A&P Ch. 2: Anatomy, Physiology, and Kinesiology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Anatomy
studies the form and structure of the body
Form and function are…
interrelated
Function
always reflects structure
Homeostasis
maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions despite continuous changes in environment; a dynamic state of equilibrium
Vivisection
Furthered knowledge of anatomy
Gross or macroscopic anatomy
study of large, visible structures; regional, systematic, surface, deep, comparative
Microscopic anatomy
cytology (microscopic study of cells) and histology (microscopic study of tissues)
Physiology
Examines the function of body structures, focusing on the molecular and cellular level
Subdisciplines of Physiology
Cardiovascular, neurophysiology, respiratory, reproductive, pathophysiology
Cardiovascular
heart, blood vessels, blood
Neurophysiology
nerves and nervous system organs
Respiratory
respiratory organs
Reproductive
reproductive hormones and the reproductive cycle
Pathophysiology
body system during disease or injury to the system
Characteristics of anatomic position
upright stance, feet parallel and flat on the floor, upper limbs at the sides of the body, palms face anteriorly, head is level, eyes looks forwards
Section
slice that exposes internal anatomy
Plane
imaginary flat surface passing through body; coronal (frontal), transverse, midsagittal, sagittal, oblique
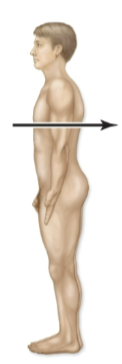
Anterior
in front of (ventral)
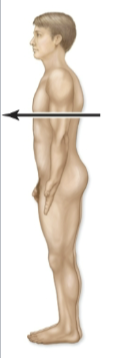
Posterior
back of body/behind (dorsal)
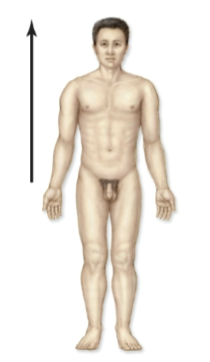
Superior
Inferior
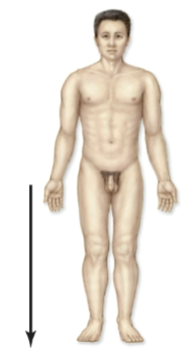
Medial
toward middle of body
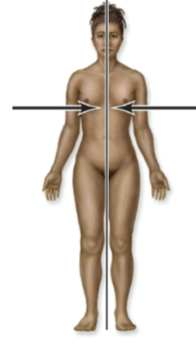
Lateral
away from midline
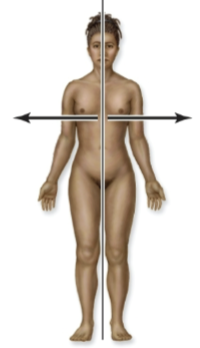
Proximal
closer to the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
