MICB 3301 - Exam 2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
nutrients
substances used in biosynthesis and energy release
required for microbial growth
microbial cell dry weight
macronutrients: C, O, H, N, S, P, Fe
micronutrients: cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese
sources of nitrogen
ammonia (NH3)
nitrate (NO3)
some use nitrogen gas (N2)
nitrogen fixation
N2 reduced to ammonia
Rhizobium: in symbiosis with plants, lives in soil, forms root nodules
Azotobacter: free living in soil
acquiring nutrients
food must enter:
at high rates
across membranes
selective fashion
often against a concentration gradient
passive transport
no energy required
high → low gradient
passive diffusion: only small molecules and certain gases
facilitated diffusion: uses membrane carrier proteins, still requires gradient
active transport
energy dependent
moves against gradient
uses ATP or proton motive force
primary active transport: ABC transporters
binding of nutrient and protein
conformational change caused by complex
2 ATP used to drive movement of nutrient into cytoplasm through ABC transporter
ABC transporter types
Uptake ABC: move nutrients in
Export ABC: Multidrug Efflux, move substances out
in bacterial cells move antibiotics out, bacteria becomes resistant to antibiotics
in cancer cells move anitcancer drugs out, tumor becomes resistant
Secondary Active Transport
uses potential energy of ion gradients
e- transport across a membrane generates H+ gradient
can be used to move another nutrient
ex. Lac Permease, moves lactose powered by proton moving in
Group Translocation
nutrient is chemically altered
ex. phosphate group is added
energy from phosphoenolpyruvate attaches P to sugars, glucose → pyruvate
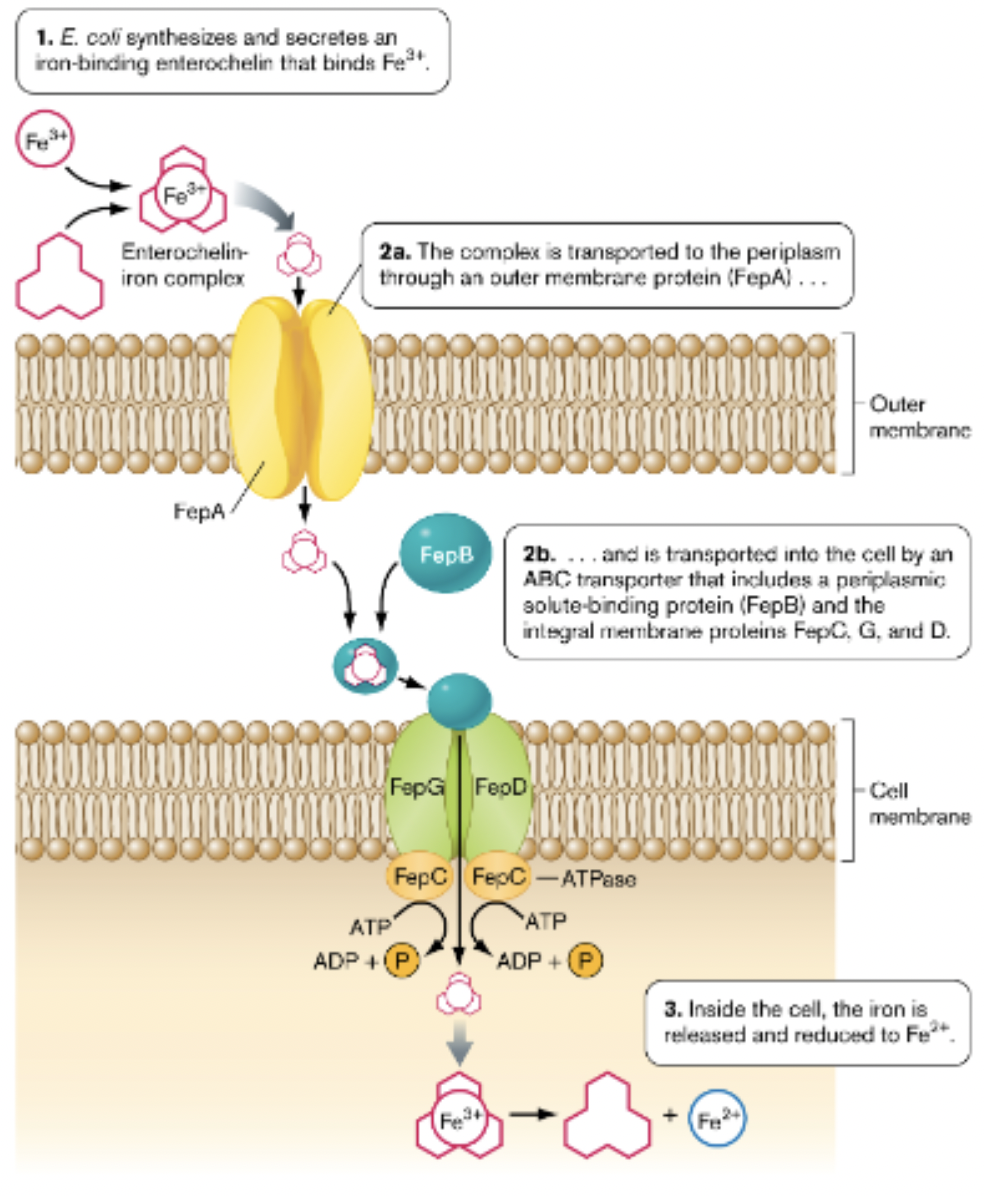
Iron Uptake
all microbes require Fe, little free Fe available
solution: microbes release siderophores to acquire Fe, siderophore-iron complex then transported into cell often using ABC transporter
ex. Enterobactin, E. coli siderophore
Metabolism
all chemical reactions in a cell
catabolism: breakdown of complex molecules into smaller ones with release of energy
anabolism: reactions that build cells
Adenosine Triphosphate
ATP
phosphate group
ribose sugar
Adenine base
P removal (hydrolysis): large negative standard free energy change
Energy generating systems
Oxidative phosphorylation: aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration
Substrate level phosphorylation: fermentation
Photophosphorylation: photosynthesis
ribozymes
catalytic RNAs
lowering activation energy
enzymes increase local concentration of substrates
orient substrates properly for reactions to proceed
redox reactions
oxidation: removal of electrons
reduction: gain of electrons
donor: substance oxidized
acceptor: substance reduced
uses electrons and protons, ex. NAD+/NADH
reduction potential
equilibrium constant for redox reactions
measures tendency of donor to lose electrons
more negative Eo better donor
more positive Eo better acceptor
greater difference in potential → more energy released
Classes of e- carriers in redox
freely diffusible (in cytoplasm)
NAD+, NADP+
reducing forms (NADH, NADPH) are “reducing power” of cell → biosynthesis
membrane-bound
flavoproteins, cytochromes, quinones
important components of ETC
Microbe transfer of energy
reduced food molecules (glucose) → diffusible carriers in cytoplasm → membrane-bound carriers → O2, metals or oxidized forms of N/S
autotrophs
use CO2 as C source
synthesize organic compounds used by hetertrophs
primary producers
heterotrophs
reduced, preformed organic compounds as C source
convert large amounts of C to CO2
sources of energy for growth
phototrophs: light
chemotrophs: oxidize chemical compounds (often same as C source)
source of electrons
lithotrophs: inorganic molecules as electron donors, unique to few Bacteria and Archaea (prokaryotes)
organotrophs: organic molecules as donors, ex. glucose
Eukarya
photoautotrophs (plants and algae)
heterotrophs (animals, protozoa, fungi)
Photoorganoheterotroph (table 11.1)
energy: photo-light
electrons: organo-organic compounds
carbon: hetero-organic compoundsn
aerobic respiration
completely catabolizes organic energy source to CO2 using glycolysis, TCA cycle, ETC
produces ATP indirectly via e- transport
Glycolysis
Embden-Meyerhof
most common form of glucose breakdown
occurs in cytoplasm
functions in presence and absence (fermentation) of O2
TCA Cycle
pyruvate completely oxidized
occurs in mitochondria of eukaryotes, cytoplasm of prokaryotes
generates: CO2, NADH and FADH2, precursors for biosynthesis
Electron Transport and Ox Phos
net yield 2 ATP from oxidation of glucose
most ATP from NADH and FADH2 oxidation in ETC
Electron Transport Chain
electrons from NADH and FADH2 generated by oxidation of organic substrates transferred through series of membrane bound electron carriers to a final electron acceptor
e- flow from carriers with more negative E0 to more positive E0 - energy released used to make ATP by ox phos
3 ATP per NADH
Where does ETC occur?
