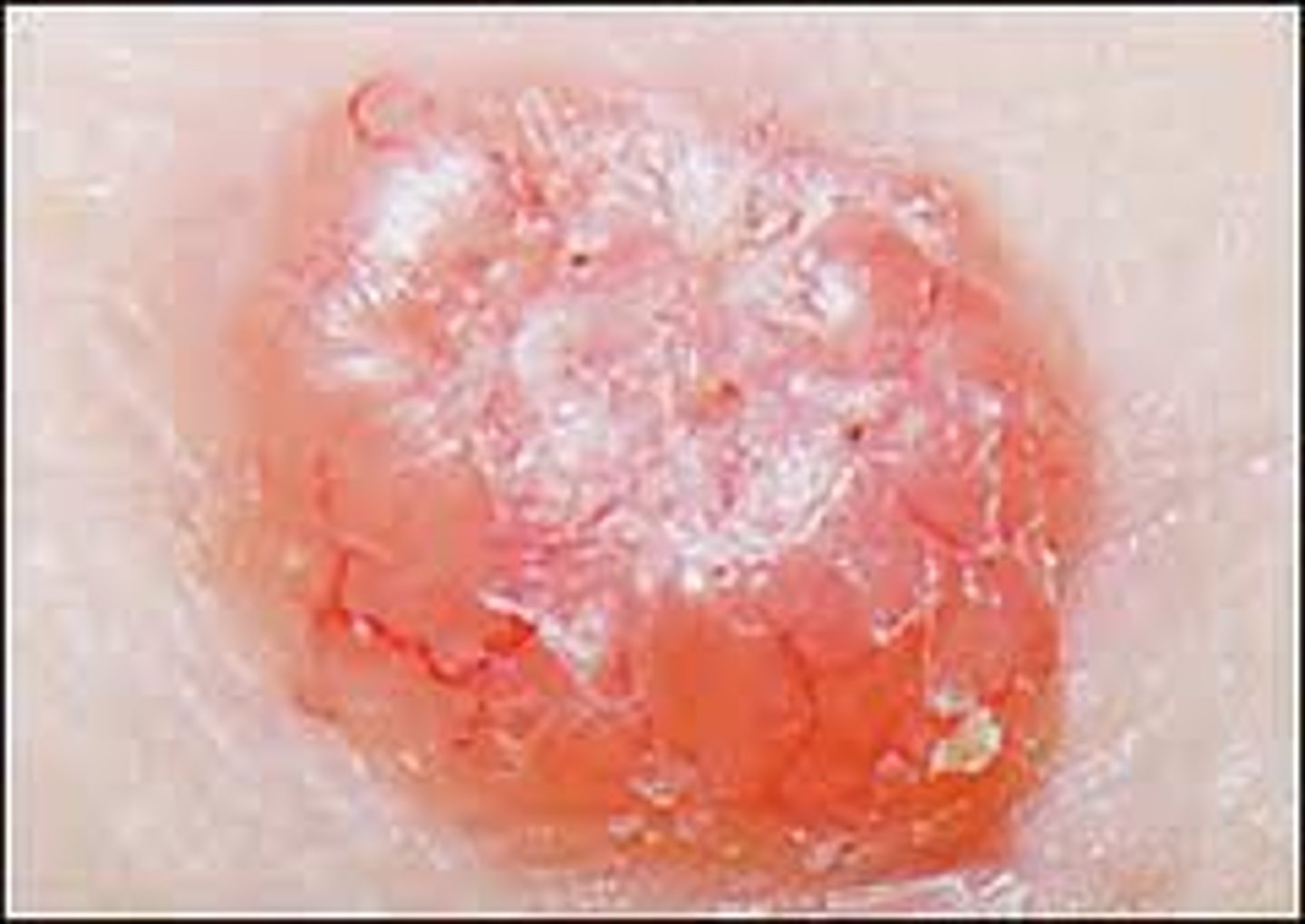
Basal Cell Carcinoma
-most common skin cancer and most common cancer in humans
-derived from basal layer of keratinocytes of epidermis
-slow growing, rarely mets
-several types: superficial, nodular, pigmented, etc
-nodular is most common
-2 million Americans per year
Basal Cell Carcinoma - RF
-chronic UV exposure, light phenotype
-can be seen at any age
-more common in men, but increasing incidence in women
Basal Cell Carcinoma - Presentation
-slowly enlarging lesion that does not heal and bleeds easily
-usually pink, pearly white, sometimes can be pigmented
-look for telangiectasia
-flattens centrally, rolled border
Basal Cell Carcinoma - Dx
-shave bx or punch if worried about melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma - Tx
-complete excision
