BIOLOGY TISSUES AN CELL CYCLE
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous
4 General Types of Tissues
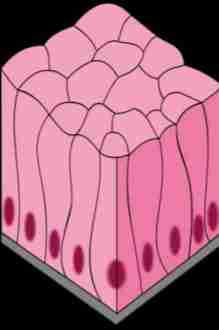
Epithelial Tissues
consists of sheet of cells that cover organisms and their organs
Epithelial Tissues
Mouth, gut, lungs, Heart, Blood vessels
Squamous, Columnar, Cuboidal, Ciliated
Epithelial cell can vary in shape
Simple Squamous Epithelium
One layer of thin cells Ex. Kidney, lungs, heart, etc
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
One layer of cube-shape cells Ex. Kidney tubules, etc
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Made up of more than one layer of cells Ex. Linings of esophagus, mouth,
vagina, and anus
Simple Columnar Epithelium
One layer elongated cells Ex. Digestive Tract
Connective Tissues
Tissue that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body
ligaments
binds bone to bone
tendons
bins muscle to bone
collagen
a structural protein, makes up the 3 types of connective tissues
Collagenous, Reticular, Elastic
3 types of connective tissues
Collagenous Connective Tissue
(formed by type I collagen) Ex. Dense regular connective tissues in
tendons
Reticular Connective Tissue
(formed by type III collagen) Ex. Supporting framework of hematopoietic
Elastic Connective Tissue
(formed by type II collagen) Ex. Commonly found in trachea and bronchi
Muscular Tissues
your body form is mostly shaped by
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
3 different kinds of muscular tissues
Voluntary
Those that can be controlled by the nervous system
Involuntary
beyond the control of the nervous system
Skeletal muscles
made up of very long, cylindrical, and
multi-nucleated cells capable of quick and forceful
contractions – usually voluntary
Cardiac muscles
composed of elongated branched
individual cells. Capable of involuntary, vigorous, and
rhythmic contractions
Smooth muscles
collections of cells that do not show
cross striations – not subject to voluntary control. Ex,
digestive tube
Nervous Tissues
is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities. It stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning.
Sensory Neurons, Motor Neurons
two different group of nervous
tissues
Sensory Neurons
Carry information obtained from
the interior of the body and the
environment to the Central
Nervous System (CNS)
Motor Neurons
Carry impulses from the CNS to the
effector organs commanded by
these centers
Meristematic or Embryonic, Non-Meristematic or Permanent
two general types of Plant tissue
Meristematic or Embryonic Tissues
located at the tips of roots and shoots of plants, growing points of plants (one of the 2)
Apical, Intercalary, Lateral
3 different kinds based on
location
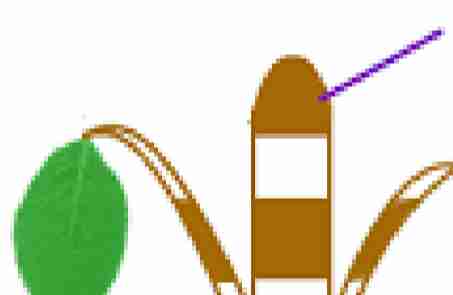
Apical meristems
found at the tips of shoots and
roots
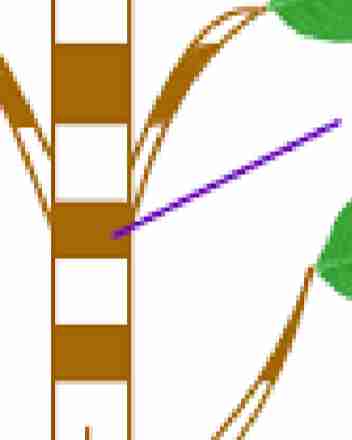
Intercalary meristems
found at the vicinity of nodes which
occurs at intervals along stems
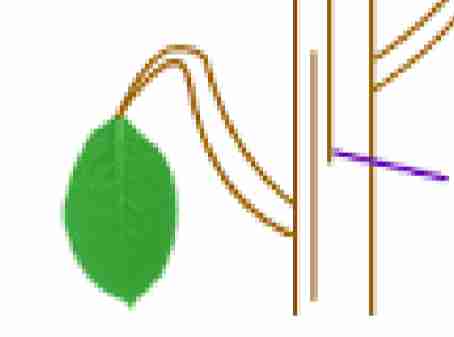
Lateral meristems
increase the girth or diameter of
plants
Dermal, Fundamental, Vascular
the three general kinds of non-
meristematic tissues
Dermal Tissues
the outer layer of cells that form a protective covering (Plant)
Epidermis
protecting outer layer of
non-woody plant and young
woody plants.
