Evolution of personality traits - Lecture 9
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is natural selection?
Reducing variation to identify the most adaptive trait for the environment the individual finds themselves in and this characteristic is passed on across generations
traits have fitness which indicate adaptation in terms of what?
Fecundity
survivorship
What is Fecundity?
The number of offspring
what is survivorship?
Living long enough to reproduce
What is sexual selection?
natural selection arising through preference by one sex for certain characteristics and traits in individuals of the other sex that are desireable. .
What is inter-sexual selection?
Intersexual selection occurs between members of the opposite sex. It is the females choice and it often results in showy characteristics for males.
What is intra-sexual selection?
intra-sexual selection occurs between members of the same sex like when males directly compete for mating opportunities or territories.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
When allele frequencies in a population are not changing/remain constant (therefore the population is NOT evolving)
What happens as a cause of the hardy-weinberg principle?
genetic equilibrium
What is Copy Number Variation (CNV)?
individual differences in repetition of DNA segments - may be due to replication/duplication errors
What is Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)?
Replication errors via base pair substitution
What are translocations or inversions?
- re-arrangements of large chromosomal regions (major detriments)
What is mutation-rate?
Speed at which new mutations enter the functional genome
Humans 1.67 per individual per generation. About 1 in 5 are born without a new mutation
- symmetry across body symbolises low mutation rate.
What is a mutation load?
Older, mildly harmful recessive mutations
How many mutation loads does a human have roughly?
500
What is directional selection?
selection which occurs when a phenotype at one extreme is at a disadvantage
- e.g Darwin's Finches Bills - most adaptive (greater fitness) and is selected for model of evolution of IQ
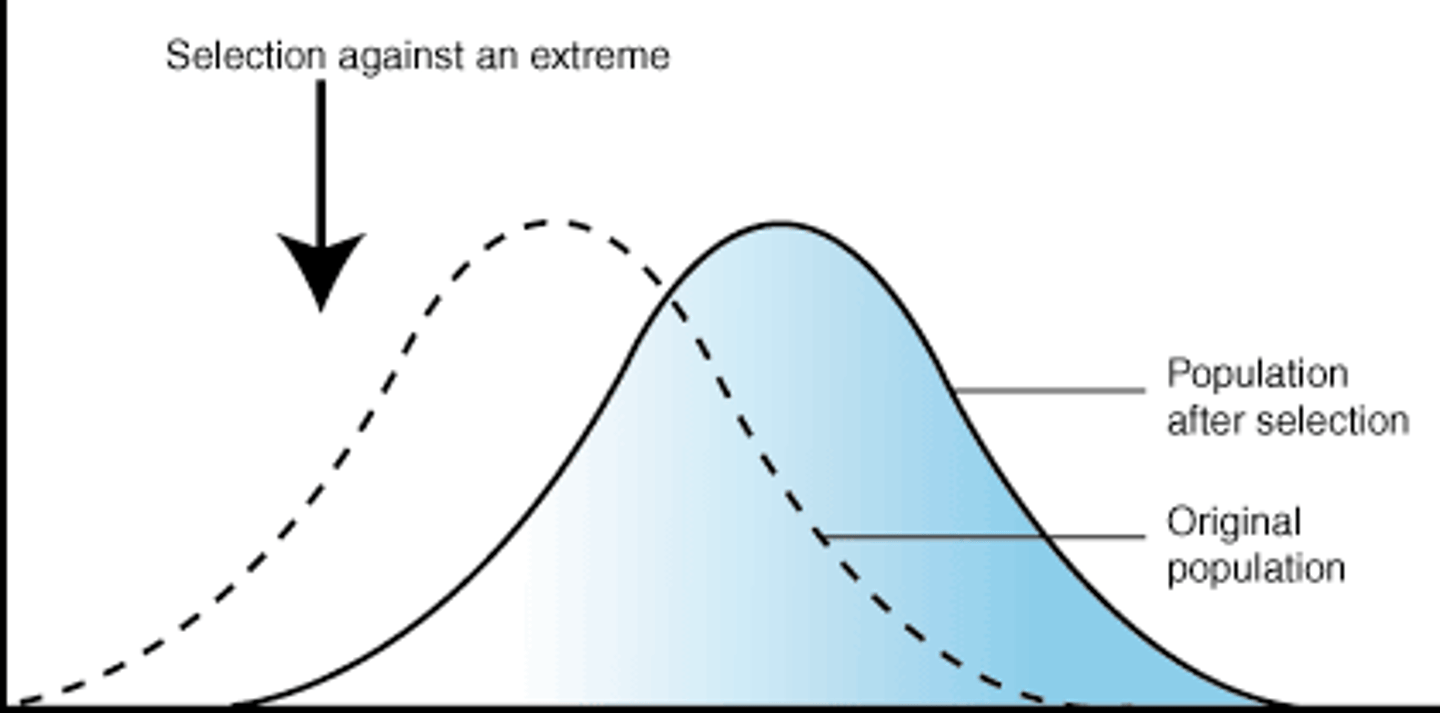
What is Stabilising selection?
Individuals closest to the mean are favoured, and any new characteristics are selected against.
- Extremes are selected
against. Common in
stable environments.
- Extreme birth weight in
babies is selected agains
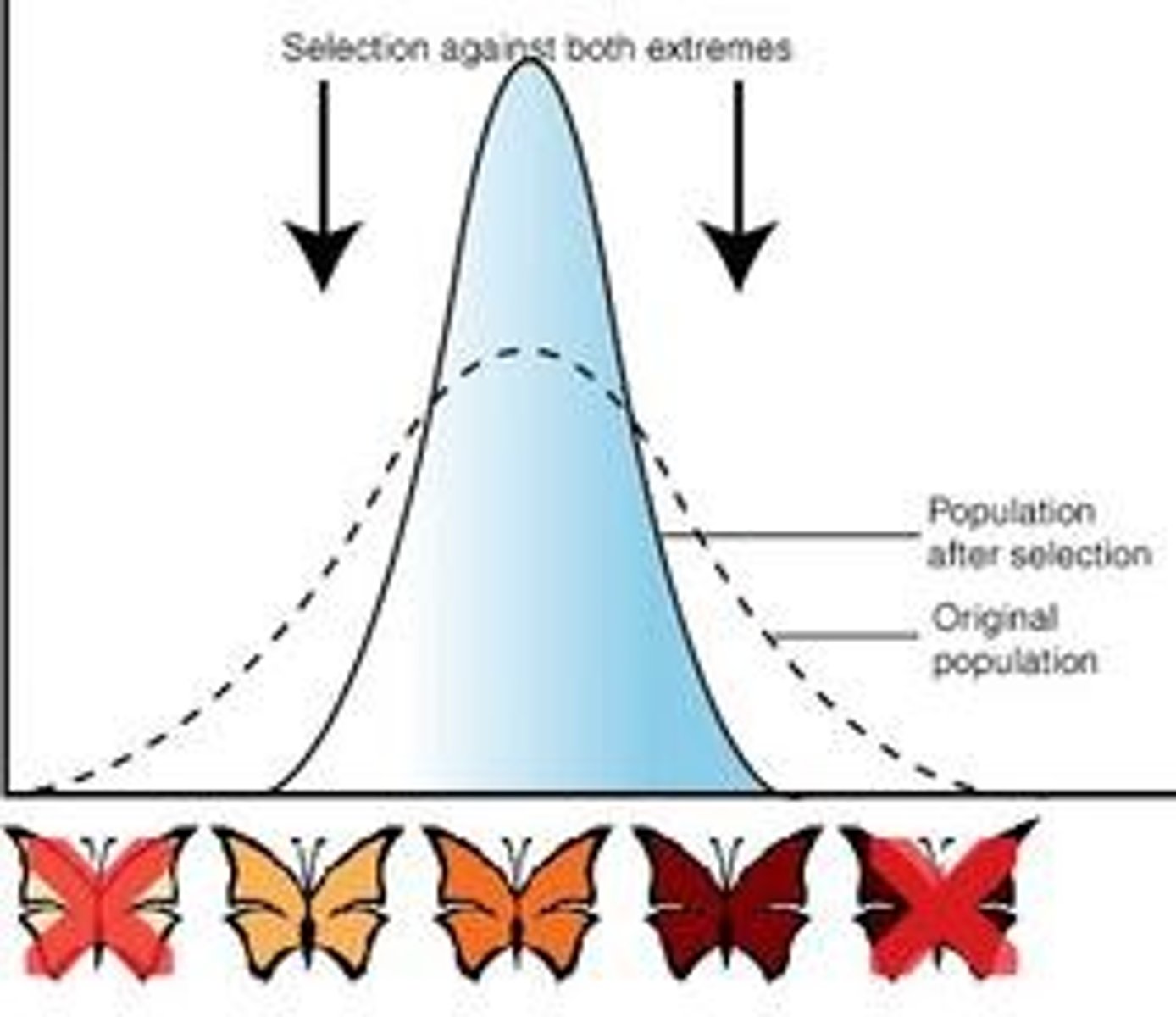
What is Disruptive selection?
