Bio - EOYT.
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Mitosis
A form of cell division resulting in two daughter cells from a mother cell - identical
Chromosomes
Condensed forms of DNA located in the nucleus of a cell
Chromatid
One half of a chromosome
Centromere
The region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids are joined and where spindle fibers attach during cell division.
spindle
cell pole
equator
Come from centrioles (used to separate chromatids)
opposite sides of a cell
the mid plain of a cell
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosome pairs, one from each parent, that are similar in shape, size, and genetic content.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse gametes, crucial for sexual reproduction. - except for 3 polar bodies in oogenesis
Diploid vs haploid
double vs half (full chromosome set vs half set)
Cell cycle - interphase
G1 phase - initial growth phase + copying of organelles
S phase - DNA duplication phase - centrosomes duplicated
G2 phase - further growth
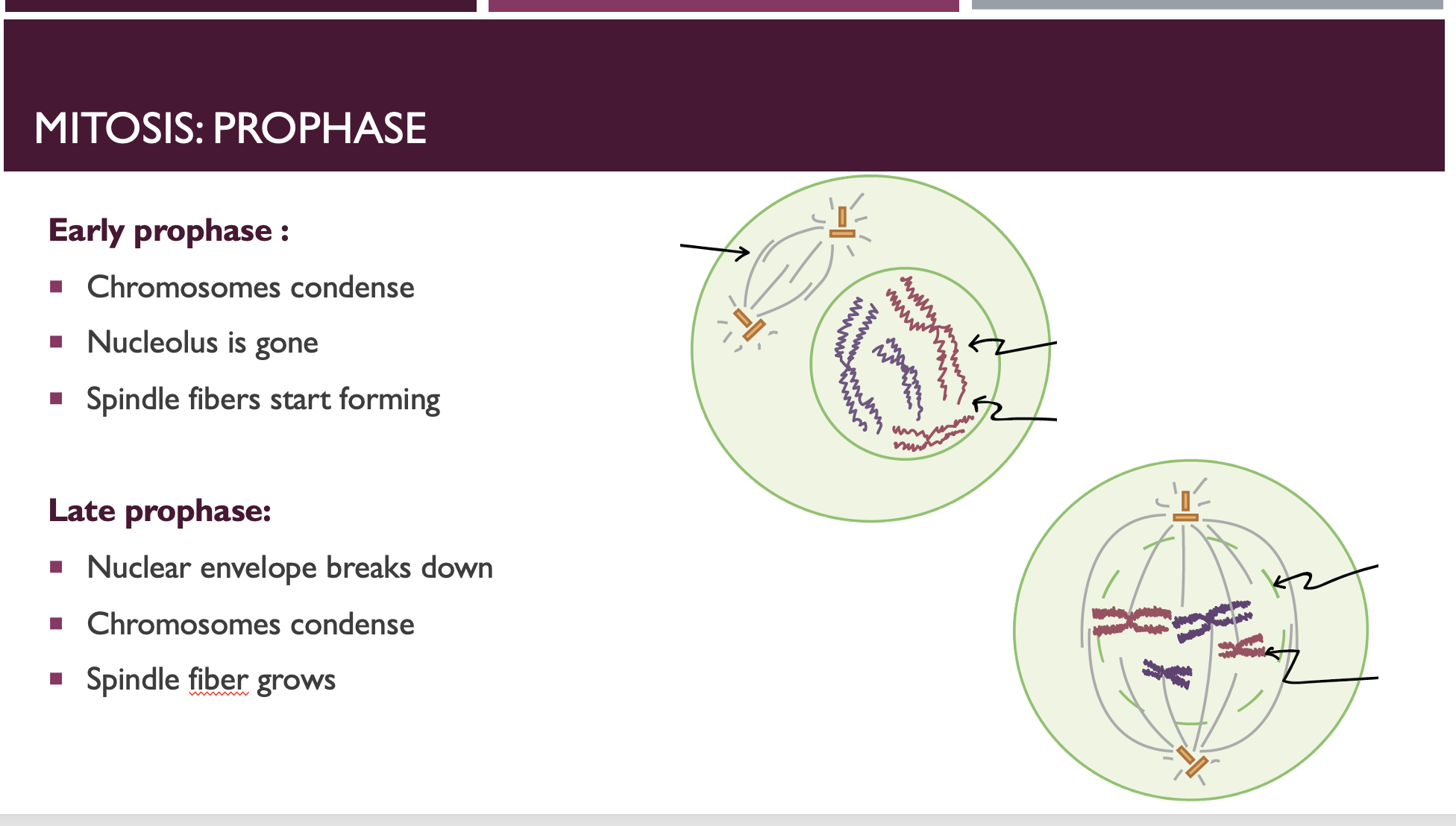
Prophase - mitosis
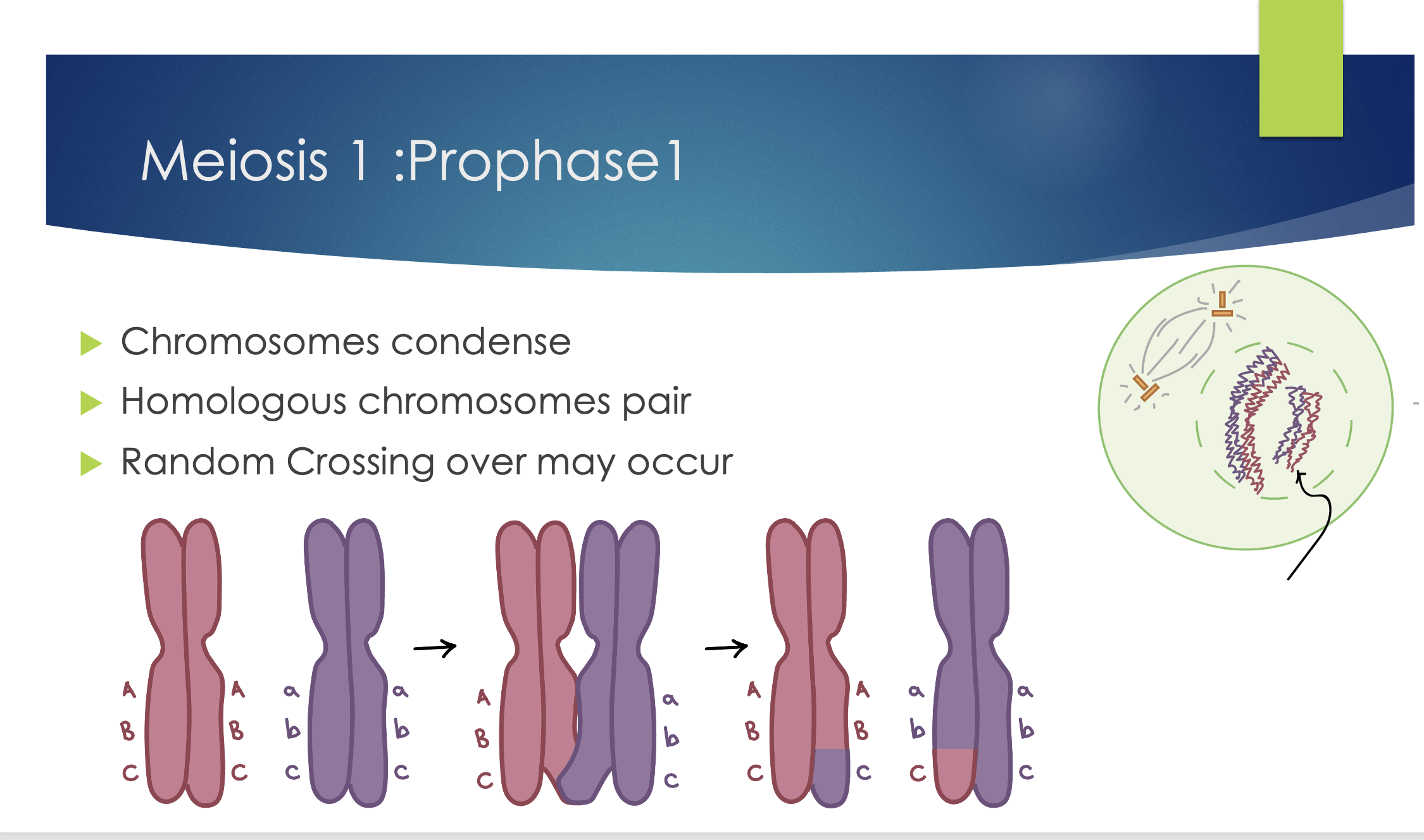
Prophase - meiosis
Metaphase