-mohs in some cases
-sometimes treat with ED&C or imiquimod
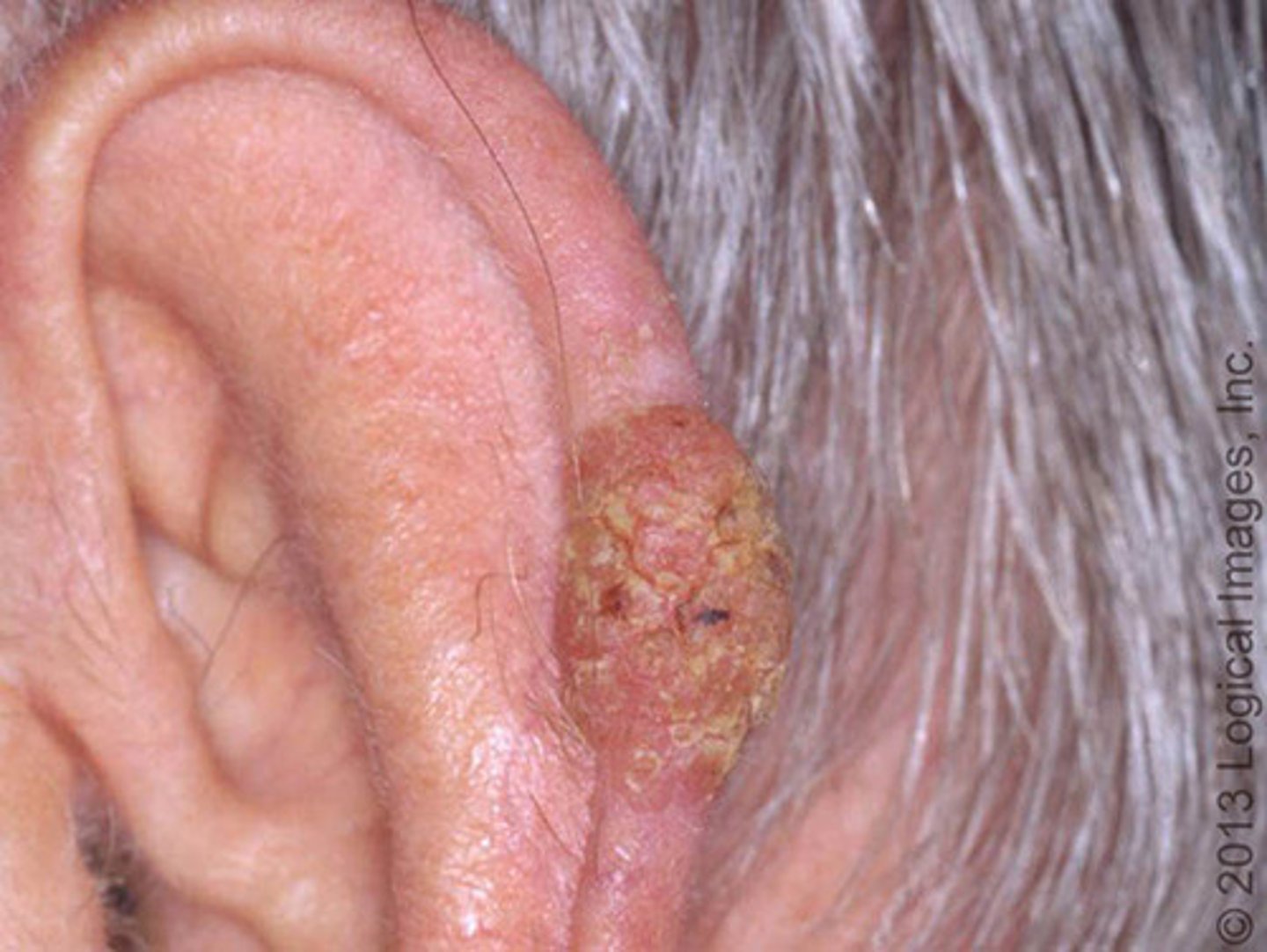
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-2nd most common skin cancer
-invasive, cutaneous malignancy arising from keratinocytes most commonly on face, head, neck, hands
-may develop from AKs
SCC - Incidence
-lifetime risk is 9-14% for men
-4-9% for women
SCC - RF
-sun exposure
-radiation
-tobacco use
-HPV
-age
-light phenotypes
SCC - Presentation
-tender, easily bleeding
-pink/red, crusted
-dome shape with yellow/white scale
-enlarging
SCC - Dx
-biopsy
-prognosis is good if caught early
-5 yr survival rate >90%, but does have metastatic potential, usually to lymph node
SCC - Tx
-excision
-mohs
Bowen's Disease
-squamous cell carcinoma in situ (meaning it is in the superficial layer (epidermis)) and not extending into the dermis