favours individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
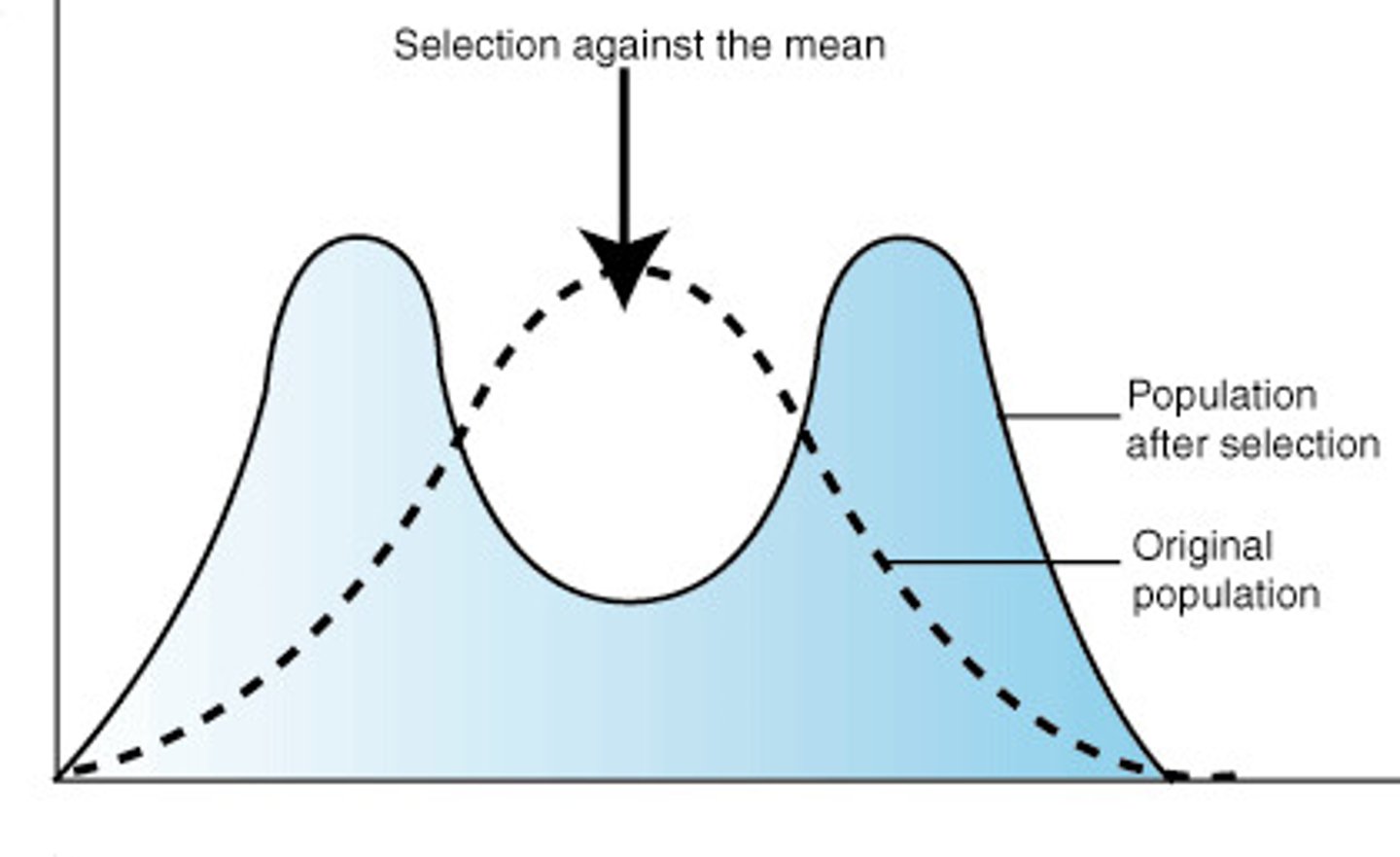
What leads to increased genetic variation in the trait? (selection neutrality)
Fitness nertral mutations that build up - effected by genetic drift
Traits do not influence fitness but...
affect many fittness outcomes
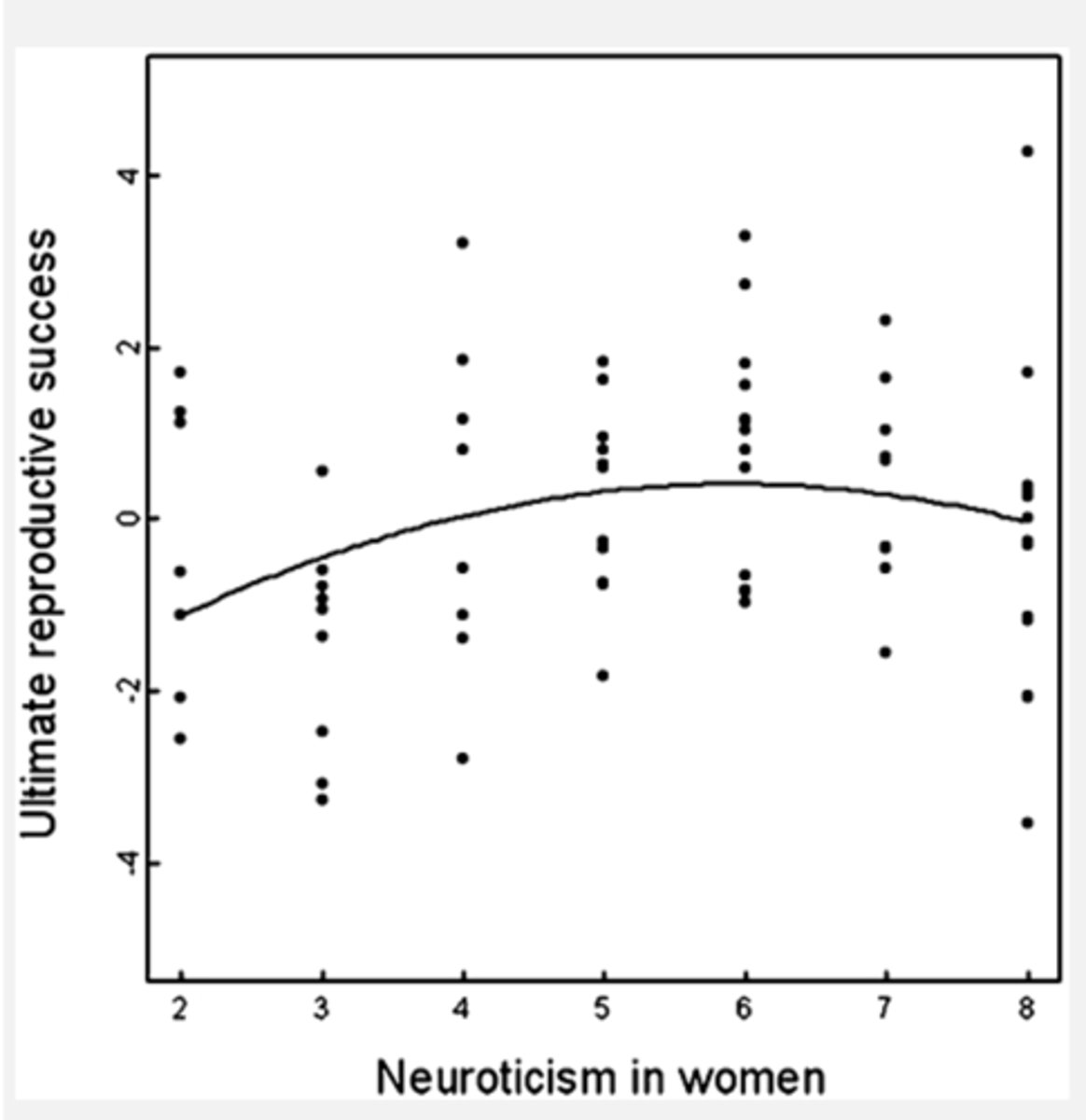
What did Alvergne et al (2010) find on women and neuroticism?