Periderm
found in older woody plants as
part of secondary growth
Periderm
replaces the epidermis to form
cork and woody stems in roots
Fundamental Tissues
functions for photosynthesis, storage, and support
Parenchyma cells
Soft parts of apple consists of, secretes liquids
Collenchyma cells
allows plant to
grow upward in a crowded plants, for support
Sclerenchyma cells
Shells of nuts and stones of
fruits consists of
Vascular Tissues
transports water, minerals, and sugars to different parts of the plant
Xylem
transport
nutrients from
roots going
upwards
Phloem
transport
nutrients downward
Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis
Three main stages of Cell cycle
Regulatory Proteins
are responsible for regulating the cell cycle
Internal Regulators
proteins found inside the cell.
Ex. Cell Growth hormones
External Regulators
proteins that respond to
events outside the cell
Ex. Growth hormones and
Wound healing hormones
Proliferation of Cancer
A diminishing loss of control in the cell cycle
leads to the
Metastasis
process of spreading Cancer Cells
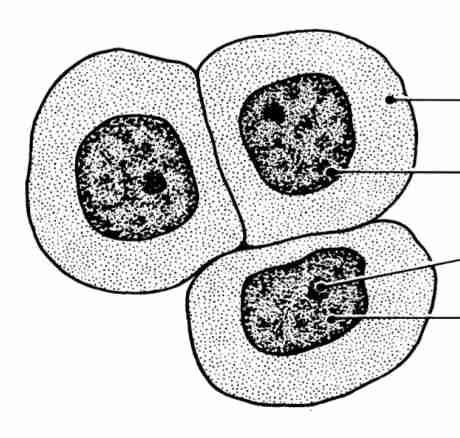
Normal
Large cytoplasm, single nucleus, and nucleolus, fine chromatin
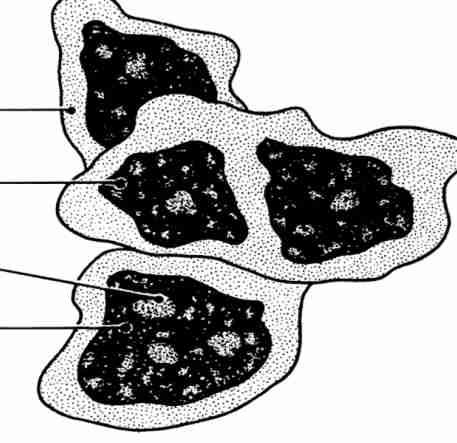
Cancer
Small cytoplasm, multiple nuclei and large nucleolus, coarse chromatin
Apoptosis
natural cell
death
