PCT Exam
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Extra Protective Cream
Apply to buttocks, provides protection for incontinence.
Moisture Barrier Ointmemt
Not for buttocks, extra moisturizer, works well on lower extremities.
Moisturizer/Lotion
Appropriate for skin on entire body, helps prevent skin tears.
5 Moments of Hand Hygiene
1) Before touching patient and their surroundings.
2) Before an aseptic task.
3) After contact with bodily fluids.
4) After touching patient.
5) After touching patient surroundings.
Donning
1) Gown.
2) Mask.
3) Goggles.
4) Gloves.
Doffing
1) Gloves.
2) Gown.
3) Goggles.
4) Mask.
Where should CHG treatment not be used?
The patients face.
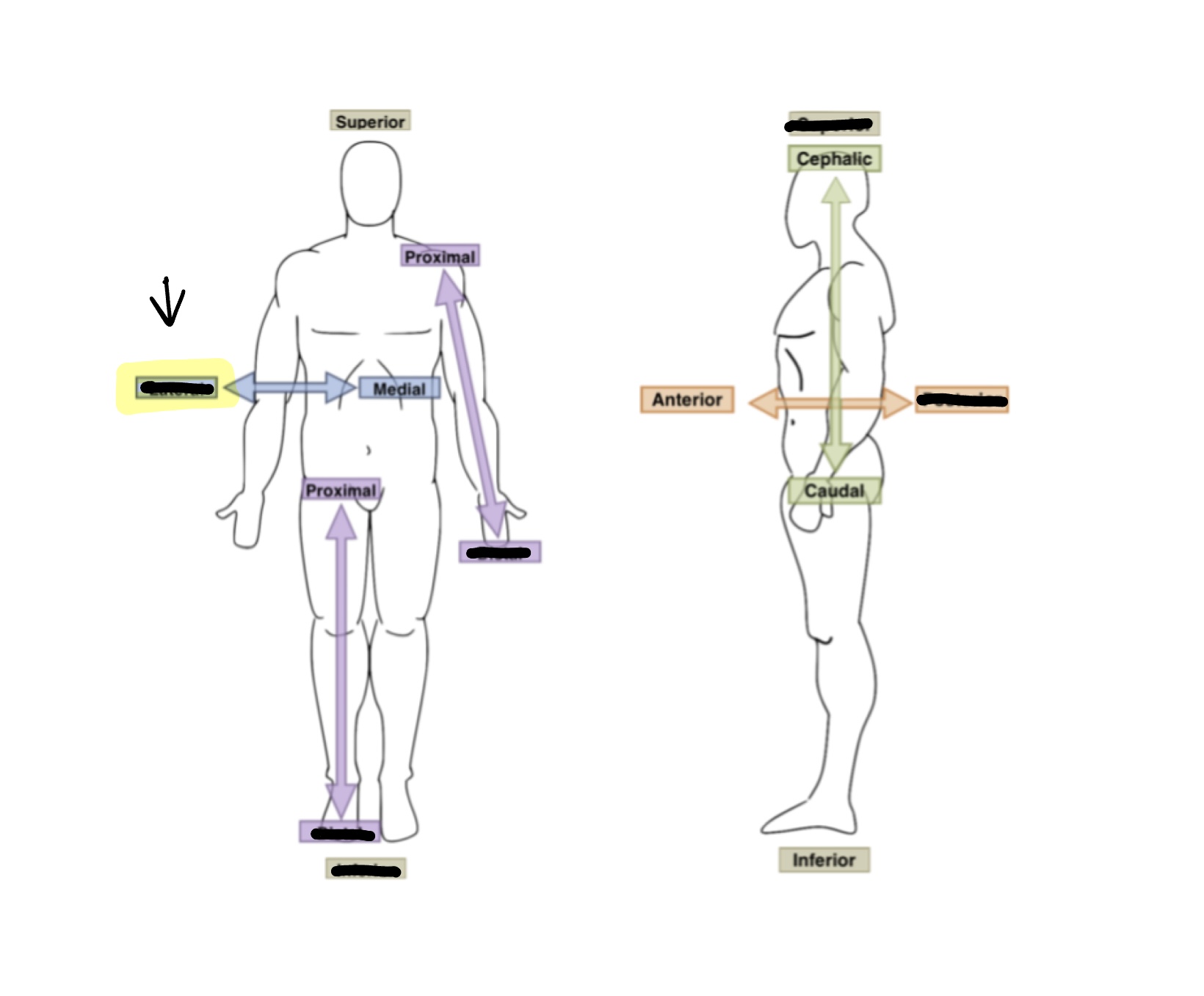
What is the anatomical term for highlighted box?
