IB Biology HL: Human Reproduction - D3.1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
sexual reproduction
two parents, and uses gametes
asexual reproduction
only one parents, mitosis. chromosomes are identical to parent
internal fertilisation
done in land aminals, as wet environment needed
external fertilisation
done by water animals, such as frogs or fish
animals doing asexual reproduction
starfish
sharks
komodo dragons
pythons
advantages of asexual reproduction
very quick
comparatively lower energy required (no looking for mates)
more efficient
disadvantages of asexual reproduction
sum of (negative) mutations
less genetic variation
can adapt less quickly
advantages of sexual reproduction
variation in species is maintained
best genes manage to reproduce
better survival rates
Causes of genetic variation in sexual reproduction
in meiosis 1, genetic material is exchanged between non sister chromatics (not the same) of homologous chromosomes: crossing over
when members of homologous pairs separate during meiosis 1, maternal and paternal pairs split up: gametes have different variations of homologous chromosomes
adapations of sperm cells
flagellum to propel cell to egg cells
mitochondria to perform respiration, produce atp
acrosome: has enzymes to break down egg cell membrane
streamlined shape
no waste of space in head; head mostly nucleus
parts of ovum
haploid nucleus
large stores of lipids in cytoplasm
cortical granules
layer of protective glycoproteins (zona pellicula)
layer of follicle cells (corona radiata)
male reproductive system
bladder: sack that store urine
penis: used for internal fertilisation, to allow sperm to be as close as possible to egg cells
prostate: produces fluid that helps in transport and nurishment of sperm
sperm duct: transports sperm from testes to urethra
epididymis: store sperm (right behind testicles)
testis: outside the body to prevent overheating
urethra: releases urine from bladder and sperm from seminal vesicle
erectile tissue: part of penis, artery at the base of penis, which when needed will bring much blood, increasing tension
female reproductive system
vagina; opening for penis, to allow internal fertilisation
cervix: way from vagina to uterus
fallopian tubes: site where fertilisation happens, attachment where ovary attaches to uterus
ovaries: site of egg production and maturation
hermaphrodites
an organism with both female and male reproductive parts
example of hermaphrodite animals
earthworms
snails
banana slugs
primordial follicle
bunch of small cells surrounding actual egg cell, before having matured.
the follicle doesn’t get released, and it breaks down into a corpus luteum
ovarian cycle
follicular phase ( follicle maturation )
ovulation phase ( mature follicle gets release )
luteal phase ( corpus luteum gets broken down
uterine cycle
menstruation: uterine lining breaks down and gets thinner
menbrane thickens, 14 days in ovulation occurs, 28 days if no fertilisation membrane breaks down as decrease in hormones
LH
luteinizing hormone: made by the pituitary gland. Promotes ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum. stays relatively constant, when it peaks is ovulation
FSH
follicle stimulating hormone: made by pituitary gland. Promotes development of the follicles in the ovary. Peaks when ovulation occurs
estrogen
made by the developing follicle and corpus luteum in the ovary. promotes thickening of uterine lining. level of oestrogen is increasing as follicle develops. Peaks right before ovulation.
At low concentration, first 10 days, aestrogen inhibits LH production
after 10 days, aestrogen levels rise, and now has a positive effect on LH production
after ovulation, oestrogen inhibits progesterone
progesterone
made by corpus luteum. maintains thickened uterine lining. Increases right after ovulation
whole process of menstrual cycle
drop in progesterone = menstruation
FSH stimulates development off follicule in the ovary: follicle starts developing
the follicle produces aestrogen which stimulates the thickening of uterine lining
the peak of LH stimulates ovulation at day 14
corpus luteum starts disintegrating but continues releasing progesterone
progesterone increases, which maintains uterine lining
eventually decreases
Outline the functioning of the hormones influencing menstrual cycle (7)
decrease in progesterone leads to breakdown of uterine walls, and leads to menstruation
FSH and LH are from the pituitary glands
FSH gets released, stimulating the development of primary follicles
development of Primary follicles secretes oestradiol
oestradiol stimulates build up of uterine lining
oestradiol concentration peaks, inhibits FSH, stimulates LH.
no more FSH → prevents multiple follicles from developing
LH peaks stimulates, ovulation, leads the follicle to turn into a corpus luteum
corpus luteum secretes progesterone
progesterone maintains uterine walls and inhibits FSH and LH secretion
low FSH and LH lead to corpus luteum to degrade
no more corpus luteum = no more progesterone = uterine walls break down, menstruation
if egg is fertilised, releases a hormone which maintains corpus luteum until 16 weeks, after which placenta takes over. (human chorionic gonadotrophin)
why does fertilisation need to occur in a wet environment
sperm need to be able to swim
advantages and disadvantages of internal fertilisation
more efficient: fertilisation more likely to happen
parentage is more easy to determine
but
mating rituals energy consuming
require time in vulnerable state
advantages and disadvantages of external fertilisation
already in wet environment
less energy required, animals musn’t be immobile
but
more vulnerable to environmental threats
less certainty of fertilisation
requires more gametes produced
how does the sperm cell get in the cell ?
