RBC Morphology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
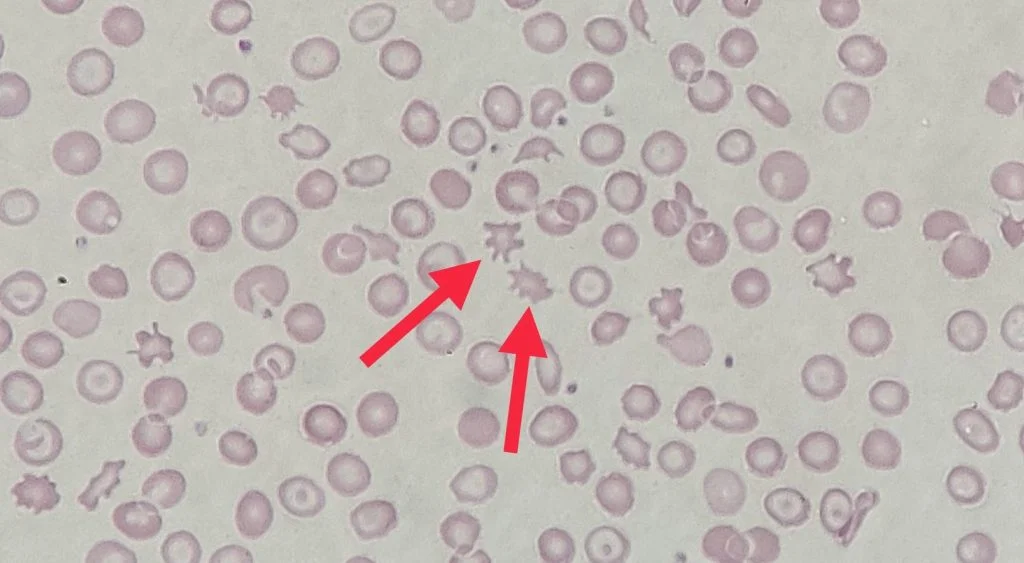
Identify this type of red cell
Acanthocyte. A type of red blood cell characterized by its spiky surface. It is sporadically seen with severe liver disease or post-splenectomy. Also seen with rare disorder of abetalipoproteinemia.
What is anisocytosis?
Variation in size of RBC’s
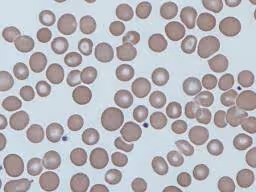
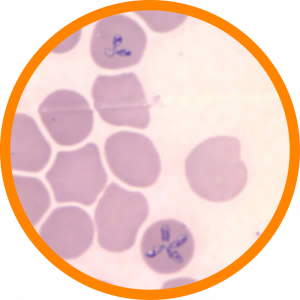
What is this?
Babesiosis. Similar to ring forms of malaria
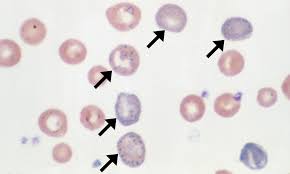
What are these cells exhibiting?
Basophilic stippling. Small aggregates of RNA are seen as small blue dots in the RBC. Fine stippling may be a feature of reticulocytes, whereas coarse stippling can appear with toxic marrow damage, myelodysplasia, and thalassemias.
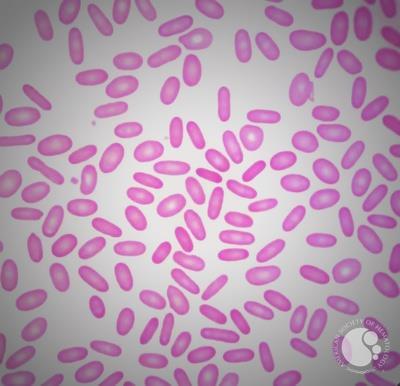
Identify the type of red cells seen in the image.
Elliptocytes. They are elongated, elliptical cells. They are non-specific when occasionally seen. Large presence of them can be seen in a rare disorder of hereditary elliptocytosis.
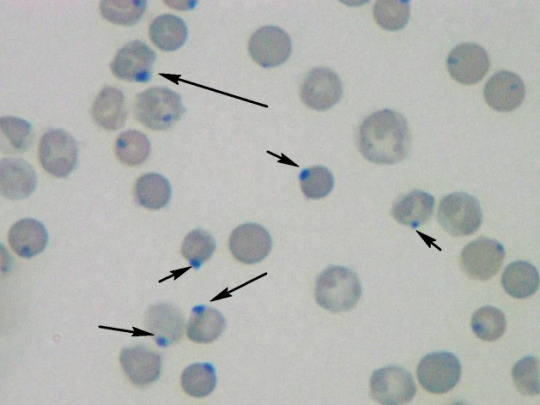
Identify this type of red cell.
