Medical Physics ABR Part 1 Clinical
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
300 Terms
Rate the body systems in order of decreasing radio-sensitivity.
1. Hematopoietic, Reproductive (2-5 Gy)
2. Skin, cornea, lens of eyes, GI organs (10 Gy)
3. Bone and cartilage
4. Lungs, kidneys, Liver, Pancreas
5. Muscle, brain, nerves, spinal cord (20 Gy)
a. What are the components of the cell cycle & their order?
b. What is the relative radio-sensitivity of each?
Mitosis (M), Gap 1 (G1), Synthesis (S), Gap 2 (G2)
a. M -> G1 -> S -> G2
b. M > G2 > G1 > S
Cerebellum:
a. Function
b. Location
a. Motor control, balance
b. Directly posterior to the brain stem.
Cerebrum:
a. Function and properties
b. Divisions
a. Higher functions: thought, action.
b. 4 lobes: frontal (anterior), parietal (superior), occipital (posterior), temporal (lateral x 2).
Cerebral cortex
Sheet of neural tissue outermost to the cerebrum. Grey matter
Brain steam function
Basic vital life functions (breathing, heartbeat, etc.
Corpus callosum
Connects the two parts of the cerebrum.
{Lets the two hemispheres talk to each other, i.e. "call" each other}
Alveoli
a. Location
b. Function
a. Lungs
b. Air-lung interface. Diffusion of O2, CO2.
Hiatal hernia
a. Describe condition
b. Imaging modality to diagnose?
a. Part of the stomach sticks upward into the chest through opening in the diaphragm.
b. UGI x-ray after ingestion of barium.
Upper gastrointestinal.
UGI. Esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
Lower gastrointestinal
LGI. Small and Large intestine. Stool.
US transducers:
a. What is the angle of orientation of the two surfaces?
b. How thick are the transducers in terms of the wavelength?
c. Are the pressure waves and voltage in phase or out of phase?
a. 180 degrees.
b. lambda/2
c. pressure: in phase. Voltage: out of phase.
Stroke
a. Describe
b. Effects
a. sudden loss of consciousness resulting when the rupture or occlusion of a blood vessel leads to oxygen lack in the brain
b. Loss of brain function, ischemia, hemorrhage
Ischemia
