Lecture 17 - Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number - Chapter 8
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is Polyploidy?
A type of aberrant euploidy, where an organism has more than two complete sets of chromosomes
What is Autopolyploidy?
Where an organism has multiple complete sets of chromosomes, all originating from the same species
What causes Autopolyploidy?
Cause by Complete Nondisjunction
(gamete retains extra chromosome sets)
Where is Autopolyploidy common in?
Common in experimental induction with colchicine, which disrupts spindle formation, preventing chromosome separation
What is Allopolyploidy?
Where an organism has two or more complete sets of chromosomes that originate from different species
What causes Allopolyploidy?
Hybridization followed by chromosome doubling
What does Initial Hybrid result in?
A sterile allodiploid (no homologous pairing)
What does Chromosome Doubling result in?
Fertile allotetraploid where each chromosome has a homolog
How does polyploidy affect agriculture crops that have an odd number set of chromosomes?
The plants (bananas and watermelon) will be sterile and will have seedless fruits
How does polyploidy affect agriculture crops that have an even number set of chromosomes?
The plants would be fertile and will be useful in crop breeding
How does Colchicine Treatment work in crops?
Colchicine treatment artificially induces tetraploid tissues and will be propagated to yield stable polyploid plants
What are the two primary ways the structure of chromosome can be altered?
1. The total amount of genetic material in the chromosome can change
2. The total amount of genetic material remains the same, but is rearranged
In what ways can the total amount of genetic material in a chromosome change?
Deletions and Duplications
What is Deletion?
The loss of a chromosomal segment
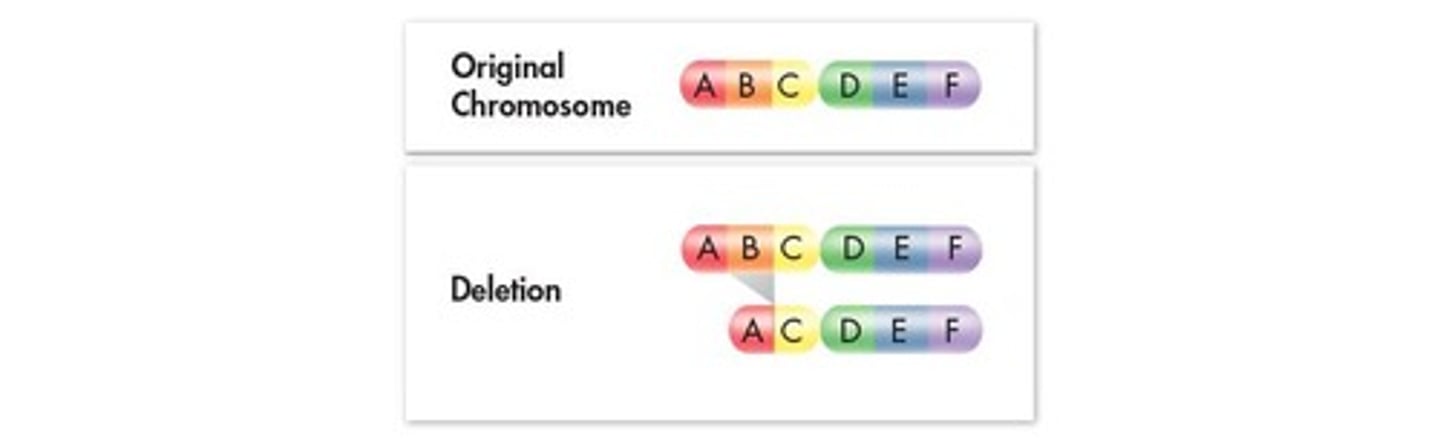
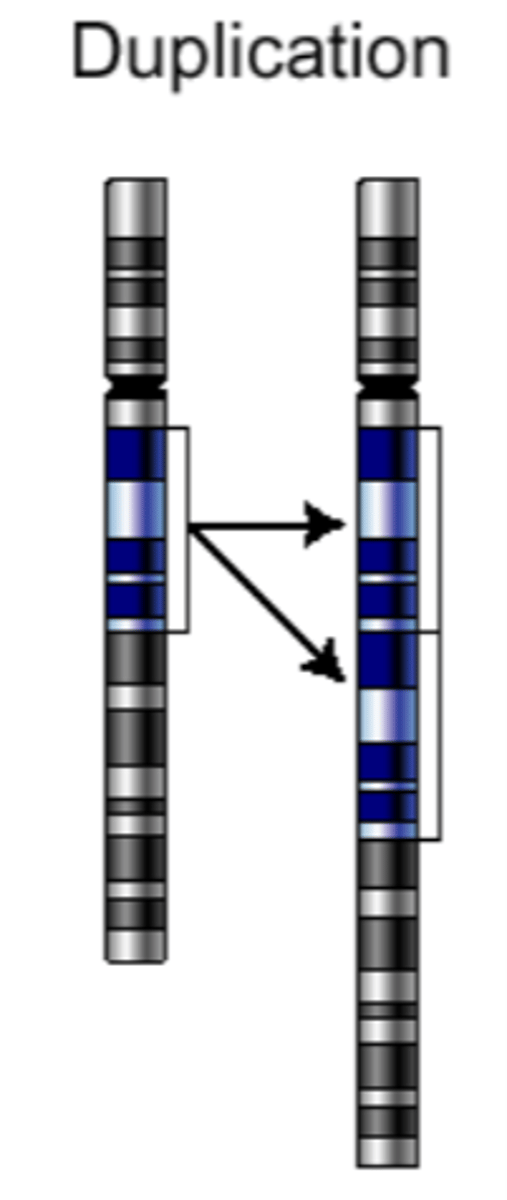
What is Duplication?
The repetition of a chromosomal segment compared to the normal parent chromosome
In what ways can the total amount of genetic material in a chromosome be rearranged?
Inversions and Translocations
What is Inversion?
A change in the direction of part of the genetic material along a single chromosome

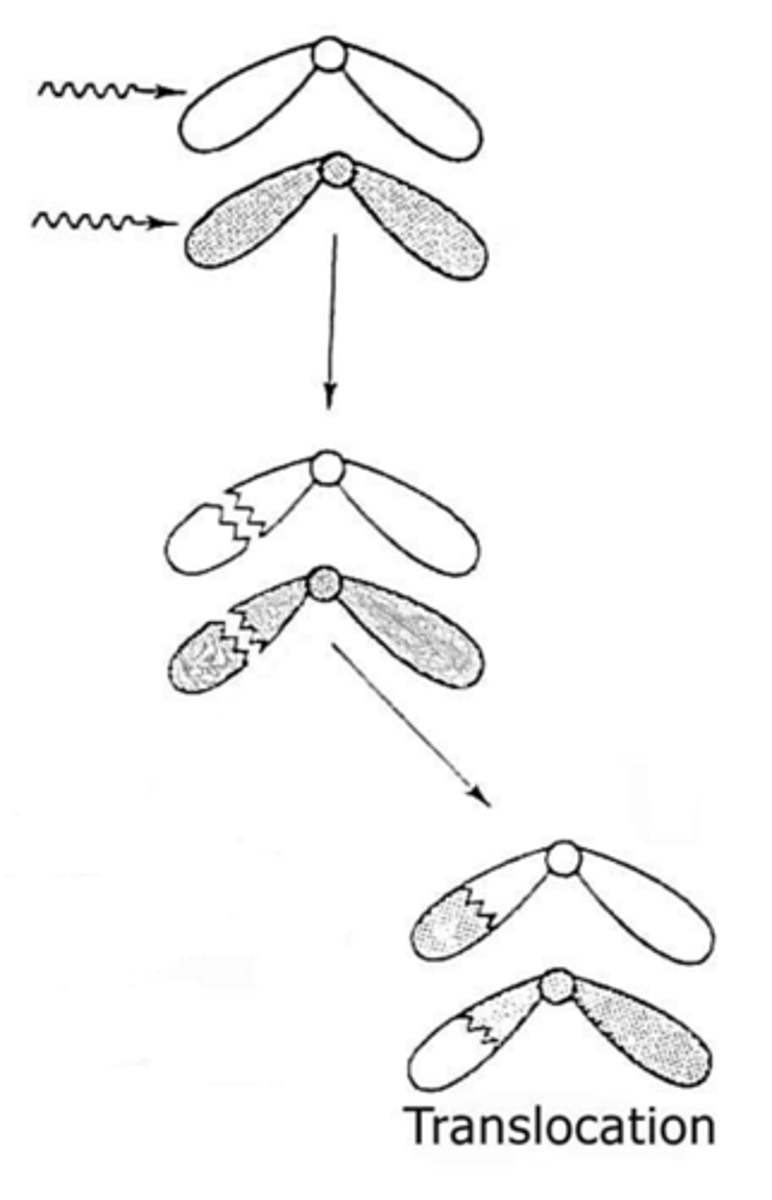
What is Translocation?
