Lecture 21: Ganglion Cell Parallel Paths
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What cell type provides the only output from the retina to the brain?
Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs).
Their axons form the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract.
What is the primary pathway that conveys image-forming visual information?
The retino-geniculate-cortical pathway:
Retina → LGN (lateral geniculate nucleus) → V1 (primary visual cortex).
What proportion of retinal ganglion cells project to the LGN?
~90%
Which cortical area receives input from the LGN and is essential for reconstructing visual images?
Primary visual cortex (V1) in the occipital lobe.
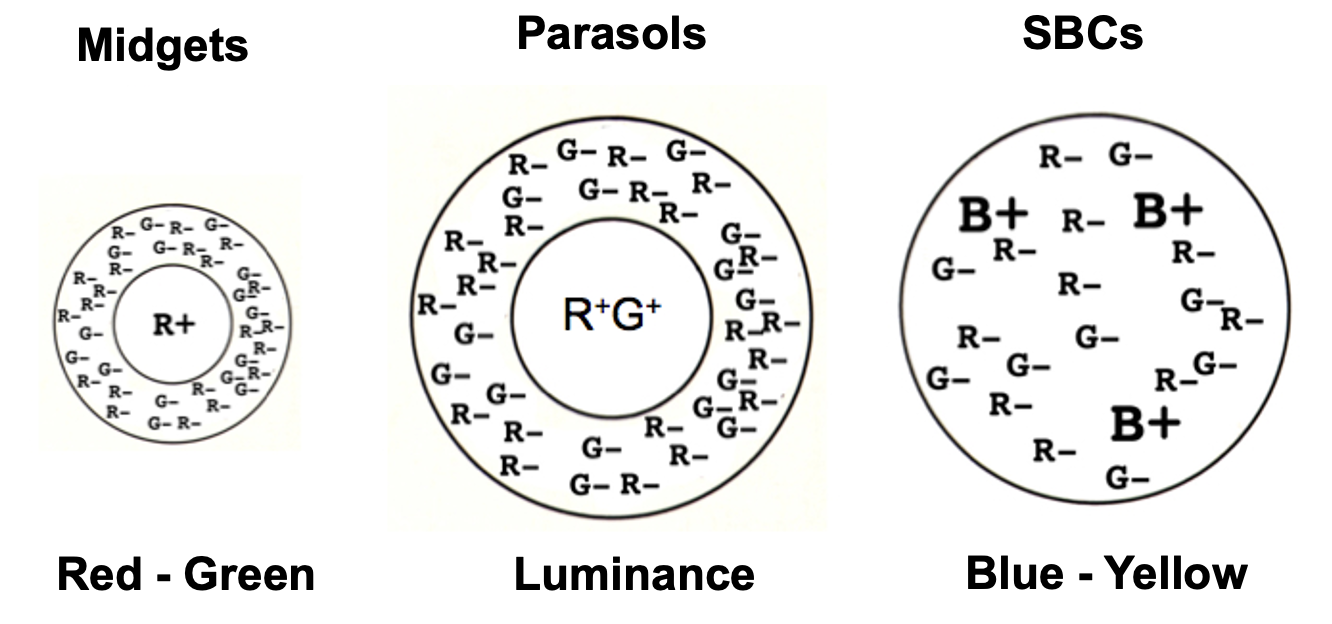
What are the three dominant retinal ganglion cell types in the image-forming pathway?
Midget (MG), Parasol (P), and Small bistratified (SBC) ganglion cells.
What defines the midget (MG) ganglion cell circuit?
One cone → one midget bipolar cell → one midget ganglion cell
Separate ON + OFF pathways (IMB = ON, FMB = OFF)
Dominant in the fovea
High spatial acuity (fine detail)
How do parasol ganglion cells differ from midget ganglion cells?
Receive input from diffuse bipolar cells (DBs)
Each DB contacts multiple cones (promiscuous)
Lower spatial resolution, higher temporal sensitivity
~1 in 10 ganglion cells
What is special about small bistratified ganglion cells?
Stratify in both ON and OFF layers of the IPL
Contribute to image formation
Important for color processing (classically S-cone pathways)
Which bipolar cells connect to which ganglion cells?
Midget bipolar → midget ganglion
Diffuse bipolar → parasol ganglion
Specialized bipolar → small bistratified ganglion
What are the key structural and opsin differences between rods and cones?
Rods: long outer segment → higher photon capture; all express the same opsin (rhodopsin)
Cones: shorter outer segment; 3 cone types = 3 cone opsins (each cone expresses only one opsin)
Why are rods more sensitive to light than cones?