Eukarya: mitochondrial membrane
Bacteria + archaea: plasma membrane
Chemiosmotic Hypothesis
energy released during e- transport used to establish proton gradient and charge difference across membrane
proton motive force
Proton Motive Force (PMF)
e- flow causes protons to move outward across membrane, ATP made when they move back in through F1F0ATP Synthase
Electron acceptors
Organic e- donor
fermentation: endogenous organic electron acceptors
aerobic respiration: O2
anaerobic respiration acceptors: NO3-, SO4(2-), CO2, fumarate
Inorganic e- donor
chemolithotrophy acceptors: O2, SO4(2-), NO3-
Anaerobic Respiration Example
Denitrification NO3- → N2
nitrate is e- acceptor, reduces to N gas
Paracoccus denitrificans: facultative anaerobe in soil
depletes soil N, lower crop yield
Escherichia coli
uses nitrate as e- acceptor, reduces first to nitrite
basis of nitrite strip test for UTI diagnosis
Fermentation
catabolism without the electron transport system and terminal acceptor
in cytoplasm
electrons from NADH → pyruvate
generates: NAD+, ATP, lactic acid, ethanol
Electron donors
organic: glucose
inorganic: chemolithotrophs - H2, NO2, Fe(2+)
Iron-oxidizing bacteria
oxidizes iron compounds as e- source using O2 as e- acceptor, yields little energy?
ex. Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
Nitrifying Bacteria
nitrification: oxidation of ammonia to nitrate
Nitrosomonas: ammonia to nitrite
Nitrobacter: nitrite to nitrate
used to remove ammonia in wastewater
often followed by denitrification
Photosynthesis - phototrophs
light reactions: light energy trapped, converted to chemical
dark reactions: chemical used to reduce CO2 and synthesize cell material
Photosynthetic production
oxygenic: oxidize H2O for e-, forms oxygen
eukaryotes and cyanobacteria
anoxygenic: e- from other source
all other prokaryotes
light absorbing pigments
eukaryotes and cyanobacteria: chlorophyll
purple, green bacteria: bacteriochlorophylls
Asccessory pigments
transfer light energy to chlorophylls
absorb different wavelengths than chlorophylls
quench toxic forms of oxygen (photoprotectants, antioxidants)
ex. carotenoids, phycobiliproteins
Photosystems
chlorophylls and accessory pigments that are assembled into light-harvesting arrays, embedded in thylakoid membranes
PSI and PSII
Plants and cyanobacteria light reactions
in thylakoids
use chlorophyll
oxygenic
PSI and PSII
cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
Green and purple bacteria light reactions
in plasma membrane
bacteriochlorophyll
anoxygenic
only PSI
only cyclic phosphorylation
Archaea (photosynthetic?)
some are but they use a pigment protein called Rhodopsin instead
Microbial rhodopsin
pigment protein
located in plasma membrane
found in human retina, enables vision in low light
absorbs light that causes conformational change in rhodopsin
pumps H+ our across membrane
Anabolism
uses ATP and reducing power often in the form of NADPH synthesis
NADH used to power e- transport chains
Calvin cycle
anabolic pathway for fixing CO2 into carbs
dark reactions
chloroplasts → plants
cytoplasm → bacteria
provides organic matter for heterotrophs
Carboxylation (CC)
enzyme RuBisCo adds CO2 to Ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate generating 2 3-phosphoglycerate
occurs in carboxysomes
18 ATP to make 1 glucose
Reduction (CC)
3 phosphoglycerate reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
requires reducing power from NADPH
Regeneration (CC)
numerous carbs are generated
Ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate regenerated