A segment of one chromosome becomes attached to a different chromosome
What are the two different types of deletion?
- Terminal deletion: Chromosome in broken into 2 pieces, end of chromosome is lost
- Interstitial Deletion: Chromosome breaks in two places, central fragment is lost
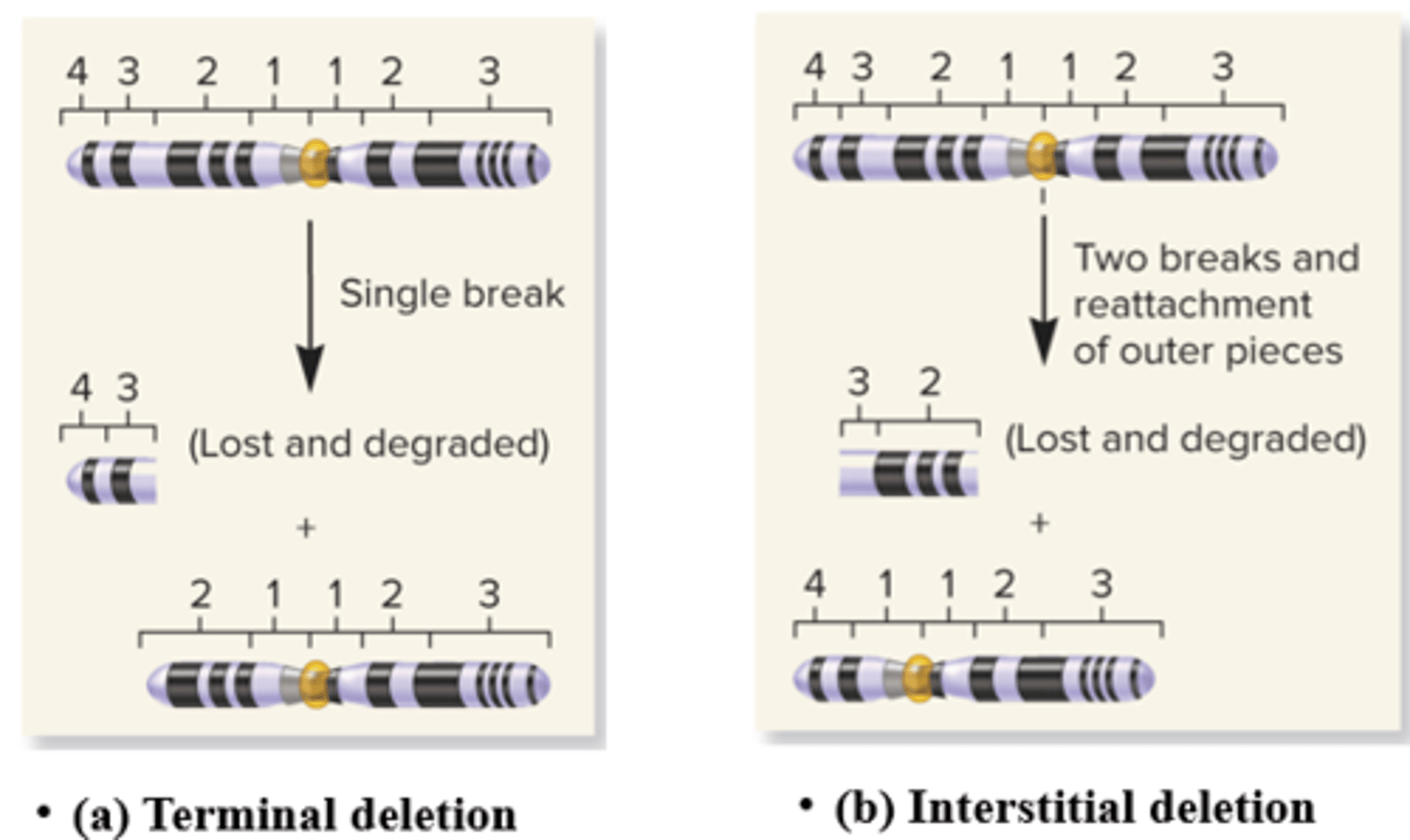
What does the phenotypic consequences of deficiencies depend on?
- The size of deletion
- The chromosomal material deleted (are genes lost?)
What is an example of chromosomal deletion?
Cri-du-chat syndrome, cause by a deletion in the short arm of chromosome 5
What usually causes Duplications?
By abnormal events during recombination, like unequal crossing over
What can Duplications cause?
Repetitive sequences can cause misalignment between homologous chromosomes, creating gene dosage imbalances
Which is more harmful, Deletion or Duplication?
Deletion
How is Duplication a source of evolutionary novelty?
Provides extra copies for gene diversification, leading to gene families
What are Gene Families?
Created by duplications that are followed by mutations that lead to divergence. Results in homologous genes sharing a common ancestor
What are Paralogs?
Homologous genes in the same species
What are Orthologs?
Homologous genes found in different species
What is the Globin Gene Family?
• Myoglobin, α-globin, β-globin — derived from ancestral globin gene.
• Over 500 million years, the ancestral globin gene has been duplicated and altered so there are now 14 paralogs in this gene family on three different chromosomes
• Different paralogs carry out similar but distinct functions
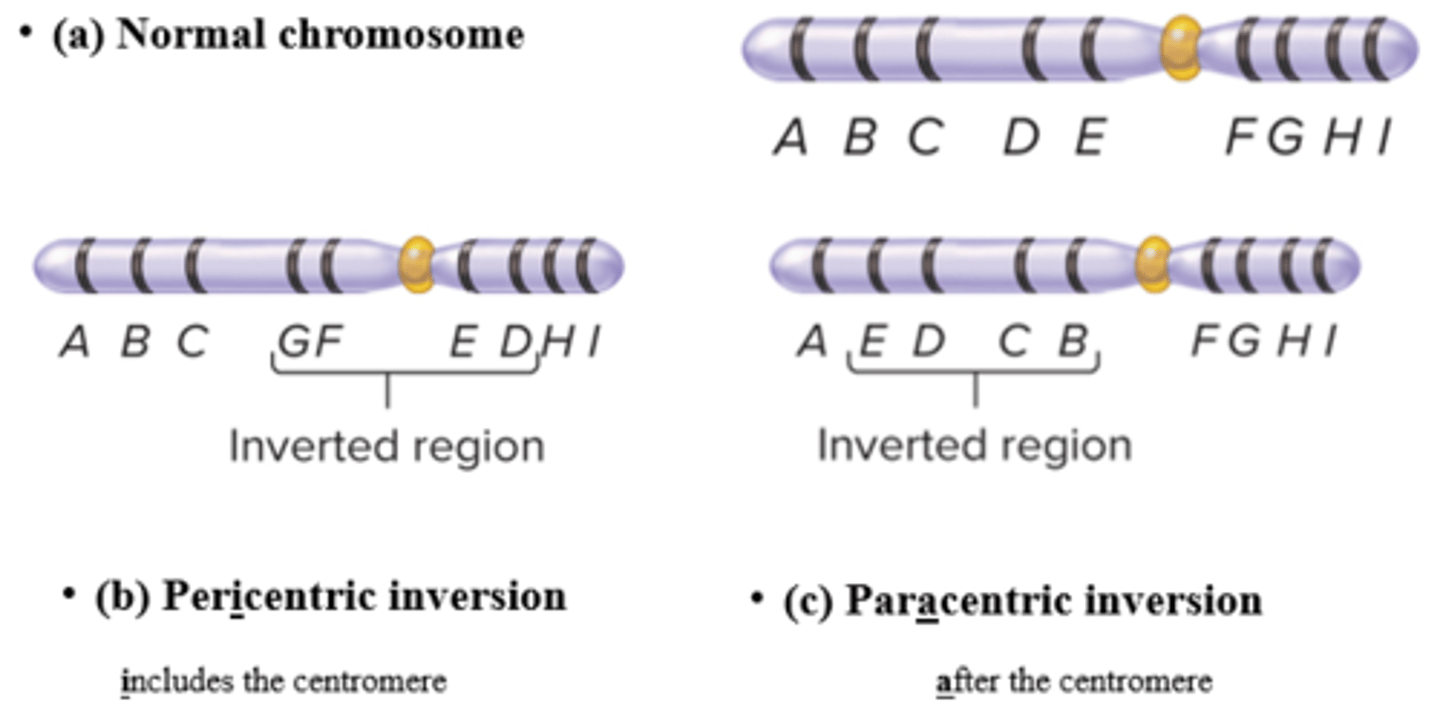
What are the two different types of Inversions?
- Paracentric: Does not include Centromere and breaks/rejoins outside centromere
- Pericentric: Includes Centromere
What effects does Inversion have on people?
Most individuals with inversions are phenotypically normal, but inversion heterozygotes face problems during meiosis due to abnormal recombination
What is an Inversion Heterozygote?
One normal chromosome an one inverted
How do homologous sequences align?
An inversion loop forms
What happens to the abnormal gametes when crossing over occurs within the loop?
Paracentric inversion:
- Dicentric (2 centromeres) + acentric (0 centromeres) fragments → inviable
Pericentric inversion:
- Recombinants with duplications/deletions → inviable
Result: ↓ frequency of viable recombinant gametes
What are the two different types of Translocations?
- Simple Translocation: One-way transfer of a segment
- Reciprocal Translocation: Exchange between two nonhomologous chromosomes → two translocated chromosomes.
What are the consequences of Translocation?
- May produce partial trisomy or monosomy in gametes → inviable offspring
- Can cause position effects — altered gene expression due to new chromosomal context
What’s the difference between autopolyploidy and allopolyploidy?
- Autopolyploidy: extra sets from same species
- Allopolyploidy: sets from different species
How does colchicine induce polyploidy?
Binds to tubulin, blocking spindle fiber formation → chromosomes fail to separate → doubling of chromosome number in daughter cells
Why are triploid plants sterile?
Homologs can't segregate evenly in meiosis → unbalanced gametes → sterility
Explain the mechanism behind Karpechenko’s cabbage–radish hybrid
- Hybrid of 2 diploid species (2n₁ + 2n₂ = 18) → sterile
- Chromosome doubling → 2n₁ + 2n₂ = 36 → fertile allotetraploid → new species
What role do duplications play in evolution?
Provide extra gene copies for mutations → lead to new gene functions (gene families)
Differentiate between paracentric and pericentric inversions
- Paracentric: doesn’t include centromere; produces dicentric and acentric fragments
- Pericentric: includes centromere; produces duplication/deletion products
What happens if crossing-over occurs inside an inversion loop?
Produces abnormal recombinant chromosomes → mostly inviable gametes
What's the phenotypic effect of large deletions vs. duplications?
Deletions usually more severe; duplications often tolerated but may affect dosage balance
How does a reciprocal translocation affect meiosis?
Chromosomes form a cross-shaped configuration; adjacent segregation → unbalanced gametes, alternate segregation → viable gametes