Muscles and Tendons of the Distal Limb
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the general features of muscles found in the antebrachium?
• Affect joints of carpus and digits
• Originate epicondyles of humerus
• Muscle belly located in antebrachium
• Tendons of insertion - are distal to carpus
Describe the following features of the extensor carpi radialis muscle:
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
Useful landmark
• Extensor carpi radialis muscle
O = lateral epicondyle of humerus
I = Metacarpal bones
• Location:
Cranial aspect of antebrachium
• Function:
Crosses dorsal aspect carpus
Carpal EXTENSOR
• Nerve supply
Radial nerve
Oblique muscle
Crosses at level of carpus
Useful landmark
Describe the following features of the common digital extensor muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
Common digital extensor muscle
• O = lateral epicondyle of humerus
• I = all digits
distal phalanx - extensor process
• Location:
• Cranio-lateral aspect of antebrachium
• Function:
Crosses dorsal aspect carpus
Carpal EXTENSOR
Crosses dorsal aspect metacarpo-phalangeal joints & interphalangeal joints
Digital EXTENSOR
• Nerve Supply:
Radial nerve
How does the branching of the common digital extensor muscle differ between species?
Dogs
4 branches (+1 to the dew claw if present)’
Horse
1 branch, attaches dorsal aspect of phalanges and protected by joint capsules'
Receives branches of the suspensory ligament
Describe the following features of the extensor carpi ulnaris / ulnaris lateralis muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
extensor carpi ulnaris / ulnaris lateralis muscle
• O = lateral epicondyle of humerus
• I = Metacarpal bone + ACB
• Location:
Lateral aspect of antebrachium
• Function:
Crosses lateral aspect carpus
Carpal EXTENSOR & FLEXOR
Depends on position of limb
• Nerve supply:
Radial nerve
Describe the following features of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
O = medial epicondyle
O = Olecranon process of ulna
I = ACB
• Location:
Caudal aspect of antebrachium
• Function:
Crosses caudal aspect carpus
Carpal FLEXOR
• Nerve supply
Median & Ulnar nerves
Describe the following features of the superficial digital flexor muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
superficial digital flexor muscle
• O = medial epicondyle
• I = all digits (middle phalanx)
• Location:
Caudal aspect of limb
• Function:
Crosses palmar aspect carpus
Carpal FLEXOR
Crosses palmar aspect of Metacarpo-phalangeal joints & Proximal interphalangeal joints
Digital FLEXOR
• Nerve Supply:
Median & Ulnar nerves
Describe species differences in the branching of the superficial digital flexor muscle.
• Dog:
4 branches (+1 to dew claw)
• Horse:
1 branch
Receives Accessory Check ligament (ACL) from radius
Proximal to carpus
Limits length of tendon / protects muscle belly from over-stretching
• Both:
Splits to allow passage of DDFT -
Inserts middle phalanx
Describe the following features of the deep digital flexor muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
deep digital flexor muscle
• O = medial epicondyle
• O=radius & ulna
• I = all digits(palmar process distal phalanx)
• Location:
Caudal aspect of limb
• Function:
Crosses palmar aspect carpus
Carpal FLEXOR
Crosses palmar aspect Metacarpo-phalangeal joints & both interphalangeal joints
Digital FLEXOR
• Nerve Supply:
Median & Ulnar nerves
Describe species differences in the branching of the deep digital flexor muscle.
