ap bio main terms and concepts
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
properties of water
cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, high specific heat, universal solvent, capillary action
elements of each macromolecule
carbohydrates and lipids CHO, proteins CHON, nucleic acids CHONP
ionic bonds
formed between two atoms when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to the other
covalent bond
Formed when electrons are shared between atoms. If the electrons are shared equally between the atoms, the bond is called non-polar covalent. If the electrons are shared unequally, the bond is called polar covalent.
dehydration synthesis
when two molecules bond. A water molecule is lost in the reaction, and a larger compound is formed.
hydrolysis
when water is added to break down a polymer into monomers
what are proteins composed of?
amino group (–NH2), a carboxyl group (–COOH), a hydrogen, and an R-group
what makes amino acids hydrophobic
methyl CH3 group
structures of the protein (the levels)
primary structure is a linear chain sequence of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
the last thing remaining when a protein denatures
secondary structure is created btwn the carboxyl grp and amino group
tertiary structure is the overall 3D shape of the protein composed of many interactions btwn the side chains/groups of various amino acids; these bonds stabilize the protein
quaternary structure is the overall protein structure that is frm aggregation of polypeptide subunits
what are nucleotides made up of?
nitrogenous base, five carbon sugar (pentose), phosphate group(s)
pyramidines
nitrogenous base: pyrimidines are one ring with 6 atoms (CTU)
purines
nitrogenous base: purines are one ring with six atoms bonded to one ring with 5 atoms (AG)
why do cells need to be small?
Cells need to be smaller to achieve a greater surface area to volume ratio so the exchange of materials is more efficient
endosymbiotic theory and evidence
theory where the mitochondria and chloroplasts are prokaryotes that were engulfed by eukaryotes evidenced by:
mitochondria and chloroplasts are the same shape and size as prokaryotes
organelles have their own DNA, double membranes, and ribosomes
ribosome
synthesize protein according to the mRNA sequence within the cell
golgi apparatus
(UPS) warehouse of receiving, sorting, manufacturing, and shipping proteins
mitochondria
folds to enhance the productivity of cellular respiration, allows more ATP to be made and where electron transport and ATP synthesis occur