-potential for lateral spread
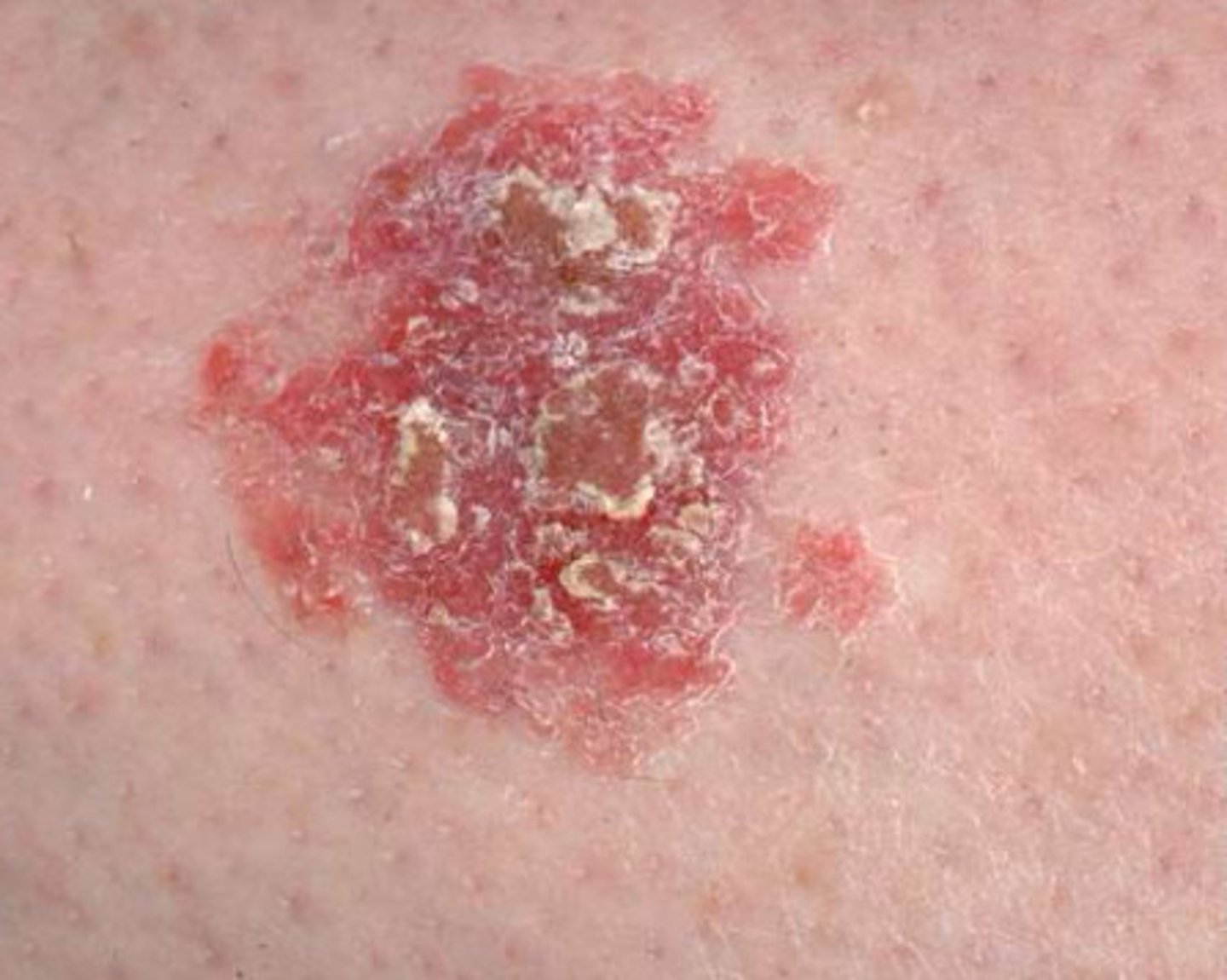
Bowen's Disease - Presentation
-scaly, red, well-demarcated plaque
-sun exposed areas
-good prognosis
Bowen's Disease - Tx
-appropriate to use creams here
-imiquimod 5x week x 6 wks
-5-FU
Paget's Disease
-rare breast cancer (1-3% in women over 55) occurring around the nipple
-redness, itching, crusting
-must biopsy
-tx: mastectomy but chemo and radiation may be appropriate
Melanoma
-aggressive malignant tumor of melanocytes of skin but sometimes in mucous membranes
-cause 80% of skin cancer deaths
-early detection and tx is key
-several types
-late dx carries poor prognosis
-mets to lymph nodes, liver, lungs, brain
-carries atypical features (ABCDE)
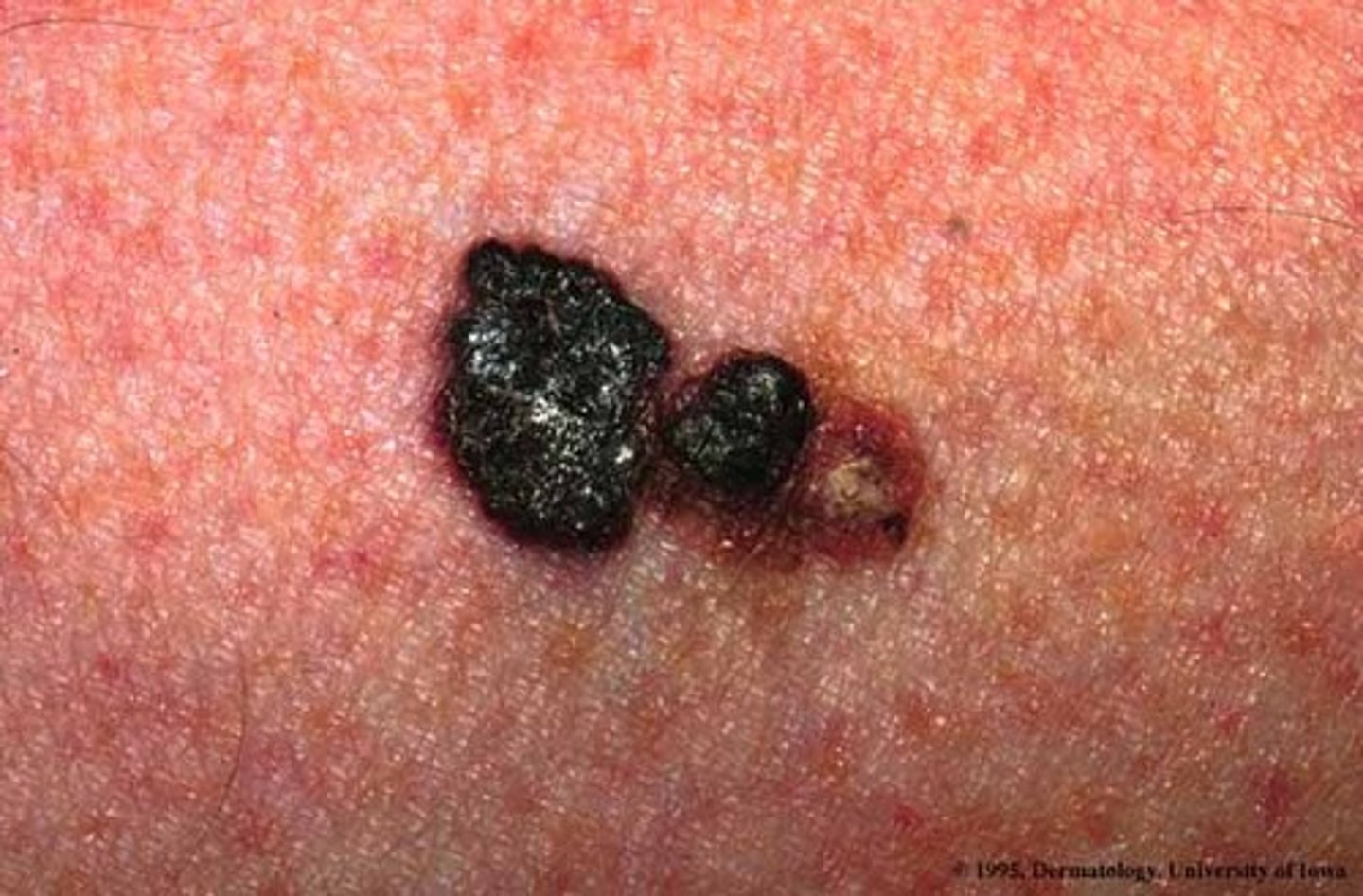
