EAB 3002: EXAM 2 REVIEW
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Fixed Ratio 15
A student earns a token after correctly completing every 15 math problems. This is an example of what type of reinforcement schedule?
Example of an interval schedule of reinforcement:
Benjamin receives a reward for the first time he asks a question after 15 minutes have passed.
Fixed interval 15
A baker checks the oven every 15 minutes to see if the bread is ready. Reinforcement (bread being done) only occurs at the end of the 15-min interval.
It generates more resistance to extinction than fixed interval schedules with the same average interval.
How does a Variable Interval (VI) schedule affect resistance to extinction compared to a Fixed Interval (FI) schedule?
Variable Interval
Which schedule is represented by a steady and uniform pattern of responses?
Reinforcement is delivered after a varying number of responses, based on an average.
What characterizes a variable ratio (VR) schedule?
To establish a new behavior quickly.
When is continuous reinforcement most appropriate to use?
Steady and constant response rate without pauses.
What is the typical response pattern under a variable ratio (VR) schedule of reinforcement?
The number of responses or time intervals between reinforcements.
In a variable schedule of reinforcement, what changes?
Daniel has 2 minutes to answer a question correctly before the reinforcement is no longer available.
A scenario in which limited hold contingency is in place:
fixed interval
Which schedule shows a scallop pattern where responding pauses after reinforcement and accelerates as the interval ends?
A response ratio that is too high to sustain behavior.
The cause of ratio strain in reinforcement schedules:
Schedules of Reinforcement Graphs
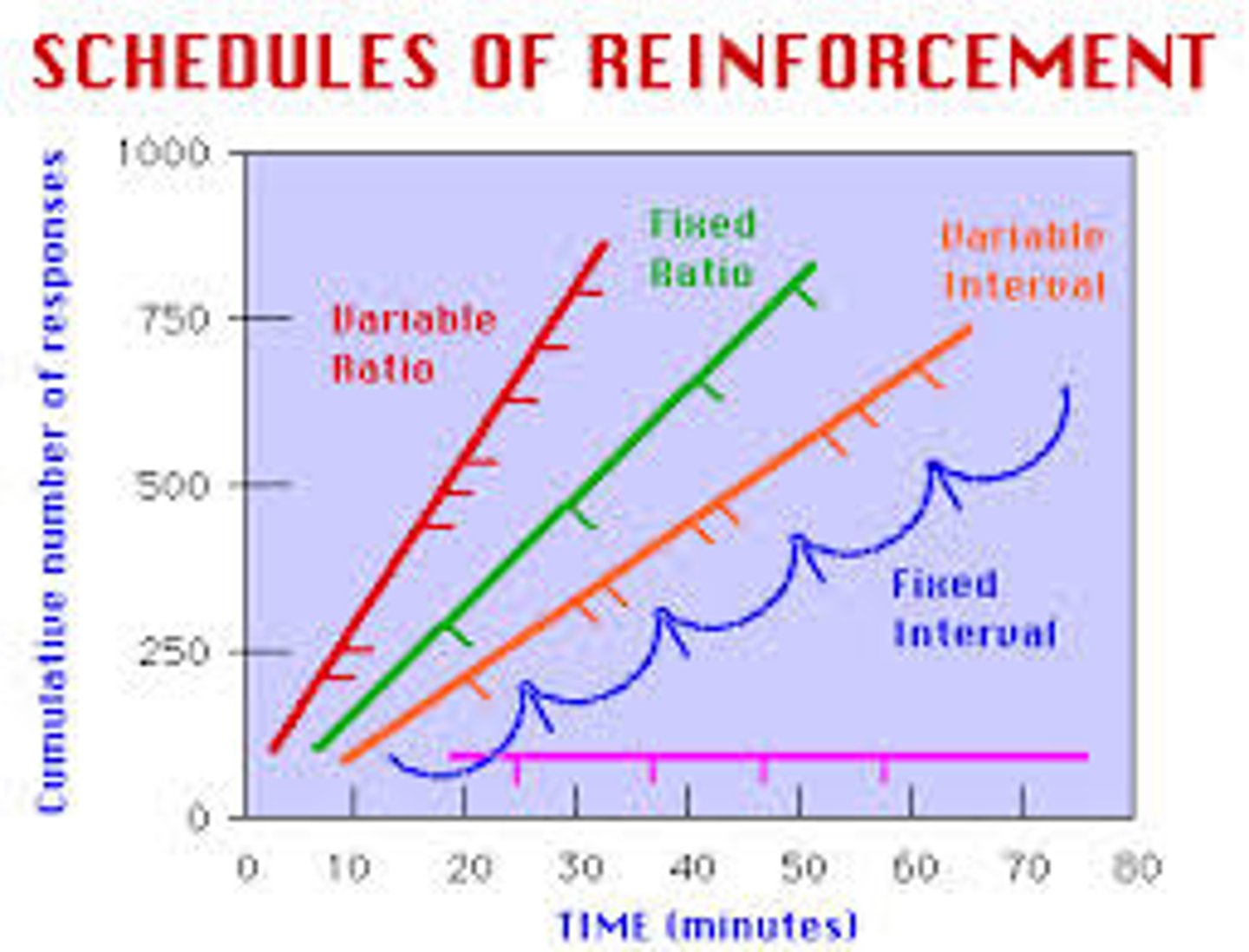
A vending machine dispensing a snack every time money is inserted.
