Menstruation, Birth Control, and Pregnancy Overview
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
Menstrual Cycle
Cyclic changes in ovaries and uterus preparing for fertilization.
Menstruation
Excretion of endometrium through the vagina.
Toxic Stress
Long-lasting effects from excessive stress response activation.
Stressors
Environmental challenges causing psychological and physical responses.
Fight-or-Flight Response
Physiological reaction to perceived threats boosting energy.
Healthy Pregnancy
Dependent on a well-functioning reproductive cycle.
Hormonal Regulation
Control of the menstrual cycle by hormones.
Estrogen-based Birth Control
Prevents ovulation by mimicking natural hormones.
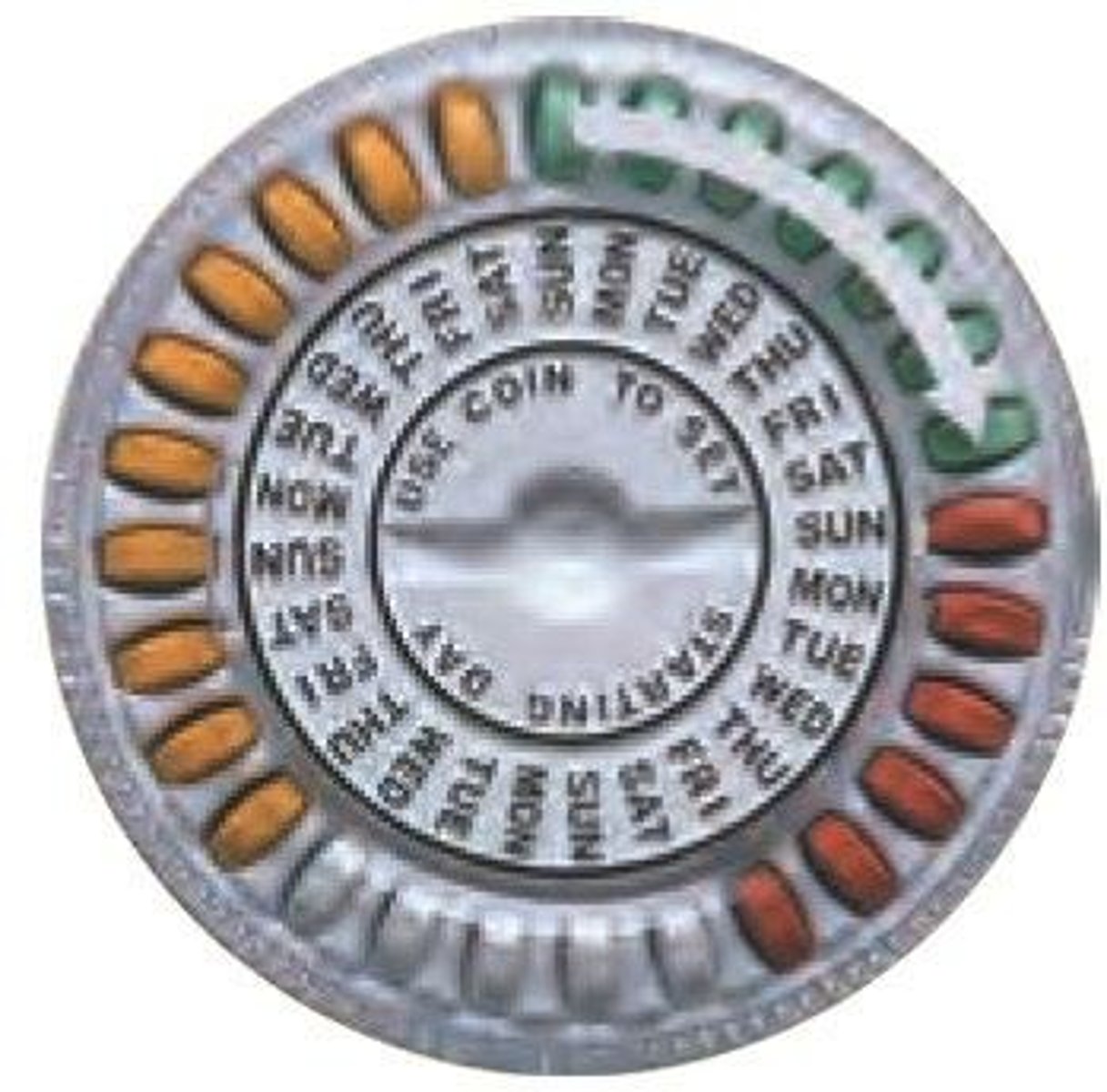
Progesterone-based Birth Control
Thickens cervical mucus to block sperm.