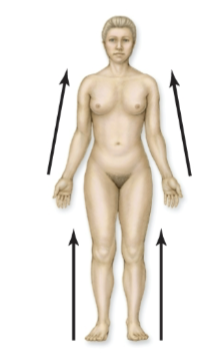
Distal
further from the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
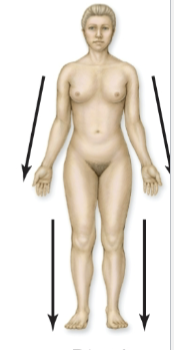
Bilateral
2 sided; Affecting both sides equally. We are bilaterally symmetrical
Ipsilateral
Located on same side of body, right and left leg
Contralateral
on opposite side, right arm and left leg (OR right arm and left arm)
Superficial
toward the body’s surface (external)
Deep
away from body’s surface (internal)
Axial
head, neck, trunk
Appendicular
upper and lower limbs
Dorsal (posterior) cavity
completely encased in bone
Ventral Cavity
larger than posterior cavity, anteriorly placed in the body
The ventral cavity is partitioned into a…
superior thoracic cavity and inferior abdominopelvic cavity
Subdivisions of ventral cavity are lined with…
2 layers of serous membranes
Parietal layer
lines internal surface of body wall
Visceral layer
covers external surface of organs
Serous cavity
space between membranes
Serous fluid
liquid secreted by cells in serous membrane
Serosa
thin, double-layered membrane, lines walls of ventral body cavity and outer surfaces of organs
Visceral serosa
covers organs
Parietal serosa
lines cavity walls
Pleurisy/Peritonitis
Causes roughening of pleurae or peritoneum causes organs to stick together and drag across are another — very painful
Clinical views of normal ranges for body temperature
98.6
Clinical views of normal ranges for blood glucose
80-110 mg/dL
Clinical views of normal ranges for blood pressure
90-120/60-80 mmHg
Receptor
monitors environment, responds to stimuli
Control center
determines set point and appropriate response
Effector
receives output from control center; response either negative feedback or positive feedback
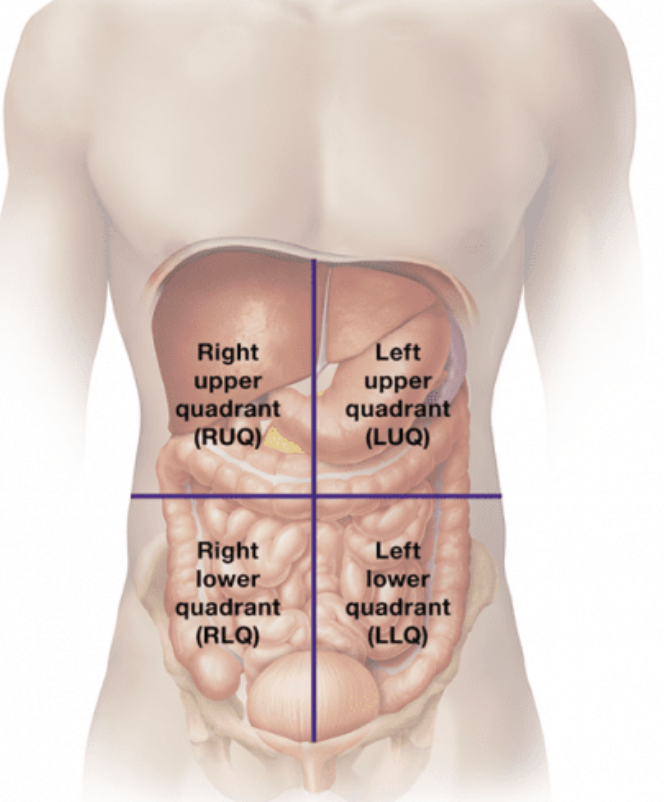
Abdominopelvic Regions
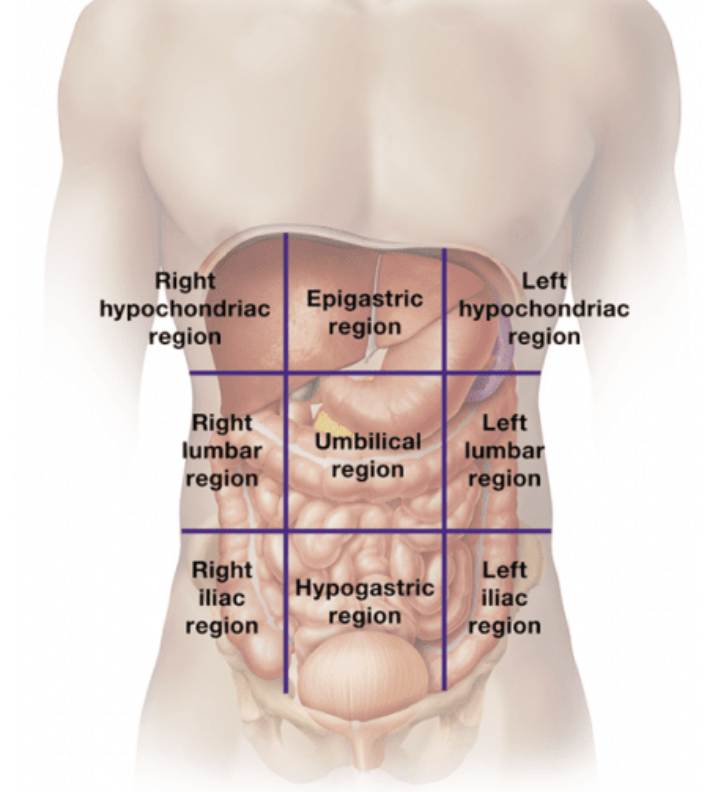
Abdominopelvic Quadrants