Insufficient blood flow to an area
Hemorrhage
Flow of blood from a ruptured blood vessels.
Transurethral resection
Small pieces of tissue from a nearby structure (typically prostate) are removed through the wall of the urethra.
Foramen magnum
A large hole in the occipital bone (base of skull) for the passage of nerves into the spinal cord.
Liver cirrhosis
a. Describe
b. Causes
c. Effects
a. Cells are progressively destroyed and replaced by fatty and fibrous tissue that surrounds the intrahepatic blood vessels and biliary radicles, impeding the circulation of blood through the liver.
b. Caused by chronic alcohol abuse (alcoholism); hepatitis B, C, and D (causes liver inflammation and injury leading to cirrhosis); and ingestion of poisons.
c. Hypertension, intestine bleeding.
Sarcoidosis
Chronic inflammatory disease in which small nodules (granulomas) develop in lungs, lymph nodes, and other organs
Meiosis
a. Describe
b. Result
a. Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
b. 4 haploid cells
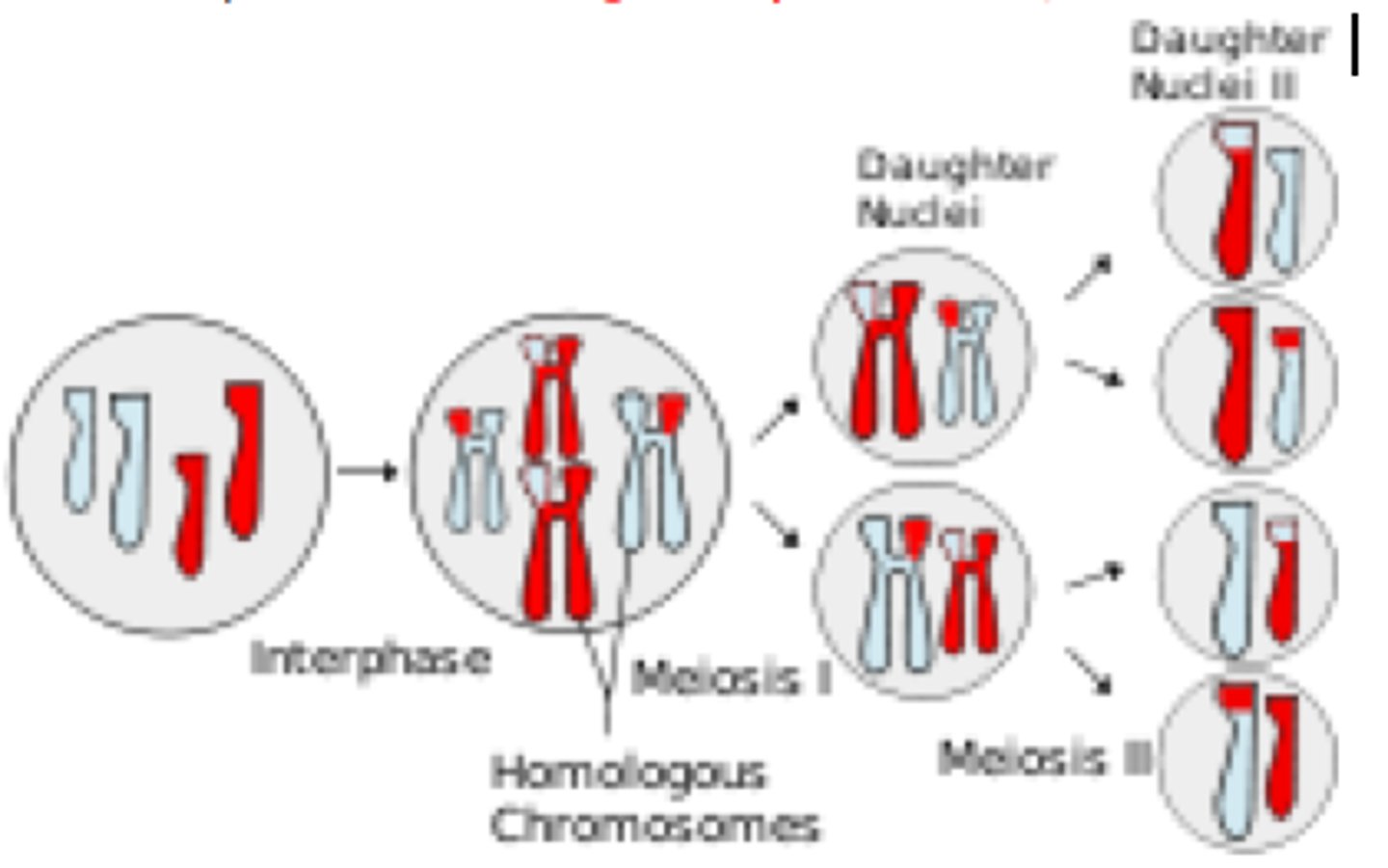
Haploid cells
A cell containing only one set of chromosomes.
Diploid
Cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number.
How many essential minerals to human health. List them.
17.
7 major: Calcium, Sodium, Chloride, Magnesium...
Phosphorus, Sulfur, Potassium.
10 trace: Manganese, Chromium, Copper, Selenium...
Zinc, Iodine, Fluoride, Molybdenum.
{Sing Mexican Hat Dance. Iodine = "EyeDine"}
How many and what are the major elements of the body?
4.
H (63%)
O (26%)
C (9%)
N (1%)
Number of Cranial (CNS) nerves
12 types (but are paired, so 24 total)
Oh Once One Takes The Anatomy Final Very Good Vacations Are Here.
What are the thresholds for whole body acute radiation (rem/rad or Sv/Gy) for given symptoms?
rem <=> rad; Sv <=> Gy
50 rem (0.5 Sv): Blood count change
100 rem (1 Sv): Vomiting
150 rem (1.5 Sv): Death threshold
350 rem (3.5 Sv): LD 50/60 with minimal care
500 (5 Sv): LD 50/60 with supportive medical care
1000 (10 Sv): LD 50/60 with intensive medical care (bone marrow transplant)