has a acrosome which contains digestine enzymes
it allows it to get through the zona pellucida
once one sperm gets in, cortical granules go towards cell wall, hardening the wall
In vitro fertlisation step
downregulation of menstrual cycle
superovulation: high levesl of FHS are injected over 10 days, to stimulate multiple follicles
after that, an injection of human chorionic gonadotropin hormole is injected, to start egg maturation process
after 36 hours, the egg cells are collected under general anesthesia
eggs are prepared, removed from follicles, and combined with sperm
fertilised eggs are incubated before implantation
for 2 weeks after implantation, progesterone is given, keep getting given until pregancy is confirmed
success rate is about 40%, so 1-2 blastocysts are added per attempt
what hormone is regulates FSH and LH ?
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) , from hypothalamus
anterior pituitary gland
next to Hypothalamus, produces LH and FSH
effect of LH and FSH on males
carried to testes
LH stimulates release of testosterone
testosterone increase leads to GnRH inhibition, which inhibits FSH and LH production
negative feedback mechanism
FSH stimulates sperm production
hormonal feedback mechanism in females
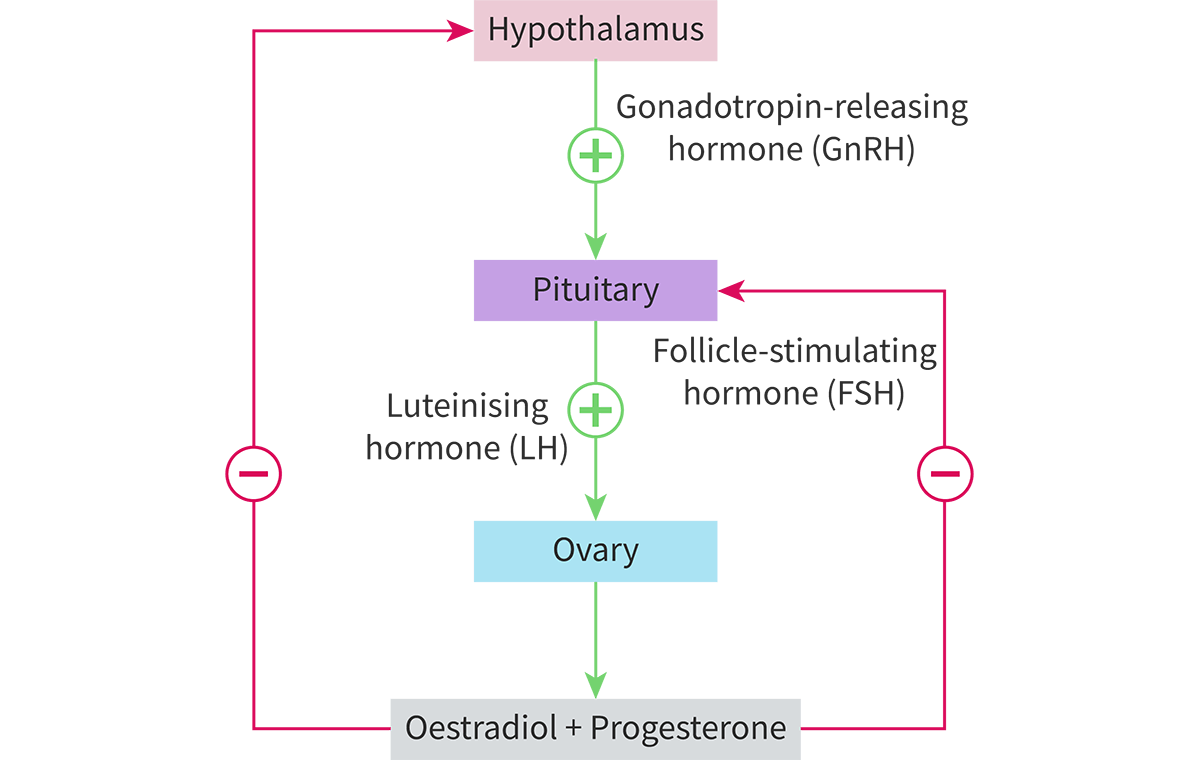
Which hormone(s) secreted by the anterior pituitary gland increase the sex hormone production in male and female reproductive systems?