melanoma - etiology
-incompletely understood
-UV radiation is beleived to play a role
Melanoma - incidence
-# of new cases in US rising
-lifetime risk 2.1%
-lowest incidence but highest chance of death
Melanoma - RF
-family hx or prior personal hx of melanoma
-hx of severe or blistering sunburns
-changing nevi
-giant congenital nevus (over 20 cm)
-increasing age
-light phenotype
-multiplea typical nevi
Melanoma - Porgnosis
-depends on thickness and depth
-early dx and tx has favorable prognosis
-all melanomas get close follow up
-skin checks q3 months x 1 year, then q6 months x1 year then back to yearly unless multiple nevi, dysplastic nevi
Superficial Spreading Melanoma
-most common type of melanoma (70-80% of cases)
-typically on sun-exposed skin
-men: head, neck, trunk
-women: arms and legs
-UV radiation, genetics are RF
-remains thin for a while, then grows vertically
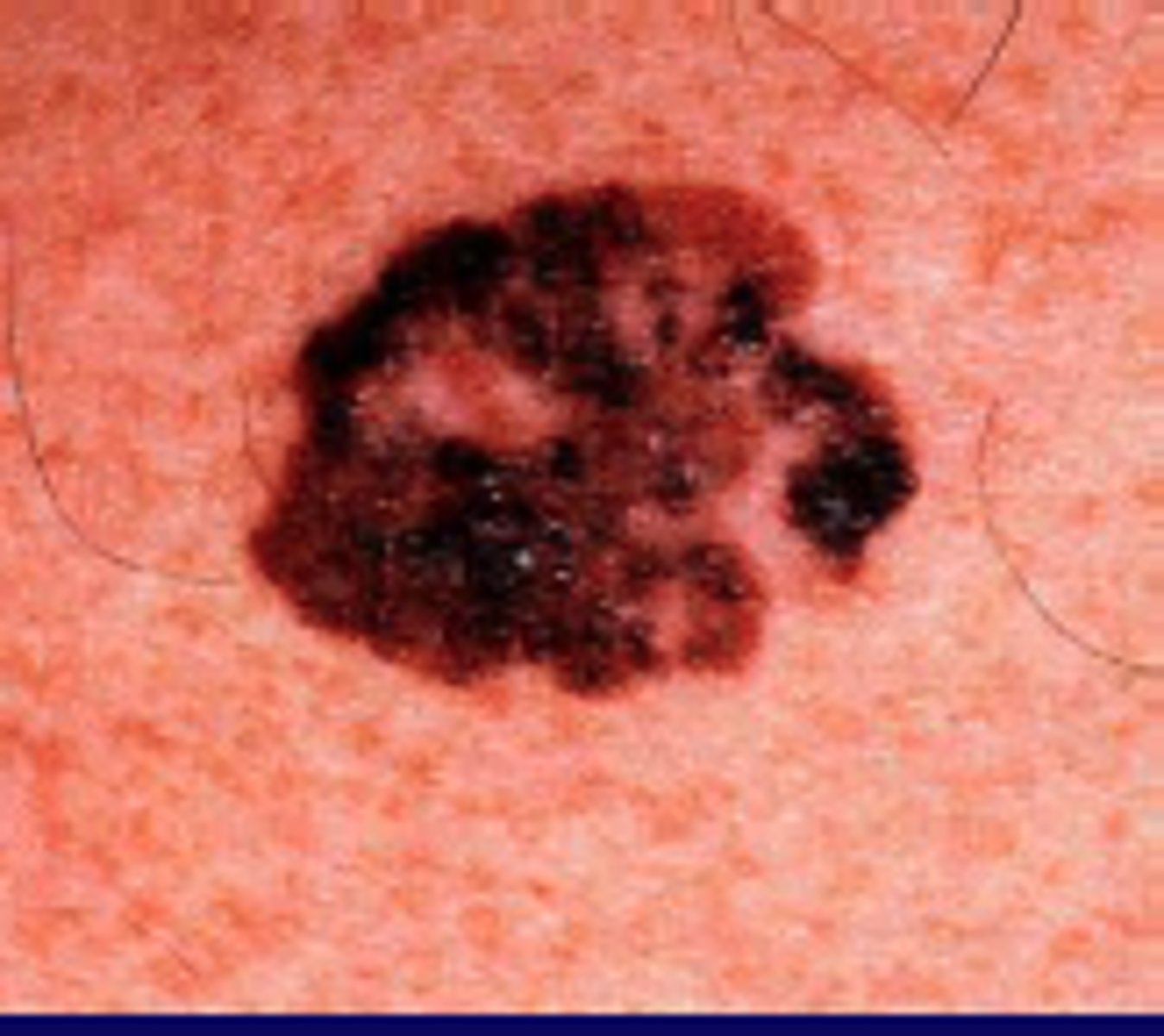
Superficial Spreading Melanoma - Presentation
-new dark spot >6 mm
-flat
-ABCDEs
Superficial Spreading Melanoma - Tx
-wide local excision with possible SLNB, slow mohs if face or if tissue is too tight
-prognosis: best when detected early
Nodular Melanoma
-most deadly form of melanoma
-incidence: accounts for 10-15% of all melanoma cases
-equal incidence in males and females
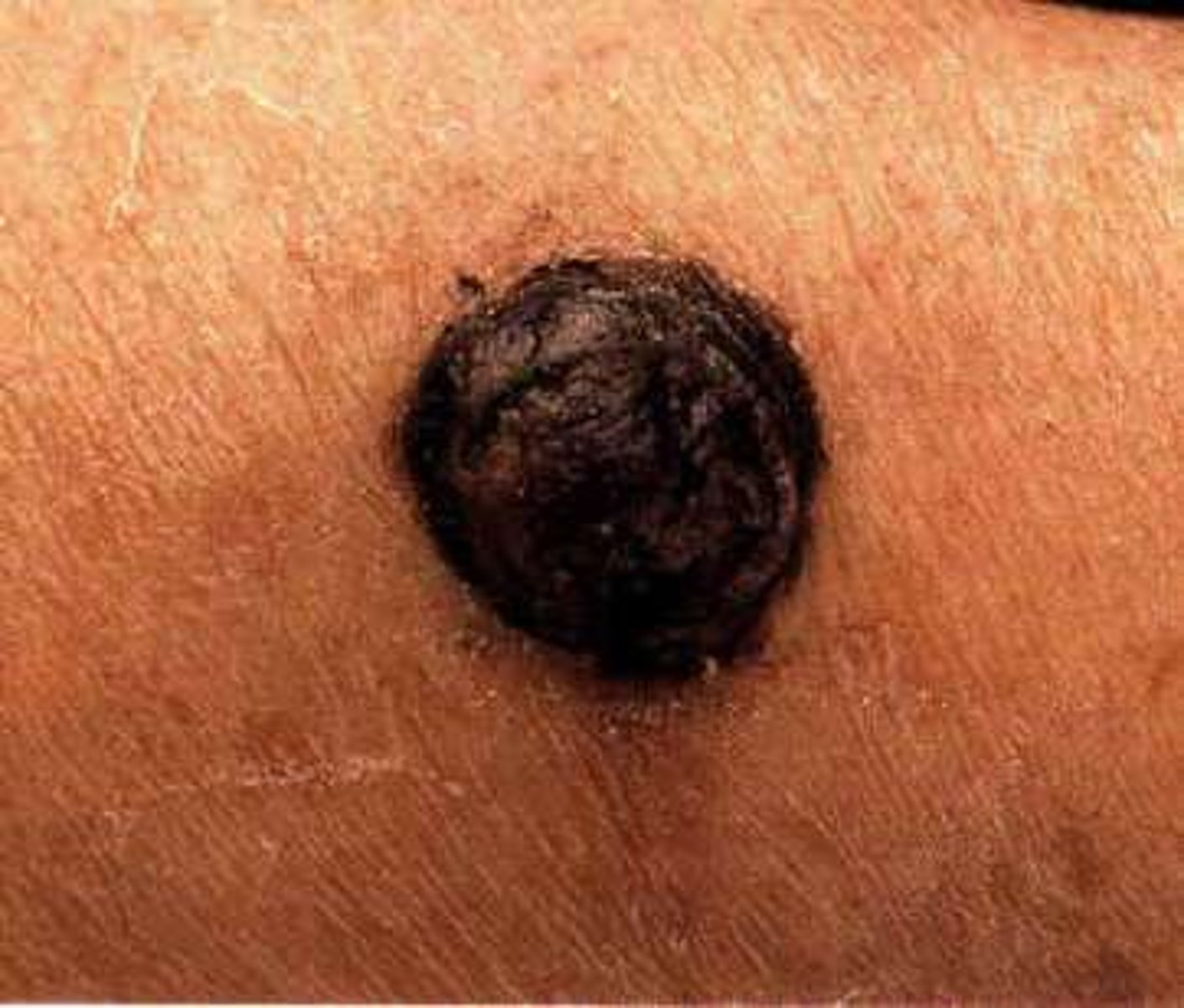
Nodular Melanoma - Presentation
-often found on extremities
-raised
-brown/black in color
-rapidly appearing and growing
Nodular Melanoma - prognosis
-early stage survival rate around 90%
-later stages survival rate around 50%
Nodular Melanoma - Tx