*LD 50/60 is the lethal dose at which 50% of those exposed die within 60 days.
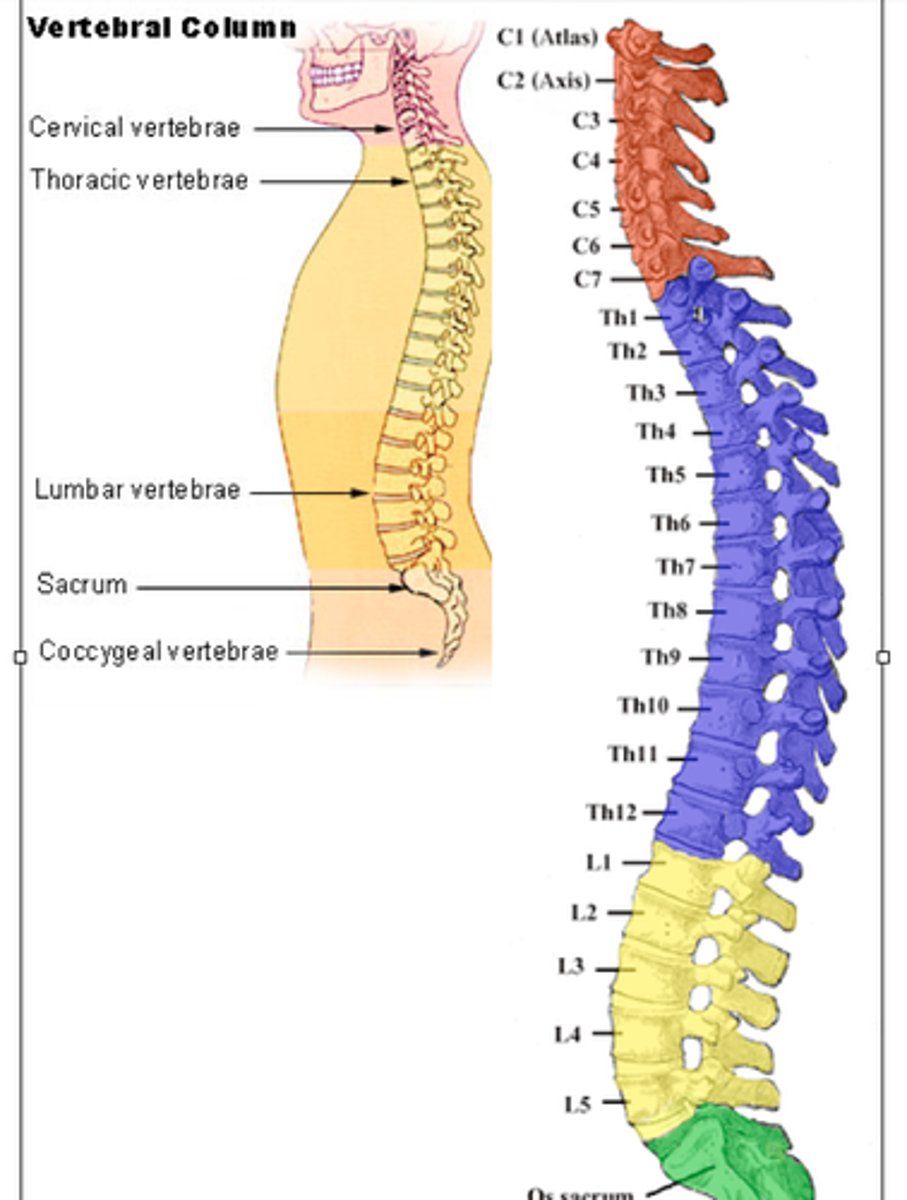
At what vertebral level is the Umbilicus?
L3-L4
Liver function
Stores glycogen;
manufactures and secretes bile; manufactures blood proteins;
destroys old red blood cells;
detoxifies harmful substances
Gallbladder function
Store & concentrate bile produced by the liver until it is needed in the small intestine
Adenoma
A benign epithelial tumor of glandular origin.
Common for pituitary.
Prolactinoma
A benign tumor (adenoma) of the pituitary gland that causes it to produce too much prolactin
Vertebral level of the Larynx
C6
Meningioma
A tumor arising in the meninges, the structure surrounding the brain and spinal cord
Hydrolysis produces what?
H+, OH-. Leads to H2O2 (relatively stable). OH- highly oxidizing/damaging.
Lens dose equivalent
The external exposure dose equivalent to the lens of the eye at a tissue depth of 0.3 centimeters (300 mg/cm2).
Transport index
Max dose equivalent rate at one meter from the surface of a package containing radioactive material.
4 Rs of Radiobiology.
Used to justify fractionation.
. Redistribution
. Repair
. Reoxygenation
. Repopulation
. (Radiosensitivity)
{DPOPS}
What is the effect of ionizing radiation on the cellular level.
Damage to DNA.
Blood vessels of the liver
Hepatic Artery (oxygenated blood from heart)
Hepatic Portal Vein (Neutrient rich blood from GI tract)
Gleason score pertains to which cancer?
Prostate
Small intestine function and division.
D-J-I
Duodenum - Digestion
Jejenum - Absorption of carbs and proteins
Ileum - Absorption of bile salts, fats.
Pineal gland
A small endocrine gland in the center of the brain near the brain stem that secretes melatonin and serotonin
{Pinae -> Pinay -> Phillipinos are happy and get lots of sun -> Secretes seretonin and melatonin}
Choroid plexus
A highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles in the brain that secretes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which cushions brain and spinal cord.