lysosome
trashcan to digest damaged cell parts or macromolecules using enzymes
plant vs animal cells
plant cells have a cell wall, large vacuole, and have chloroplasts
passive transport
movement of molecules from a high to low concentration, without the use of energy
diffusion
type of passive transport in which small nonpolar molecules (O2 , N2 , CO2) pass freely
facilitated diffusion
type of passive transport that involves transport proteins. typically for transferring hydrophilic molecules
active transport
movement of molecules from a low to high concentration (against the concentration) using energy (ATP)
osmosis
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic
hypotonic is more solute, less solvent
isotonic is equal concentrations
hypertonic is less solute, more solvent
enzymes
catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions that often end in -ase and changes in shape cause denaturation
what affects enzyme optimum range
pH levels, temperature, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, and inhibitors
catabolic and anabolic reactions
catabolic break down which is exergonic, anabolic is build which is endergonic
photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
split into light reactions in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast and the calvin cycle in the stroma of the chloroplast
light reactions vs calvin cycle
light reactions make ATP and calvin cycle uses that ATP to make carbs (glucose) to power cellular respiration
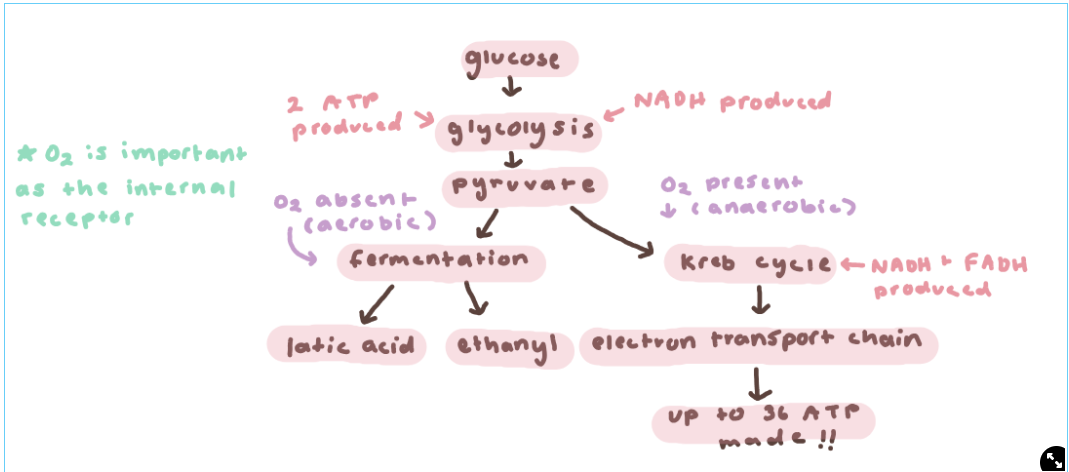
cellular respiration
glucose → glycolysis → pyruvate → krebs cycle or fermentation
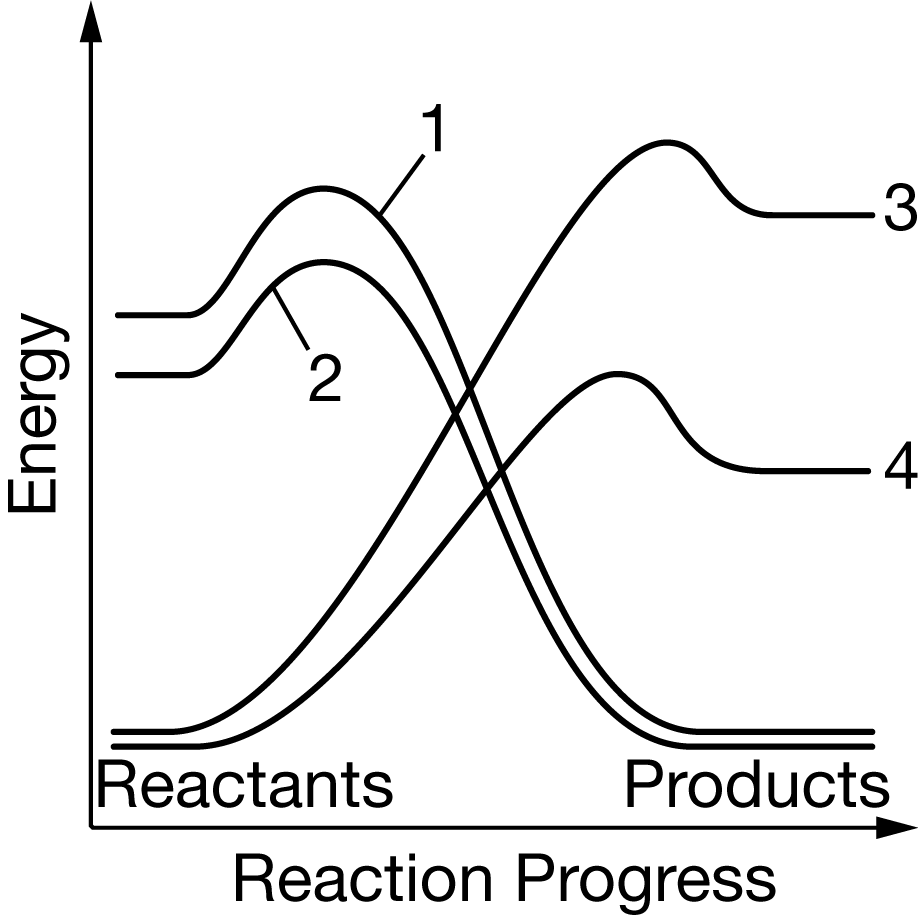
which line represents hydrolysis and phosphorylation
Line 1 represents ATP hydrolysis, and line 4 represents phosphorylation of a substrate
negative feedback
maintains homeostasis for a particular condition by regulating physiological processes
basically reverses stuff
positive
positive feedback - amplifies processes (keeps going until the wanted condition is reached)
ex: giving birth (hormones are continuously secreted until baby is born)
signal transduction pathway steps
reception detection is signal molecule coming from outside of cell
transduction convert signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response
response specific cellular response to signal molecule
the cell cycle phases
interphase and mitosis
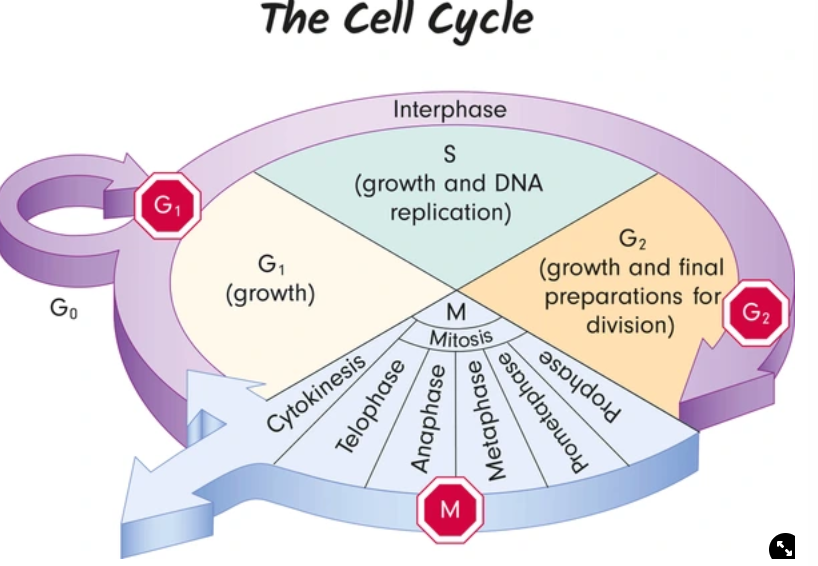
interphase phases
