24. hemoparasites (bacteriology)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
anaplasma marginale source
infected ruminants
mainly, other infected cattle
other ruminants (including wildlife)
what is a major predisposing factor to anaplasma marginale?
age
OLDER cattle = more severe illness
young animals less severely affected
how is anaplasma marginale transmitted?
ticks → dermacentor species (main vector in U.S.)
biting flies
stable flies (stomoxys)
horse & deer flies (tabanus)
iatrogenic
fomites → blood-contaminated medical equipment
transplacental
anaplasma marginale virulence factors
antigenic variability (evade host immune system)
adhesins → outer membrane protein A
facilitate binding to host cells & uptake into both tick and mammal cells
type 4 secretion system
helps invade host cells
anaplasma marginale pathogenesis
causes hemolytic anemia
organism attaching to and entering RBCs → damages RBCs and decreases lifespan
extravascular hemolysis — RBC destruction
due to phagocytosis of parasitized RBCs by macrophages
where in the body does hemolysis mainly occur? (anaplasma marginale)
primarily in the spleen (by splenic macrophages)
also other macrophages (reticuloendothelial system)
anaplasma marginale clinical signs associated with anemia & decreased O2 delivery
pallor
lethargy
weakness
icterus (from RBC breakdown — hemoglobin → bilirubin)
labored breathing
other clinical signs of anaplasma marginale (cattle)
nonspecific signs: fever, anorexia, weight loss, decreased production
abortion
death (severe cases)
anaplasma marginale diagnostics
CBC → regenerative anemia suggestive
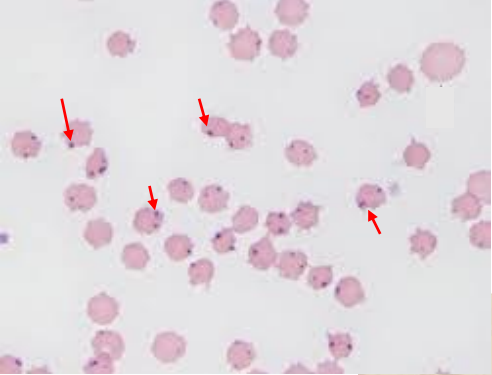
cytologic exam of blood smear → organisms within RBCs
dense cocci at RBC margins
PCR
serology
anaplasma marginale treatment
antimicrobials → tetracyclines
unlikely to eliminate carrier state
supportive care
blood transfusion if severe anemia
maintain hydration and nutrition
anaplasma marginale prevention
maintain anaplasma-free herds
control ticks and biting flies
house in areas where ticks are less likely
medical practices: good hygiene
prevent blood contamination of instruments
do not re-use needles when vaccinating
vaccines not yet commercially available (in development)
is anaplasma marginale contagious? is it zoonotic?
to other adult cattle → no; requires vector
possible from cow to calf (transplacental)
to humans → no; not zoonotic
reportable in WI
mycoplasma gram stain/morphology
gram negative
very small
lack cell wall
what disease does mycoplasma haemofelis cause?
hemolytic anemia in cats (“feline infectious anemia”)
hemotropic mycoplasmas (hemoplasmas) lifestyle
obligate RBC parasite
epicellular: attach to surface of RBCs (NOT intracellular)
requires host cell to survive
cannot be cultured in lab
what are predisposing factors to mycoplasma haemofelis?
male, outdoor cats
if infected with M. haemofelis but otherwise healthy → usually asymptomatic
clinical symptoms more likely if:
immune compromised (ex. FeLV or FIV infection)
other underlying disease
recent stress (ex. recent surgery, cat-bite abscess)
how is mycoplasma haemofelis transmitted?
transmission not definitively characterized
blood sucking arthropods? (ex. fleas)
queen to kittens (mode uncertain)
cat bite/fight possible?
iatrogenic → blood transfusion from carrier cat
mycoplasma haemofelis virulence factors
adhesins → attach to RBCs
antigenic variation
evade host immune system
contribute to cyclic increases and decreases in RBC #s
cyclic fever
mycoplasma haemofelis pathogenesis
hemolytic anemia
organism attaches to RBCs → damage → decreased lifespan
extravascular hemolysis — immune-mediated component suspected
RBC antigens exposed or altered
host makes antibodies to m. haemofelis organisms AND to parasitized RBCs
phagocytosis of parasitized RBCs → RBC lysis
by splenic macrophages
by other macrophages/reticuloendothelial system
mycoplasma haemofelis clinical signs
pale mucous membranes (pallor)
other symptoms related to anemia
lethargy, weakness, tachypnea
± icterus (uncommon) due to RBC breakdown
decreased appetite, weight loss
dehydration
± splenomegaly
± fever
mycoplasma haemofelis diagnostics
CBC → regenerative anemia
observe organisms
peripheral blood smear (part of CBC)
epicellular tiny rods, cocci, or delicate rings seen in acute phase of infection
PCR = diagnostic method of choice
mycoplasma haemofelis treatment
antimicrobial treatment → tetracyclines (first choice)
may not eliminate organisms → chronic carriers
if severe anemia: blood transfusion
mycoplasma haemofelis prevention
keep cats indoors (prevents cat fights with unknown cats)
good flea control
screen blood donor cats
is mycoplasma haemofelis contagious? is it zoonotic?
to other cats → possible via fighting; from queen to kittens
to people → unlikely; may be possible if immunosuppressed
bartonella gram stain/morphology
small gram-negative rods
bartonella hosts
cats, dogs, humans
what cells does bartonella infect?
infects RBCs (intracellular) and endothelial cells
stimulates endothelial cell proliferation
bartonellosis clinical signs in animals
usually transient, subclinical
cats: usually mild signs — transient fever, lymphadenitis (rare endocarditis)
dogs: fever, lameness, lymphadenitis, endocarditis
how is bartonella transmitted in animals?
vector: cat fleas (ctenocephalides felis)
zoonotic
what disease does bartonella cause in humans? how is it transmitted?
cat scratch fever/disease
transmission: cat scratch
cat scratch fever clinical signs
flu-like symptoms
fever, chills, malaise, headaches
usually self-limiting
immune-compromised people, children
lymphadenitis
endocarditis
bacillary angiomatosis
vascular proliferation in the skin → purplish nodules
blood-filled cystic tumors