Example of continuous reinforcement:
is more likely to occur.
(The SD signals that the reinforcement is available if a specific behavior occurs.)
When an SD is present the behavior:
is less likely to occur. ( S-Delta signals extinction or no reinforcement.)
When an S-Delta is present the behavior:
A change in behavior that occurs when either an SD or S-Delta is presented.
Stimulus control:
Fatima asks her grandmother for sweets when she is at home but does not ask when visiting her aunt, as she never gives her sweets.
Which of the following best illustrates stimulus control?
a. Emily checks her emails every 30 minutes regardless of the time of day.
b. Fatima asks her grandmother for sweets when she is at home but does not ask when visiting her aunt, as she never gives her sweets.
c. When shown a triangle and asked, "what's this," Isaac typically responds with different names of shapes.
d. Javier goes for a run every morning at 6 AM.
Calls all adult males "daddy," event those who are not their father.
Generalization is evident when a child:
A pigeon is trained to peck a red key for food, and then a green key is introduced gradually, starting very dim and becoming brighter with no reinforcement.
Which of the following scenarios best demonstrates errorless discrimination in a multiple schedule of reinforcement?
A. A pigeon is trained to peck a red key for food, and then a green key is introduced gradually, starting very dim and becoming brighter with no reinforcement.
B. A dog is taught to sit when given a command, but initially the command is given inconsistently until the behavior is learned.
C. A student practices spelling words and receives feedback only when a word is spelled incorrectly.
D. A child learns to raise their hand in class only when the teacher gives a subtle nod, and the nod is gradually introduced.
A visual representation that shows the relationship between response probability and changes in a stimulus.
What is a generalization gradient?
b. A green traffic light and the word "walk" sets the occasion for pedestrians to cross a street.
Which of the following best exemplifies a discriminative stimulus (SD)?
a. The sound of thunder during a rain storm
b. A green traffic light and the word "walk" sets the occasion for pedestrians to cross a street.
c. A red apple falling from a tree
d. A stop sign on a quiet road
Differential reinforcement
A student receives praise for raising their hand in math class, but not history class. Which type of reinforcement does this demonstrate?
reinforcing a response in one situation and withholding reinforcement in another
How is discrimination taught?
They signal which schedule of reinforcement or extinction is in effect.
What role do the antecedent stimuli play in a multiple schedule?
c. reinforcer, SD
Each response in a chain procedure produces a stimulus change that simultaneously serves as a ..... for the response that produced it and as a ....... for the next response in the chain.
a. extinction, SD
b. reinforcer, punishment
c. reinforcer, SD
d. SD, punishment
c. stimulus generalization. (a behavior learned in one setting occurs in the presence of new but similar stimuli.)
A dog is trained to sit when it sees its owner's red chair. Later, the dog begins to sit whenever it sees any red chair, even outside the home. This is an example of:
a. discrimination
b. extinction
c. stimulus generalization
d. not enough information, as we do not know how the dog was trained.
b. it reinforces behavior by chance, not by deliberate contingencies.
In the context of superstitious behavior, what role does coincidental reinforcement play?
a. it creates a deliberate pattern of behavior under strict control.
b. it reinforces behavior by chance, not by deliberate contingencies.
c. it directly trains new behaviors through observation.
d. it causes behavior to decrease over time.
Introducing a delay between the target behavior and the reinforcement, such as using a differential reinforcement of other behavior (DRO) procedure.
Most effective method for reducing superstitious behavior in an animal:
a. Introducing a delay between the target behavior and the reinforcement, such as using a differential reinforcement of other behavior (DRO) procedure.
b. reinforcing the behavior more consistently to avoid confusion.
c. increasing the rate of reinforcement during the extinction period.
d. using a fixed ratio schedule instead of a variable interval schedule.
a. reinforcement is given, and behavior increases.
In differential reinforcement, what happens in the presence of an SD?
a. reinforcement is given, and behavior increases.
b. reinforcement is withheld, and behavior decreases.
c. punishment is applied, and behavior is suppressed.
d. reinforcement is given inconsistently, leading to variable responses.
A child asks their dad for sweets and receives them, but their mom does not give them sweets when asked. Therefore, the child only asks dad for sweets.