Heinz body. Precipitated hemoglobin is seen as a perimembranous blue dot only after supravital staining. Seen with some hemoglobinopathies.
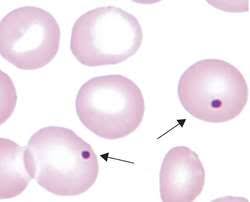
Identify this type of red cell.
Howell-Jolly body. Small, round deeply basophilic nuclear remnant. Seen when spleen is absent.
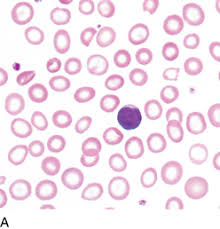
What are these cells exhibiting
Hypochromia. Cells with decreased MCH. Typical of iron deficiency.
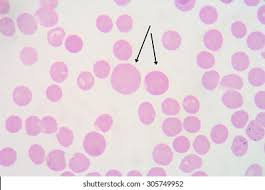
What are these cells exhibiting?
Macrocytosis. These are cells with increased MCV, typical of megaloblastic anemias.
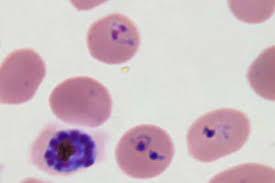
Identify the type of red cell.
Malaria. Plasmodium infection seen as “ring forms”, stippling, and gametocytes, depending upon the species.
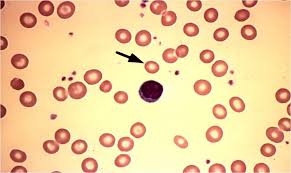
What is this red cell exhibiting?
Microcytosis. Cells with decreased MCV, typical of iron deficiency anemia and thalassemias.
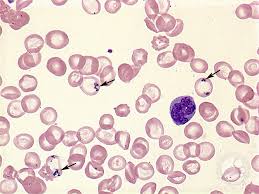
Identify the type of red cell.
Pappenheimer body. These exhibit multiple, tiny iron containing granular blue dots. They are seen when spleen is absent and with iron overload.
What is poikilocytosis?
Variation in shape of RBC’s
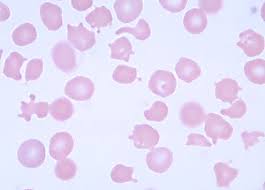
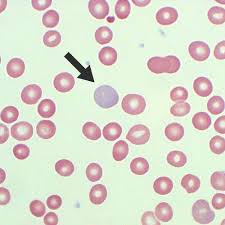
What is this cell exhibiting?
Polychromatophilia (polychromasia). This is the bluish tint seen in young RBC’s with high RNA content.
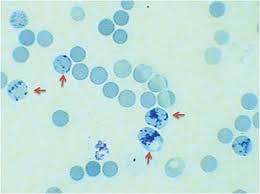
Identify these types of red cells.
Reticulocytes. Young RBC with increased RNA content that can be precipitated by supravital staining for identification and enumeration. Often stained with methylene blue.
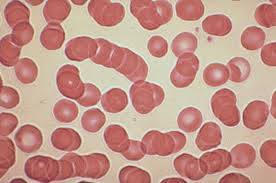
Name the arrangement of these red cells.
Roleaux. This is the linear aggregation of RBC’s that resembles a stack of coins. Seen when surface charge is reduced with increased serum protein, particularly increased fibrinogen or globulin.
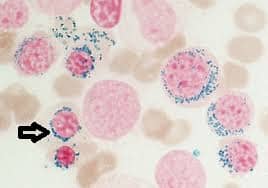
Identify this type of red cell.
Sideroblast. This is a non-nucleated RBC with stainable iron.