chromosomes align at the equator (homologous if meiosis)
Anaphase
Chromosomes or chromatids pulled apart by spindle fibers from centrioles (in the centrosomes)
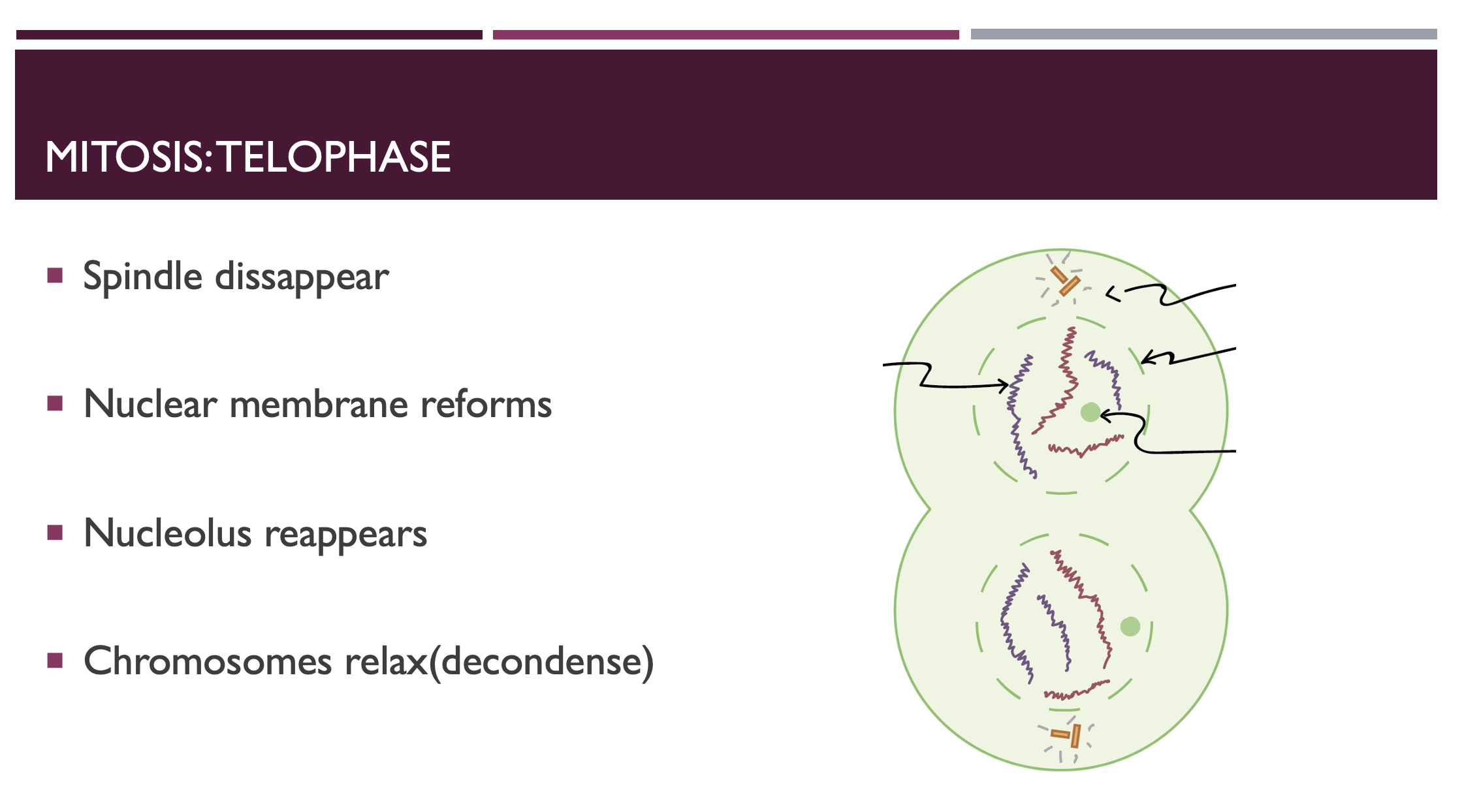
Telophase
Variation
Crossing over
Random arrangement
Random assortment
Non-disjunction/other mutations
Fertilization
Gene
Small segment of DNA that codes for a specific trait
Alleles
Alternate forms of one trait (brown hair and ginger hair)
Homozygous
Two of the same characteristics
Heterozygous
Two different alleles for one trait
Genotype
The gene composition of an individual
Phenotype
Physically visible characteristics of a certain genotype
Law of segregation
When gametes form, alleles are separated so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene
Law of independent assortment
The segregation of alleles for one gene occurs independently to that of any other gene
Law of dominance
Recessive alleles will be masked by dominant alleles
Autosomal traits
Traits that are located on any chromosome except for the sex chromosomes
Both parents affected, child unaffected
Dominant trait, heterozygous parents
All affected individuals…
..must have an affected parent - dominant trait