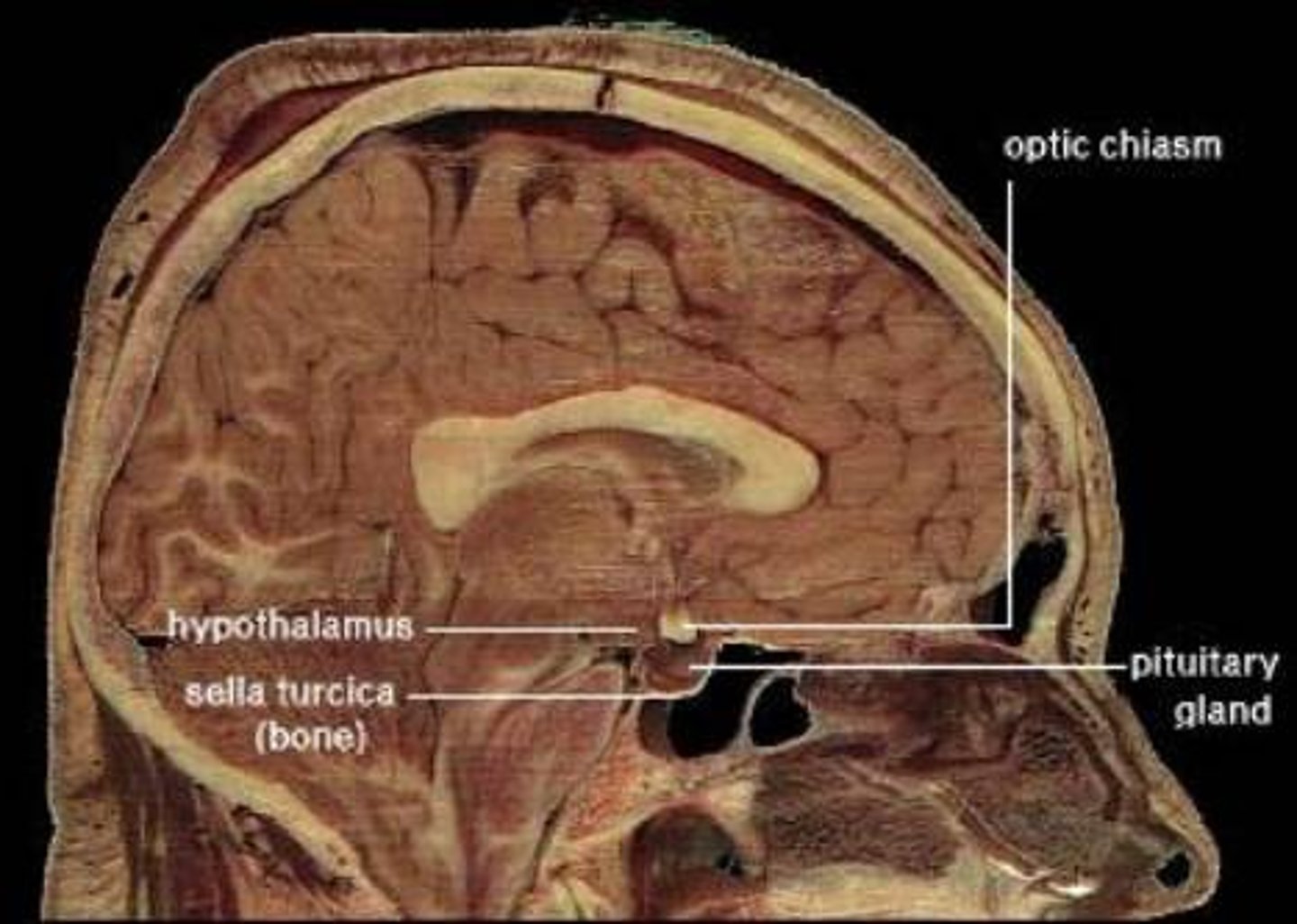
Optic Chiasm
The crossing of the optic nerves from the two eyes at the base of the brain.
Below the hypothalamus.
What systems are responsible for equilibrium?
Vestibular system (inner ear) and Cerebellum
Synovial fluid
Lubricates, nourishes, and keeps the joint moveable
Single Hit Theory (Equation and variable definitions)
S = N/N0 = e^(-D/D0)
S: Survival fraction
N: Cells remaining
N0: Initial # of cells
D: Given dose
D0: Mean lethal dose
Metastasis
Spread of cancer cells beyond their original site in the body
Sestamibi Scan
Tc99m is injected intravenously and traced to heart muscle or thyroid to observe function. Emits 140 keV gamma rays (same as standard x-ray equipment).
Peritoneum
Double-layered membrane surrounding the abdominal organs.
Cardiomyopathy
A disorder (usually of unknown origin) of the heart muscle (myocardium)
Cardiac dysrhythmia
Abnormality of heart rhythm
Ligaments of the knee
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
Transverse ligament
Meniscofemoral ligaments
Meniscotibial ligaments
Patellar ligament
Medial collateral ligament (MCL)
Oblique popliteal ligament
Arcuate popliteal ligament
Vertebral level of the caudal end of the spinal cord?
L2
Number of each type of vertebrae
Cervical (7)
Thoracic (12)
Lumbar (5)
Sacrum (1, *5)
Coccyx (1, *4)
a. What is Multiple Sclerosis
b. Best technique for imaging Multiple Sclerosis? Why?
a.CNS disease. The body's own defense system attacks myelin.
b. MRI
a. Which cancer has the shortest latency period?
b. How long?
c. How relates to others?
a. Leukemia
b. 2-15 yrs
c. Others 10-30 yrs
http://www.hicare.jp/en/09/hi04.html
Radiation equivalent man <-> Severt conversion
100 rem = 1 Sv
What is the prob. of genetic defects to offspring as a function of dose?
Approx. 1/10,000 at 10 mSv
Or 1% per Sv.