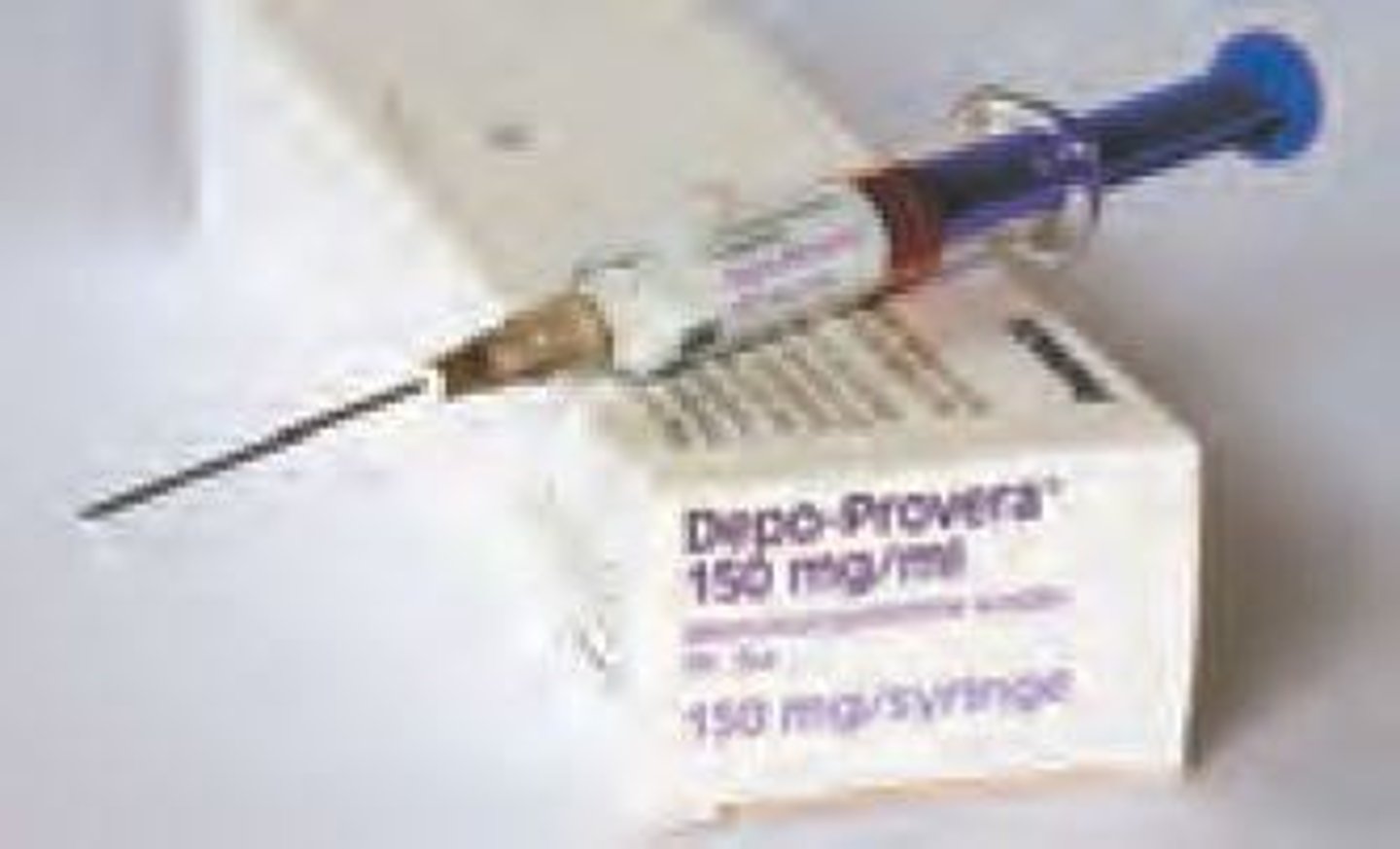
Fertilization Steps
Sperm meets egg, forming a zygote.
Placenta Development
Organ providing nutrients and waste exchange during pregnancy.
Early Development Stages
Rapid cell divisions leading to tissue differentiation.
Pregnancy Hormonal Controls
Hormones regulating pregnancy and birthing processes.
Labor Stages
Phases of childbirth from contractions to delivery.
Health Outcomes of Toxic Stress
Includes obesity, chronic disease, and depression.