Greater reproductive success in women
is linked to average levels of neuroticism
- U-curve to give optimal level.
What did Alvergne et al (2010) find on men and Extraversion?
Higher extraversion in men is linked to greater social status and more children
- need to have the resources available to raise children.
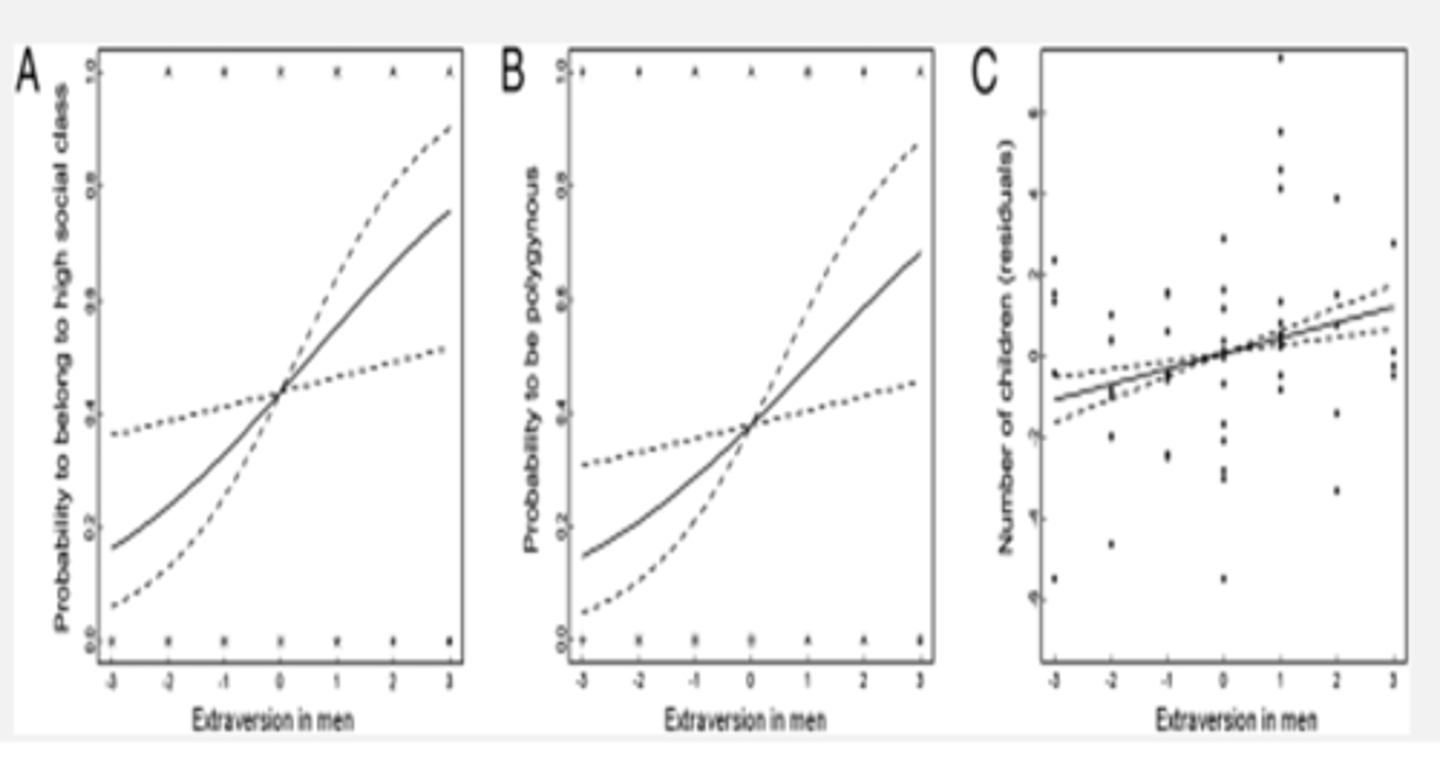
which traits are important for sexual attractiveness and show assortative mating
Openness and conscientousness ((McCrae, 1996; Balley et al., 2013))
What is Environmental Heterogeneity?
when Fitness varies across time and space, and are on average neutral across all spatio-temporal contexts
What is Frequency-Dependent Selection? positive traits:
Positive traits = favours traits with high frequency - runaway selection
What is Frequency-Dependent Selection? negative traits:
Negative = favours traits with a low frequency
What are Mono-Zygotic twins?
identical twins
what are dizygotic twins?
non-identical twins
Do MZ and DZ twins share the same environment?
assumed but not necessarily true > MZ treated by parents as more 'equal'
This may be questioned
Why may the gene-enviornment correlation in twins not be so minimal?
the genetic make up of an individual influences the types of environment they select to be in - individuals select themselves into certain environments
Does mating occur at random in Twins?
Choose similar people - this increases the DZ correlation relative to the MZ correlation and over estimates the effects of E
What is Zygosity?
degree of similarity of the alleles for a trait - ; How do you assess if twins are identical or not a long time after birth?
Is there only a genetic component to traits?
No as gene onset depends on the environment.
- there is a heritable component - higher concordance in MZ twins
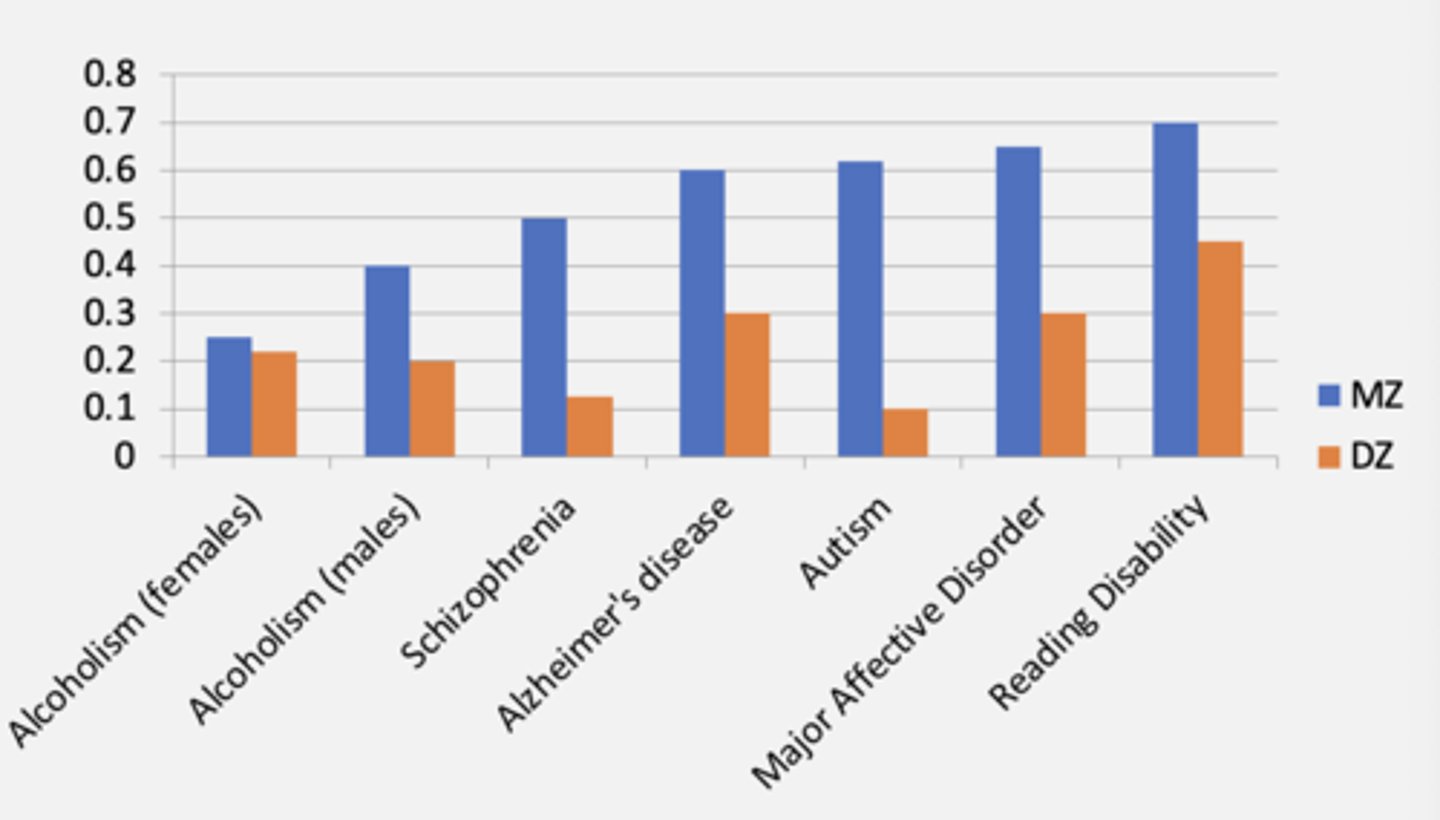
When is heritability over estimated?
if the Gene-environment correlation focuses on factors that developmentally make people similar more than they really are.
