6.1.3 manipulating genomes
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is a restriction enzyme
Enzyme that cuts DNA at specific recognition sites which produces DNA fragments
Where are Restriction enzymes normally found
Bacteria
what is a recognition site ?
Specific base sequence
Why are recognition sites palindromic ?
Read the same backwards and forwards
What are the types of cuts made by restriction enzymes
Sticky ends
Blunt ends
what is the difference between sticky and blunt ends
Sticky ends → there’s a overhang of DNA bases
Why are restriction enzymes used on Non - coding genes?
There are no mutations in Non- coding genes base sequence → easier to predict results
Function of non- coding genes
Control transcription by switching genes on and off
what is the function of Gel electrophoresis
Separate the DNA fragments as DNA is invisible
Why does DNA move through the gel when an electric current is applied?
DNA contains PO₄³⁻ anion on nucleotide this is attracted to the Positive electrode
what is the colour of DNA
Colourless
Control variables when using enzyme
Use the same restriction enzyme
Function of the gel in gel electrophoresis
Creates a matrix mesh that keeps large DNA fragments at top ( cant travel through mesh) and small at the bottom
which DNA fragments move faster and further in Gel electrophoresis
Small fragments
Function of Buffer ( Salt) solution in gel electrophoresis
maintains charge helps the current move
why are DNA fragments / banding pattern different?
Different alleles → different specific recognition sites
Different number and sizes of DNA fragment are produced
DNA fingerprinting ( Image)
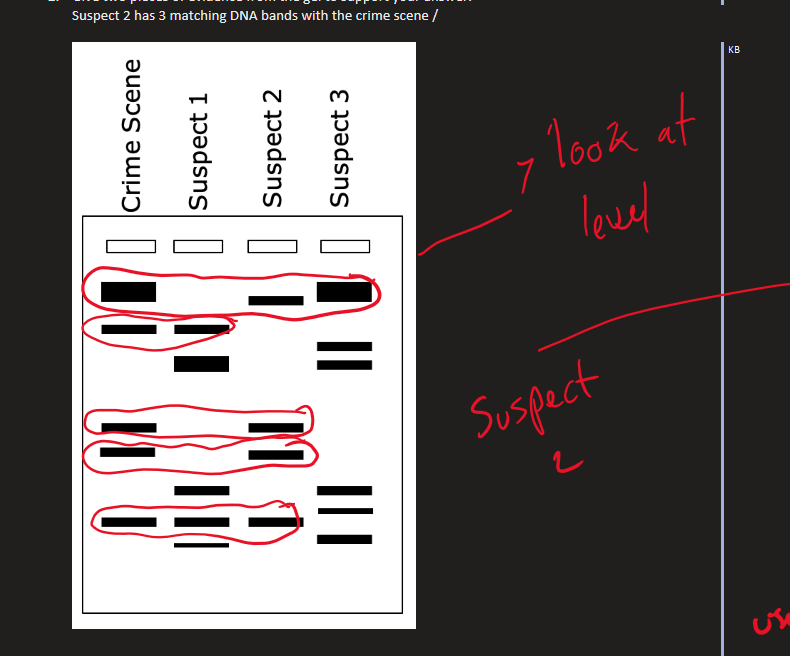
Limitations with gel electrophoresis
DNA fragments can get stuck in the gel
its not 100% could be related ( Identical twins)
Function of PCR in DNA fingerprinting
Used to amplify the DNA so there is enough to be analysed
DNA profiling method
Extract DNA
DNA fragments are placed into agarose gel
apply electric current
DNA moves to positive electrode
smaller fragments move further and faster
compare banding pattern with DNA sample to see if there similar.
Function of PCR
Amplify DNA fragment for further study or processing
What does PCR stand for
polymerase chain reaction
Uses of DNA profiling
Forensics
diagnosis of genetic disorders
What are the steps of PCR
Denaturation → separate double helix
Annealing → Primers bind to the start of the target DNA
Synthesis → Building the new strand
PCR what are primers
short pieces of DNA that are complimentary to the bases of the fragment
PCR what happens during denaturation?
DNA mixture heated to 95°C → breaks Hydrogen bonds
separates DNA strands
Why can many cycles of PCR happen without needing new enzymes
DNA polymerase doesn’t denature at high temp
PCR what happens at annealing stage
55°C temp of reaction mixture
allows primers to bind to strands
PCR what happens at the synthesis stage
72°C temp allows DNA polymerase to work
DNA polymerase joins DNA nucleotides to template strand using complimentary base pairings → forms 2 new complimentary strands
what type of DNA polymerase is used in PCR
Taq DNA polymerase → doesn’t denature at high temperatures
human does denature at 72°C
what molecules are required for PCR
DNA template
primers
nucleotides
DNA polymerase
Limitations of PCR
Expensive
Takes a long time
what molecules are required for chain termination method
DNA polymerase
Primer
DNA sample
nucleotides
Fluorescently-labelled modified nucleotide / terminator base
Chain termination method first step
Mixture of required molecules is added to separate tubes
chain termination method second step
Tubes undergo PCR
strands produced are different lengths → modified nucleotide terminates the strand ( cant extend strand)
modified nucleotide is added on different points
why do fluorescently-labelled modified nucleotides terminate the strand
No bases can be added after
Hydrogen instead of hydroxyl group on carbon 3 so cant form phosphodiester bond with next nucleotide
methods to read data in DNA sequencing
Gel electrophoresis
Capillary sequencing
electrophoresis method in DNA sequencing
electrophoresis separate DNA fragments
shine under UV light
Read from top to bottom ( smaller fragments are near top / move furtherest)
How can DNA be sequenced ?
chain termination method
Advantages of using chain termination method for DNA sequencing ?
allows for massive parallel sequencing
sequence many DNA at same time