Environmental Stressors
Factors affecting health, such as pollution or insecurity.
Gallup Poll 2019
35% of adults reported high stress levels.
APA 2020 Report
67% of adults experienced increased stress from pandemic.
Irregular Menstrual Periods
Menstrual cycles disrupted by physical or emotional stress.
Heavy Menstrual Periods
Periods that are unusually intense or painful.
Missed Menstrual Periods
Absence of menstruation due to stress or other factors.
Substance Abuse
Potential outcome of prolonged toxic stress exposure.
Chronic Disease
Long-term health conditions linked to toxic stress.
Menstrual Cycle
Cyclic changes in ovaries and uterus.
GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone from hypothalamus.
FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone from pituitary gland.
LH
Luteinizing hormone from pituitary gland.
Follicle
Developing egg cell with hormone-secreting cells.
Estrogen
Hormone secreted by ovarian follicles.
Ovulation
Release of an egg from the ovary.
Corpus Luteum
Remains of the ovarian follicle post-ovulation.
Progesterone
Hormone produced by corpus luteum.
Menstruation
Shedding of uterine lining when no fertilization occurs.
CRH
Corticotropin-releasing hormone from hypothalamus.
Cortisol
Key stress response hormone released by adrenal glands.
Negative Feedback
Inhibition of hormone production by high levels.
Hormonal Birth Control
Alters menstrual cycle to prevent pregnancy.
Cervical Mucus
Changes consistency to impede sperm ascent.
LH Surge
Spike in luteinizing hormone triggering ovulation.
Stress Effects
High CRH disrupts menstrual cycle events.
Menstrual Cramps
Pain caused by uterine contractions during menstruation.
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg leading to pregnancy.
Sperm Production
Process regulated by LH in males.
Hormonal Methods
Birth control altering menstrual cycle and ovulation.
Implantation
Attachment of embryo to uterine lining.
STI Protection
External condoms reduce risk of sexually transmitted infections.
Stress
Psychological pressure affecting reproductive choices.
Unintended Pregnancy
Pregnancy occurring without planning or intention.
Low-Income Populations
Groups with limited financial resources impacting access.
Barrier Methods
Prevent sperm and egg contact during intercourse.
External Condoms
Male contraceptive device preventing STIs and pregnancy.

Internal Condoms
Female contraceptive device preventing STIs and pregnancy.

Dental Dams
Barrier for oral sex to prevent STI transmission.
Cervical Caps
Barrier method covering cervix, less effective against STIs.

Vaginal Sponges
Spermicidal sponge blocking sperm entry into uterus.
Diaphragms
Dome-shaped barrier preventing sperm from entering uterus.
Abstinence
Choosing not to engage in sexual activity.
Hormonal Birth Control
Methods using hormones to prevent ovulation.
Combination Birth Control Pill
Contains estrogen and progesterone to prevent ovulation.
Minipill
Progesterone-only pill thickening cervical mucus.
Emergency Birth Control Pill
High hormone dose preventing fertilization or implantation.
Mifepristone
Medication terminating an established pregnancy.
Patch
Hormonal patch delivering estrogen and progesterone.
Vaginal Ring
Inserted ring releasing hormones to prevent ovulation.
Injectables
Progesterone shots every three months to prevent ovulation.
Implantables
Devices secreting hormones to prevent ovulation.

Unintended Pregnancy Rate
Percentage of pregnancies occurring with method use.
STIs
Sexually transmitted infections affecting reproductive health.
Toxic Stress
Chronic stress negatively impacting health and choices.

Unintended Pregnancy Rate
Percentage of pregnancies not planned, varies by method.
Cervical Cap
Prevents sperm-egg contact; 15% unintended pregnancy rate.
Diaphragm
Blocks sperm from egg; 12% unintended pregnancy rate.
Sponge
Spermicide-soaked; 12% (no children) or 24% (with children) unintended pregnancy rate.
Female Condom
Internal condom; 21% unintended pregnancy rate.
Male Condom
External condom; 18% unintended pregnancy rate.
Spermicides
Kills sperm; 28% unintended pregnancy rate.
Fertility Awareness
Abstinence during ovulation; relies on temperature and mucus.