Rods: express slow GRK1 → large, long-lasting hyperpolarization from a single photon
High sensitivity
Cones: express fast GRK7 → small, brief response to a single photon
Faster, less sensitive responses
Which cone types are found in the very center of the fovea (foveola)?
L (red) and M (green) cones only
No S (blue) cones + no rods
What determines a cone’s spectral sensitivity?
The cone opsin it expresses
Each cone expresses one opsin
Three cone opsins → three cone types
Are cones “blue, green, and red detectors”?
No.
Each cone responds to a range of wavelengths
Color perception comes from comparing activity across cone types, not from a single cone
What wavelength range is visible to humans?
Approximately 400–700 nm
~400 nm = blue
~700 nm = red
Why do most animals detect light near ~500 nm?
It penetrates air and water best
It is the dominant wavelength reaching Earth’s surface
It can reach depths of ~30 m in water
What is ‘normalized absorbance’?
Probability that a photoreceptor will capture photons
2 things about photon capture curves?
Curves are identical (bc shape is result of chromophore, 11-cis retinal, used by all PRs) except for location of their maximums (wavelength of light at which PR most easily captures photons).
Curves are broad. Range of almost 200 nm —> extensive overlap.
What are the two independent variables that determine a cone’s response?
Wavelength of light and intensity (number of photons). Both affect photon capture probability.
Why can’t a single cone tell wavelength (color) from intensity?
More hyperpolarization could mean longer-preferred wavelength or higher intensity. This ambiguity is resolved only by comparing responses across different cone types (chromatic contrast).
How does opsin structure determine which wavelengths a cone absorbs best?
Opsin holds 11-cis retinal via a protonated Schiff base.
Amino acids around this site control how easily the positive charge on retinal becomes delocalized, which tunes the wavelength range absorbed.
How does charge delocalization shift wavelength sensitivity in cones?
Less delocalization (more stable Schiff base) → absorbs shorter wavelengths (S-cones).
S-cone opsin (blue)
More delocalization (less stable Schiff base) → absorbs longer wavelengths (L-cones).
L-cone opsin (red)
Why is red–green color blindness so common in men?
L (red) and M (green) opsin genes are on the X chromosome, sit side-by-side (tandem array) + genes are identical over long sequences in exons AND introns, making them prone to recombination errors during meiosis → ~10% of men have red–green color blindness.
Only 5 amino acids account for their 30 nm shift in absorption of light.
Why is blue (S-cone) color blindness rare?
The S-cone opsin gene is on chromosome 7 + looks nothing like genes around it → ~1 in 50,000 people (men and women).
2 midget circuity facts:
Each red or green cone of fovea contacts a pair of midget bipolar cells.
Horizontal cells grab input from several red + green cones + synapse w/ cone terminals to form RF surrounds of bipolar cells.
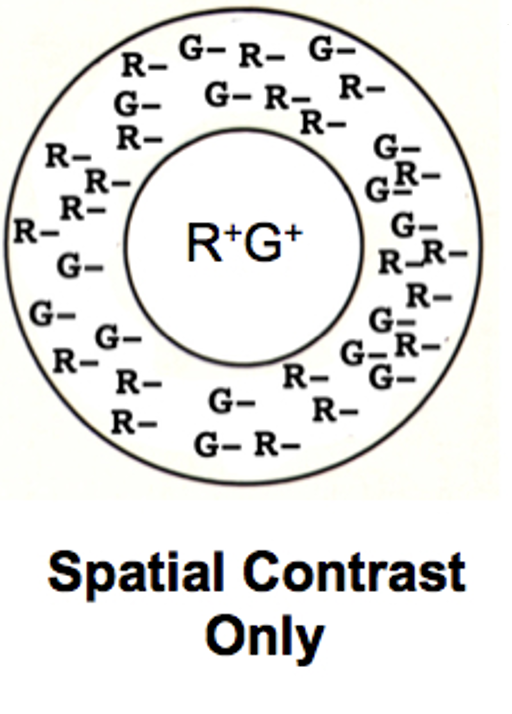
What is spatial contrast in midget ganglion cells?
A center–surround receptive field where the center is ON and the surround is OFF (or vice versa), encoding luminance differences across space.
How does adding cone type information create chromatic contrast?
The center is driven by a single cone type (either L or M), while the surround is a mixture of L + M cones, enabling color (red–green) opponency.
Why do midget ganglion cells support red–green color vision?
