Other STIs (bacterial, Viral, and Parasitic)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Sexually transmitted HPV infections are common and often asymptomatic, untreated cases in women are the main cause of cervical cancer
- sexually transmitted virus that causes cancer
- More than 100 types of HPV have been found so far
- 15 have been identified as putting women at high risk for cervical cancer
how Human Papillomavirus (HPV) causes cancer
1. Virus in the cervix enters cells through micro-abrasions, Infects cells
2. Several weeks later, HPV replicates. Infection spreads. 90 percent of cases heal within 2 years
3. 10 to 30 years later, 0.8 percent of cases develop cancer. HPV invades deeper layers of tissues and turns cancerous
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
A recurring viral STD that produces painful genital lesions
Two strains of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) exist
Type I (HSV I) represents 5-10% of genital herpes lesions; it primarily causes oral-labial lesions and resides in the trigeminal ganglion
Type 2 (HSV 2) causes 90-95% of all genital herpes lesions; it lives in sacral dorsal root ganglia.
Type 1 vs. Type 2 Herpes Simplex Virus
The difference between the two types of HSV is in their site of preference. HSV-1 is usually found in the trigeminal ganglion, a collection of nerve cells near the ear. From there, it appears on the lower lip or face. HSV-2 is found in the sacral ganglion at the base of the spine and tends to reoccur in the genital area.
Most people are not aware that both types can be spread to the genitals and therefore cause the idea that one is worse than the other, when in fact they are very similar.
Pathogenesis of HSV 2 or Genital herpes infection
Primary infection occurs when HSV-2 infects epithelial cells covering the mucosa.
The virus then migrates to the nearest ganglion (sacral ganglia) via neurons where it replicates and establish latency for life.
Once its reactivated, it travels back through neurons to the site of the primary infection and causes recurrent infection.
Once the virus enters the human body it remains for life (latency)
Syphilis (sexually transmitted disease)
Caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidium
primary stage 1, secondary stage 2, and tertiary stage 3
syphilis has 3 stages:
Primary stage 1 and secondary stage 2 are curable
sore that occurs 3 to 90 days after exposure to syphilis
primary stage 1:
body rash that occurs 4 to 10 weeks after initial infection
secondary stage 2:
affects internal organs 3 to 15 years after initial infection
tertiary stage 3:
Treponema pallidum
bacterium that causes syphilis
gram-negative bacterium
spirochete (spiral shape)