Lateral
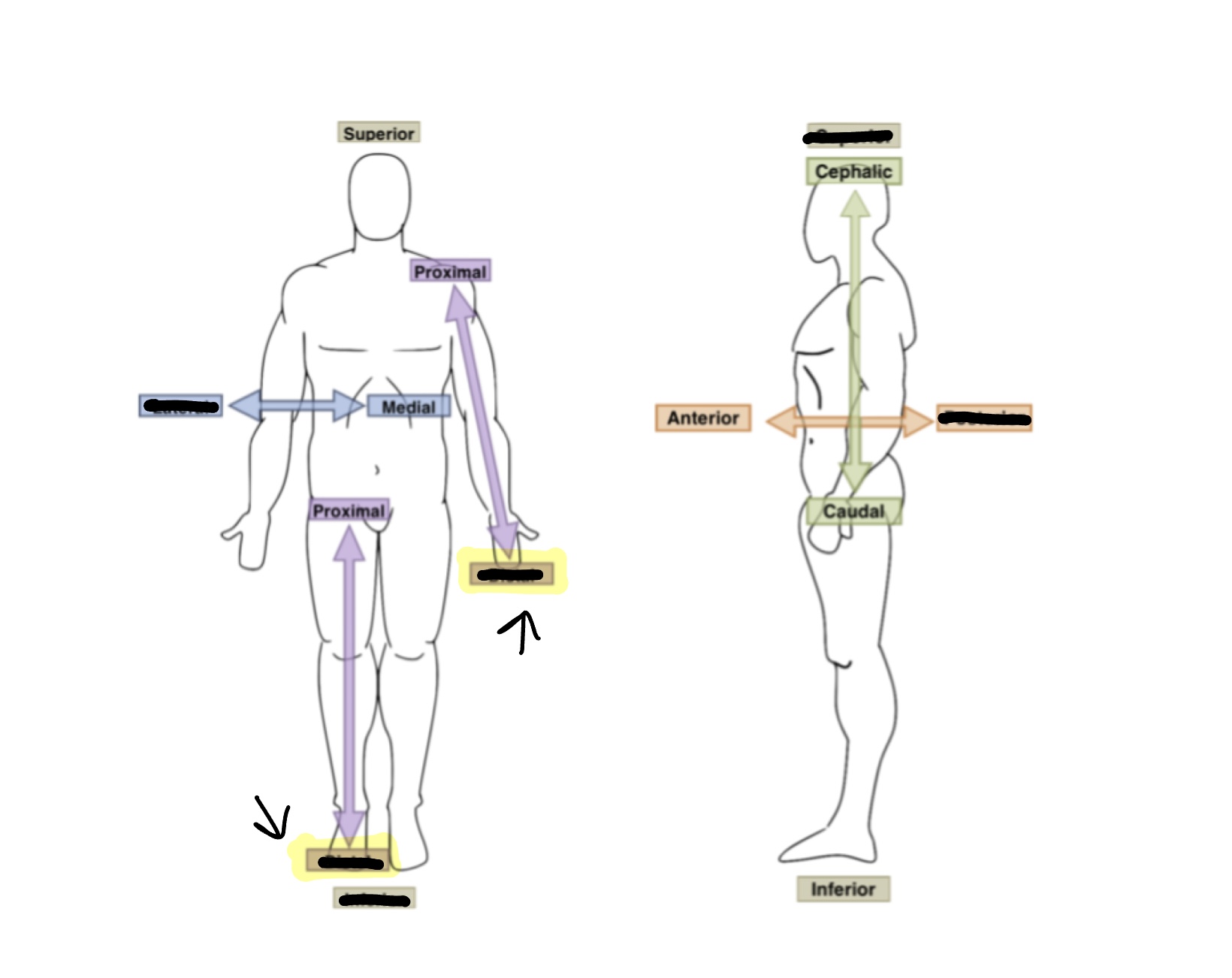
What is the anatomical term or for highlighted boxes?