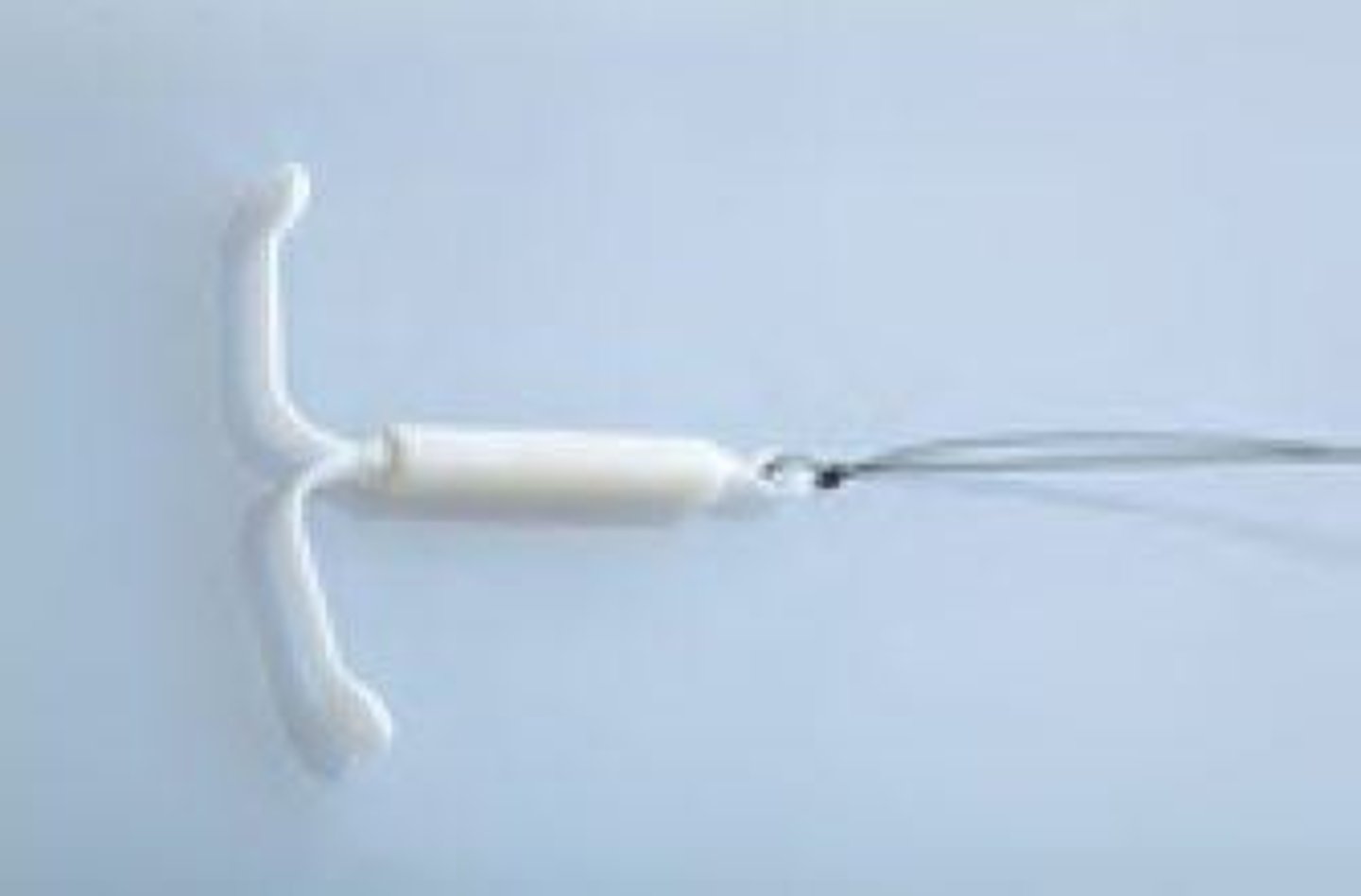
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
Prevents fertilization; 1% unintended pregnancy rate.
Vasectomy
Male sterilization; 0.15% unintended pregnancy rate.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Potential risk from IUD insertion.
Chlamydia
Bacterial STI; causes pelvic pain, treat with antibiotics.