-same as other melanomas
-WLE vs mohs +/- SLNB
Lentigo maligna melanoma
-subtype of melanoma in situ
-enters a vertical growth phase and invades the dermis
-RF: UV exposure, usually seen in older people
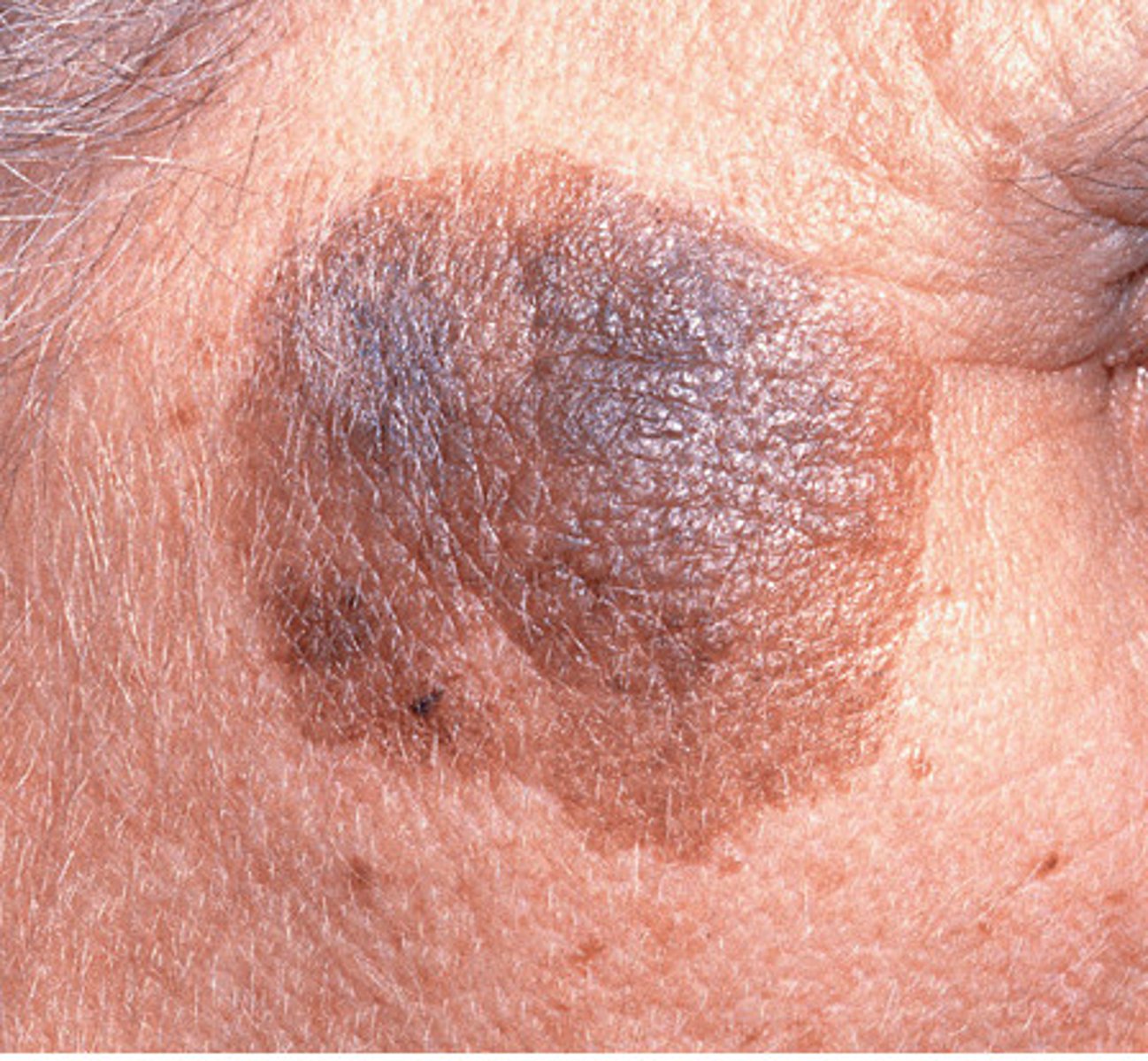
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma - Incidence
-about 80% of melanoma in situ cases
-accounts for 5-10% of all melanomas
-males and females equally at ris
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma - Presentation
-develop over several years on sun exposed skin - face, neck, arms
-flat and irregularly outlined
-may look grey
-sometimes the only diagnostic clue is that it is darker than surrounding lentigines
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma - Dx
-dermoscopy, biopsy