Because their center comes from one cone (L or M) via a single midget bipolar cell, and their surround pools both L and M cones through horizontal cells → L vs M comparison.
Midget ganglion cells do double duty: their center–surround organization gives spatial (luminance) contrast, and single-cone centers with mixed-cone surrounds give chromatic (red–green) contrast.
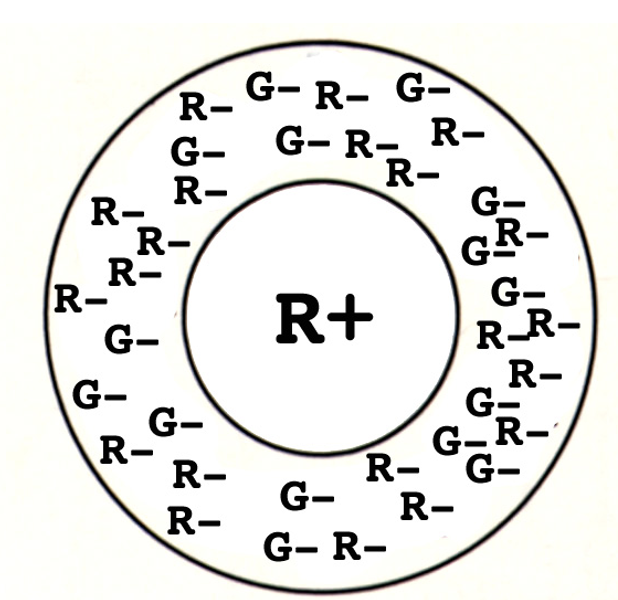
What kind of receptive field do small bistratified ganglion cells have?
S (blue) cones form synapses w/ blue bipolar cells (ON).
Blue bipolar cell (ON) + OFF diffuse bipolar cell form synapses w/ small bistratified ganglion cells.
Results in receptive field w/ no surround. Center-only response that is ON for blue + OFF for red/green.
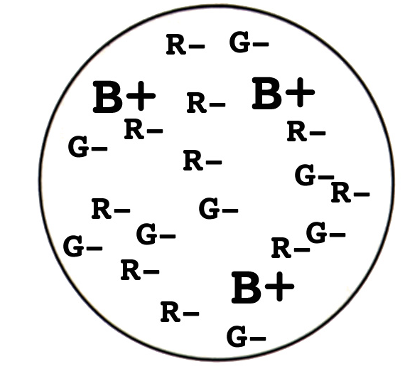
Why do parasol ganglion cells have spatial contrast but no chromatic contrast?
Parasol ganglion cells receive pooled L + M cone input via diffuse bipolar cells in both center and surround, giving opposite-sign center–surround (spatial contrast) but canceling color differences (no chromatic contrast).
How is the Inner Plexiform Layer (IPL) organized with respect to ON vs OFF bipolar cells?
The IPL is split into two halves:
OFF bipolar cells synapse in the outer IPL
ON bipolar cells synapse in the inner IPL
What is the difference between midget bipolar cells and diffuse bipolar cells?
Midget bipolar cells contact one cone only (L or M)
Diffuse bipolar cells contact multiple cones (L + M ± S)
What do FMB and IMB stand for?
FMB = OFF Foveal Midget Bipolar cell
IMB = ON Input Midget Bipolar cell
Which bipolar cell type contacts only rods?
Rod bipolar cells (RB) contact only rods and project to the ON layer of the IPL.
Draw receptive fields for midgets, parasols, and SBC
Why are rods much more sensitive to light than cones?
A single photon hyperpolarizes a rod (~1 mV); cones need ~50 photons for the same effect
Rod phototransduction has stronger amplification
Rhodopsin stays active longer than cone opsins
Rod GRK-1 is slow → rhodopsin activates more transducins
Cones use GRK-7, which shuts opsin off faster → lower sensitivity
What does it mean that rods converge onto rod bipolar cells + why does it matter?
Many rods → one rod bipolar cell (high convergence)
All rod bipolar cells are ON (express mGluR6)
Result: very high sensitivity (can detect very few photons)
Trade-off: poor spatial acuity due to signal pooling
What is the high-sensitivity rod pathway + how does rod input reach ganglion cells?
Rods → rod bipolar cells (RBs) only
Rod bipolar cells are all ON (express mGluR6)
RBs depolarize A-II amacrine cells
A-II amacrines:
Excite ON bipolar axons via electrical (gap junction) synapses
Inhibit OFF bipolar axons via glycinergic chemical synapses
Result: very high sensitivity (single/few photons detected), routed into both ON and OFF ganglion cell pathways