When is heritability under estimated?
under-estimated if the Genetic-environment correlation focuses on factors that developmentally make people dissimilar
Is it nature or nurture?
NO - it's nature and nurture.
What examples suggest that genetic effects only emerge with respect to environmental exposure?
•Can't smoke if cigarettes are not available
•Corn selected for height in one generation will be small in the next if there is little rain fall
•Traits can be inherited across generation but means levels differ as environments change (Flynn Effect; Twenge Effect)
Genes and the environment...
interact dynamically. - expression of the gene is contingent on the environment and vice versa.
What are Active Genetic effect correlations with the environment
Your phenotype actively moves you towards different enviornments. e.g if you are 6'7 you may think to try out basketball that will be compatible with your phneotyle
What are passive Genetic effect correlations with the environment
Your phenotype may passivley move you towards different environemnts. e.g if your parents play the piano and have one in the hosue - sets up the enviornent for you genes to operate on this
What are Evocative Genetic effect correlations with the environment
people respond to people differently depending on you phenotype - this affects then how you interact with the enviotnment/change your bhevaioru which changes how the gene is expressed
How do shared environments (c2) start?
Prenatally - uterus
- Choroin
How do post natal shared environments (c2) effect correlations with the environment
Extrafamilial
Age
Sex
Sibs as environment
Parent-Child
How do non-shared environments (e2) influence the role of the environment?
- Postnatal Experience
- Chance prenatal events
- Temporal Fluctuations - how things change over time
How do Gene-environment factors interact?
Prenatal
Postnatal - unspecified E
Postnatal - measured E
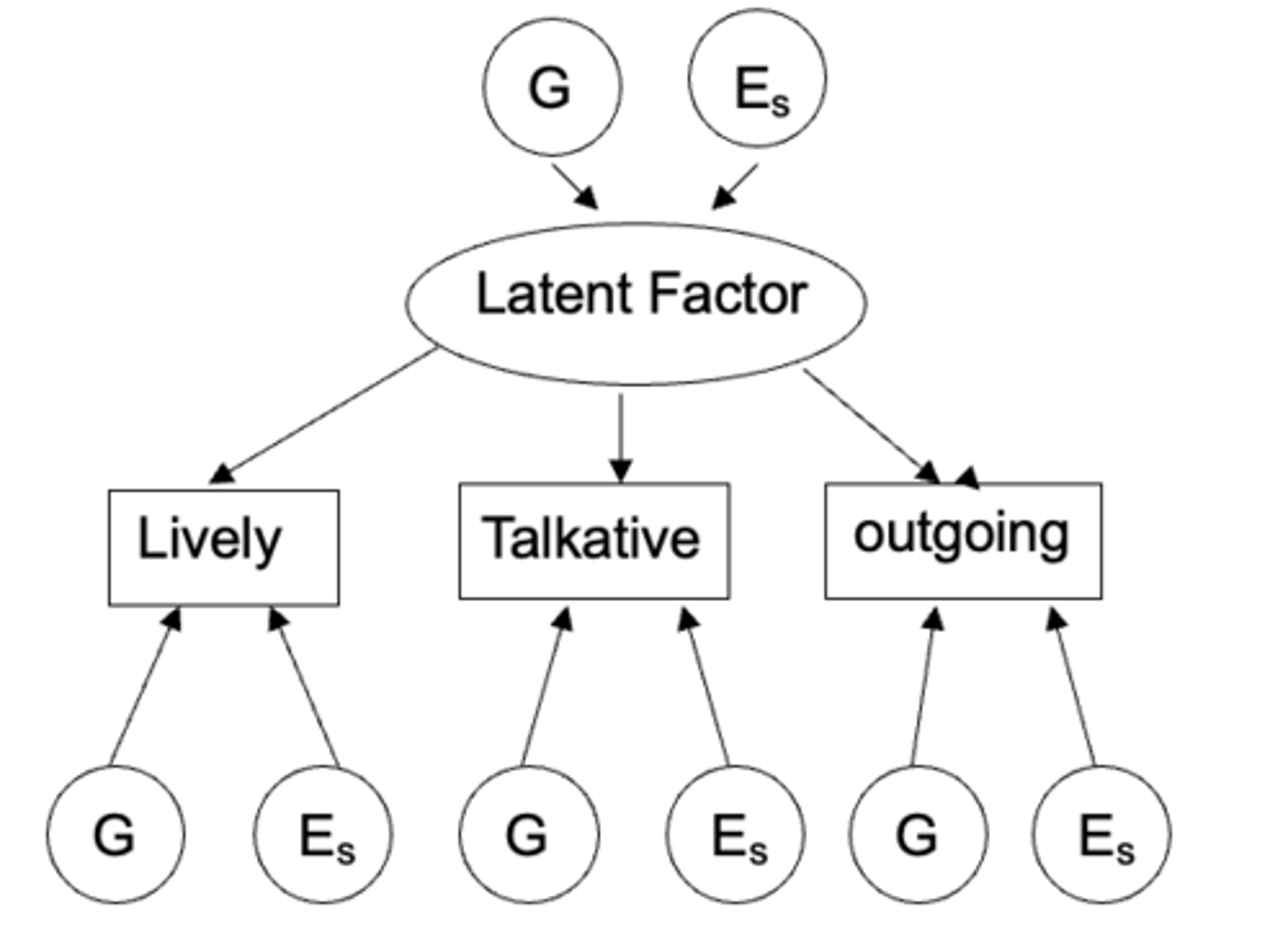
What is the Cholesky Decomposition?