-if large or in cosmetically sensitive area, multiple smaller biopsies may be considered
-alternating skin exams with another provider
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma - Prognosis and tx
-prognosis: best of all melanoma types
-tx: complete surgical excision (mohs, SLNB)
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
subtype of melanoma that occurs on acral surfaces (palms, soles, subungual areas)
Acral lentiginous melanoma - incidence
-accounts for 5% of melanoma cases
-males > females, usually older adults
-most common melanoma in asians and african americans
-least common in caucasians
Acral Lentiginous melanoma - RF
-unknown, typically occurs in minimally sun exposed areas and in patients of all phenotypes
Acral Lentiginous melanoma - presentation
-most commonly found on LE (78%)
-black, variegated brown, multicolored, irregularly shaped papule, macule, patch
-nail apparatus: Hutchinson's sign
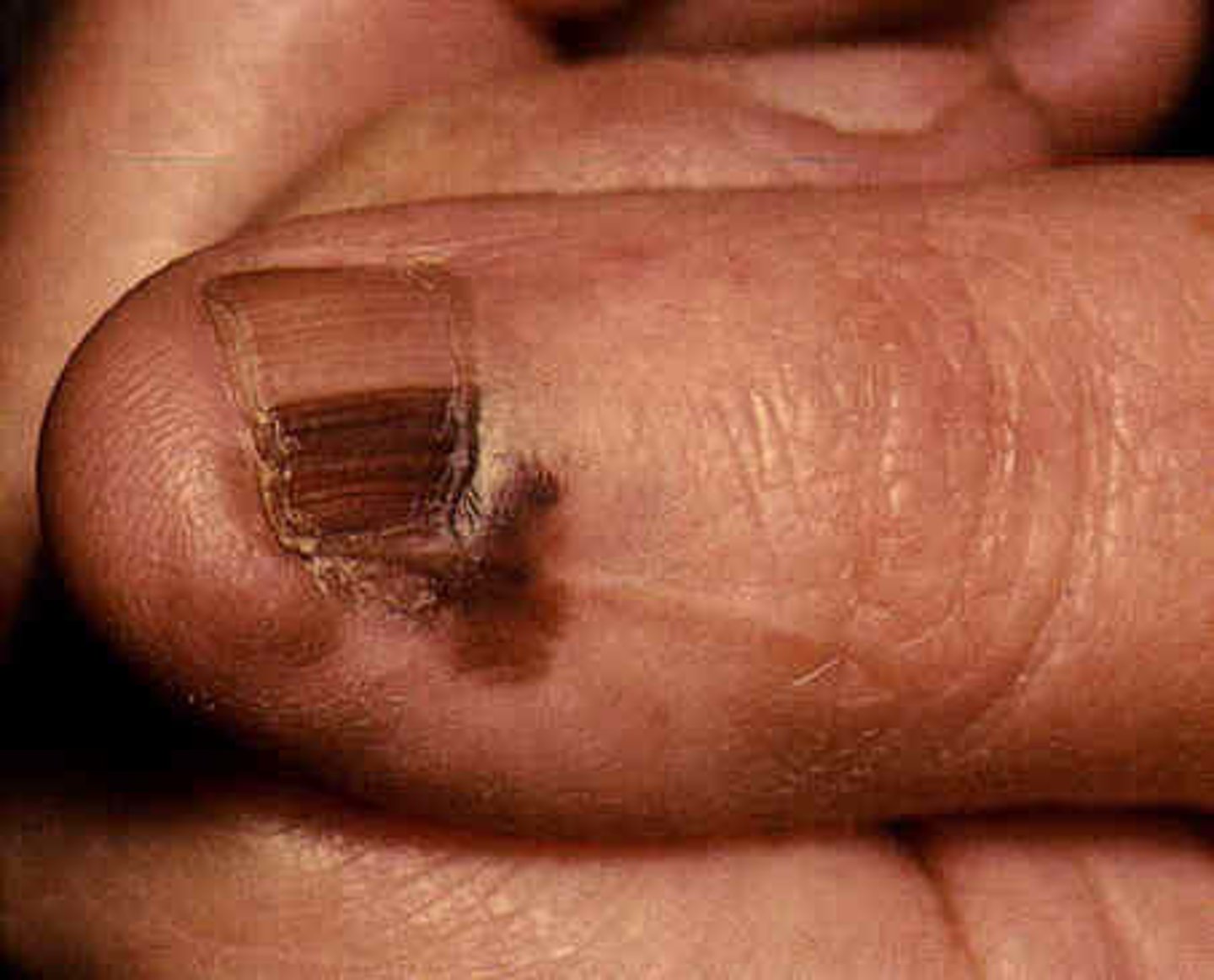
Acral Lentiginous melanoma - dx
-dermoscopy: parallel ridges
-nails: brown band that extends the length of nail that are homogenous in color and regular in pattern indicate benign lesion
-if irregular --> malignant lesion
-biopsy!
excise, immunotherapy
what is the tx for acral lentiginous melanoma?
Dysplastic Nevus
-melanocytic proliferation showing atypia and sharing some features of melanoma
-controversial d/t a lack of consensus on how it is defined and what it represents biologically (mild mod or severe)
-believed to correlate with the overall number of melanocytic lesions in an individual and are thought to confer a 4-15 fold increased risk of melanoma