moves using parts called endoflagella (these are protein filaments located inside its body that help it twist and move)
it needs a host to survive and uses the host's energy, which means it’s an obligate parasite
It usually enters through the skin or mucous membranes.
Common entry sites include the external genitalia and the mouth
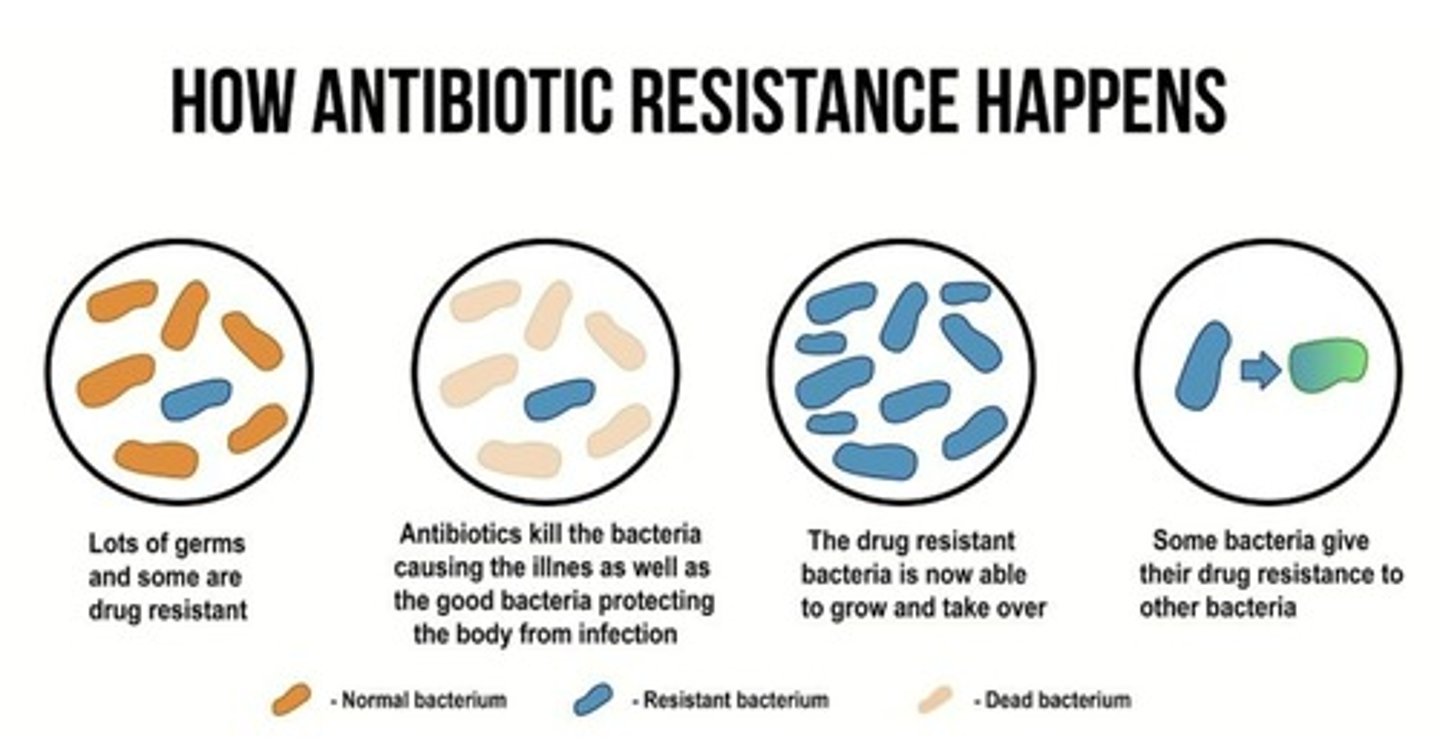
how antibiotic resistance happens
1. Lots of bacteria, and some are drug-resistant
2. Antibiotics kill the bacteria causing the illness, as well as the good bacteria protecting the body from infection
3. The drug-resistant bacteria are now able to grow and take over
4. Some bacteria give their drug resistance to other bacteria
Chlamydia
Testing for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea) is generally done simultaneously as the two organisms have similar clinical presentations. A definitive diagnosis is important since the symptoms of chlamydia can resemble those of gonorrhea, and the two infections require different antibiotic treatment
Doxycycline 100 MG orally twice daily for 7 days
treatment for chlamydia:
ceftriaxone 500 MG IM once
treatment for gonorrhea:
Chlamydia general characteristics
Gram-negative obligate intracellular organism
Non-motile
Observed in cell culture under a microscope
Chlamydia unique development cycle
1. Replicate within the host cell, forming inclusion bodies
2. Differ from viruses, have both DNA and RNA
3. The cell wall is similar in structure to Gram-negative bacteria
4. Restricted metabolic activity-reactions do not produce energy but use ATP produced by the host cell. "energy parasites"
Chlamydia trachomatis, STD pathogen meaning it causes STDS in humans
chlamydia includes:
Chlamydia trachomatis diseases
Trachoma -An eye infection that can lead to blindness if untreated
Inclusion conjunctivitis -Another eye infection, often seen in newborns or adults exposed to the bacteria
Lymphogranuloma venereum or LGV -A sexually transmitted infection that affects the lymph nodes; it's less common in the U.S
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or PID -A serious infection of the female reproductive organs, caused by Chlamydia spreading upward from the cervix
Life Cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis
1. enters a susceptible host cell as an elemental (or elementary) body
2. prevents phagocytosis due to the rigid membrane
3. reorganizes into a reticulate body rich in RNA
4. begins to divide (binary fission)
5. Transform back into an elemental body
6. Elemental bodies emerge from the cell
In a pap smear from a woman's cervix, Chlamydia infected cells appear pink while uninfected cells appear blue upon staining with a dye
what does the image tell us?
