gcse music all
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
when and where the blues developed
Southern states of USA, early 1900s
influences
Africa and America
how it developed
from free slaves in the USA who used to sing work songs.
what were the lyrics about
often hardship and melody of working as a slave
typical melodic features of blues
Use of blues notes/the blues scale, portamento/slides, improvisation, AAB phrasing
when they started playing beyond the southern states
early 20th century
it became popular at this time with a black and white audience
by the 1920s
traditional blues instruments
banjo, flute, violin, piano, harmonica and guitar, double bass and voice
blues scale
C, Eb, F, Gb, G, Bb, C
harmony and tonality of blues
12 or 16 bar blues progression, dissonance (use of 7th chords, blue notes), use of chords I, IV & V, major tonality
melody of blues
melisma, AAB phrase structure, riff
rhythm, meter and tempo of blues
Swing rhythms, syncopation, 4/4, slow tempo
structure of blues
Strophic, 12 or 16 bar blues, call and response
Portamento
a smooth gliding from one note to another
melisma
Use of many notes on one syllable of text
3 samba instruments
agogo, ganza, surdo
ostinato
a repeated phrase or pattern
syncopated
off-beat
reggaeton
style of music in the late 2000s in Latin America
salsa
a popular form of dance music
- often in minor key
- call & response vocals
- the clave rhythm is a key feature
tango
- serious and intense
- steady/slow tempo
- tonic & dominant baseline
rumba
dance and party music
- upbeat and syncopated
- features complex polyrhythms
- highly percussion based, with a singer
3 folk music instruments
accordion, banjo, penny whistle
compound duple
6/8
compound quadruple
12/8
simple triple
3/4
simple quadruple
4/4
features of folk music
