D103 Discovery of cyclins using biochemistry (Video 35, ALS 22)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
mitosis
portion of cell cycle when a fully grown cell segregates the duplicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a microtubule scaffold (spindle)
cytokinesis
process of cleavage between fully grown cell to produce 2 daughter cells
interphase
the portion of the cell cycle during which cells grow and replicate their dna
hypothesis for mitosis control
factor in a dividing cell that are responsible for cell division can promote division of a resting cell
early exp evidence for the existence of an inducer of the G2 → M transition
exp method for mitosis control
fuse mitotic (M) cell with a cell that is in interphase (G1)
shortly afterwards, fix cells and stain DNA (chromosomes)
examine heterokaryons (fused cells) using microscope
results of mitotic control exp
nuclear envelope of interphase G1 cell disassembles
chromosomes of interphase G1 cell try to condense
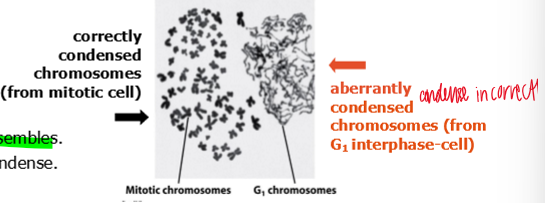
interpretation of mito control exp
a factor in mitotic cell causes interphase cells to disassemble their nuclear envelope, condense their DNA, and enter mitosis prematurely, regardless of which stage the interphase cells are at in the cell cycle
we now know the identity of this factor to be mitotic cyclin
biochem appraoch to study control of mitosis
requires a relatively large amount of synchronously dividing cells
what sort of systems can be used to provide material for control of mitosis
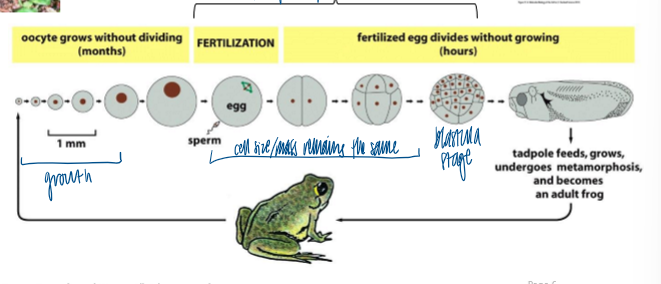
early embryos from frogs, sea urchins, and clams
external fertilization
using eggs and sperm; enables analysis fo the cell cycle during early stages of embryo development in thousands of oocytes fertilized at some time
when cells are undergoing synchronous division
how are frog oocytes used
provide sufficient material for biochem analysis of meiosis and mitosis
1st division = 90 min post fertilization
divisions 2-12 = 30 min each
2^12 cells after 700 hours
only S and M (simplies analysis)
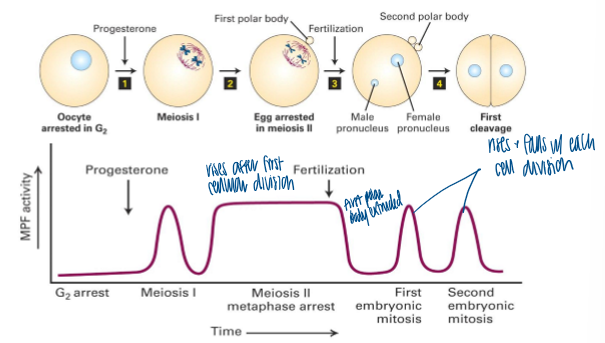
what happens when frog oocytes are treated with progesterone
undergo meiotic maturation (including a cell divsion) in vitro