Distal
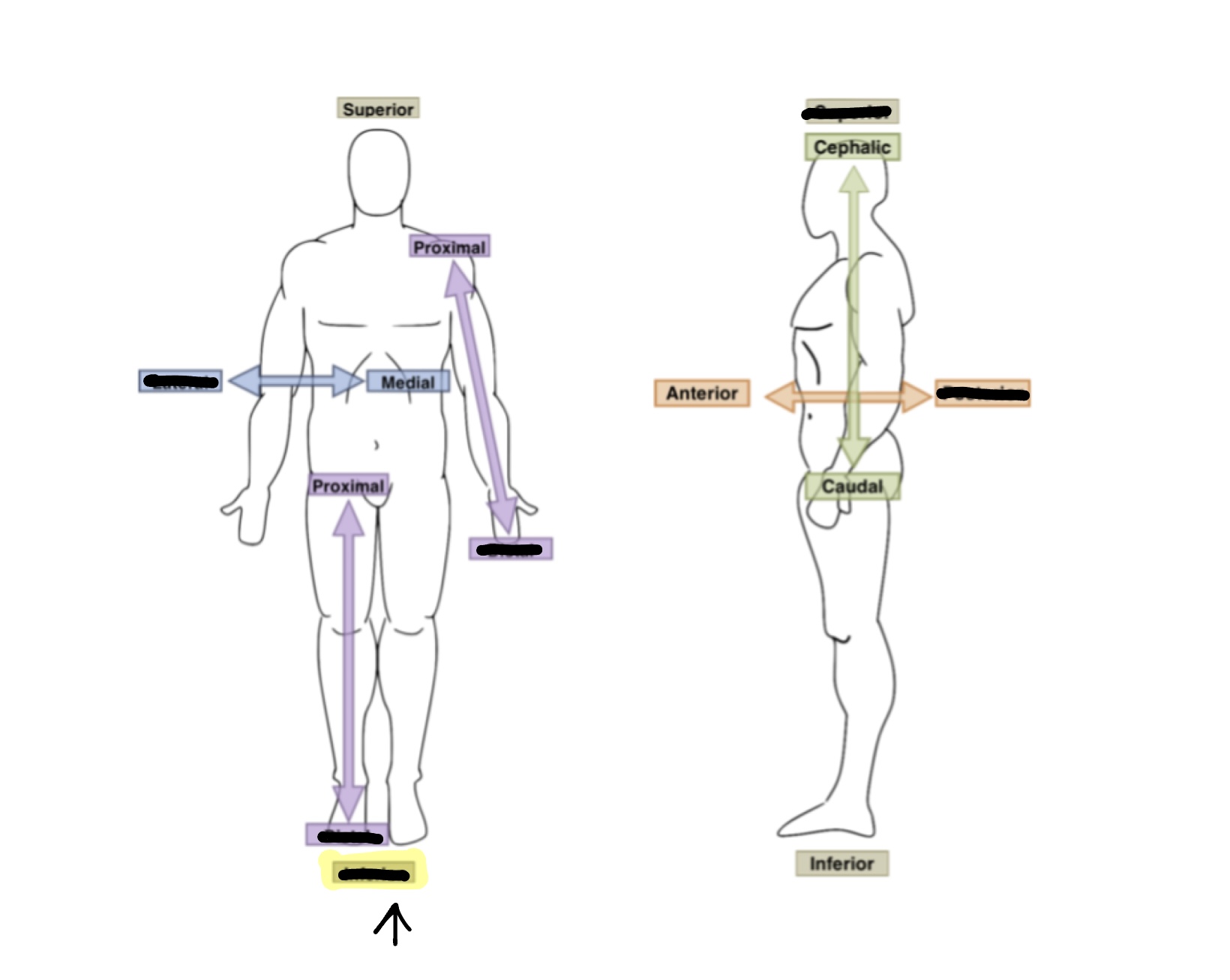
What is the anatomical term for the highlighted box?