Both parents are unaffected, then children also unaffected
Parents would be homozygous recessive and trait dominant
If both parents are unaffected and child is affected..
Trait must be recessive (parents are heterozygous carriers)
If both parents show trait, child must too
Homozygous recessive for trait
Co-dominance
Both genotypes are dominant and are equally represented in the phenotype
Incomplete dominance
Both genes mix together to create a new and unique phenotype
Sex-linked traits
Sex linkage refers to when a gene controlling a characteristic is located on a sex chromosome (X or Y)
Rule 1:
Only females can be carriers (a heterozygote for a recessive disease condition), males cannot be heterozygous carriers (they have only 1 X-chromosome)
Rule 2:
Males will always inherit an X-linked trait from their mother (they inherit a Y chromosome from their father)
Rule 3:
Females cannot inherit an X-linked recessive condition from an unaffected father (must receive his dominant allele)
so he is unaffected and therefore doesn’t have the recessive gene, so daughter wouldn’t inherit it from him but perhaps would from mother
Unlinked genes
Gene loci on different chromosomes and are independent of one another
Di-hybrid cross
Determines the genotypic and phenotypic rations of two unlinked traits (so hair colour and eye colour)
Discontinuous variation
Organism either has it or not
Qualitative
Only determined by genes
eg. blood type or sex
Continuous variation
determined by genes and environmental influence
every organism shows gene but to different extent
several genes acting together
quantitative
use di-hybrid cross to express
Causes of mutation
Mistake in copying DNA
DNA damage
eg. radiation, chemicals, etc.
Adaption
An organism that is well –suited to make the most out of the limited resources within its environment is said to show adaptation
Process of evolution
Over production/genetic variation
Struggle for existence/environmental pressure
Variation/adaption
Natural selection/survival of the fittest
speciation
Evidence of evolution
analysis of fossils - compare to existing creatures and create family tree
bio-geographical location - continental drift
comparative anatomy - homologous(same structure different function) + analogous (different structure, same function)
DNA (mitochondrial) - passed down from mother and can analyse tree line