G2 arrested oocytes can be stimulated to undergo meiotic maturation (advance to arrest in metaphase II) in vitro by exposure to progesterone
involves a cell division (formation of first polar body)

frog oocytes with microinj of cytoplasm from oocytes arrested in metaphase II
promote meiotic maturation (cell division)
inj of cytoplasm from a metaphase II oocyte into G2 arrested oocyte causes non-progesterone treated G2 arrected to enter meiosis
cytoplasm of progesterone treated contains an oocyte maturation-promoting factor

mpf activity
cyclical and relatively high as cells enter meiosis and mitosis
correlates with entry of cells into meiosis or mitosis
experiment for mpf activity
take extract from oocytes and early embryos at different stages of development and use microinjection assay in preceding slide (inj into oocytes arrested in G2) to detect when oocytes and embryos have MPF activity
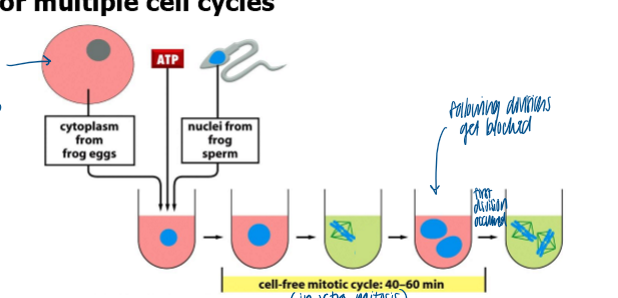
what does this exp system allow us to analyze
if MPF is protein, RNA, or both
monitor decondensation of sperm pronucleus, rep of dna, and mitosis as evidence of mpf
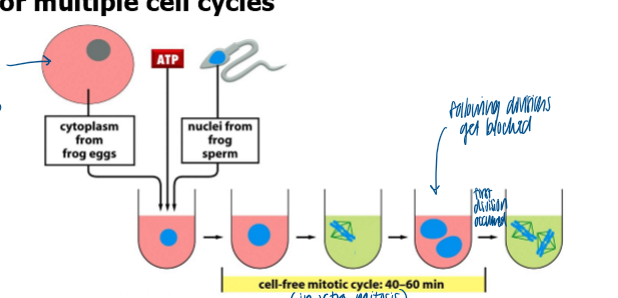
is oscillation in MPF activity in early xenopus eggs independent or depend of oocyte nuc
independent
cytoplasmic extract from Xenopus eggs contains all materials necessary for multiple cell cycles
what indicates new protein synthesis is required to generate MPF each cycle
MPF activity is blocked by addition of cycloheximide (protein syn inhibitor)
studying cyclins in clams
induce clams to release sperm and eggs
fertilize eggs to generate synchronous population of developing embryos in presence of S35 methionine
collect samples of embryos at different times following fertilization
analyze newly synthesized (radioactive) proteins by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with autoradiography against x-ray film
how was mitoic cyclin first identified in clam embryos
cyclin A (S cyclin) and B (M cyclin) accumulate during interphase, are greatly reduce at the end of mitosis, then reaccumulate during subsequent interphase
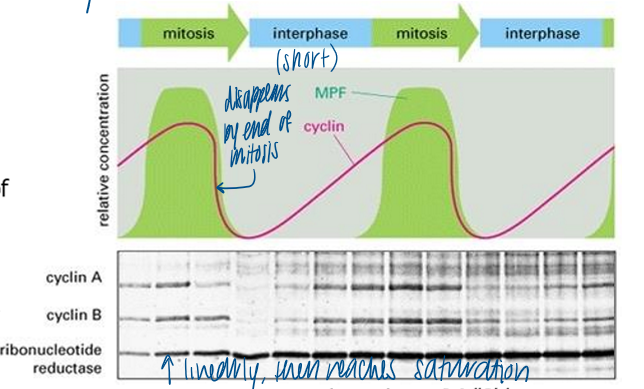
ribonucleotide reductase
a house-keeping protein which serves as an internal control for comparison of a newly synthesized protein that is not degraded with each round of mitosis