Necrosis
cell
death cause by
external factors
Gap 1 stage, Synthesis stage, Gap 2 stage
Interphase (3) stages
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Mitosis (4)
Gap 1
Growth stage
Synthesis stage
DNA synthesis
Gap 2 stage
growth and preparation for mitosis
Mitosis
cell division stage (not cytokinesis)
Prophase
Nuclear envelope
starts to disintegrate
and nucleolus
disappears
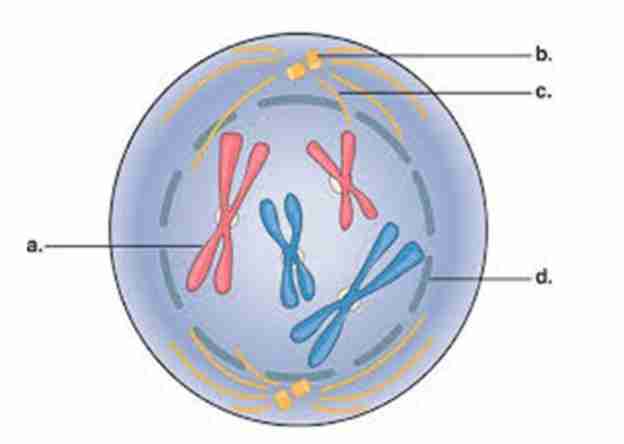
Metaphase
Spindle fibers are
fully developed and
the chromosomes
align at the
equatorial plate
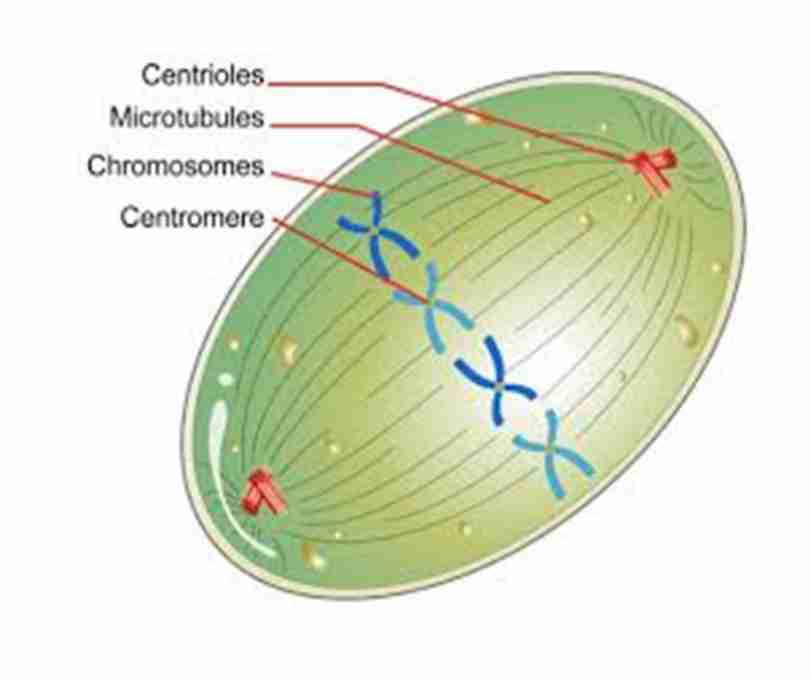
Anaphase
Separation of
chromosomes, Spindle fibers lengthen
and elongate the cell
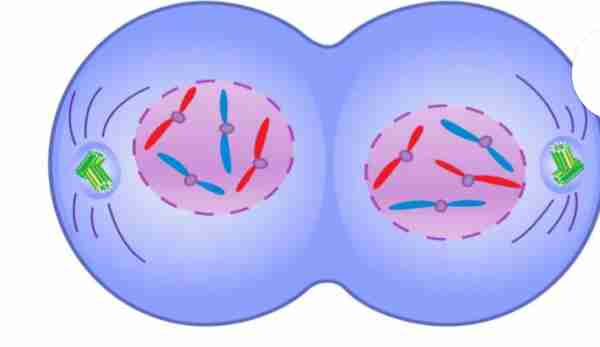
Telophase
complete sets of
chromosomes are
cordoned off into new
distinct nuclei of the
daughter cells. Nuclear envelope and
nucleolus starts to
reappear
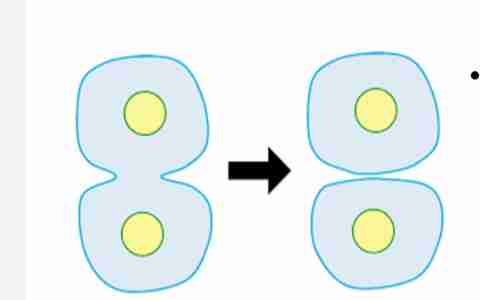
Cytokinesis
Completes the full stage
of cell cycle. Occurs when the
cytoplasm from the
original cell divides and
forms two new cells
Meiosis
another process of cell division that takes place in sexually mature
organisms
Meiosis
It is a process that results in the
reduction of chromosome number
from diploid to haploid in the egg cell
and sperm cell
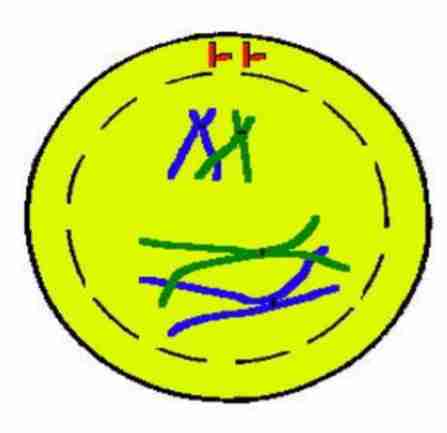
Prophase I
Nuclear membrane and
nucleolus starts to