- harmony is very simple and may only use a few chords
a lot of music is improvised
More folk music features
- most pieces are in compound time
how is folk music learnt
by ear
Caribbean music styles
ska, bubble rhythm, mento
reggae features
bass riffs, slow tempo, drums emphasizing back beat.
reggae instruments
electric guitar, jazz organ, bass drum kit
traditional African music singing
call & response, a Capella, cries/yodels, unison, close harmonies
A Capella
- cries/yodels
- unison
- close harmonies
African drumming
- djembe
- dun dun
- cowbell
African music features
call and response, repetition, cross/polyrhythms
- repetition
- cross rhythms
- polyrhythms
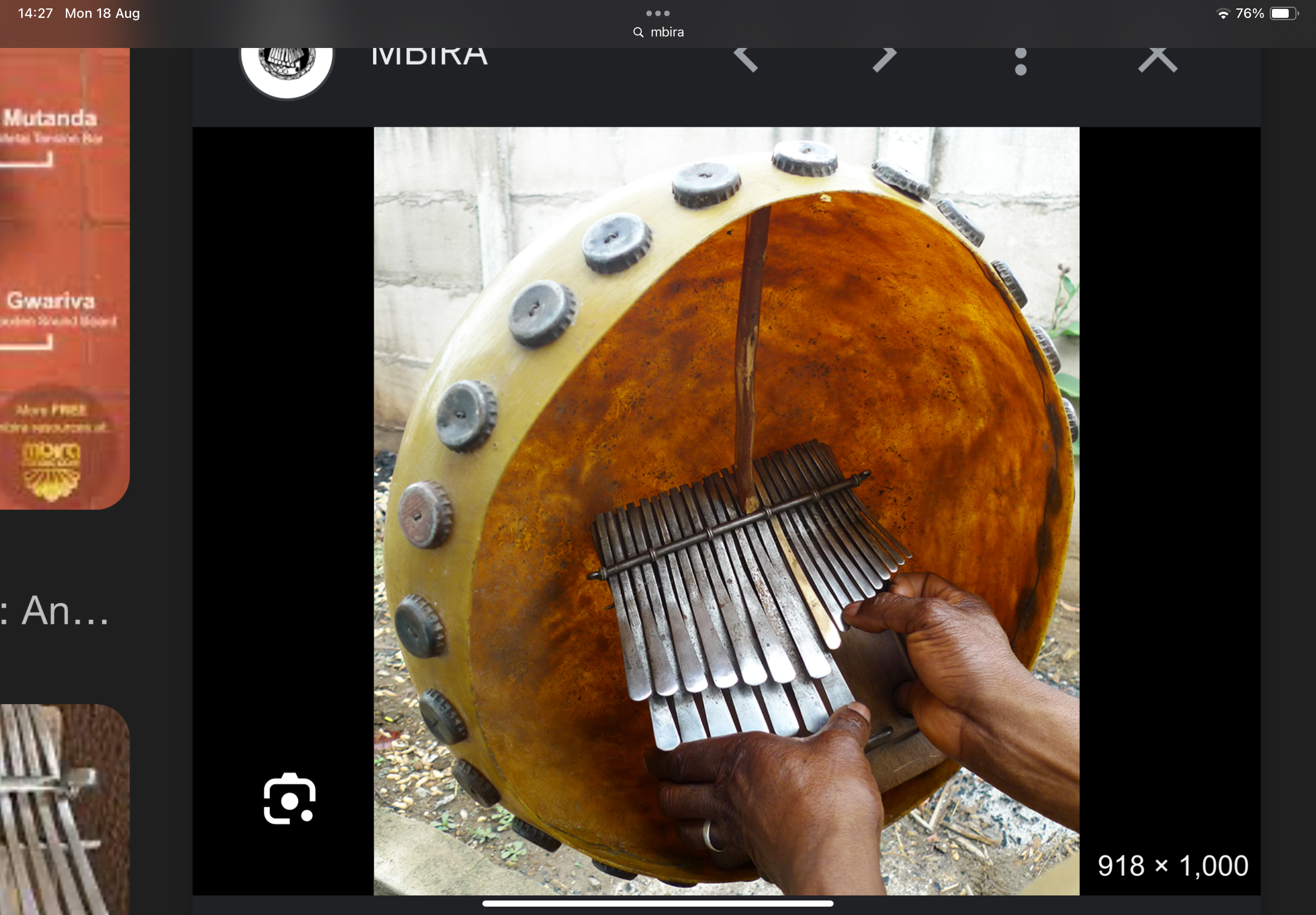
Mbrira
thumb piano
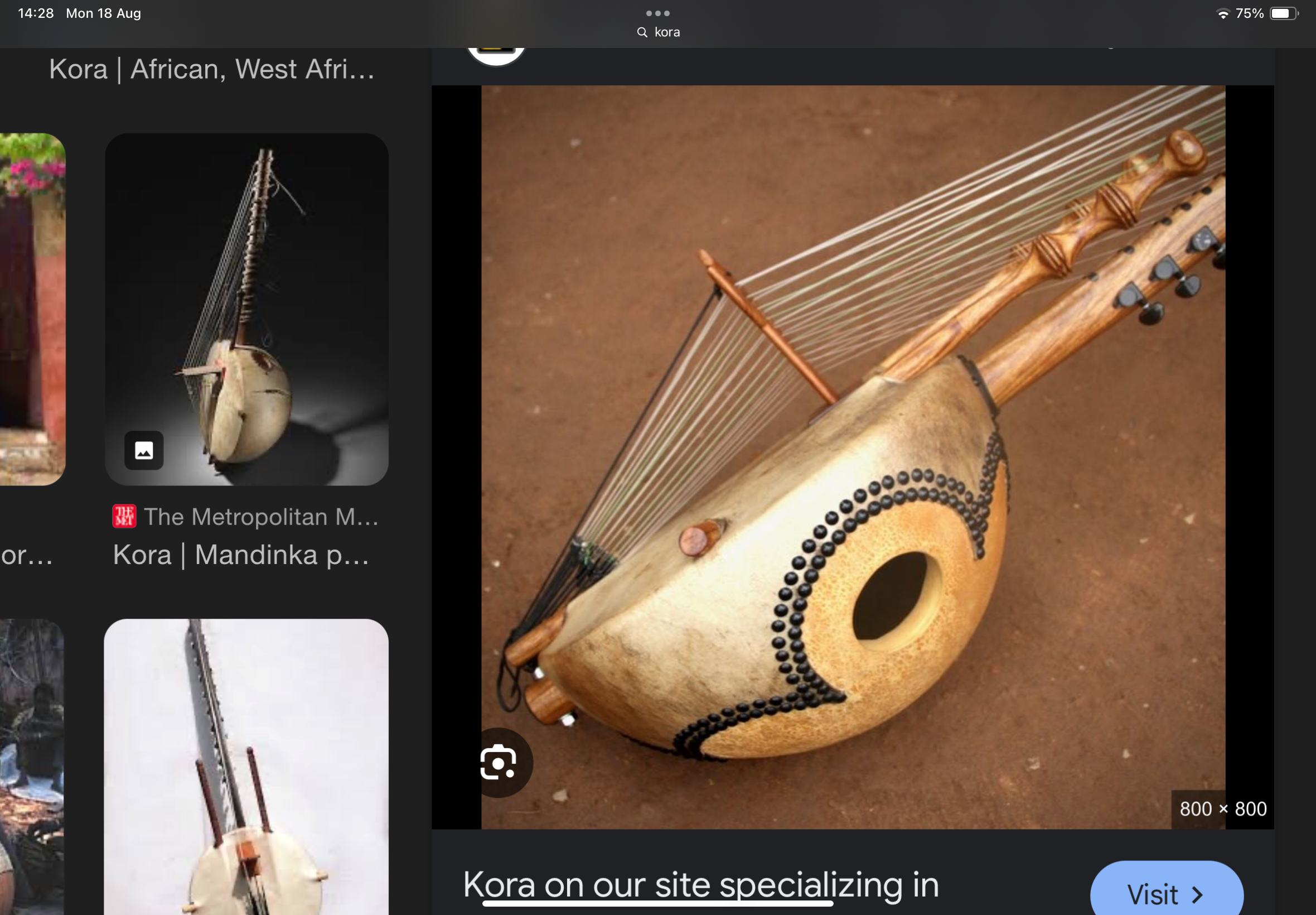
kora
guitar-like instruments which sounds like a harp
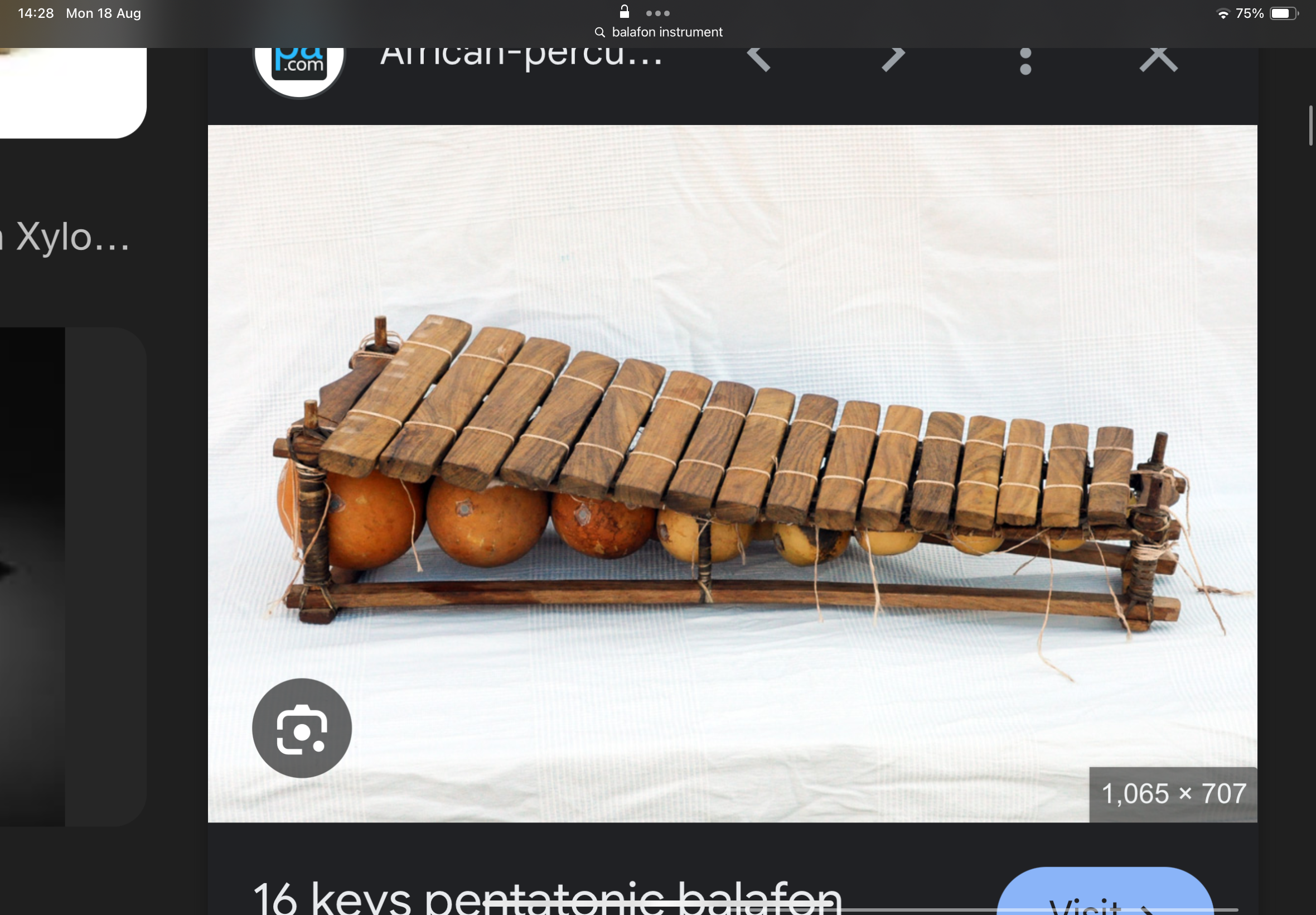
balafon
looks like a xylophone. The smaller the size, the lower the pitch.