Example of differential response:
c. a baby looking at an object, then looking at the mother's facial expression, and reaching for the object if the expression is joyful.
Which of the following is an example of a response chain in social referencing?
a. a teacher asking a question and a student answering immediately
b. a mother smiling when a baby reaches for an object.
c. a baby looking at an object, then looking at the mother's facial expression, and reaching for the object if the expression is joyful.
d. a child reaching for a toy when their friend reaches for it first.
a. the subject selects the matching comparison stimulus across novel samples.
Which outcome indicates successful training in a matching-to-sample procedure?
a. the subject selects the matching comparison stimulus across novel samples.
b. the subject only responds when reinforcement is available.
c. the subject ignores all comparison stimuli presented.
d. the subject consistently chooses the non-matching stimulus.
c. an increase in response rate in one component when the rate of reinforcement decreases in another component.
In the context of multiple schedule, behavioral contrast refers to:
a. the consistent application of reinforcement across all components.
b. a change in behavior due to a new discriminative stimulus.
c. an increase in response rate in one component when the rate of reinforcement decreases in another component.
d. an unchanging response rate regardless of reinforcement changes.
c. escape
A child runs out of class each time he is presented with a math worksheet. He is able to skip out on math and this leads to an increase in his behavior. This behavior is most likely maintained by the function of:
a. access to tangible items
b. automatic reinforcement
c. escape
d. attention
c. social negative punishment
A child says a curse word during dinner and their mom takes their phone away for a day. They are less likely to curse at the dinner table afterwards. This behavior is most likely influenced by:
a. automatic negative punishment
b. social positive punishment
c. social negative punishment
d. negative reinforcement
c. automatic negative reinforcement
Omar's alarm clock goes off and begins to make a loud, beeping noise. Omar reaches over and slaps the snooze button to shut it off for 5 minutes. In the future, he is more likely to hit the snooze button when his alarm goes off. This behavior is likely maintained by:
a. social positive reinforcement
b. social negative reinforcement
c. automatic negative reinforcement
c. social positive reinforcement
Carlo shares one of his toys with a sibling and his parent praises him. He's more likely to share his toys with his siblings in the future. This behavior is likely under the influence of:
a. automatic positive reinforcement
b. automatic negative reinforcement
c. social positive reinforcement
d. social negative reinforcement
d. tangible
Every time Isabella's mom is on the phone, she begins to shout and her mom gives her a cookie. What is most likely the function of this behavior?
a. attention
b. escape
c. automatic reinforcement
d. tangible
c. is delivered after a response sometimes, but not always.
Intermittent reinforcement:
a. is delivered after every response.
b. is delivered after every two responses.
c. is delivered after a response sometimes, but not always.
d. is delivered after ANY response.
b. a teacher provides praise to a student after an unpredictable number of responses, but on average, it happens after every 5 responses.
Which of the following is an example of a variable ratio (VR) schedule of reinforcement?
a. a teacher provides praise to a student at the end of each 5 minute interval.
b. a teacher provides praise to a student after an unpredictable number of responses, but on average, it happens after every 5 responses.
c. a teacher provides praise after every response from a student
d. a teacher changes from reinforcing each response to reinforcing every SECOND response from the student.
fixed-interval schedule
Lee rewards himself with a segment off a chocolate every 30 minutes, during a 2 hour
study session, he rewarded himself with 4 pieces of the chocolate bar. What schedule of reinforcement is Lee using for his own behavior?
a. is a stimulus that is removed after a response and increases the likelihood of that behavior
occurring again in the future.
A negative reinforcer:
a. is a stimulus that is removed after a response and increases the likelihood of that behavior
occurring again in the future.
b. Is a stimulus that is added after a response and decreases the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future.
c. is another term for punishment
d. is another term for extinction
c. A behavior which prevents the onset of an aversive stimulus.
Which of the following describes an avoidance response?
a. A consequence that prevents the likeliness of a behavior occurring again in the future.
b. A behavior that was once reinforced but is now being punished.
c. A behavior which prevents the onset of an aversive stimulus.
d. A behavior that occurs after an aversive stimulus has been introduced
c. Blinding sunlight that shines in through your windshield while driving in the morning.
Which is an example of a primary aversive stimulus?
a. getting an F on an exam
b. a speeding ticket
c. Blinding sunlight that shines in through your windshield while driving in the morning.
d. your grandmother scolding you with a disappointed tone.
Negative reinforcement involves the removal of a stimulus that results in an increase of that behavior in the future while punishment involves the addition/removal of a stimulus that decreases the behavior in the future.
The difference between negative reinforcement and punishment:
b. preference
The tendency to select one option more frequently than others when there are multiple sources of reinforcement available refers to which term?
a. choice
b. preference
c. discrimination