disappear. Each chromosome is
composed of two sister
chromatids. Crossing over takes
place between two non-
sister chromatids
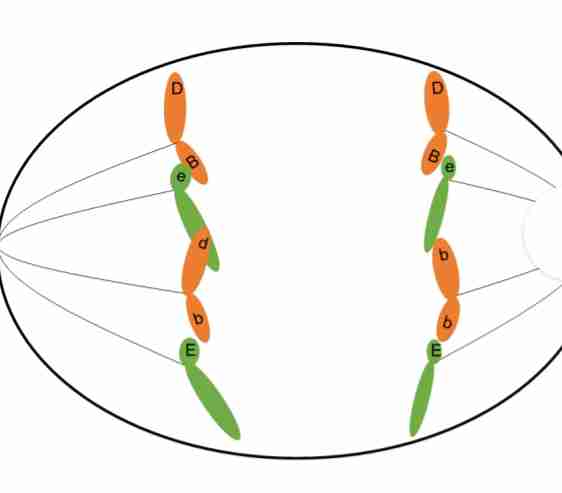
Metaphase I
Paired homologous
chromosomes are
moved by the spindle
fibers to the equator of
the cell
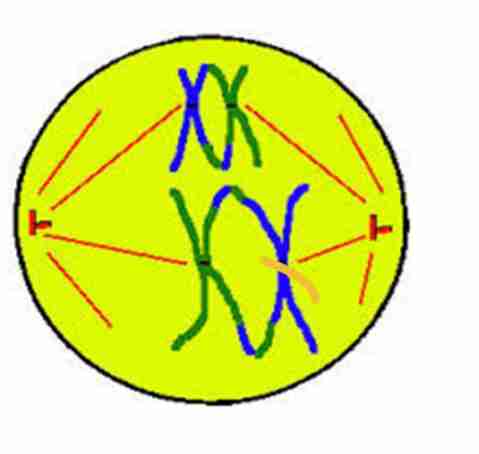
Anaphase I
Homologous pairs of
chromosomes separate
and migrate toward
their respective poles
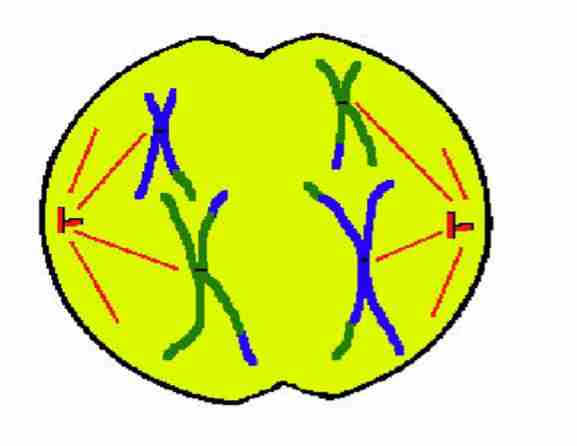
Telophase I
Two daughter cells are
completely divided. Nuclear envelope and
nuclei reappear
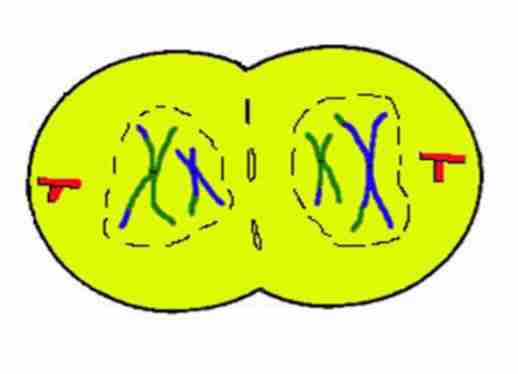
Interkinesis
short pause between meiosis I and meiosis II
Interkinesis
is similar to interphase except
DNA synthesis does not occur
Prophase II
Nuclear envelope and
nucleoli disappear. Chromatids start to
shorten and thicken
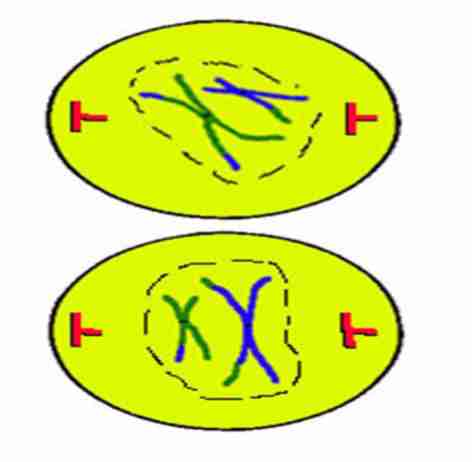
Metaphase II
Each chromosome is
composed of two sister
chromatids that are
joined by a centromere
and are attached to the
spindle fiber
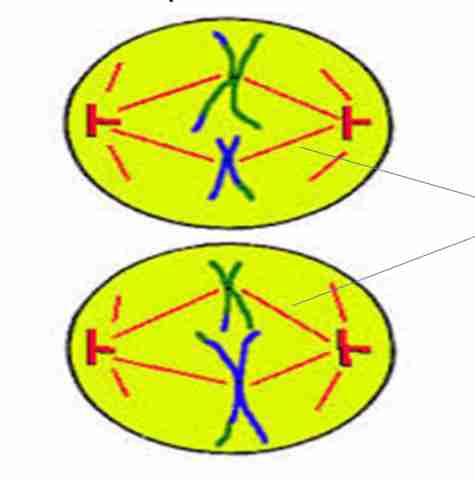
Anaphase II
Microtubules pulls the
sister chromatids apart
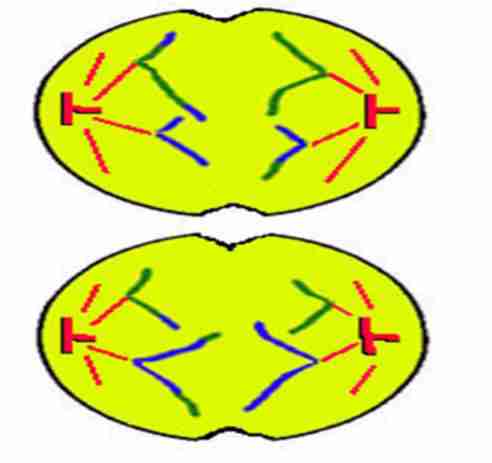
Telophase II
Spindle fibers
dissolved. 2 daughter cells
produced by each
diploid cell forming 4
haploid cell
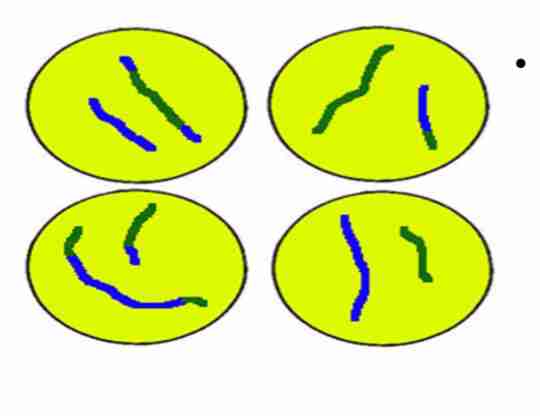
Mitosis
Produces genetically identical cells. Result in diploid chromosome