Melody
repetitive
Rhythm/tempo/meter
Fast tempo
Tonality
Dynamics
Instrumentation
Piano
Harmony
Cadences
Texture
Polyphonic
Structure
Strophic
polyphony
2 or more independent melodies playing at the same time
Homophony
parts playing together as chords
hetrophony
parts playing the same line together but with slight variation.
unison
different voices/instruments playing the exact same thing.
features?
- melodies are often pentatonic scale and have major tonality.
- often repetitive.
- may feature some improvisation.
the baroque period
1600-1750
famous baroque composers
Handel and Bach
ground bass
usually 4-8 bars long, repetitive, other melodies layer on top.
harpsichord
- popular keyboard instrument of baroque time.
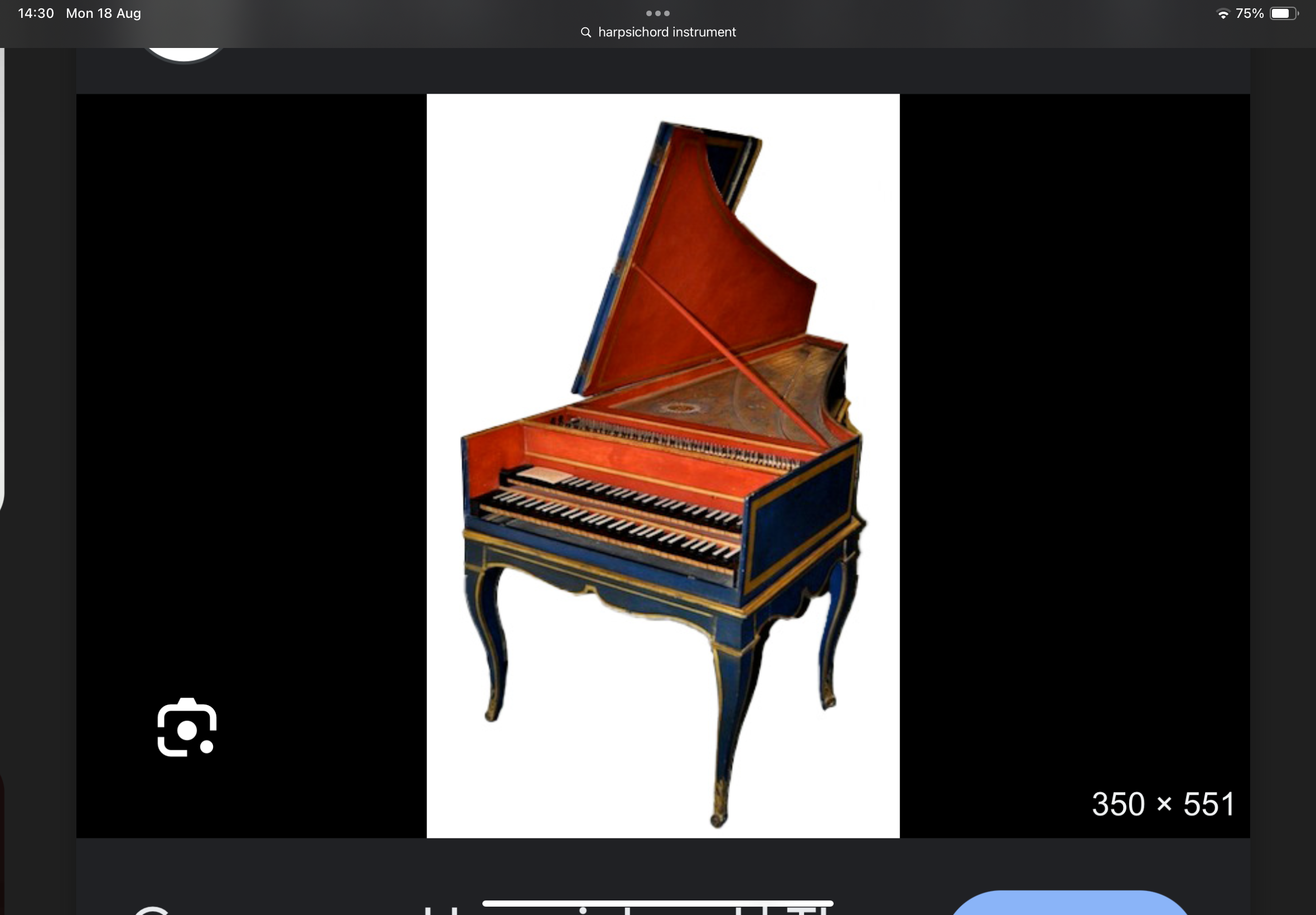
- pieces were very ornamented as the instrument could not sustain notes.
oratorio
a type of large scale musical work.
Recitetive
half spoken, half sung narrative. There is no clear pulse.
aria
a solo song reflecting emotion.
chorus
more powerful, all singers and orchestra playing together.
Rubato
When the tempo speed up/slows down naturally
Polyrhythm
When 2 contrasting rhythms play at the same time