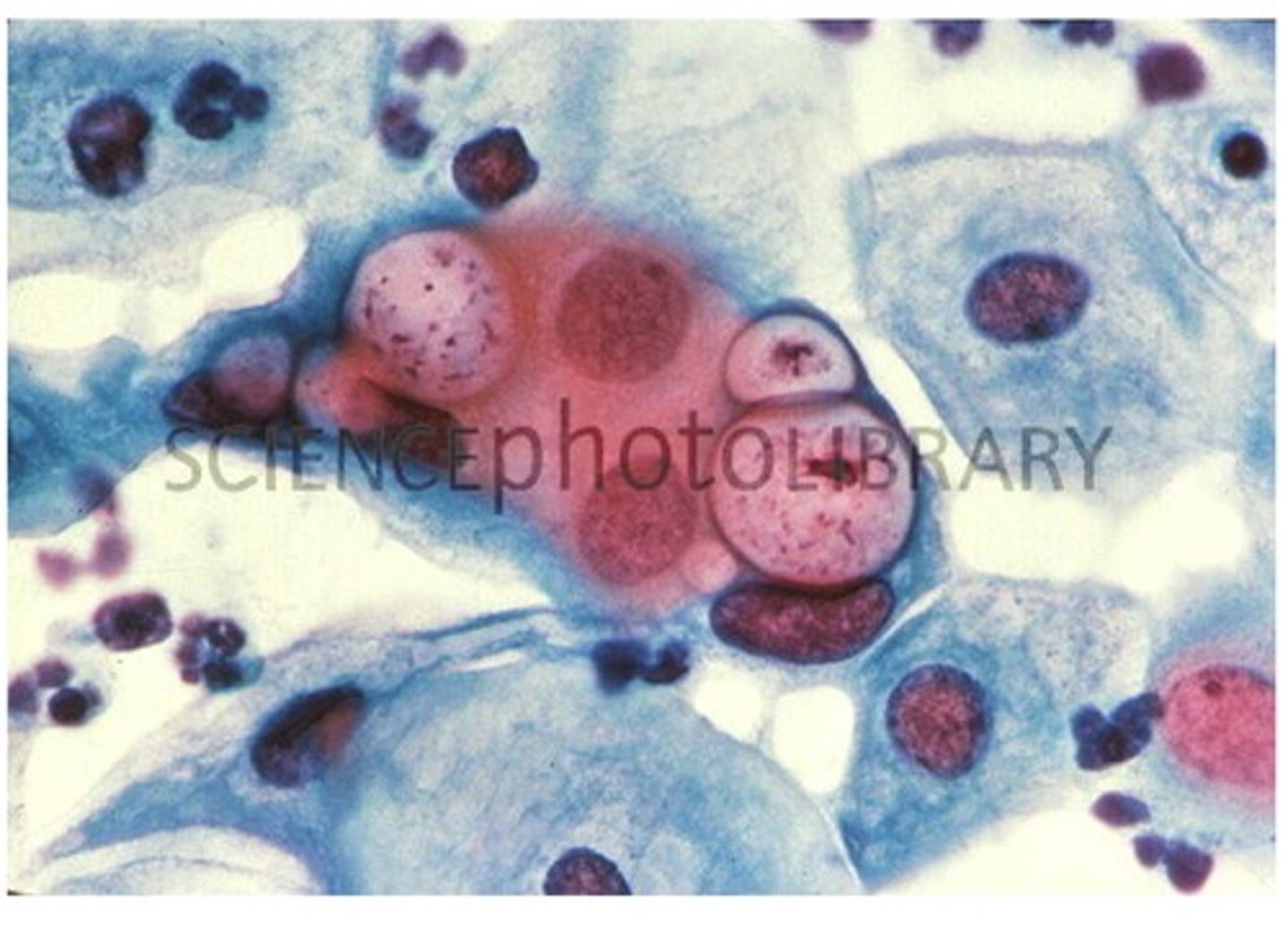
Chlamydia
The most commonly reported bacterial STI in the U.S.
Caused by infection with the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia is very similar to Gonorrhea in its symptoms and pattern of transmission
Women and men infected with chlamydia do not have any symptoms and may not be aware that they have the infection
Chlamydia infection can cause permanent damage to the fallopian tubes in a woman and can lead to future infertility and an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy
Chlamydia infection during pregnancy also increases a woman's risk of preterm labor
Infected mother can pass the infection to baby during vaginal birth. The most common complications of chlamydia acquired through the birth canal are eye damage and pneumonia in the newborn
Symptoms of Chlamydia infection can include vaginal and penal discharges as well as abdominal pain and pain during micturition (UTI symptoms)
penile discharge, burning or painful sensation, and testicular swelling
Chlamydia symptoms in men:
vaginal discharge, burning or painful sensation, and bleeding between periods
Chlamydia symptoms in women:
1 in 8 women with a history of pelvic inflammatory disease experience difficulties getting pregnant
Untreated sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) which is a serious condition in women:
Trachoma
Trachoma is a bacterial infection that affects your eyes
It's contagious, spreading through contact with the eyes, nose, or throat secretions of infected people, and handkerchiefs
Trachoma is the leading preventable cause of blindness worldwide.