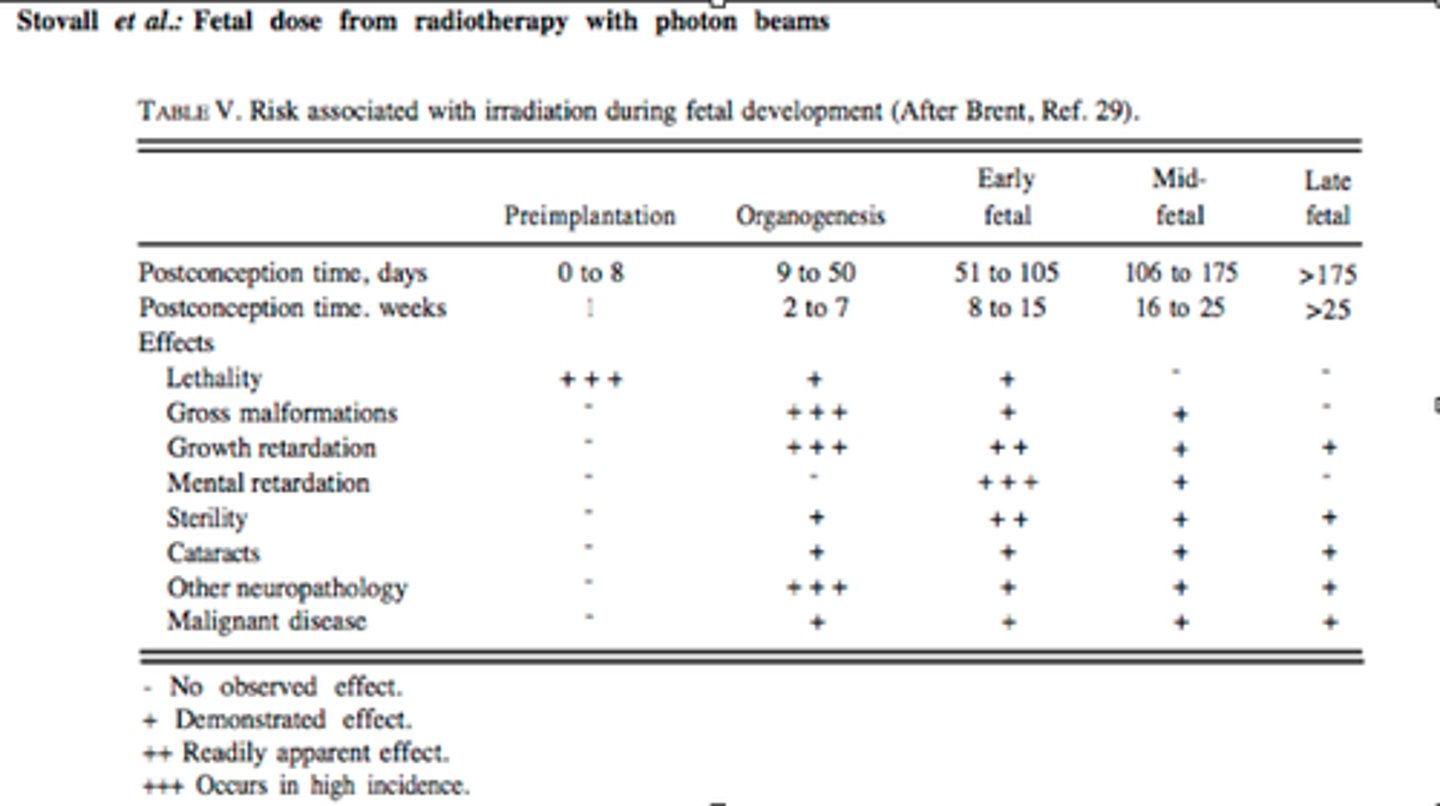
Risks of radiation exposure at stages of gestation (weeks)?
1 week: Lethality
2-7 weeks: Gross malformations, Growth retardation, general neuropathology
8-15 weeks: Mental Retardation most, but also Growth retardation, Sterility
16-25 weeks: lower risk of all above except lethality.
Congenital
Present at birth but not necessarily hereditary
Parasympathetic vs. Sympathetic control
Part of the autonomic nervous system.
Oppose each other (complementary).