the variance within and the covariance between personality traits across each assessment are decomposed into their genetic and environmental components
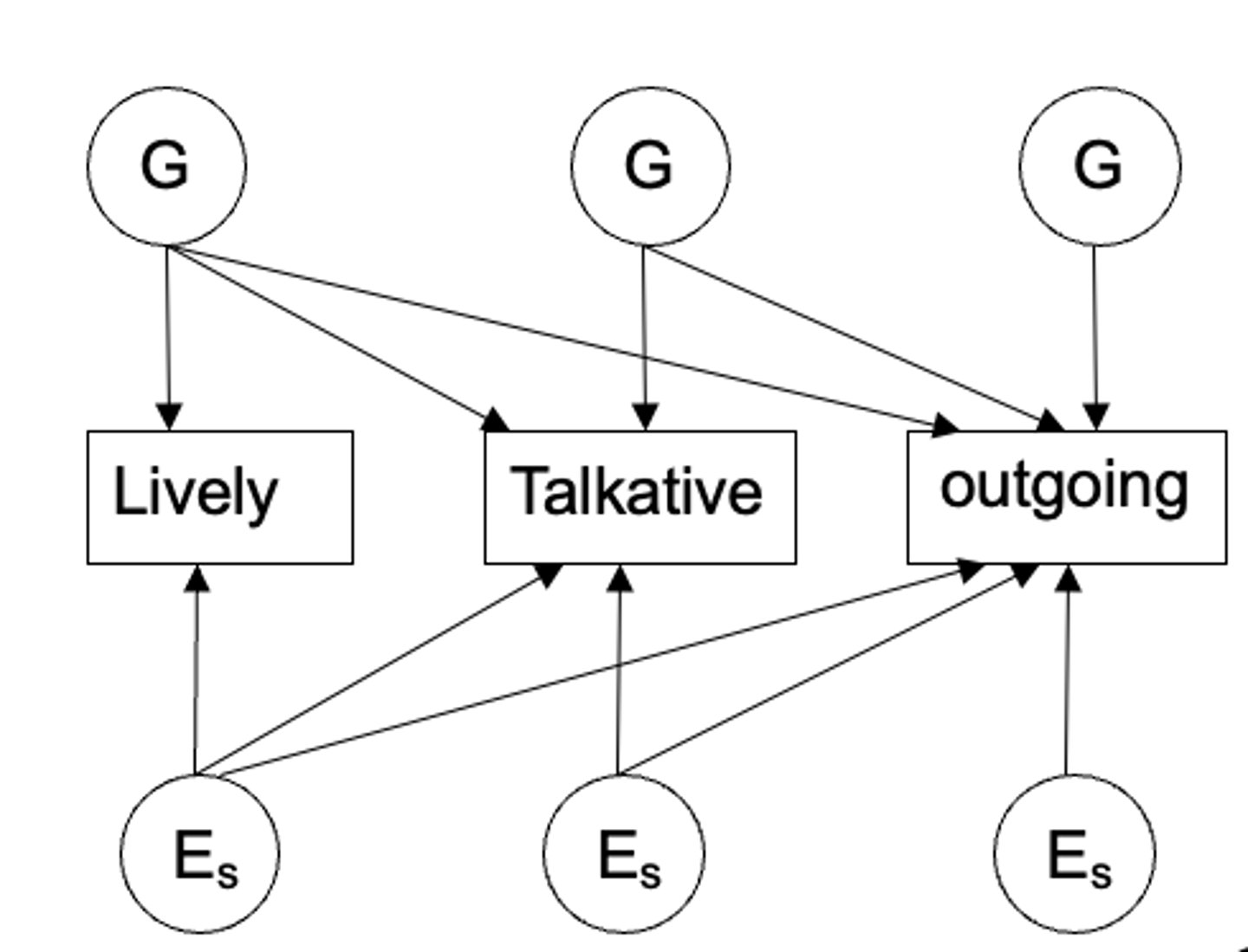
What is the Independent Pathways model?
- posits that common genetic and environmental factors influence observed variables directly, without an intermediate higher-order factor
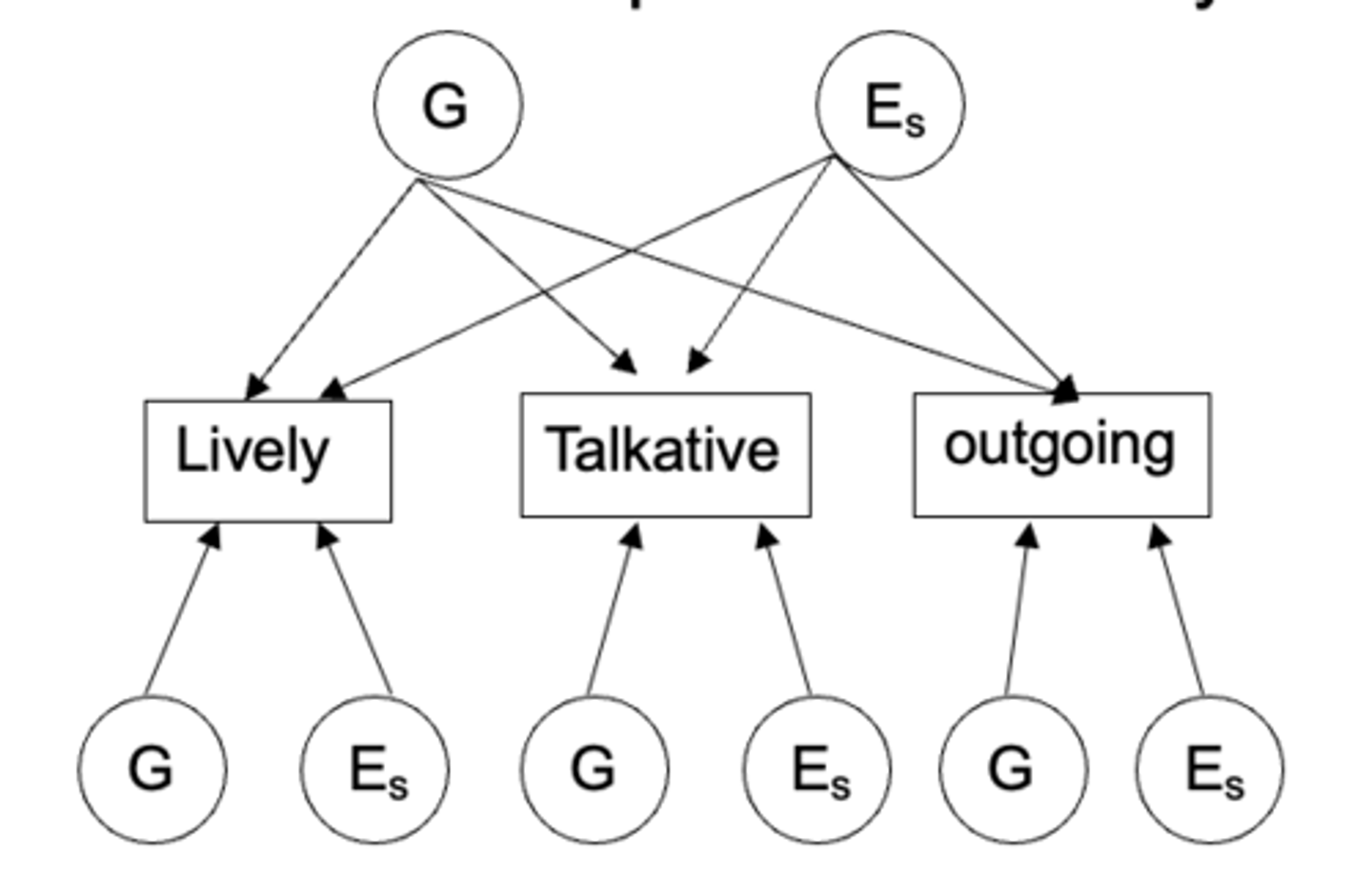
what is the Common pathway model?
each common latent factor (e.g extraversion) have its own environmental affects but the behaviours that are elicited have their own genetic effects.
- suggest that genetic and environmental factors influence all variables through a single, underlying latent factor
What may trait expression depend on?
Yes - sometimes - you may exhibit extraverted behaviours if you are extraverted but People should have a preferred way to express their trait (their average score on a personality trait) but also be able to express aspects depending on context
- your personality is your average across all contexts.
What do behavioiral reaction norms do?
Look at how traits and enviornments are linked
- how people change in their expression of behaviour as the environments they are in change.
What is an example of behavioural reaction norms?
•A person high in extraversion will be quite in a library, but probably less so than a person who is more of an introvert.
- express introverted and extraverted behaviours depending on the context
What is personality?
the average behavioural response across contexts. This is how personality is traditional defined (average response) what traditional personality measures are supposed to tap into
what is behavioural plasticity?
the flexible expression of the trait. That is, it is acknowledged that people have an average response but that they can vary their behaviour depending on context
- the trait changes as context changes.