Most blinding trachoma occurs in poor areas of Africa.
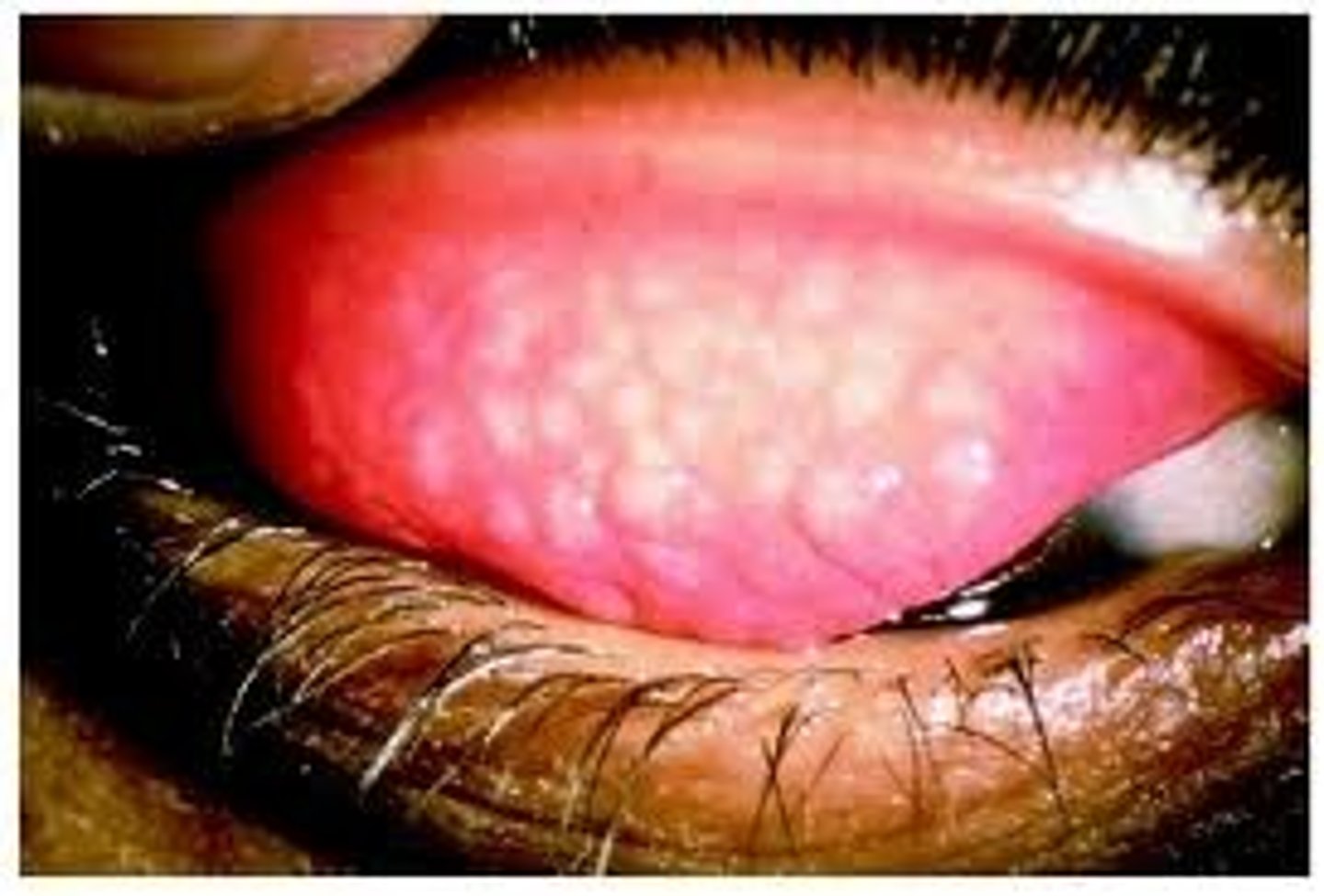
Inclusion conjuctivitis
Adult inclusion conjunctivitis is caused by sexually transmitted Chlamydia trachomatis. It's a follicular trachomatis
In most instances, adult inclusion conjunctivitis results from sexual contact with a person who has a genital infection
