Perception & Action: Colour & Lightness Constancy (L2 P1)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is colour constancy?
Perceiving consistent color despite lighting changes
What is lightness constancy?
Perceiving consistent lightness despite illumination changes
What does visible light form?
Bands of electromagnetic spectrum frequencies.
Why do objects appear coloured?
Because they absorb and reflect light of different wavelengths
What does red hue produce?
Long wavelength light
What does violet hue produce?
Short wavelength light
What is hue?
Color tone based on light wavelength
How much of the electromagnetic spectrum is covered by visible colours?
400 nm
What does the cornea protect the eye from?
Ultraviolet
Why can babies see ultraviolet?
Their cornea have not yet hardened
What gives objects 'colour'?
Different objects obsorb and reflect different wavelengths of light.
What does colour also depend on?
The light source
What is perceived colour determined by?
Hue, intensity and saturation
What is the psychological attribute of Wavelength?
Hue
What is the psychological attribute of Intensity?
Brightness
What is the psychological attribute of spectral purity?
Saturation
What is reflectance?
Proportion of light reflected from a surface
What is lightness?
The perceived shade of a surface
What is the difference between lightness and reflectance?
Lightness is a perceptual quality, reflectance is a physical quality
What is the difference between blue and red?
Different hues
What is the difference between light and dark blue?
Different intensities
What is the difference between light and dark objects?
Dark objects absorb almost all wavelengths
What is the difference between red and pink?
Different saturation
What is saturation?
Amount of pure hue in a color
What is intensity?
Brightness of reflected light
What is the Trichomatic theory?
There are 3 different cone types at the back of the eye: short, medium, long
Who came up with the Trichomatic theory?
Helmholtz
What is the Opponent Process theory?
There are 3 opponent processes: Red - Green, Blue - Yellow, Black - White.
Explains subjective experience of 4 primary colours and colour after effects.
Who came up with the Opponent Process theory?
Hering
What is the Dual Process theory?
The trichromatic stage involves the retina/photoreceptors and the opponent-process stage involves Ganglion cells/LGN
What is luminance?
Amount of light reflected from a surface
What is illumination?
Amount of light emitted from a light source
What is the equation for luminance?
Illumination X reflectance
What is the problem of lightness perception?
Reflectance tells us about the lightness of a surface.
But we only receive information about luminance, not reflectance.
What is the inverse problem of lightness perception?
A particular luminance could have been produced by infinite combinations of illumination and reflectance
What are some incorrect theories of lightness constancy?
Adaptation theory, unconscious inference theory
What is the adaptation theory of lightness constancy and what is the problem with it?
The visual system becomes less/more sensitive in bright/dull conditions
Adaptation is slow, can't account for fast changes in lighting
What is the unconscious inference theory of lightness perception?
Prior experience allows us to estimate illumination.
We aren't sensitive to absolute levels of illumination
What is spectral purity?
The degree of color saturation
What is a relational theory of lightness constancy?
Lightness perception is based on the relationship between different objects
What are some relational theories of lightness constancy?
Wallach (1948), Importance of Edges, Retinex theory (Land & McCann 1971)
What did Wallach (1948) find in relation to lightness constancy?
Luminance ratios determine lightness perception.
Ps matched luminance ratios rather than absolute luminance regardless of lighting condition.
What illusion demonstrates the importance of Edges in determining lightness perception?