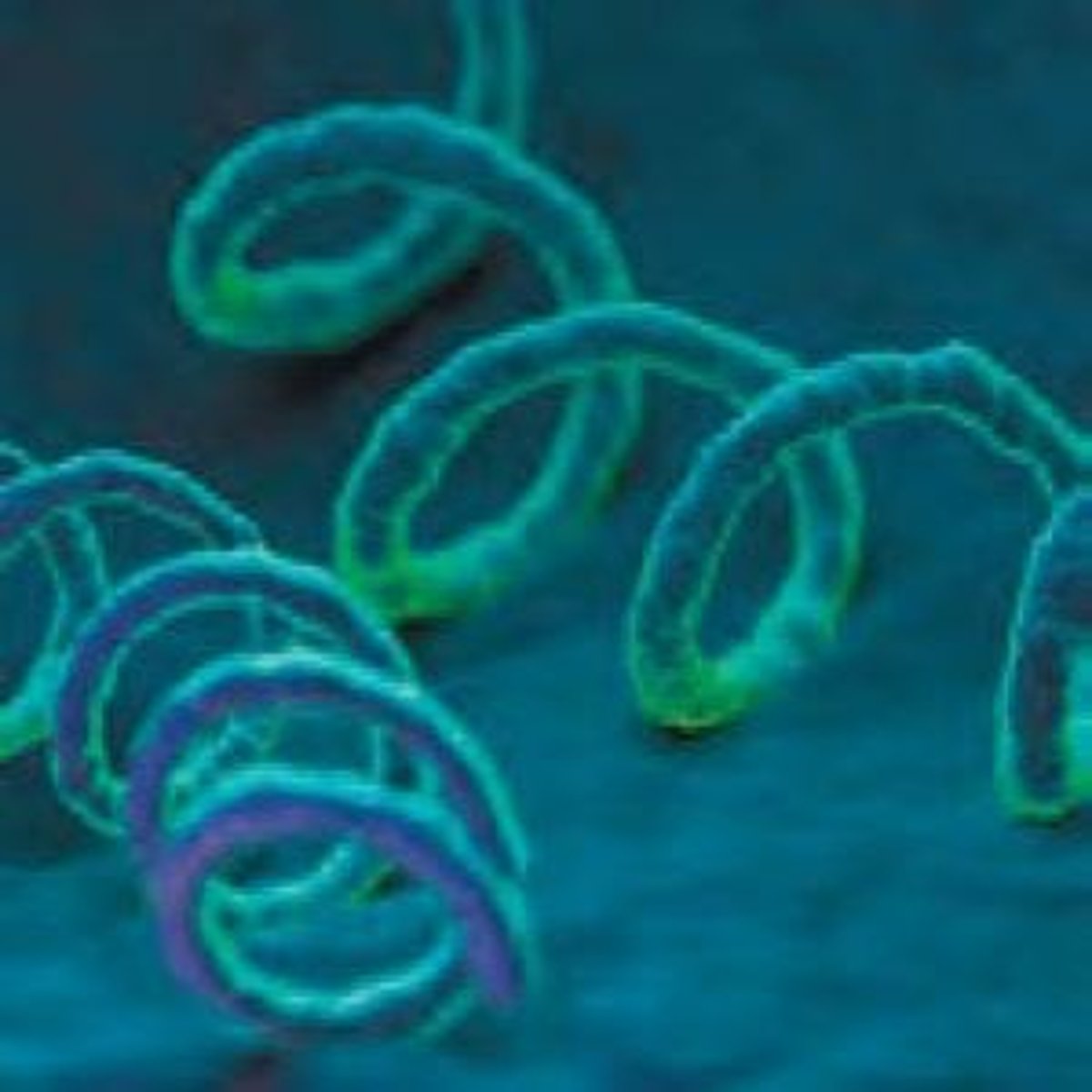
Gonorrhea
Bacterial STI; thick discharge, treat with antibiotics.
STI Prevention
Condom use reduces transmission of STIs.

Spermicide Forms
Available as gels, suppositories, sponges, and films.
Ovulation Charting
Tracks ovulation for fertility awareness method.
Cervical Mucus Monitoring
Observes changes for fertility awareness.
Temperature Increase Post-Ovulation
Indicates ovulation has occurred.
Ectopic Pregnancy
Risk associated with IUD if pregnancy occurs.
Sperm and Egg Contact
Blocked by various barrier methods.
Flexible Ring in Female Condom
Holds condom against cervix for effectiveness.
Unintended Pregnancy Rate of IUD
1% per year, effective long-term birth control.
Premature Birth
Birth occurring before 37 weeks of gestation.
Low Birth Weight
Infants weighing less than 5.5 pounds at birth.
Treponema pallidum
Bacteria causing syphilis, treatable with antibiotics.
Chancres
Infectious sores associated with syphilis.
Neurological Problems
Severe complications from untreated syphilis.
HIV
Virus causing AIDS, no cure available.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Virus that weakens the immune system.
Condom Use
Reduces transmission of sexually transmitted infections.
Genital Warts
Growths caused by human papillomavirus (HPV).