What is the Fleeson & the Density Distribution approach? phenotypic expression
•Traits reflect ‘accumulation of everyday personality states’: Personality
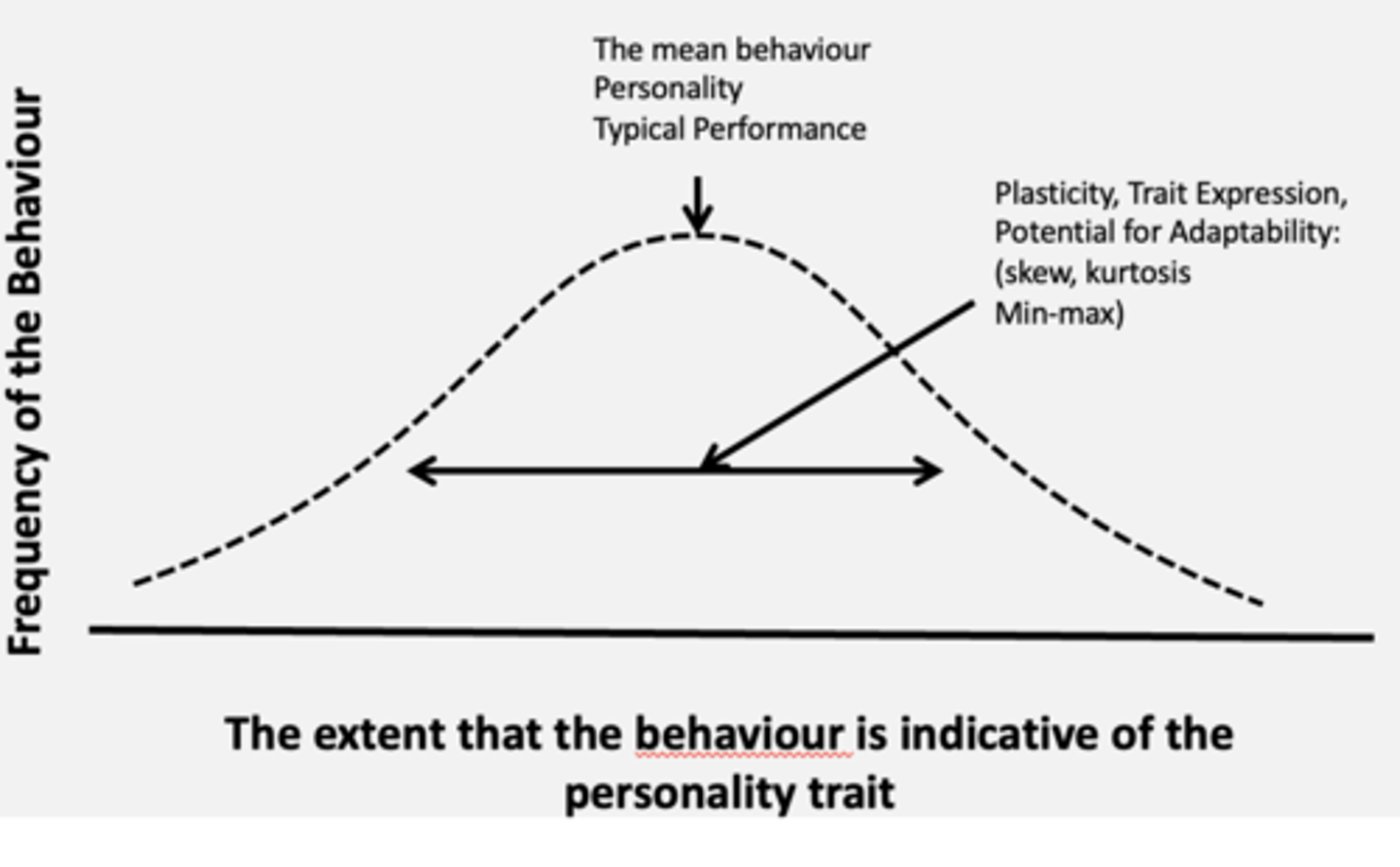
What is Experience Sampling Methodology (ESM)?
- Use experience sampling methods (ESM). Looking at the natural history of behaviour.
- Assess people at multiple time point (4-8 times a day
- In the last half hour how hardworking have you been...
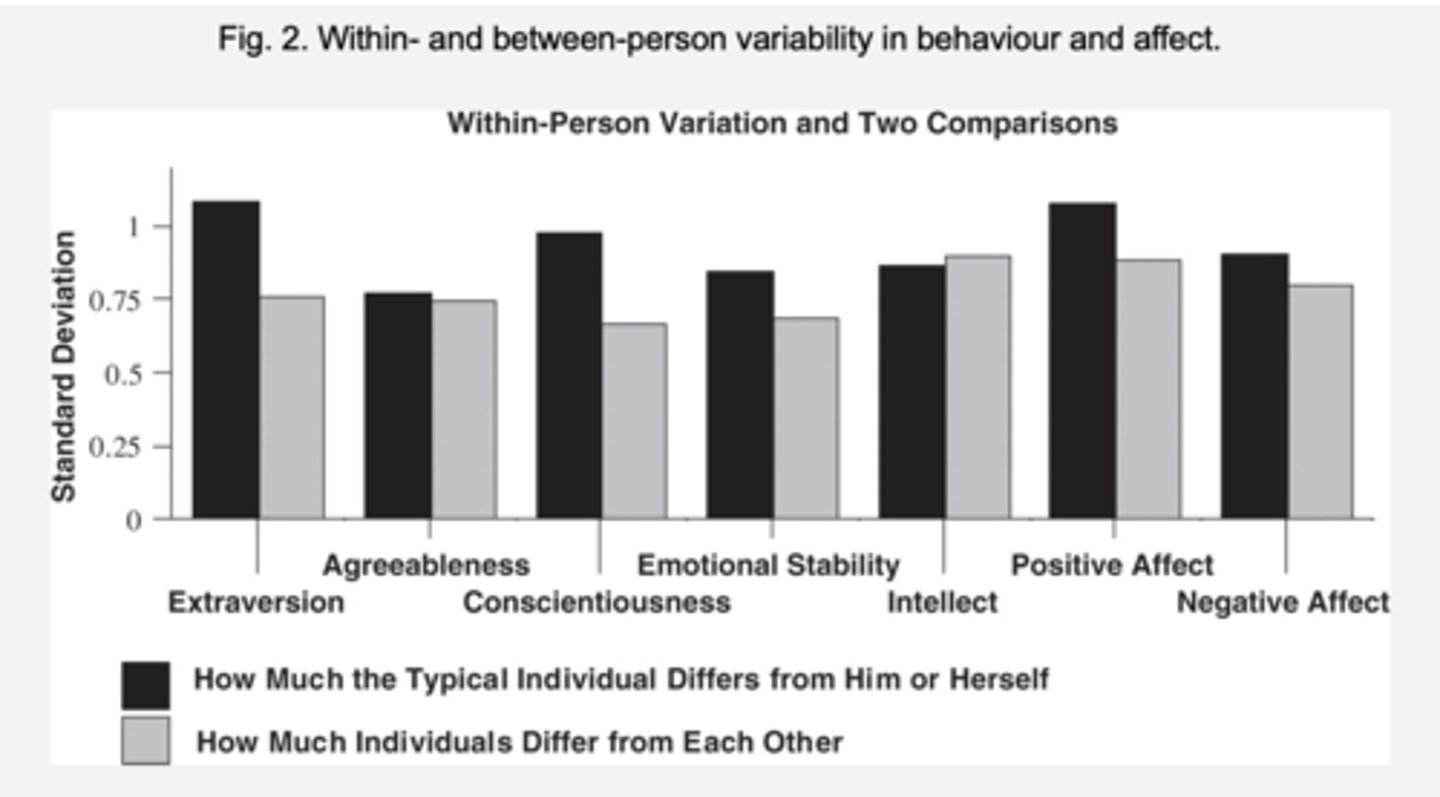
what is found about variation from Experience Sampling Methodology (ESM)?