number
Meiosis
Produces genetically unique cells. Results in haploid chromosome
number
Mitosis
Takes place throughout the
organisms’ lifetime. Involved in asexual reproduction
Meiosis
Takes place only during the
reproductive years of the organism. Involved in sexual reproduction
x, y
sex chromosomes (not gametes)
x or y
sperm cells can either be
x
egg cells only contain
46
number of chromosomes in the human body
22
how many pairs of chromosomes are called autosomes
Down Syndrome
extra copy of chromosome 21
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
XXY
Gametogenesis
Production of sex cells with
haploid number of chromosomes
Gametes
sex cells
Spermatogenesis
At the end of Meiosis II,
1 spermatogonium will
produce 4 haploid
spermatid, which
eventually develop into
sperm cells.
Oogenesis
At the end of meiosis II,
primary oocyte will
produce 1 haploid
ovum and 3 polar
bodies
G1 Checkpoint
Checks for the size of the cell
G2 Checkpoint
Checks for the integrity of DNA
M Checkpoint
Proper alignment of the
chromosomes
Simple Squamous Epithelium
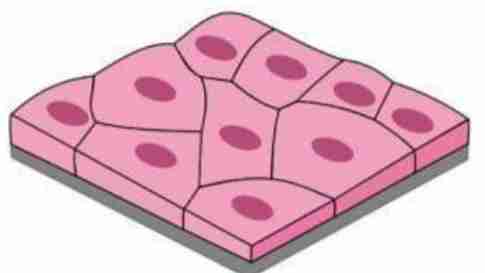
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
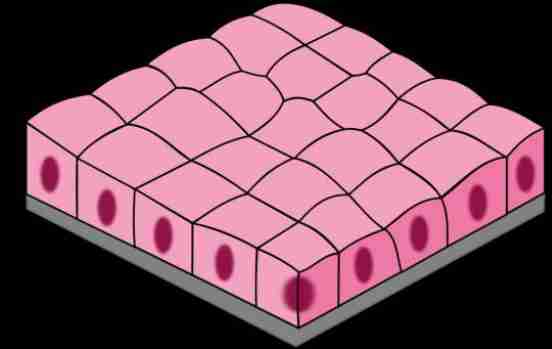
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
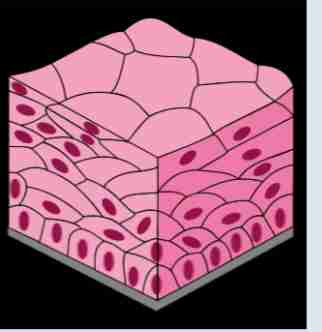
Simple Columnar Epithelium