Inferior
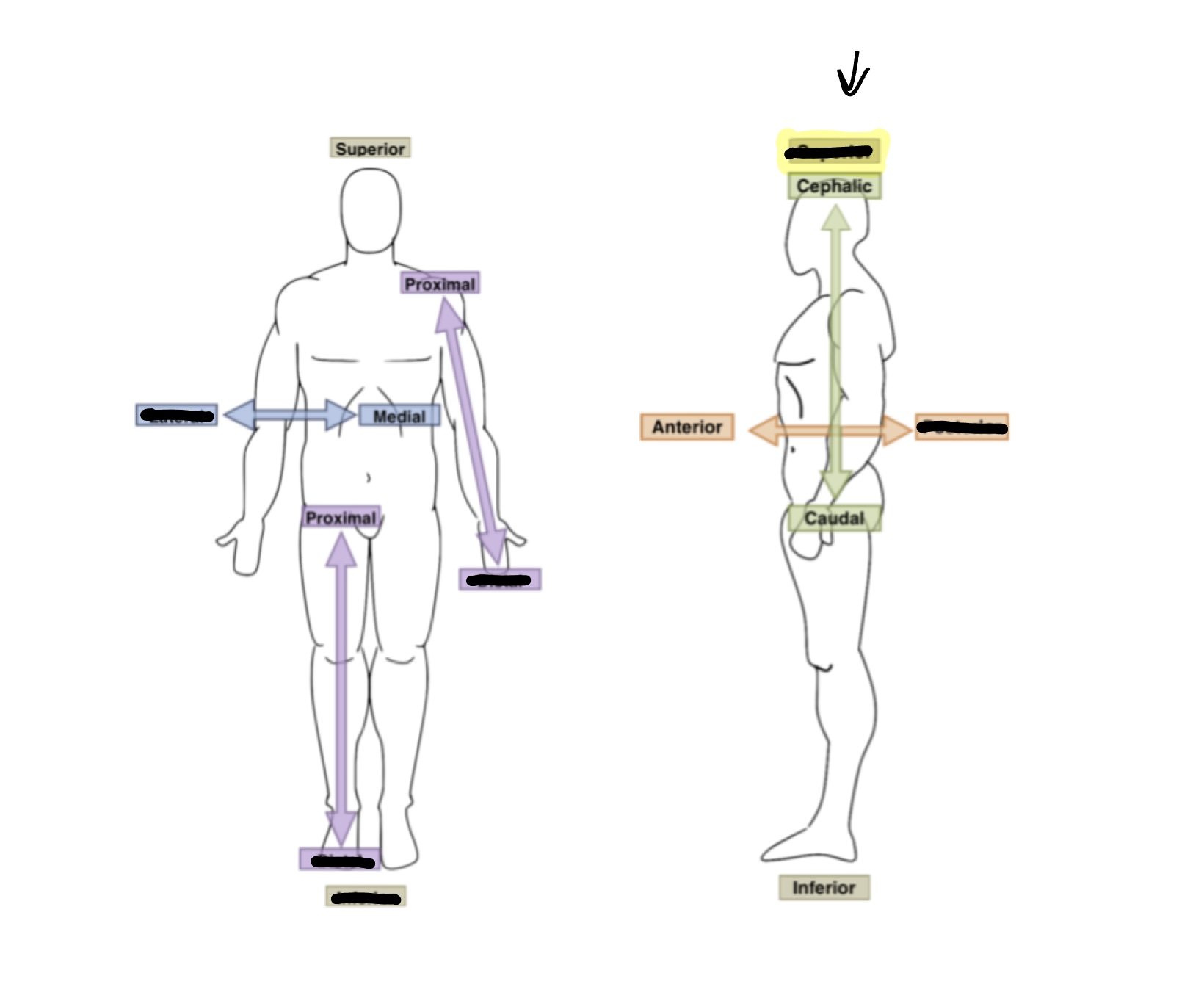
What is the anatomical term for the highlighted box?