individuals vary as much from moment to moment (with variation) as they do between each other (between variation)
- vary in how they express their conscientiousness more than they vary between someone else on conscientiousness
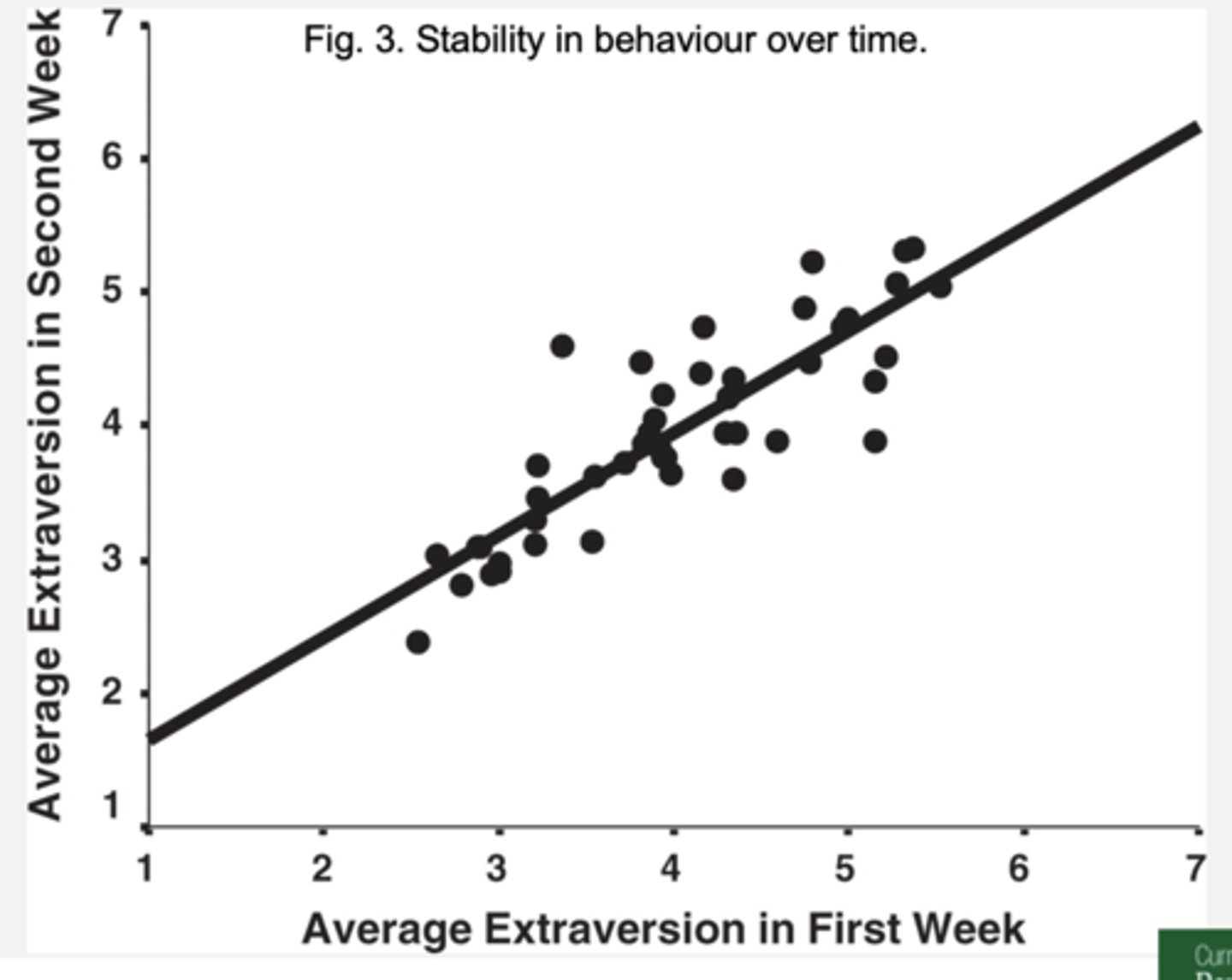
what is found about central tendency from Experience Sampling Methodology (ESM)?
- Individuals have a central tendency (mean) and these are very stable (correlation of .80 and .90)
BUT - There is also stability in the amount of variability (.50) – therefor variation is fairly stable and a part of personality to be studied
- Average of own distribution stays the same over time but you do vary across context
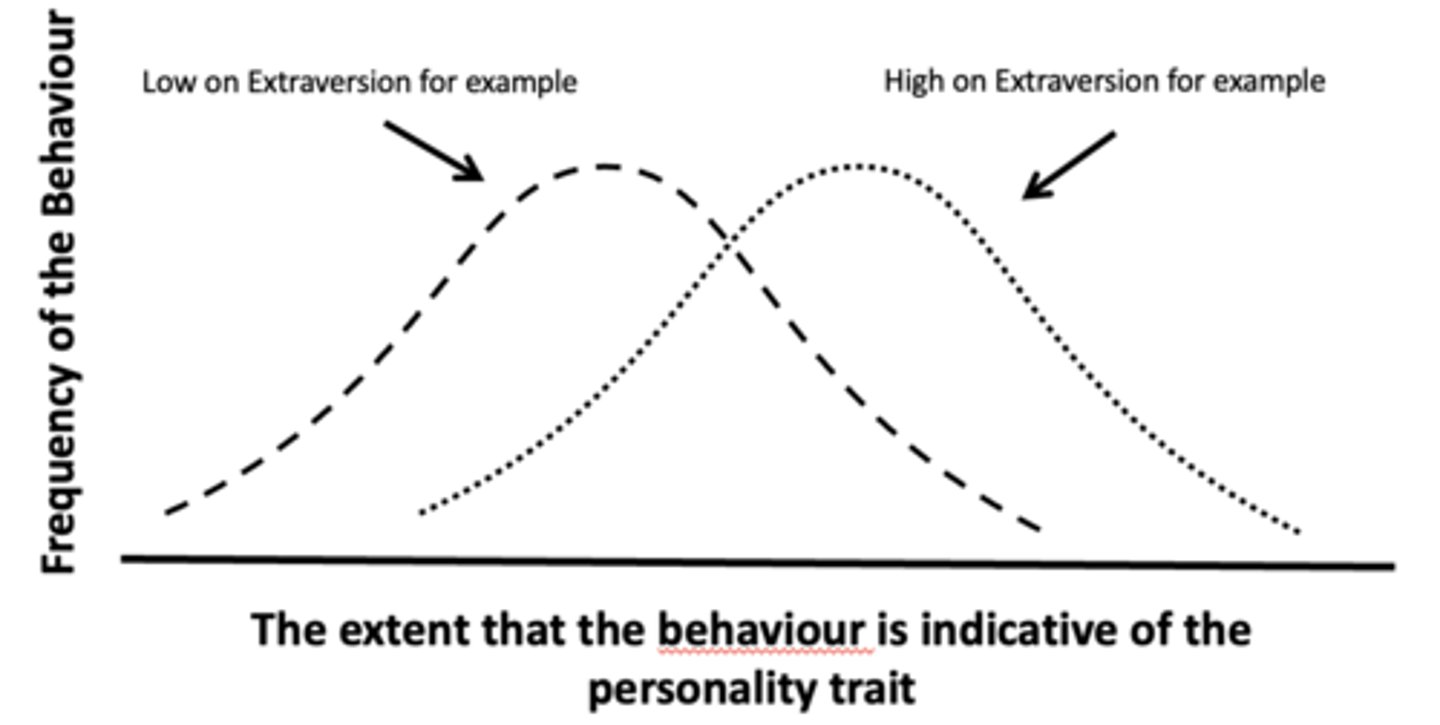
How do phenotypic expression change as a function of high and low trait scores?
- Tendency to differ with respect to average behaviours.
- Extraverts are moderately extraverted 5-10% more than introverts.