Sympathetic : police (quick response) :: parasympathetic : courts (regulated activity)
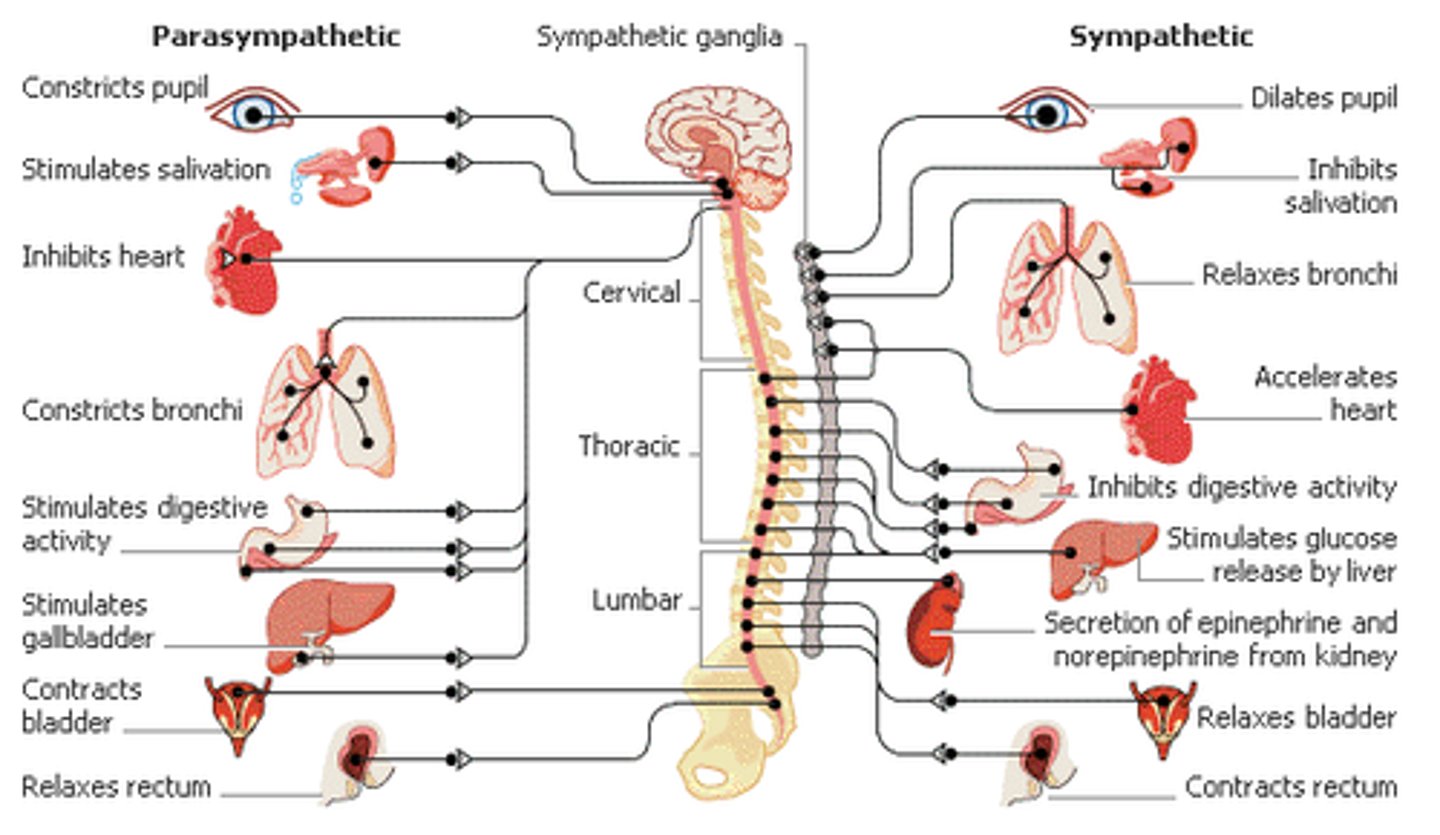
Nerves move voluntary muscles through which process?
Reflex arc.
Gray vs. Sievert
Absorbed dose (by matter) = Gray.
Equivalent dose (by biological tissues) = Sv
Sv = (Quality Factor) * Gy
Effects of 1 Gy whole body radiation?
Nausea and vomiting.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is best used for what?
Tumors of the brain.
Stenosis
Abnormal narrowing of a bodily canal or passageway
{A stent will prevent stenosis}
What is the primary mechanism for damage by LET photons?
Hydrolysis. 2/3 of damage to DNA by hydroxyl radical.
Medical term for mouth.
Buccal cavity.
Vena cava
Either of two large veins that return oxygen-depleted blood to the right atrium of the heart.
Pulmonary artery
One of two arteries that carry venous blood from the heart to the lungs
What is a barium scan used for?
Contrast for visualization of the GI tract via x-ray.
Committed dose equivalent
Dose to a specific organ or tissue that is received from an intake of radioactive material by an individual during the 50-year period following the intake.
Circle of Willis
A circle of arteries at the base of the brain that supply blood to the brain.
Surrounds the pituitary.
What does "radiation leakage" generally refer to?
Radiation going out through the x-ray tube housing in all directions rather than that of the useful beam.
Vocal cords
folds of tissue within larynx that vibrate and produce sounds
Increase in cancer risk as a fn of dose (Sv, rem)
Acute: 10%/Sv (10%/100rem)
Chronic: 5%/Sv (1%/100 rem)
What is used by nerve cells to stimulate skeletal muscles?
Calcium
Pituitary gland:
a. nickname
b. functions
Located in the brain
a. The master gland of the endocrine system.
b. Growth hormone, Thyroid-stimulating hormone, Prolactin, etc.
What type of scans can be used to stage lung cancer.
PET, CT, MRI
A person with Radium exposure: where will radon be detected.