Rarely, adult inclusion conjunctivitis is acquired from contaminated, incompletely chlorinated swimming pool water
Conjunctival scraping determines whether chlamydia is present in cells taken from the conjunctiva
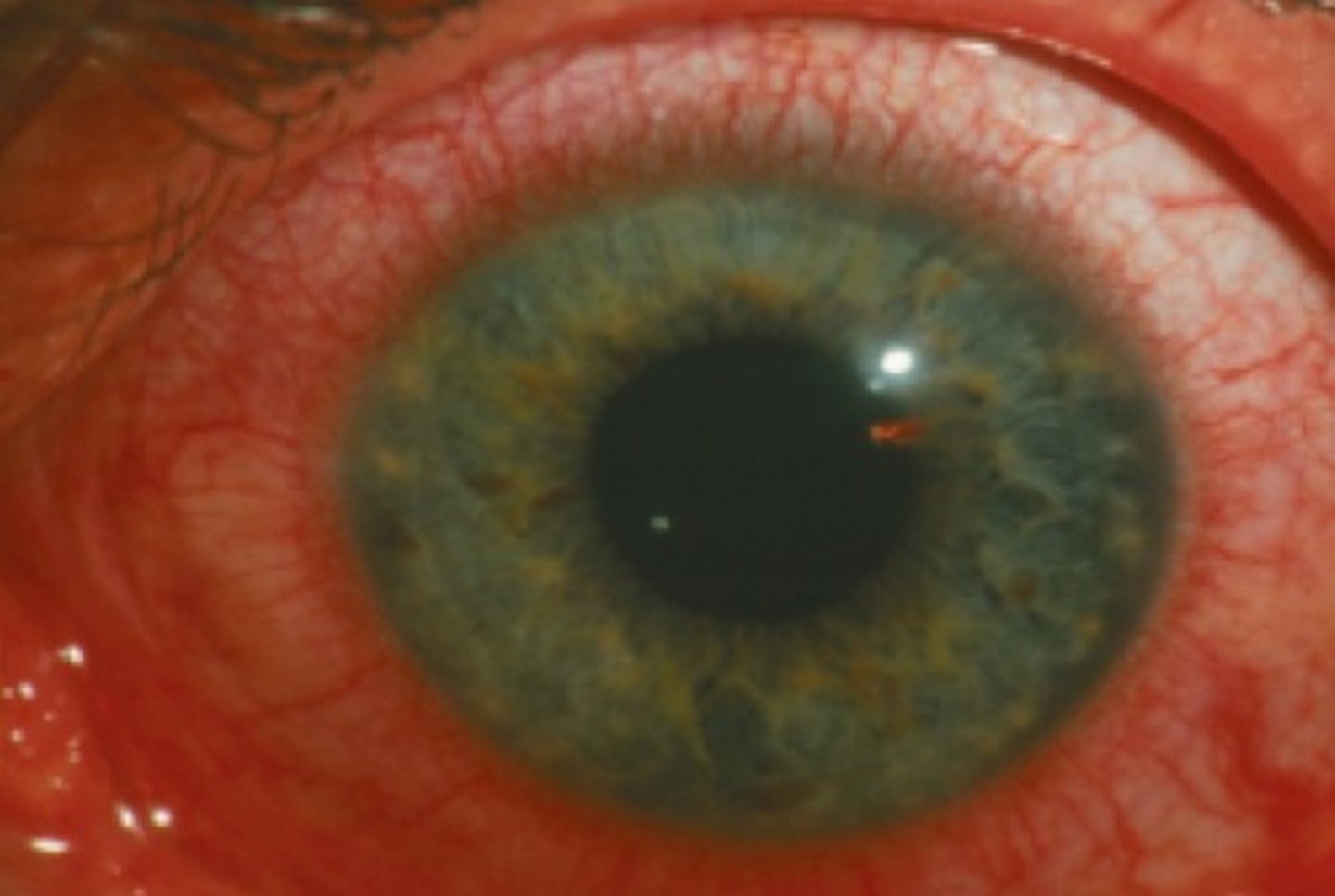
Trichomoniasis (or "trich")
is a very common sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Although symptoms of the disease vary, most people who have the parasite cannot tell they are infected.