- Personality Traits predict mean (average) and extreme behaviour
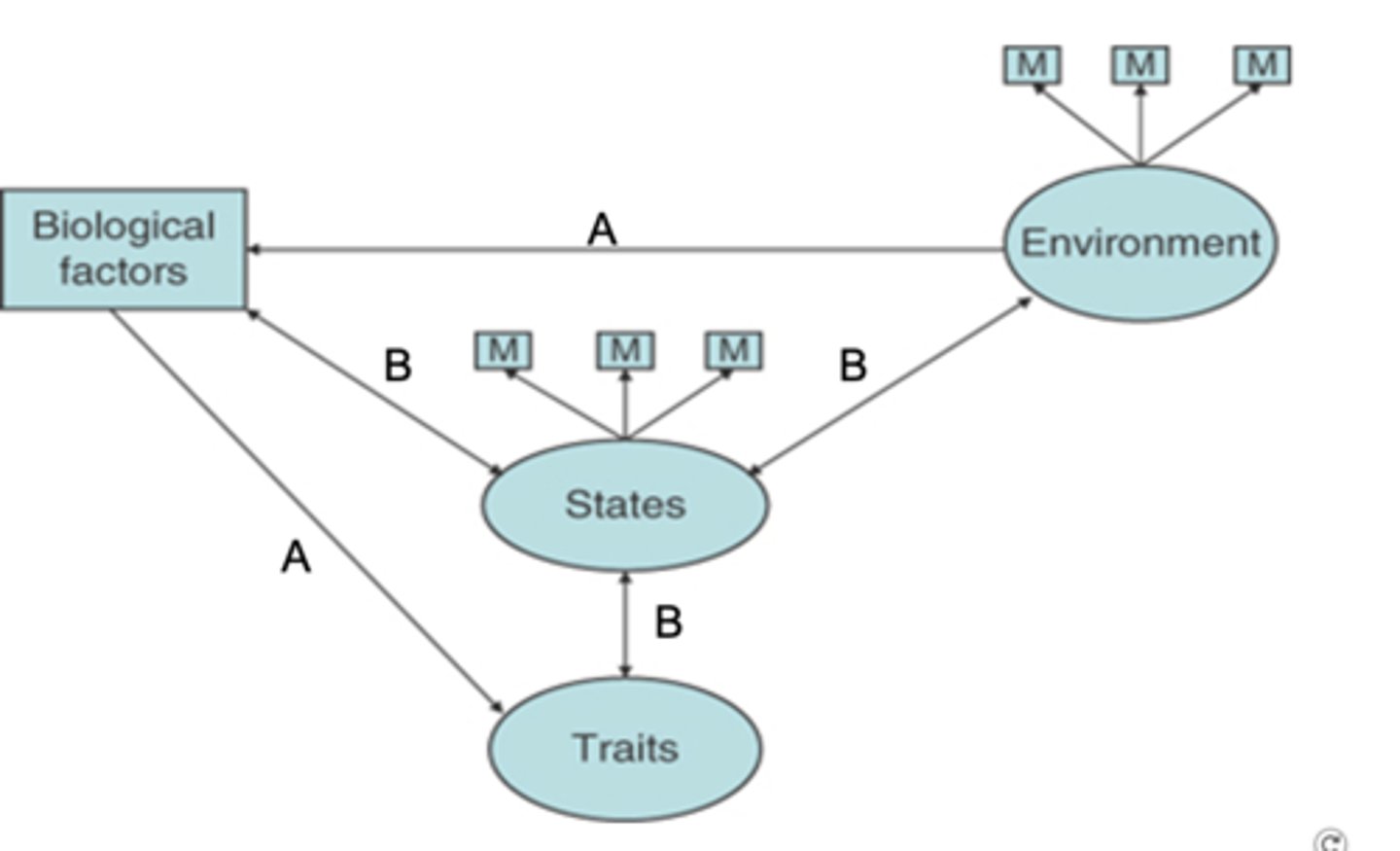
What is the socio-genomic model (Roberts & Jackson 2008)?
implies both the expression of behaviours associated with trait and the mean level of the trait can vary as a function of (1) the influence of the environment via biological factors (route A) and (2) the dynamic interaction of environment, states (emotions, values, beliefs), biology and the trait. (route B)
How do genes evolve across generations?
Genes influence triat expression > higher survuvual passes on these traist which become adaptive (fitness) and then the environment influences this trait expression which leads to more fitness
What is selection and shaping ? (Hybrid Socio-Genomic Model of Personality and Evo-Devo)
the process of us shaping and selecting our own environment
- we shape it through decisions we make to fit us.
- we don't adapt us > we adapt the environment to suit our physiology.
Why must Sexually selected traits show variability?
otherwise choice and competition are not possible.
- If we were all the same (homogeneous) on a trait, then who would you choose to be a sexual partner.
Miller & Todd’s (1998) Two-Stage Lens Model
- when choosing a mate for reproduction, we look for certain traits in that person that we want.
- 4 cues we may use to identify (e.g personality and intelligence)
What does Miller & Todd’s (1998) Two-Stage Lens Model sugest?
Certain traits may survive as
they are the basis of selecting a
long-term mate.
- This implies that the preference for
the trait and the trait itself are
heritable
Iredale et al (2008) - what did they investigate?
The theory that People should express desirable traits more in the presence of someone they may think about having a relationship with.
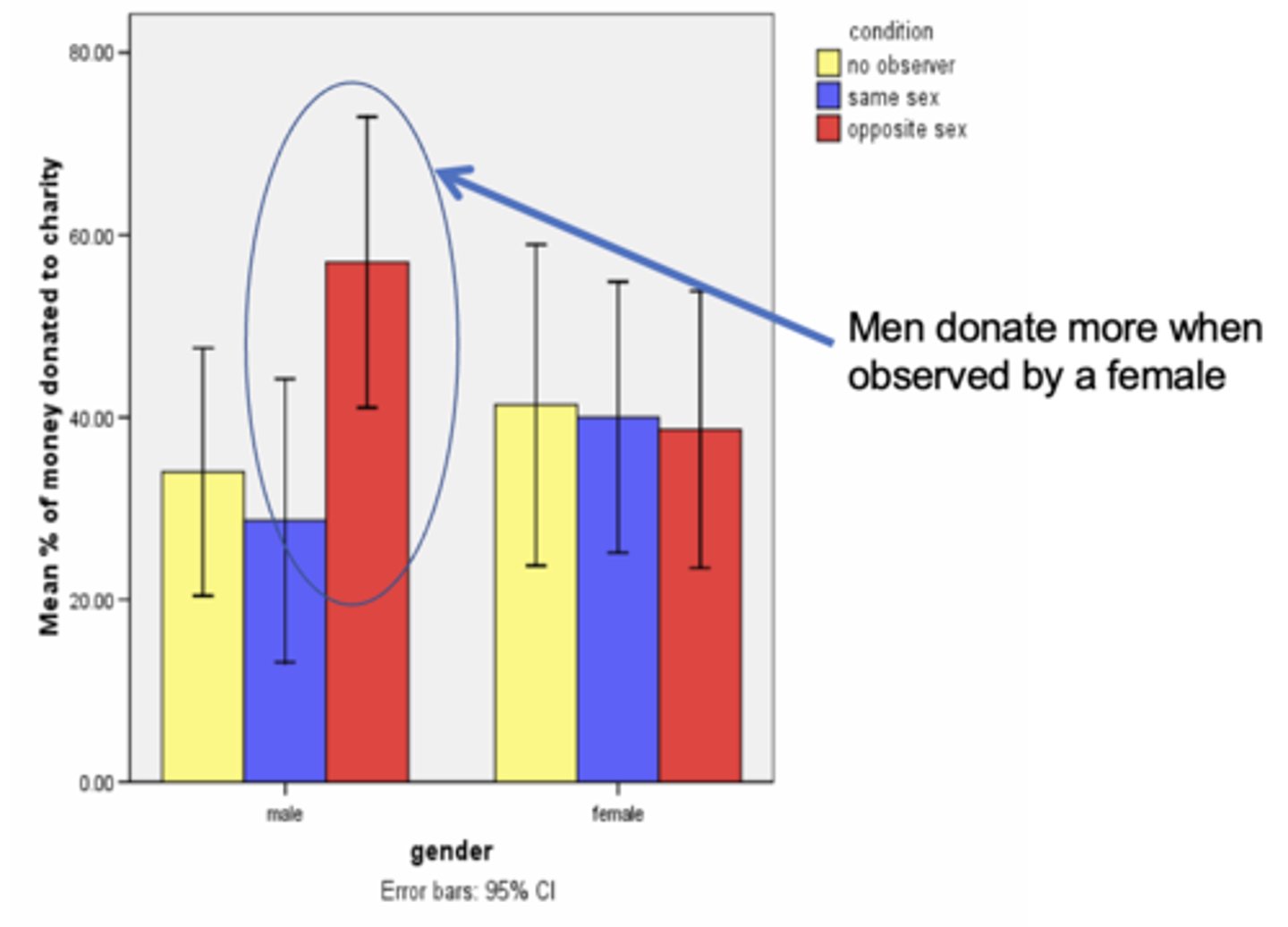
Iredale et al (2008) - what did they find?
Men change their behaviour in the presence of women whereas women don't change their behaviour in the presence of men
- creates a problem of trustworthiness...are they truly desirable?
What is the costly signalling theory?
When its Hard to fake indicators of an animal's fitness
Costly signals offer a solution to the problem of cheating/lying/faking
How do costly signalls offer a solution to the problem of cheating/lying/faking?
The signal has to be high cost, so that only healthy, high-status, high-condition animals are able to produce and maintain it. Therefore, it is a reliable indicator of evolutionary fitness
Why should Preferences and Trait Expression Show a Genetic Correlation?
in order for it to be passed on to the next generation
do Preferences and Trait Expression show a Genetic Correlation?
Yes - 68% of the co-variation in the
phenotypic correlation is due to genetic variation