what is cycling of MPF activity and mitotic events dependent on
regulated production and destruction of M cyclin
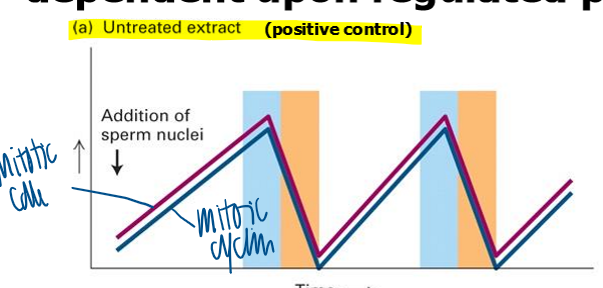
positive MPF control
experimental system works
increase in mitotic cdk and cyclin correlate
RNAse treated extract (negative control)
no increase or change = need RNA for mitosis

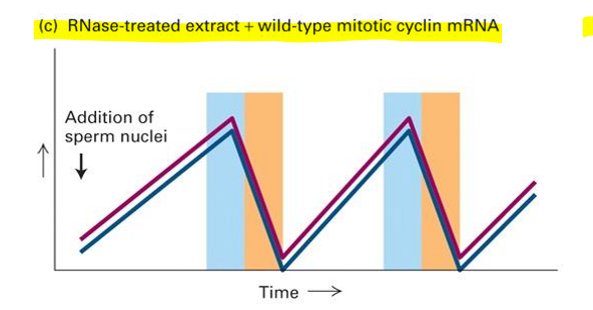
RNAse-treated extreact + WT mitotic cyclin mRNA
M-cyclin RNA is the key mRNA required to allow undergo mitosis in this assay
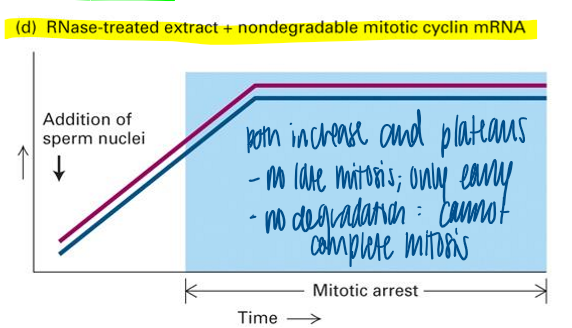
RNase treated extract + nondegradable mitotic cyclin mRNA
M cyclin must be destroyed to allow completion of mitosis in this assay
both increase and plateau
no late mitosis; only early
no degradation = cannot complete mitosis
visualization of GFP-cyclin B in mammalian cells during mitosis
example of control of cyclin/CDK activity by subcellular localization and destruction of cyclin
cyclin B moves to nuc during prophase, then is destroyed at anaphase
what controls irreversible destruction of M cyclin
APC/C + 2 related co-factors via polyubiquitinylation durign late mitosis and G1 of the next cell cycle
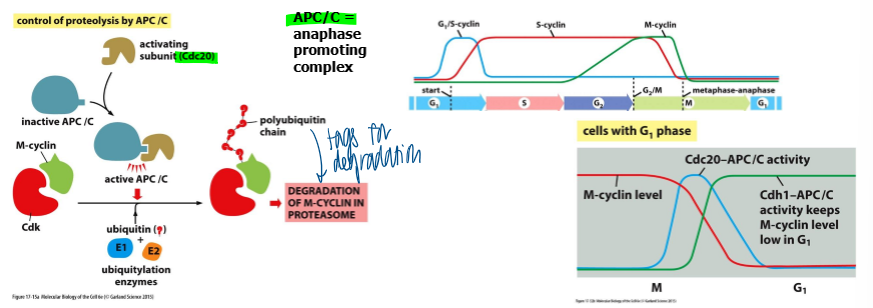
m cyclin and mitosis progression
M cyclin must be degraded to complete mitosis
APC/C + Cdc20 initates degradation of M-cyclins at anaphase
APC/C + Cdh1 completes degradation of M cyclin during late mitosis and early G1 of next cell cycle
What caused premature condensation of G1-phase chromosomes in a cell fused with a cell in mitosis ?
A. Something in the nucleus of the cell in mitosis.
B. Something in the cytoplasm of the cell in mitosis.
C. The condensed mitotic chromosomes signaled to the non-condensed chromosomes to undergo condensation.
D. Something attached to the plasma membrane of the mitotic cell.
E. Without additional experiments, it is impossible to tell what caused premature condensation of the G1 chromosomes and where the activity is localized in the cell.
E. Without additional experiments, it is impossible to tell what caused premature condensation of the G1 chromosomes and where the activity is localized in the cell.
Which stages of the cell cycle are absent from cells during early embryonic development of Xenopus frog embryos ?
A. G1 and S
B. G1 and M
C. G2 and S
D. S and M
E. G0 and G
E. G 0 and G2