G0 - also called cell arrest, where cell division no longer occurs, as cells can reenter division with appropriate signals (they are nondividing)
not all cells undergo this phase
G1 - cell growth, cell increases in size
S - synthesis, copies of DNA are made via replication
G2 - cytoplasmic components (organelles) are replicated in preparation for division
cell cycle checkpoints
G1 Checkpoint occurs at the end of the G1 phase
cell size, nutrient, growth factor, and DNA damage check
G2 Checkpoint occurs at the end of G2 phase
DNA replication and damage check
M-spindle Checkpoint checks for fiber attachment to chromosome
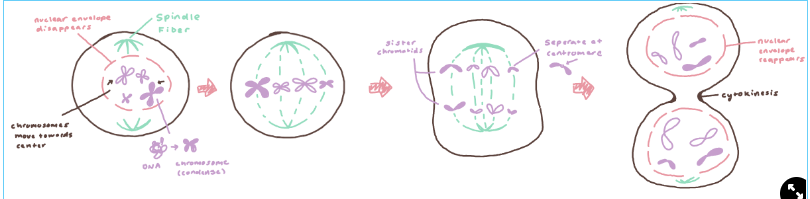
mitosis phases
Prophase
nuclear envelope disappears
DNA coils into chromosomes
fibers move chromosomes toward the center of the cell
Metaphase
fibers align chromosomes at the center of the wall
Anaphase
fibers separate chromosomes to chromatids
chromosomes separate at the centromere
Telophase
nuclear envelope reappears
chromosomes begin to uncoil
Cytokinesis
the actual splitting of the cell into two new daughter cells
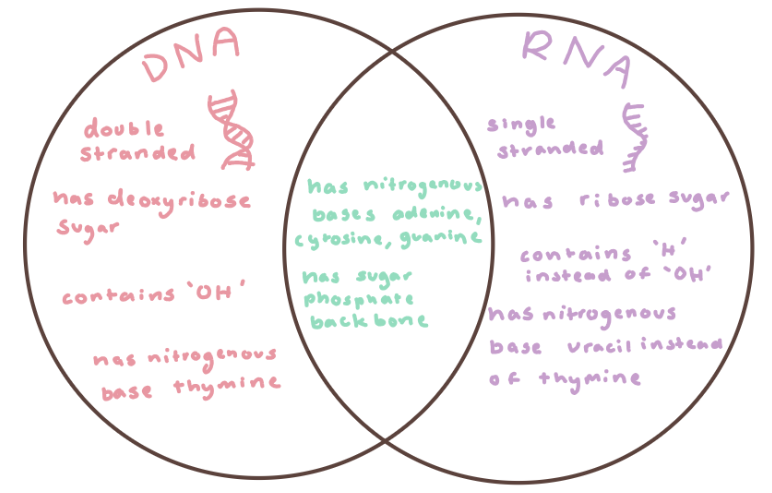
DNA vs RNA
plasmids
are small extra chromosomal, double stranded DNA molecules
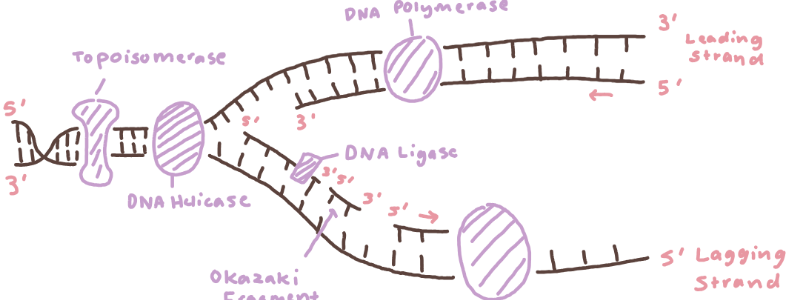
DNA replication
topoisomerase - relaxes the supercoil at the replication fork
replication fork - the area the 2 strands separate
DNA helicase unwinds (unzips) the DNA strand
DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands (the builder)
needs RNA primers to START synthesis
attaches to 3’ of template strand
builds strand in 5’-3’ direction
DNA ligase joins the okazaki fragments together on the lagging strand (works as “glue”!)
transcription
process where the enzyme directs the formation of the RNA molecule
translation
process of generating polypeptides using the info carried on a mRNA molecule
crossing over
where non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes exchange segments
law of segregation
describes the inheritance of genes and traits on different generations
null hypothesis
states that there is no relationship or difference between the two groups of data
incomplete dominance
when neither allele is fully dominant and offspring expresses a new phenotype (usually a mixture)
ex. red and white make pink flower
codominance
two alleles that effect phenotype are both expressed
ex. blood type AB
nondisjunction
failure of chromosomes to fully separate during the formation of gametes
what is evolution influenced by?
environmental stability, genetic variation, adaptations, and fitness
convergent evolution
process in which similar environmental conditions select for similar traits in different populations or species
genetic drift
random change in the frequency of a particular allele within a population (nonselective)
gene flow
movement of individuals between populations causing an exchange of alleles between populations
bottleneck effect
type of genetic drift in which a population is reduced by a large amount often due to natural disasters or competition
homologous vs analogous structures
homologous are variations in a structure that was present in a common ancestor while analogous are unrelated organisms that have similar traits
speciation
creation of new species
allopatric vs sympatric speciation
allopatric is evolution of new species due to geographical isolation while sympatric is due to reproductive isolation
reproductive isolation
prevents gene flow between populations
prezygotic and post zygotic barriers
prezygotic barrier list
prevent production of a fertilized egg
habitat isolation is where species occupy different habitats and rarely come in contact
temporal isolation is where species breed during different times of day, seasons or years
behavioral isolation is where species have different courtship behaviors/mate preferences
mechanical isolation is where reproductive structural differences prevent successful mating and reproduction
gamete isolation is where sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize the eggs of another species
postzygotic barriers
barriers that prevent a zygote from developing into a viable, fertile offspring
niche
extinction provides newly available niches which describes the role an organism plays within its environment
endotherms vs exotherms
endotherms use thermal energy from metabolism to maintain body temperature
exotherms lack these, relying on behaviors and environment
interactions: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, herbivory,
Symbiosis - when 2 or more species live in direct contact with one another:
Parasitism: (+/-) when one organism (parasite)
derives nourishment from another (host)Mutualism: (+/+) when both organisms benefit from
the relationshipCommensalism: (+/0) when one organism benefits
and the other is neither harmed nor benefited
Herbivory: (+/-) relationship where one organism
eats part of a plant or alga
trophic cascade
the negative effect the removal/decrease of a key species has on tropic levels
niche partitioning
decrease in competition over limited resources because of each species accessing resources differently