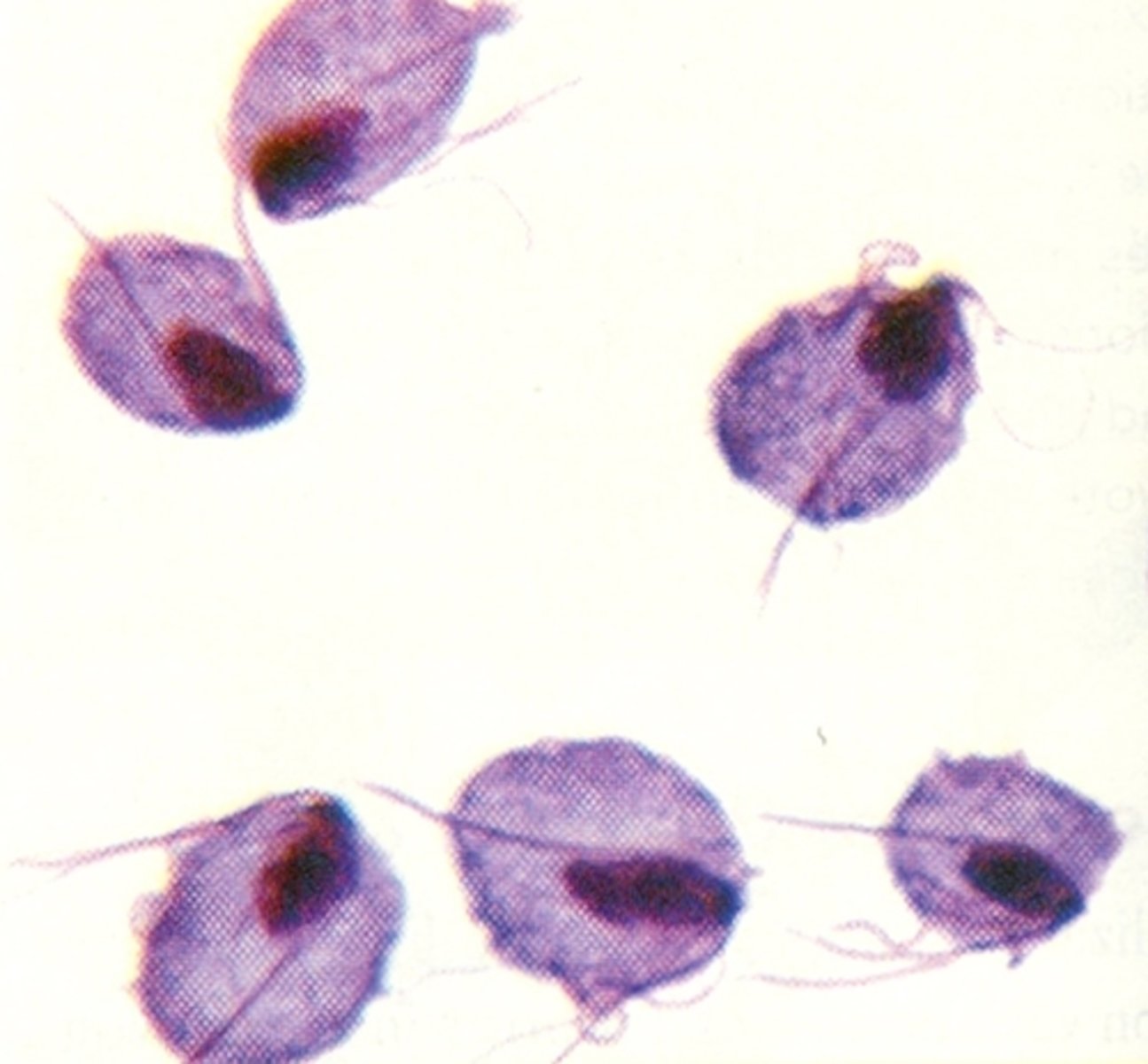
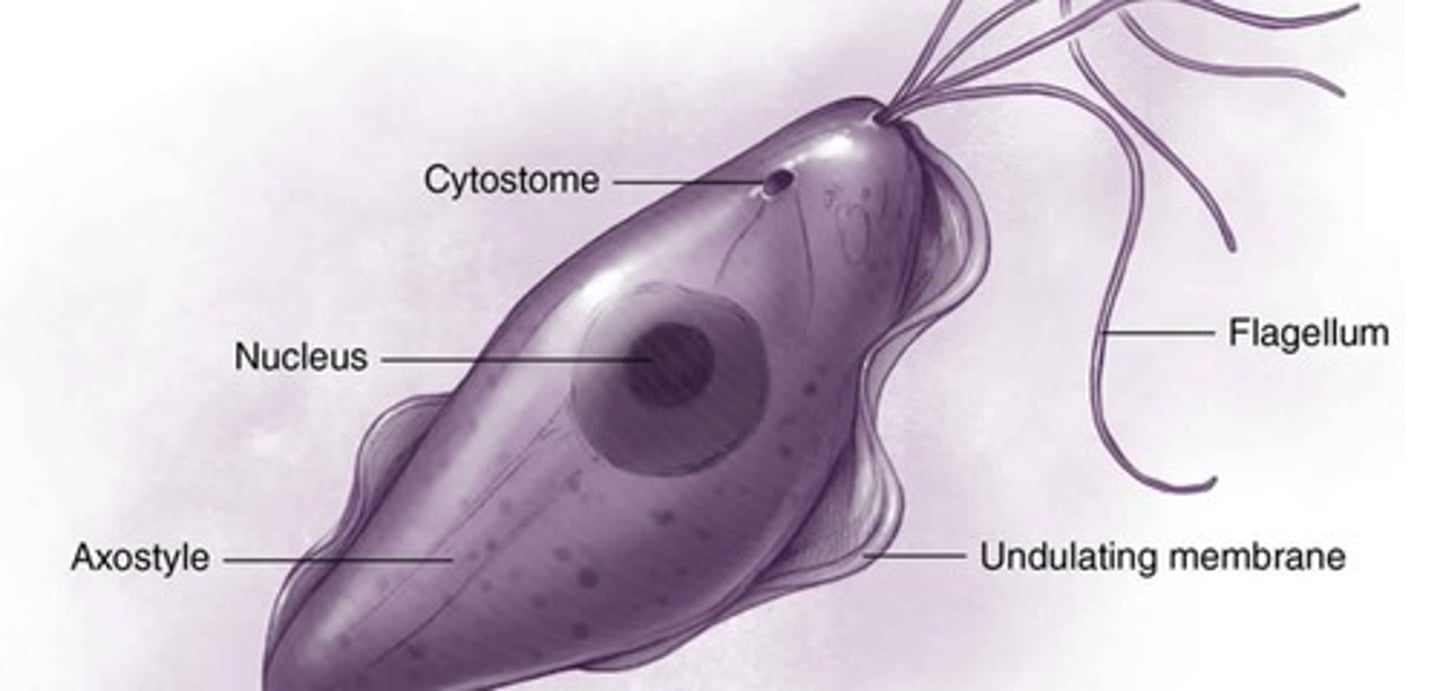
Parts of Trichomonas vaginalis
Includes the Nucleus, cytostome, flagellum, Axostyle (a stiff structure that gives the parasite support and helps it attach to surfaces), and Undulating membrane (A wavy edge of the parasite that also helps it move through fluids)
Trichomonas vaginalis Life Cycle
1. Trophozoite stage in fluids
The parasite, called a trophozoite, lives in vaginal or prostate fluids and urine.
This is the diagnostic stage, meaning this is what doctors look for in lab tests.
2. Multiplication
The trophozoite multiplies by splitting in half (called longitudinal binary fission).
3. Transmission to a new host
The trophozoite moves into the vagina or urethra of a sexual partner during intercourse.
This is the infective stage, the stage that spreads the infection.
discharge from the urethra, burning during urination or after ejaculation, and urge to urinate frequently
Trichomoniasis symptoms in men:
grey or yellowish vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding, genital burning, genital swelling, frequent urge to urinate, and pain during sex
Trichomoniasis symptoms in women:
chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis
bacteria STIs are:
HPV and herpes
viral STIs are: