NEUROSCIENCE - Neurons,Neuroglia & Development of NS
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception of stimuli and the conduction of the nerve impulse.
Each possess a _____ from which one or more processes called ____
Neurons
Cell body ; neurites
Neurites responsible for receiving information and conducting it toward the cell body are_______.
The single long tubular neurite that conducts impulses away from the cell body is the _______. Dendrites and axons are commonly referred to as _________
Dendrites ( can also transmit to another neurons)
Axon
Nerve fibers
Neurons are found in the ____,_____ and ______
Do neurons undergo division and replications as we mature?
Brain, spinal cord & ganglia
Nope
Neuron Types : Shape
_ neurons have a single neurite that divides a short distance from the cell body into 2 branches, one proceeding to some peripheral structure and the other entering the central nervous system (CNS)
In this type of neuron, the fine terminal branches found at the peripheral end of the axon at the receptor site are often referred to as the _______.
Example: _____
Unipolar Neurons
Dendrites
Posterior root ganglion ( dorsal root of spinal nerve)
Neuron Types: Shape
_ have an elongated cell body, with a single neurite emerging from each end.
Example: ______,_____ & ______
Bipolar neurons
Retinal bipolar cells (vision) and the cells of the sensory cochlear (hear) and vestibular ganglia (motor control).
Neuron Types: Shape
_ have a number of neurites arising from the cell body. With the exception of the long process, the axon, the remainder of the neurites are dendrites.
Most neurons of brain and spinal cord
Multipolar neurons
Neuron Types: Size
______ have a long axon that can stretch 1m or more in length In extreme cases. The axons of these neurons form the long fiber tracts of the ______ and _______ and the nerve fibers of _____ nerves.
Examples: _________( action potential) , _______ ( coordination & learning) and _______ (muscles and glands)
Golgi type 1
Brain & Spinal Cord
peripheral nerves
(1) Pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex (2) Purkinje cells of the cerebellar cortex (3) Motor cells of the spinal cord
Neuron Types: Size
_ neurons have a short axon that terminates in the neighborhood of the cell body or is entirely absent.
Greatly outnumbers type 1 and star shaped in appearance
Examples: ______ and ______. Often inhibitory in function
Golgi Type 2
Cerebral and cerebellar cortex
Neuronal Structure
A neuron's cell body, like that of other cells, consists essentially of a mass of cytoplasm in which a nucleus is embedded bounded externally by a __________.
The volume of____within the nerve cell body Is often far less than the total volume of cytoplasm in the ________.
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
Neurites
_______ which stores the genes, centrally located within the cell body and ls typically large and rounded. It refers to a discrete group of nerve cell bodies in the CNS.
In mature neurons, the ________ no longer duplicate themselves and function only in gene expression. Therefore, the chromosomes are not arranged as compact structures but exist in an uncoiled state. Thus, the nucleus is pale, and the fine chromatin granules are widely dispersed
Nucleus
chromosomes
Nucleus
In the female, one of the two X chromosomes is compact and ls known as _______ . It is composed of sex chromatin and sits at the inner surface of the nuclear envelope.
The ________ is continuous with the cytoplasmic rough, or granular, endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The envelope is double layered and possesses ________ through which materials can diffuse into and out of the nucleus.
Therefore, the substance in the nucleus and the cytoplasm can be considered as functionally continuous. Newly formed ribosomal subunits can be passed Into the cytoplasm through the nuclear pores.
Barr body
nuclear envelope
fine nuclear pores
is rich in rough (granular) and smooth (agranular) endoplasmic reticulum and contains the following organelles and inclusions: (a) Nissl substance; (b) the Golgi complex; (c) mitochondria; (d) microfilaments; (e) microtubules; (f) lysosomes; (g) centrioles; and (h) lipofuscin, melanin, glycogen, and lipid.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
__________ Consists of granules that are distributed throughout the cytoplasm of the cell body, except for the region close to the axon, called the axon hillock. ( Present in proximal parts of dendrites but not axon )
It synthesizes protein which flows along the dendrites and the axon and replaces the proteins that are broken down during cellular activity.
Shape: Granules of Rough ER
Appearance: Broad cistemae; ribosomes are basophilic
Fatigue or neuronal damage causes the Nissl substance to move and become concentrated at the periphery of the cytoplasm. It gives the impression that the Nissl substance has disappeared, _______
Nissl substance
chromatolysis
Cytoplasm
_________ clusters of flattened cistenae and small vesicles made up of smooth endoplasmic reticulum. it is temporarily stored and where carbohydrate may be added to the protein to form glycoproteins.
At the ___ side of the complex, the macromolecules are packaged in vesicles for transport to the nerve terminals.
Also thought to be active In lysosome production and in the synthesis of cell membranes.
Important in the formation of synaptic vesicles at the axon terminals.
Adds carbohydrate to protein molecule
Golgi Complex
trans
________ are found scattered throughout the cell body, dendrites, and axons .
spherical and rod shaped
double membrane
Important in nerve cells for production of chemical energy
Mitochondria
Cytoplasm
_________ are numerous and run parallel to each other through the cell body into the neurites.
Run from dendrites through cell body to axon
Determines the shape of the neuron
___________ form the main component of the cytoskeleton. It develops and regenerates nerve fibers. However, it degenerates in Alzheimer
Forms neurofibrillary tangles - site of degeneration of neurofilaments
Neurofibrils
Neurofilaments (size: micro→neurofilaments → microtubules)
Cytoplasm
_________ measured about 3 to 5 nm In diameter and are formed of actin. (smallest)
Play a key role In the formation of new cell processes and the retraction of old ones
Assist the microtubules in axon transport.
Facilitate NGF
Microfilaments
Cytoplasm
__________ They measure about 25 nm in diameter and are found interspersed among the neurofilaments.
In the axon, all the microtubules are arranged in parallel, with one end pointing to the cell body and the other end pointing distally away from the cell body.
Cell transport
Main skeletal frame of neuron
Microtubules
Cell Transport
_________ is mediated by two motor proteins associated with the microtubule ATP-ase sites.
________ - away from cell movement ( ______ coated organelles are thought to move toward one end of the tubule
_______ - toward the cell movement ( ____-coated organelles are thought to move toward the other end of the tubule.)
Rapid transport
Anterograde; kinesin ← Fast anterograde
Retrograde; dynein ← Fast Retrograde
Cell Transport
__________ (0.1 to 3.0 mm/day) Involves the bulk movement of the cytoplasm and includes the movement of mitochondria and other organelles.
It occurs only in the ______ direction.
Slow Transport
anterograde
Cytoplasm
________ are membrane-bound vesicles measuring about 8 nm in diameter. They serve the cell by acting as Intracellular scavengers and contain hydrolytic enzymes.
3 Forms:
_______ - just have been formed
_______ - contain partially digested material (myelin figures)
_______ - enzymes are inactive and the bodies have evolved from digestible materials such as pigment and lipid.
Lysosomes
Primary Lysosomes → Secondary Lysosomes → Residual Bodies
Structures of Nerve Cell Body
_______ are small, paired structures found in immature dividing nerve cells.
Hollow cylinder whose wall is made up of microtubule bundles
Associated with the formation of the spindle during cell division and in the formation of microtubules.
In mature nerve cells, involved in _______
Centrioles
maintenance of microtubules
Structures of Nerve Cell Body : Inclusion Bodies
________ occurs as yellowish- brown granules within the cytoplasm
Forms as the result of lysosomal activity
Represents a harmless metabolic byproduct
Accumulates with age.
residual bodies from lysosomes
Lipofuscin
Structures of Nerve Cell Body : Inclusion Bodies
_________ found in the cytoplasm of cells in certain parts of the brain
blackish pigment in neurons at substancia nigra
Related to formation of dopamine
Disappears from the substancia nigra ( at midbrain) and the locus ceruleus in _______ disease = develop motor & cognitive problems
Melanin Granules / neuromelanin
Parkinson’s disease
not all patients will present lewy body
Structures of Nerve Cell Body : Inclusion Bodies
________ - Inside cytoplasm of neuron; eosinophilic intra-cytoplasmic ( Present in Parkinson’s Disease)
_______ - Found in hippocampus with Alzheimer’s Disease
______ - Found in brains of people with rabies
Lewy Bodies
Hirano Bodies
Negri & Lyssa Bodies
__________ Forms the continuous external boundary of the cell body and its processes, and, in the neuron, it ls the site for the initiation and conduction of the nerve Impulse.
Carbohydrate molecules are attached to the outside of the plasma membrane and are linked to the proteins or the lipids, forming what is known as ______ or ______
Plasma membrane and the cell coat together form a semipermeable membrane that allows diffusion of certain ions through it but restricts others.
Plasma Membrane
Cell coat or glycocalyx
Nerve Excitation & Conduction
The permeability of the membrane to K+ ions is much greater than that to Na+ ions; thus, the passive efflux of K+ is much greater than the Influx of Na+. This results in a steady potential difference of about ___ mV. This potential is known as the _________
280 mV
resting potential
Nerve Excitation & Conduction
In the resting unstimulated state, ____ mV is the Resting membrane potential ( Snell)
A nerve Impulse (AP) starts at the _________ and Is a self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that passes rapidly along the surface of the axolemma. Once generated, the AP spreads away from the site of initiation and is conducted along neurites as the _____
-80 mV
Initial segment of the axon
nerve impulse
Nerve Excitation & Conduction
For a short time after the passage of a nerve impulse along a nerve fiber, while the axolemma Is still depolarized, a second stimulus, however strong, is unable to excite the nerve. This period of time is called the ____________
This period Is followed by a further short Interval during which the excitability of the nerve gradually returns to normal. This latter period Is called the _________
Multiple excitatory stimuli applied to a neuron surface result in _______
Absolute refractory period ( Na channels become inactivated and no stimulation can open the gates)
Relative refractory period
Summation
Nerve Excitation & Conduction
The conduction velocity of a nerve fiber is proportional to the cross-sectional area of the axon, with the thicker fibers conducting more rapidly than those of smaller diameter. In the large motor fibers (a fibers), the rate may be as high as 70 to 120 m/s; the smaller sensory fibers have slower conduction rates
The AP at one node sets up a current in the surrounding tissue fluid, which quickly produces depolarization at the next node. This leaping of the AP from one node to the next is referred to as saltatory conduction.
Classification of Nerve Fibers by Speed of Conduction and Size
A Fibers → Conduction Velocity → Fiber Diameter → Function
a → ______ → 12-20 um →______ → Myelinated & Least sensitivity to local anesthetics
B → 40-170 → 5-12 um →_________ → Myelinated
Y → 10-50 → 3-6 um → _______ → Myelinated
δ → 6-30 → 2-5 um → _______ → Myelinated
70-120 m/s → motor, skeletal muscle
Sensory, touch, pressure & vibration
Muscle Spindle
Pain (sharp, localized), temperature, touch
Classification of Nerve Fibers by Speed of Conduction and Size
Fiber Type → Conduction Velocity → Fiber Diameter → Function
B Fibers → 3-15 → < 3 um → _______ → Myelinated
C Fibers → ___ → 0.4-1.2 um → ________________ → Unmyelinated → Most Sensitive to Local Anesthetics
Preganglionic Autonomic
0.5 - 2.0 → Pain (diffuse, deep}, temperature, postganglionic: autonomic
Nerve Cell Processes
_________ are the short processes of the cell body. Their diameter tapers as they extend from the cell body. In many neurons, the finer branches bear large numbers of small projections called _______
_______ is the longest process of the cell body. It arises from a small conical elevation on the cell body, devoid of Nissl granules, called the ________
Dendrites ( No Golgi Apparatus)
Dendritic spines
Axon ( No nissl substance; can be myelinated or unmyelinated)
Axon hillock
Nerve Cell Processes
The distal ends of the terminal branches of the axons are often enlarged; they are called ____. Some axons (especially those of autonomic nerves) show a series of swellings resembling a string of beads near their termination; these swellings are called ______.
Axon diameter varies considerably with different neurons. Those of larger diameter conduct impulses rapidly, and those of smaller diameter conduct impulses very slowly.
Terminals
varicosities
Nerve Cell Processes
The plasma membrane bounding the axon ls called the ______; the cytoplasm of the axon is the _______.
Axonal survival depends on the transport of substances from the cell bodies.
axolemma
axoplasm
Nerve Cell Processes
_______ transport of 100 to 400 mm/day refers to the transport of proteins and transmitter substances or their precursors.
_______ transport of 1-5 mm/day refers to the transport of axoplasm and includes the microfilaments and microtubules.
______ explains how the cell bodies of nerve cells respond to changes in the distal end of the axons.End of axons to cell body ;100-200mm/day. Transport degraded materials like NGF, viruses and toxins to be digested.
Axon transport is brought about by _____ assisted by the ______.
Fast anterograde
Slow anterograde
Fast Retrograde
microtubules; microfilaments
Degeneration & Regeneration
____________
Occurs toward the proximal end of an axon, including the cell body (pataas)
Takes place in both the CNS and the PNS
Reaction begins days or sooner after insult and reaches a maximum in about __ days
Involves
○ Disappearance of Nissl substance (chromatolysis)
○ Swelling of the cell body
○ Flattening and displacement of the nucleus to the periphery
Retrograde Degeneration
2 days → 20 days
Degeneration & Regeneration
____________
Occurs toward the distal end of the axon (pababa)
Takes place in both the PNS and the CNS
Is characterized by successive fragmentation of fibers and disappearance of axons and myelin sheaths and by secondary proliferation of Schwann cells
Can recover from Schwann cells
Anterograde (Wallerian) Degeneration
REGENERATION OF THE PERIPHERAL NERVE FIBER (READ)
A myelinated peripheral nerve fiber consists of an axon, a myelin sheath and its basement membrane, and a delicate connective sheath, the _______
The severed distal nerve fiber maintains its integrity and provides a tube of basement membrane and endoneurium into which an axon sprout grows schwann cells proliferate along a degenerating axon and myelinate a new axon sprout, which grows at the rate of 3 mm/day
If the path of regenerating axons is blocked, a traumatic ____ forms at the site of obstruction (amputation neuroma)
endonerium
neuroma
REGENERATION OF AXONS IN THE CNS
No basement membranes or endoneurial investments
surround axons of the CNS
Effective regeneration does not occur in the CNS
TRANSSYNAPTIC (TRANSNEURONAL) DEGENERATION
Interruption of certain CNS pathways results in degeneration of denervated elements
Transection of the optic nerve results in degeneration of neurons in the lateral geniculate body
Neurotransmitters
________ ls widely used as a transmitter by different neurons In the central and peripheral parts whereas
_____ Is released by neurons In the substantia nigra.
______, another transmitter, is found principally in synapses in the spinal cord.
_______ transmitter responsible for mood
acetylcholine (ACh)
dopamine ( movement & cognition)
Glycine
Serotonin
Neurotransmitters at Synapses
________
Rapid excitation
Ion channel receptors
Open cation channel ( FAST EPSP)
Located in main sensory and motor systems
_______
Rapid inhibition
Opens anion channel for Cl - ( fast IPSP)
ACH ( nicotinic), l- glutamate
GABA
Neuromodulators at Synapses
_______
modulation and modification of activity
G protein-coupled receptors
Opens or closes K or Ca channels ( Slow IPSP and slow EPSP)
Systems that control hemeostasis
ACh( muscarinic), serotonin, histamine, adenosine
Neurotransmitter Distribution and Fate
_______ is found at sympathetic nerve endings. In the CNS, it Is found in high concentration ln the hypothalamus. _____ ls found in high concentration In different parts of the CNS, such as in the basal nuclei (ganglia).
NE
Dopamine
___________ are gap junctions containing channels that extend from the cytoplasm of the presynaptic neuron to that of the postsynaptic neuron: They are rare ln the human CNS. The neurons communicate electrically;
Electrical Synapses
Neuroglia
The neurons of the CNS are supported by several varieties of non-excitable cells, which together are called _______
Are generally smaller than neurons and outnumber them by 5 to 10 times; they comprise about half the total volume of the brain and spinal cord.
neuroglia
arise from neural tube and crest like neuron
ectodermal derivatives
it can repair mabagal lang
Types of Neuroglia
Have small cell bodies with branching processes that extend in all directions.
Largest glial cells
Develop into tumors (most common)
2 types:
______ Found mainly In the white matter, where their processes pass between the nerve fibers. Each process Is long, slender, smooth, and not much branched.The cell bodies and processes contain MANY filaments in their cytoplasm.
______ Found mainly in the gray matter, where their processes pass between the nerve cell bodies. The processes are shorter, thicker, and more branched and their cytoplasm contains FEW filaments.
Astrocytes ( Macroglia )
plays a role in metabolism of NT particularly G___, S____ & G____
Facilitates RMP
Have glial filaments / scars (tumor marker in biopsy)
Fibrous Astrocytes
Protoplasmic Astrocytes
Types of Neuroglia : Astrocytes
Many of its expansions end in ______ where they form an almost complete covering on the external surface of ____.
Astrocytic processes are also found in large numbers around the ______ of most axons and In the bare segments of axons at the ______.
Blood vessels; capillaries
Initial segment
Nodes of Ranvier
Types of Neuroglia : Astrocytes
Form a _ for the nerve cells and nerve fibers. Their processes are functionally coupled at gap junctions.
In the embryo, serves as ______ for migration of immature neurons.By covering the synaptic contacts between neurons, they may serve as _______ preventing axon terminals from influencing neighboring and unrelated neurons. It also take up excess K+ ions so that they may have an important function during _____ of a neuron.Also stores ____ in the cytoplasm which is broken down and release in response to NE.
supporting framework
scaffolding, electrical insulators ( limits neurotransmission), repetitive firing
glycogen
Types of Neuroglia : Astrocytes
Astrocytes may serve a by taking up degenerating synaptic axon terminals. Following the death of neurons , astrocytes proliferate and fill in the spaces previously occupied by the neurons, a process called ________.
It also serve as a conduit for the __________ from blood capillaries to the neurons . They enable ions to pass from one cell to another without entering the extracellular space (gap junctions). Plays a role in ________ as the astrocyte processes terminate as expanded feet at the basement membrane of blood vessels.
phagocytes
replacement gliosis
passage of metabolites or raw materials
blood brain barrier
Types of Neuroglia
Have small cell bodies and a few delicate processes; their cytoplasm does not contain filaments. Found in rows myelinated nerve fibers and surround nerve cell bodies. However, only one process joins the myelin between two adjacent nodes of Ranvier.
Oligodendrocytes (Macroglia)
satellite cells : g___ matter
Interfascicular oligodendrocytes :
w___ matter
Types of Neuroglia : Oligodendrocytes
Responsible for formation of ______ of nerve fibers in the CNS. ______ is responsible for myelin of peripheral nerves . It is not surrounded by _______. Myelinatlon begins at ___ week of Intrauterine life and continues postnatally until by the time the child is walking. It also surround nerve cell bodies and thought to influence the biochemical environment of neurons.
myelin sheaths (electrical insulator and increases speed of nerve conduction)
Schwann
Basement membrane
16th week
Types of Neuroglia
_____ derived from macrophages outside the nervous system. It is the _____ and scattered in the CNS. It _____ during infection/degenerative processes in the nervous system.
Microglia (travel via circulatory system)
Smallest, increases
Types of Neuroglia
_____ line the cavities of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. It is ____ or ___ in shape and possess microvilli and cilia. Their movements contribute to the flow of the _________
Ependyma ( wall off the CSF)
arises from the blepharoplast
Cuboidal or columnar; CSF
Types of Neuroglia: Ependyma
_____ line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord and are in contact with the CSF.
_______ line the floor of the 3rd ventricle overlying the median eminence of the hypothalamus.
_______ cover the surfaces of the choroid plexuses. It prevents the leakage of CSF into the underlying tissues.
Ependymocytes ( circulate/absorb CSF)
Tanycytes ( Transport substances from CSF to hypophyseal-portal system; produces CSF)
Choroidal epithelial cells ( Produces CSF)
Types of Neuroglia: Ependyma
_______ are involved in the productions and secretion of CSF from the choroid plexus
Choroidal epithelial cells
Early Development of NS
Before the formation of the NS in the embryo, three main cell layers differentiate. The Innermost layer, the _ , gives rise to the gastrointestinal tract. the lungs, and the liver. The . gives rise to the muscle, collectlve tissues, and the vascular system. The third and outermost layer, the , formed of columnar epithelium, gives rise to the entire nervous system.
Entoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
Early Development of NS
During the 3rd week of development. the ectoderm on the dorsal surface of the embryo between the primitive knot and the buccopharyngeal membrane thickens to form the . The plate, which is pear shaped and wider cranially, develops a longitudinal neural groove. The groove now deepens so that it is bounded on either side by ______
neural plate
neural folds
Early Development of NS
With further development, the neural folds fuse, converting the neural groove into a _______.Fusion starts at about the midpoint along the groove and extends cranially and caudally so that, in the earliest stage, the cavity of the tube remains in communication with the amniotic cavity through the_______ and _________
Neural tube
anterior and posterlor neuropores
Early Development of NS
The anterior neuropore closes at _____(first) while the posterior neuropore closes ___ days later.Thus, normally, the neural tube closure is complete within __ days.
24-26th day; 2 days later; 28 days
Early Development of NS
During the invagination of the neural plate to form the neural groove, the cells forming the lateral margin of the plate do not become incorporated in the neural tube but instead form a strip of ectodermal cells that lie between the neural tube and the covering ectoderm, the _______. Ultimately, the neural crest cells will differentiate Into the cells of the ________, ______,______, _____ and ______.
neural crest
posterior root ganglia, the sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves, autonomic ganglia, the cells of the suprarenal medulla and the melanocytes
Early Development of NS
Meanwhile, the proliferation of cells a the cephlic end of the neural tube causes it to dilate and form 3 primary brain vesicles: the _____ , ______ and ___vesicles . The rest of the tube elongates and remains in smaller diameter that will form the ________,
forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain
spinal cord
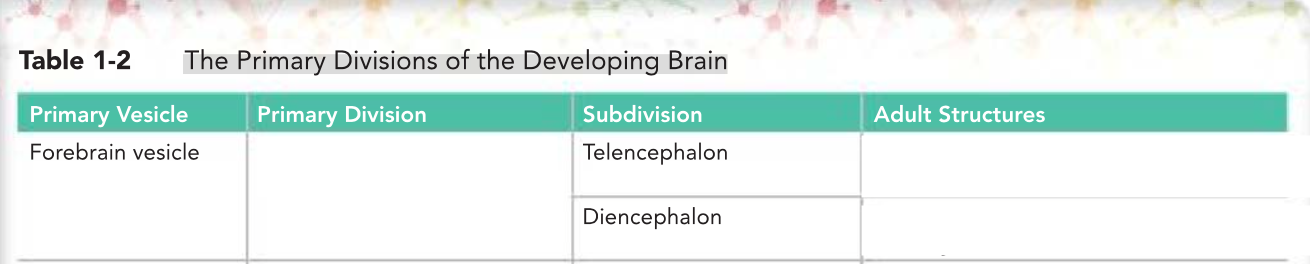
Cavity
________
_________
Procencephalon
Adult Structures:
Telencephalon - cerebral hemisphere (comprehension & learning) , basal ganglia (initiation of movement) & hippocampus (memory & learning)
Diencephalon - Thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal body & infindibulum
Cavity
1st ventricle; 3rd ventricle

Cavity
______
______
Mesencephalon → Mesencephalon → Tectum( eye movements, avoidance and approach),tegmentum(cardiorespiratory function) , crus cerebri ( motor of face and neck) → aqueduct of the Sylvius
Rhombencephalon → Metencephalon & Myelencephalon → Pons ( breathing, unconscious process), cerebellum (maintain balance, refine) & medulla oblangata ( heartbeat, breathing & blood control) → 4th ventricle (upper and lower)
Any interuption of ventricles /CSF = ____ for children while _____ for adult
Hydrocephalus; Brain Herniation
Failure of closure of Ant. neuropore is _______ while ________ for post. neuropore
Anencephaly ( failure of brain to develop)
Spina bifida ( spinal column does not form properly)
Lokin Talks:
Bundles of nerve fibers are called ________
Found in Peripheral nerves
Unmyelinated nerve fibers are found in the ______
nerve tracts
Autonomic nervous system
Lokin Talks:
faster conduction of impulses in ________ synapse due to a connexon forming gap junctions.
In the chemical synapse, there is a synaptic delay of _____
Neuroglia
Cilia can be only seen during ______
electrical synapse ( no delay)
0.3ms
embryonic stages of humans
Lokin Talks: Peripheral Neuroglia
_______ makes myelin for peripheral nerves
derivates of _____
Oligodendrocytes of CNS can myelinate _____ fibers while ____ for schwann cells
Myelin of PNS can function in regeneration of injured nerve fibers compared to CNS.( 3mm per day of growth )
schwann cells ( also called neurolemma)
neural crest
30-60 fibers; 1:1 internode
Lokin Talks:
_______
Degeneration due to disuse of neurons which can affect the neuronal pathway
Trans-neuromal degeneration
“Effective regeneration does not occur in CNS but as we learn from research, there might be a possibility through Physical Therapy”
😉 ← Doc Lokin