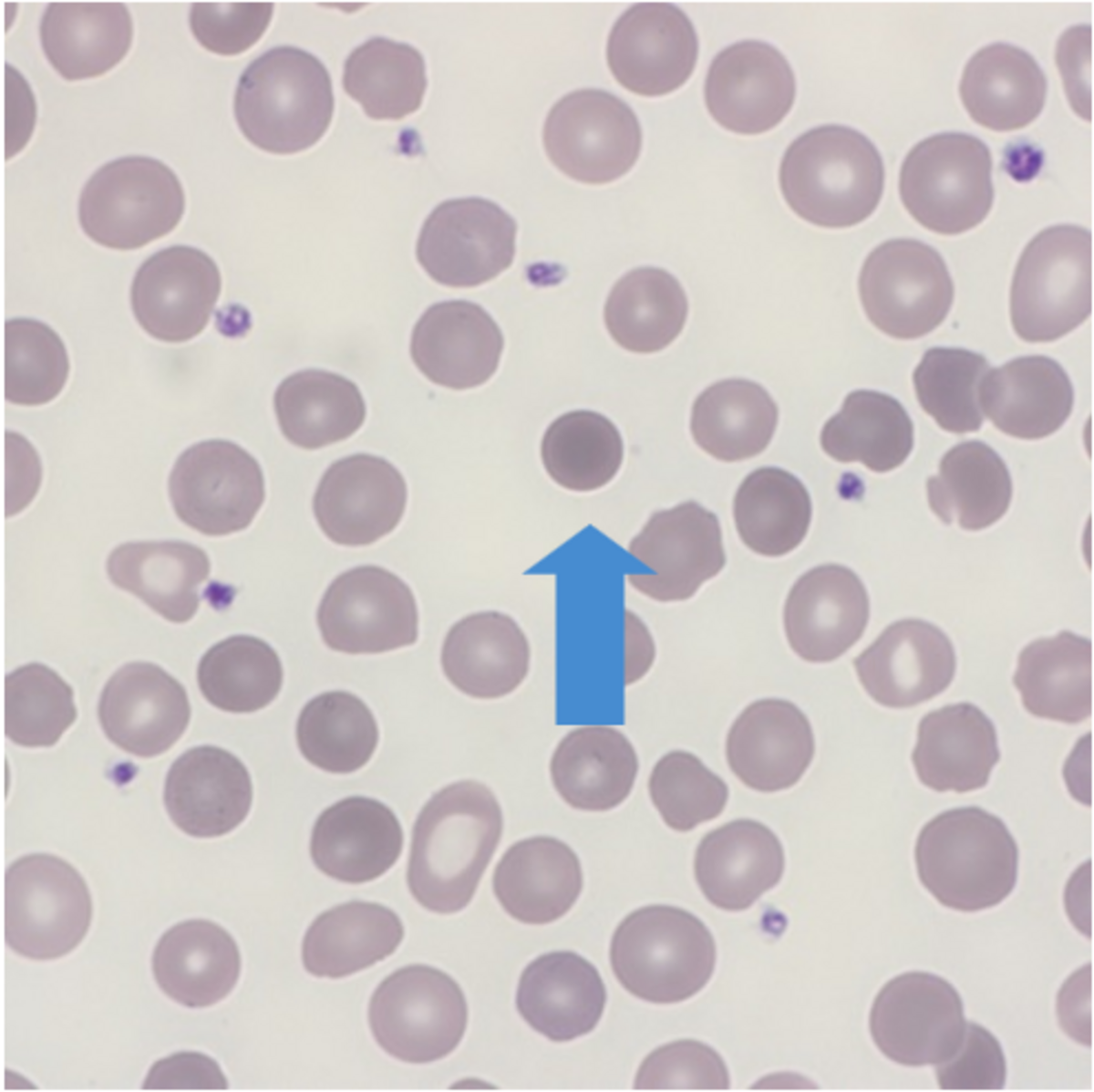
Identify this type of red cell.
Spherocyte. Small, round dense cell without central pallor. Suggestive of extravascular (splenic) hemolysis in previously normal persons. With hereditary spherocytosis there is increased osmotic fragility.
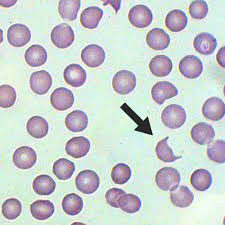
Identify this type of red cell.
Schistocyte. Fragmented, irregularly shaped red cell, seen with intravascular hemolysis such as microangiopathic hemolytic anemias (DIC, TTP). A variant called a “helmet cell” appears cut in half.
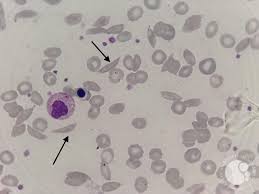
Identify these types of red cells.
Drepanocytes (Sickle cells). Curved, banana-shaped cell with pointed ends found in sickle cell disease from aggregation of hemoglobin S.
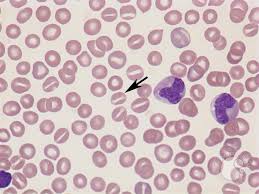
Identify this type of red cell.
Stomatocyte. Cell with slit-like central pallor. Occasional stomatocytes are non-specific or an artefact. Many are seen with rare hereditary stomatocytosis.
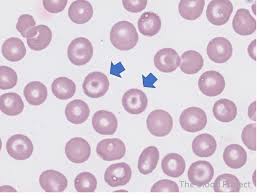
Identify these types of red cells.
Target cells. Cells with central and peripheral staining with intervening pallor due to increased redundancy of RBC membrane. Seen with liver disease, in some thalassemias, and with hemoglobin C.
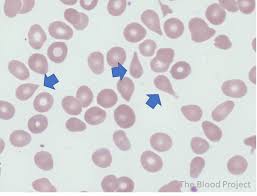
Identify these types of red cells.
Dacrocytes (tear drop cells). Cells pinched at one end, prominent in myelofibrosis and myelophthisic conditions.