Craik-Cornsweet-O'Brien illusion
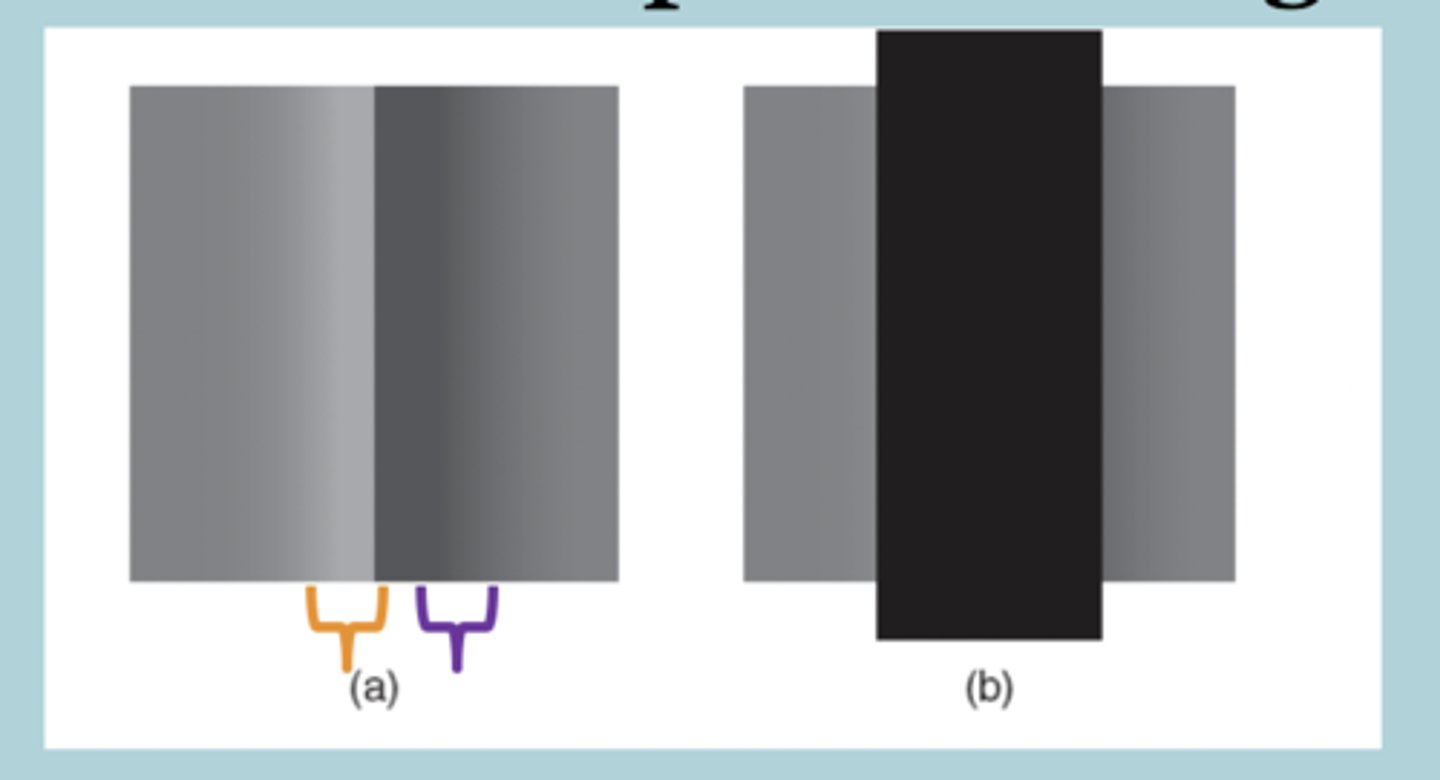
What is the Retinex theory?
Calculate luminance ratios at edges.
Ignore gradual changes in luminance (assume due to illumination changes).
Tells us relative reflectance of surfaces
What is the scaling problem for relational theories of lightness constancy?
Issue in determining lightness ratios due to infinite possible combinations
What can be used to solve the scaling problem?
An anchoring heuristic
What is an anchoring heuristic?
Assuming highest luminance as white then scale other regions relative to this
Why are illumination vs reflectance edges a problem for relational theories of lightness constancy?
Retinex theory assumes all changes in illumination are gradual so can't account for sudden changes in illumination.
What are illumination edges?
Neighboring regions receive different amounts of light
What are reflectance edges?
Neighboring regions have different reflectance e.g. different material or paint
What can be used to solve the illumination vs reflectance edges problem for relational theories of lightness constancy?
Fuzziness heuristic, Planarity heuristic, ratio magnitude heuristic
What is the fuzziness heuristic?
Illumination edges are fuzzy, while reflectance edges are sharp
What is the planarity heuristic?
If depth info indicates two regions aren't coplaner (i.e. dont have same 3D orientation), its likely an illumination edge.
What is the ratio magnitude heuristic?
If the luminance ratio is very high its likely to be an illumination edge