Superior
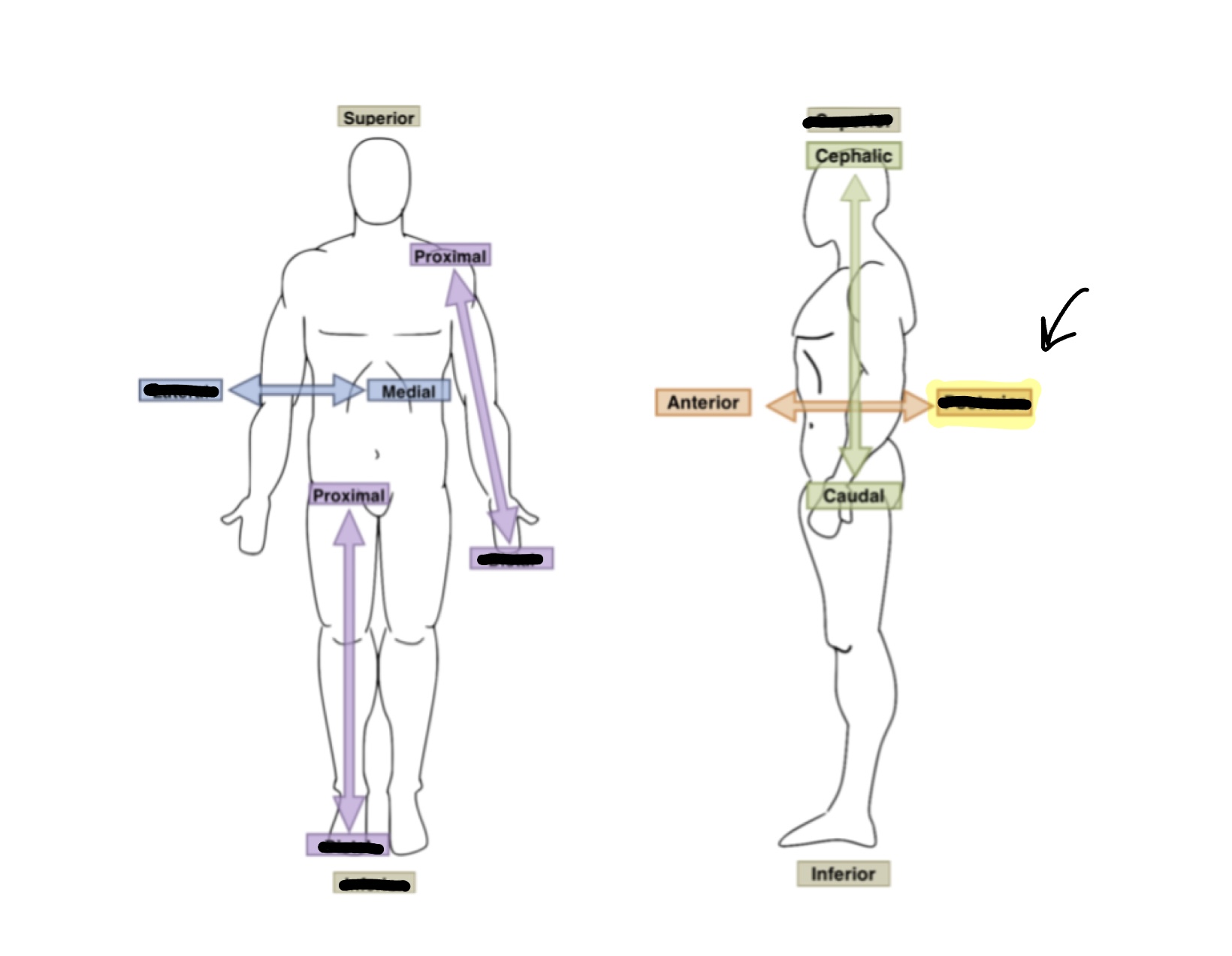
What is the anatomical term for the highlighted box?
Posterior
Hypotension
Low blood pressure.
BRP
Bathroom privileges.
BM
Bowel movement.
AC
Before meals.
QID
Four times a day.
Anemia
Without/low red blood cells.
How often does the PSA document when sitting?
Every 15 minutes.
When a suicidal patient is using the bathroom and asks for privacy what do you say?
Explain that for their safety they need to be within arms reach.
How often should you check on a patient with nonviolent restraints?
After the initial 15 minutes every 2 hours.
What does evening care consist of?
Toileting, oral care, fresh water, warm blanket.
What are the most common areas for pressure injuries?
Coccyx, hips, heels, ankles, elbows, scapula, back of head/ears/nostrils.
When are all four side being up not considered a restraint?
Seizure precautions, waking up from anesthesia, specialty bed, moving patient, direct care.
When are lock limb restraints used?
Only psychiatric and ED have access. Violent patients only. Security get involved.
Mittens
Only a restraint when used with another device. Covers patients hands while still allowing some airflow.
Wrap belt
Considered a restraint when patient is incapable of undoing the device. (Velcro is in the back) Patient has to demonstrate they can undo it for it to be an alternative.
Roll belt
Restraint when patient can't get undone. Connects to bedframe.
Freedom splint restraint
Always a restraint! Stops patient from pulling out tubes, picking at incisions, etc.
Soft limb
Goes around wrists and/or ankles. Connects to bedframe and requires a bed alarm. Looks like handcuffs.
How often do sitters need to document?
Every 15 minutes.
If someone's respiratory rate is <12, what would that be?
Bradypnea
What is the normal respiratory rate to adults?
12-20 breaths per minute
What is a good position for patients in respiratory distress to go in?
Tripoding
What needs to be done before diabetic patients eat?
Check blood glucose
BG >200
Hyperglycemia
BG <70
Hypoglycemia
Polyuria, hunger, thirstiness, blurry vision, and sleeping are signs of what?
Hyperglycemia
Sweating, dizziness, anxiety, weak, and headaches are symptoms of what?
Hypoglycemia
What is a piece of equipment is used for patients who have a hard time breathing? (Breathing treatments)
Incentive spirometer
What does B in BEFAST stand for?
Balance
What does the E in BEFAST stand for?
Eyesight
What does the F in BEFAST stand for?
Face
What does the A in BEFAST stand for?
Arm
What does the S in BEFAST stand for?
Speech
What does the T in BEFAST stand for?
Time
Why are stroke/seizure patients NPO until they get their swallow/dysphagia screen?
They could aspirate.
How often should high risk stroke patients get their vitals taken?
Q4
Acute pain
Short duration, occurs quickly.
Chronic pain
Ongoing and constant.
Cancer pain
Due to tumor invasion/progression or treatment. (Acute or prolonged)
Phantom pain
Occurs after amputation.
Ischemic
Clot
Hemorrahgic
Bleed
Transient ischemic attacks (TIA)
Warning "mini stroke".
Tenecteplase (TNK)
The "clot busting drug".
Hemiplegia
Paralysis of one side of the body.
Paraplegia
Paralysis of lower extremities.
Quadriplegia
Paralysis of all four extremities.
When transferring a patient what side do you use?
The strong side.
Delirium
Acute change in mental status due to a reversible medical condition.
Dementia
Chronic disorder, rarely reversible.
Tonic phase
Muscles stiffen, personal loses consciousness and falls to the floor.
Clonic phase
Muscles contract and relax, jerking and shaking movements occur, incontinence may occur.
Absence seizure
Staring and rapid breathing.
Focal (partial) seizures
Body parts may twitch or have sensation changes.
When a patient asks us to grab something out of their purse, what do we do?
Hand them the whole purse.
What is very important when communicating with a patient experiencing psychosis?
Redirect them! Don't argue.
What does CAUTI stand for?
Catheter associated urinary tract infection.
Dysuria
Painful urination.
Hematuria
Blood in urine.
Nocturia
Increased urination at night.
Oliguria
Low urine volume.
Anuria
No urine production.
What is the B.R.A.T. diet?
Bananas, rice, applesauce, toast.
Colostomy
Portion of colon is brought to the abdominal wall, creating a stoma. (For stool)
Urostomy
Bringing ureters to outside of body to create a stoma. (For urine)
What is used for suctioning stomach contents and/or delivering nutrition, water, and medicine?
Nasogastric tube
When should an ostomy bag be emptied?
When it is 1/3 full.
If turning a patient with a feeding tube, what needs to be done first?
Ask the nurse to pause the feed.
What is important when bathing a patient with a cast?
Don't get it wet!
To communicate with a patient who is hearing impaired what should you do?
Use a whiteboard, assist with hearing aids, and get an interpreter.
Now often do you do catheter care for a patient?
Q8 and as needed.
How often do you do oral care on unconscious patients?
Q2
When putting a gaitbelt on a patient how should the tag be facing?
Outwards
If someone is pregnant or has drains, where do you place the gaitbelt?
Above breasts or low hips.
How often do you do hourly rounding on night shift?
Q2
Do you wake a patient when needing to get vitals?
No!