Breath. Radon is a heavy element so if it enters the lungs it will sink to the bottom and linger.
a. Embolus b. embolism
a. An abnormal particle (e.g. an air bubble or part of a clot) circulating in the blood.
b. occlusion of a blood vessel by an embolus (a loose clot or air bubble or other particle)
What is the defining characteristics of MTFs?
Better preservation of resolution => higher MTF per spacial frequency.
Usually MTF (on y axis) vs. Spacial Freq. (on x asis)
a. Telangiectasia = ?
b. How long after radiation does it develop?
Describes capillaries that have been damaged and are now larger; or distended blood vessels. Commonly called couperose skin.
What is the lower limit of detection for radio-contamination?
μCi or 10^4 Bq
Ci to Bq conversion
1 Ci = 3.7 x 10^10 Bq
Shallow-Dose Equivalent
(SDE).The external exposure dose equivalent to the skin or an extremity at a tissue depth of 0.007 centimeters (7 mg/cm2) averaged over an area of 1 square centimeter.
Carina
Point at which the trachea bifurcates (divides) into the left and right mainstem bronchi.
{Car => Driving a car => see forks in the road => Fork in trachea}
Chart of chromosome-type aberrations.
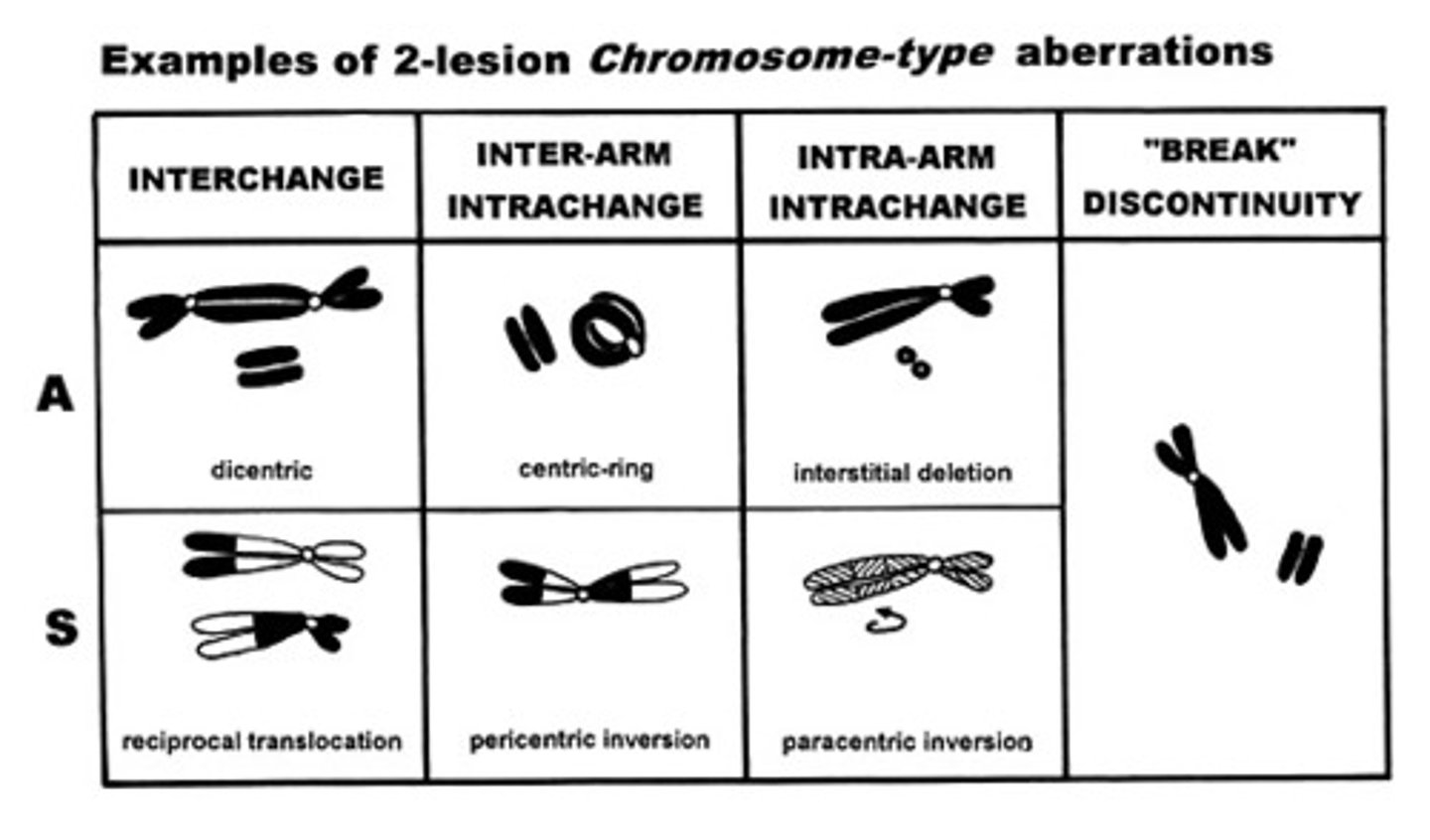
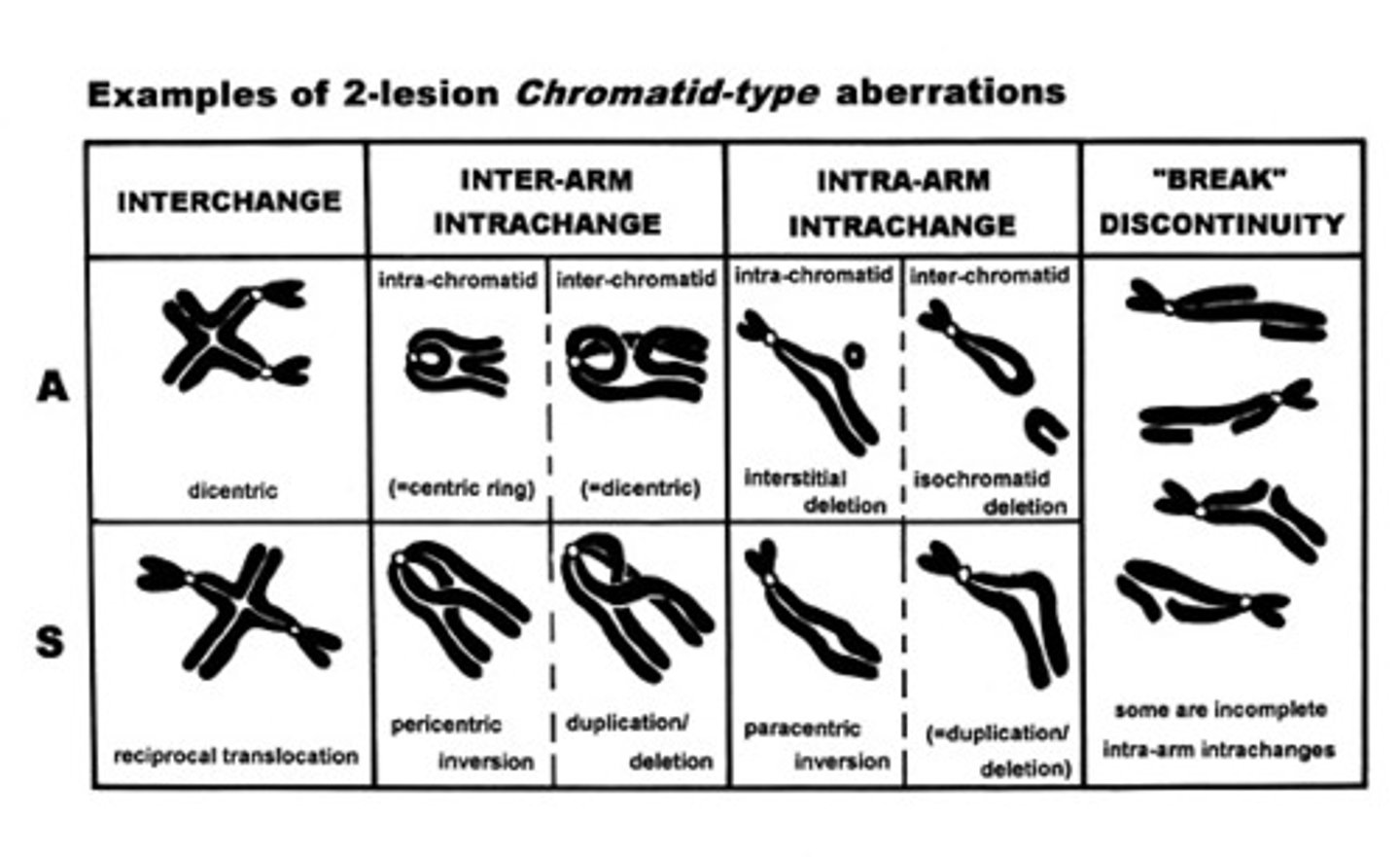
Chart of chromatid-type aberrations.
Asymmetrical rejoining
Chrom-atids, -osomes re-join in such a way that an acentric fragment is always formed.
What does symmetrical rejoining refer to?
Chrom-atids, -osomes
100 Gy acute dose. Result?
CNS death.
1 Gy to gonads. Result?
Temporary sterility/infertility.
Recommended safe dose limit to fetus?
0.5 rem (5 mSv) for entire gestation period.
Recommended safe dose limit for non-radiological workers?
0.100 rem (1 mSv) per year.
Approx dose limits per year for:
a. Extremities
b. Skin and organs
c. Lens of eye
a. 0.5 SV
b. 0.5 SV
c. 0.15 SV
Approx. safe whole body chronic dose limit per year?
5 mSv per year.
Average size of normal prostate?
35 cc
Cardiac catheterization
Introduction of a catheter through a vein or artery into the heart. Often to inject contrast media for fluoroscopic radiography (x-rays). Often includes interventional procedures such as angioplasty and atherectomy.