LH and FSH
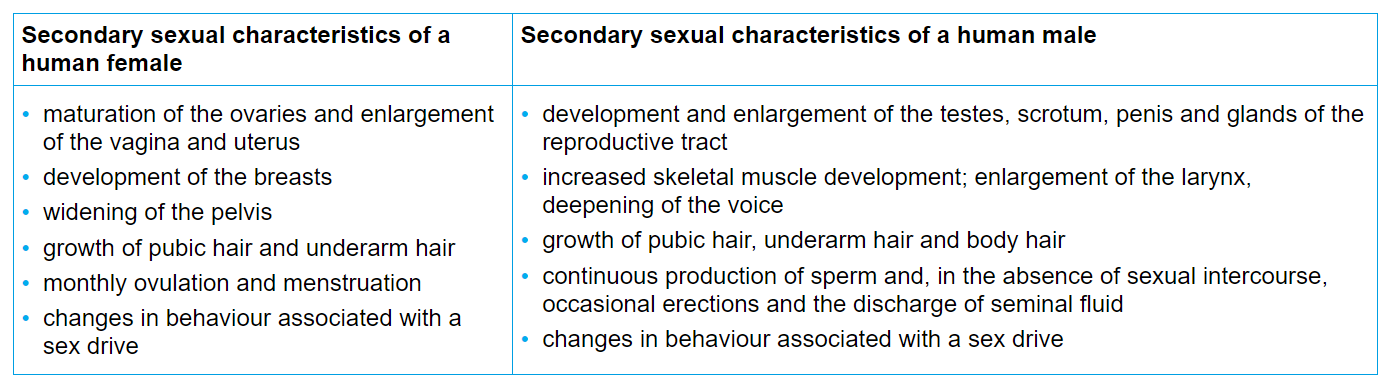
What is the effect of estradiol (oestrogen) and testosterone on puberty?
expression of secondary sexual characteristics
all secondary sexual characteristics
gametogenesis of egg cells
Oogenesis
featal phase
oogonia, through mitotic division, turns into primary oocytes during faetal develpment
girls are born with all of the ovocyte, which stopped at prophase of meiosis 1. Called mitotis arrest. Continues when/if that egg gets ovulated
ovulation
meiosis 1 finished: First polar body + secondary oocyte → turns into n
meiosis 2 starts and stops at metaphase
fertilisation
meiosis 2 : second polar body + Ovym → n. Stops at metaphase of meiosis 2, unless fertilisation by a sperm occurs
Gametogenesis of sperm cells
spermatogenesis
sperm mother cell 2n: spermatogoonia
much mitosis: primary spermatocyte → 2n
meiosis 1: 2 secondary spermatocytes → n
meiosis 2: 2 spermatids → n
spermatids turn into sperm (spermiogenesis)
one primary spermatocyte = 4 sperms
spermiogenesis
from spermatid (n) to sperm (not the whole process !)
changes during spermiogenesis
flagellum gets formed
acrosome caps get added
shed extra cytoplasm
prevention of polyspermy
plasma membrame becomes impermeable due to changes in membrane potential
corticle reaction:
when sperm reaches the plasma membrane of the secondary ovocyte,
cortical granules fuse with plasma membrane
Release their contents (hydrolytic enzymes) by exocytosis so sperm get destroyed
and the zona pelucida hardens preventing the sperms from making any more progress
pre-implantation embryonic development stages
rapid mitotic division (cleavage)
Morula
blastocyst
trophoblast from blastocyst (outer layer) eventually differentiates into placenta
zona pellucida is shed
will eventually, after 7-8 days, implant into uterine endometrium
morula
16 cells
day 4
zona pellucida still surrounds it
same size as zygote, as only division no growth
blastocyst
32 cells
hollow
two layers
outer: trophoblast (placenta)
inner cell mass (the actual body)
fluid filled cavity: blastocoel
will eventually shed zona pellucida
hCG
human Chorionic Gonatropin
role of hCG in pregnancy
trophoblast cells secrete hCG
hCG maintain corpus luteum during pregnancy
this causes it to continue secreting progesterone
by month 3, not as necessary, placenta takes place of corpus luteum and secretes progesterone and oestradiol
how do pregnancy tests work
test for presence of hCG in urine
contains monoclonal antibodies
will bind to hCG if positive, causing a colour change
role of placenta
exchange of resources from embryo to mother.
mother sends oxygen and nutrients
embryo sends waste and CO2
maternal portion of placenta
uterine endometrium
embryonic portion of placenta
chorionic villi
contains large surface area, to take in nutrients from material blood in the intervilious space
space between enbryomic and maternal section of placenta
intervillious space; mothers blood is present there, enters by endometrial arteries and comes back from endometrial veins. No direct contact between maternal blood and foetal blood
progesterone along pregnancy
stays high until month 7
starts to plateau, and eventually start declining when preparing for childbirth
effect of foetus pressure on uterus walls
detectors on uterine walls detect stretch
stimulates cortisol productions
stimulates production of specific type of oestradiol: oestriol
oestriol inhibits progesterone production by placenta
and makes smooth uterine muscles more receptive to oxytocin
hormones during childbirth
oxytocine is released by posterior pituitary gland
vauses uterine contractions initiating parturition
foetus responds, send prostaglandings, intensifying uterine contractions
this causes posterior pitiutary gland to release more oxytocin
this is a rare example of a positive feedback loop
hormone replacement therapy
menopause marked by decrease of oestradiol and progesterone levels= bad side effects
HRT is a treatment which relieves these symptoms
oestradiol-progestin is given
initially research suggested positive effects on CHD, but after controlling for income it was less conclusive