Lecture 19.2
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What chemical keeps lipids soluble during digestion?
Bile
Lipoprotein
a protein contains a core is of neutral lipids including TAGS and cholesterol esters
surrounding the core is a layer of phospholipids in which varying proportion of proteins and cholesterol are embedded
Lipids in diet are transported by
chylomicrons (digestion)
Fatty acids from storage in adipose tissue are transported by
serum albumin (mobilization)
TAGs synthesized in the liver are transported by
VLDLs (synthesis)
LDL
transport of endogenous lipids (cholesterol) to tissues (receptor mediated)
HDL
transport of lipids and cholesterol from cells in the vasculature to liver
VLDLs and LDL are
atherogenic ( beginning of atherosclerosis)
HDL
anti-atherogenic (good cholesterol)
Acetyl CoA can be converted to
fatty acids
amino acids
ketone bodies
TAG storage is regulated by
Insulin and Glucagon
high levels of insulin stimulate TAG synthesis
Storage (synthesis) of TAGS
Step 1: glycolysis produces DHAP then Glycerol-3-Phosphate
Step 2: Transfer FA from CoA to G-3-P (occurs in adipocytes)
DHAP
one point where lipid metabolism and carbohydrate metabolism are linked
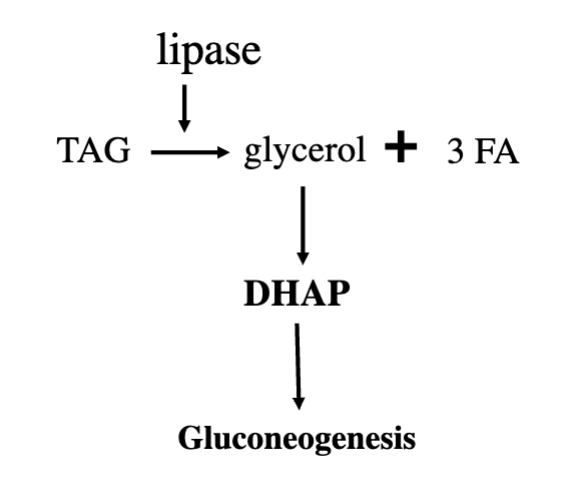
Mobilization (hydrolysis) of TAGs
low insulin levels and high glucagon levels stimulate triacylglycerol lipase in adipocytes.
Fates of Fatty Acids in the Cell
Activation of FA by the addition of CoA: Energy cost = 2ATPs
Binds to carnitine for transport5 into mitochondria matrix via a pore formed by large enzyme complex.
Oxidation of FA with even number of carbons to acetyl (beta-oxidation of Fatty Acids)
Fatty Acid Spiral
Introduction of a double bond
H20 is added to the double bond producing an alcohol
The alcohol is oxidized to a ketone
A c-c bond is broken
Beta-oxidation of fatty acids is a _____ pathway
spiral
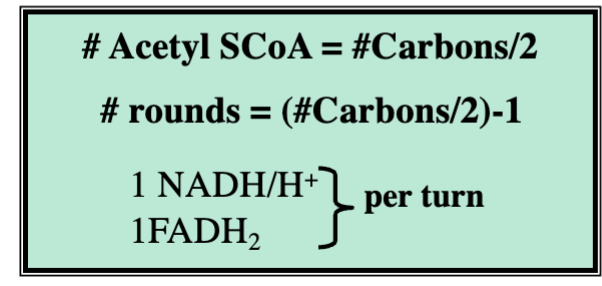
Energy from Fatty from Fatty Acid Oxidation
Step 1: activate the FA and trap it in the cell by adding CoA - 2ATP
Step 2: the activated FA will go through FA spiral
Step 3: acetyl CoAs enter the TCA cycle
Step 4: reduced coenzymes enter the ETC
Fatty Acid Oxidation
occurs in the mitochondria
enzymes different from synthesis
intermediates carried by coenzyme A
coenzymes FAD, NAD+
carbon atoms removed two at a time
Fatty Acid Synthesis
occurs in cytosol
enzymes different from oxidation
intermediates carried by acyl carrier protein
coenzyme": NADPH
carbon atoms added two at a time
Ketone bodies
compounds produced in the liver that can be used as fuel in muscle and brain tissue (3-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, acetone)
Ketogenesis
the synthesis of ketone bodied from acetyl-SCoA
3 ketones produced
Ketoacidosis
results from increased concentration of ketone bodies i the blood
blood pH drops
labored breathing
increased urination
dehydration
depression
coma death