• Dog
• 4 branches (+ 1 to dew claw) *
• Horse:
• 1 branch
Receives Accessory check ligament
Extension of carpal joint capsule
Distal to carpus
Limits length of tendon / protect muscle belly
• Both:
Pass through split in SDFT to insert
Insert distal phalanx
Horse - runs over distal sesamoid
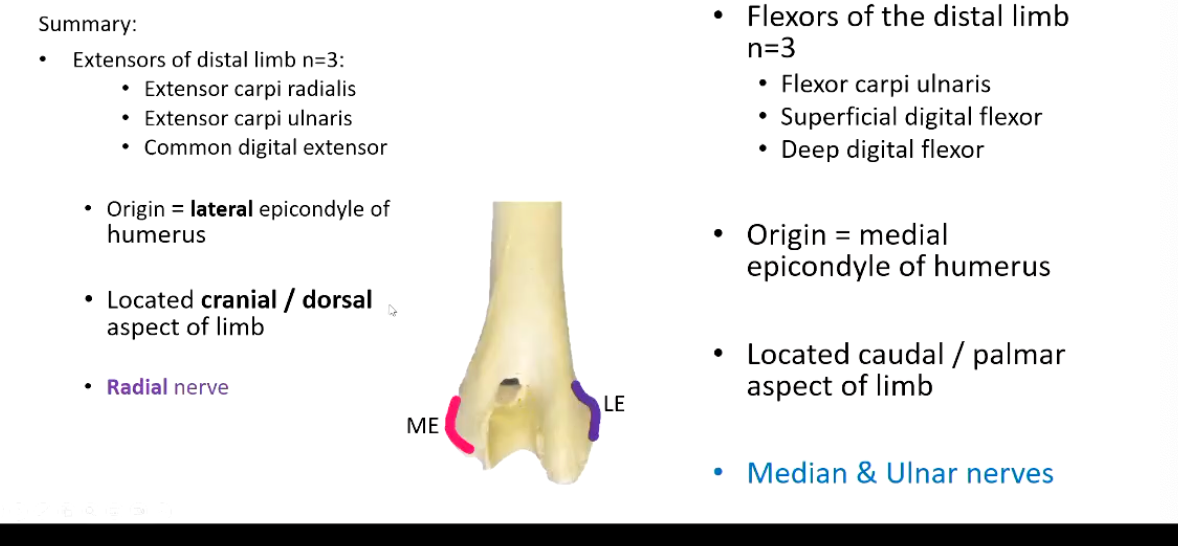
Summarize the muscles of the distal forelimb, dividing them into the:
Extensors
Origin
Location
Nerve Supply
Flexors
Origin
Location
Nerve Supply
What regions of the equine distal limb are the extensor and flexor tendons found?
Where do they run?
• Carpus:
Extensor tendons - dorsal aspect
Flexor tendons - palmar aspect
Run through carpal canal
What are the boundaries of the carpal canal?
• Boundaries of carpal canal:
Dorsal - Palmar aspect of carpal joint capsule
Lateral - ACB
Palmar - palmar / flexor retinaculum (Compression band or sleeve of fibrous tissue encasing)
What are the contents of the equine carpal canal?
How about the carnivore carpal canal?
• Contents of carpal canal in equines:
• Deep digital flexor tendon (DDFT)
• Superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT)
Blood vessels & nerves
In Carnivores:
SDFT runs OUTSIDE the carpal canal
DDFT inside
What are the purpose of tendon sheaths in the equine distal limb.
What effect can inflammation have in this location?
• Tendon Sheath:
• Fluid filled
• Protect tendons where pass through confined spaces
• Inflammation:
increased fluid volume / pressure
bulges proximally & distally
What other supportive structures are found in the distal equine limb?
Consider dorsal aspect
And palmar aspect
• Dorsal aspect limb:
• CDE held in place by retinaculum-
• Palmar aspect limb:
SDFT & DDFT held in place by
Carpal canal
• Annular ligaments
Fetlock & pastern regions
• Length limited by check ligaments
Accessory Check Ligaments
• Provide palmar support for carpus & all distal limb joints
• Protected by tendon sheaths
Summarize the type of tendons on the:
Dorsal Aspect
Palmar Aspect
• Dorsal aspect = extensor tendons
• Palmar aspect =
• Skin
a. SDFT
b. DDFT
c. Check ligament (Fuses with DDFT)
d. Suspensory ligament (Splits into 2 branches)
What are “chestnuts” on the equine limb?
Chestnuts are vestigial structure found on the medial aspect of the antebrachium, thought to be remnant of 1st metacarpal bone
Vestigial horn pad
What are “ergots” on the equine limb?
Lump in skin found on palmar aspect of MCP joint hidden by feathers
Thought to be remnant of metacarpal pad
What is the purpose of the equine stay apparatus?
A mechanism for passive weight bearing, allowing horses to sleep while standing, stand without effort.
Most of weight is borne on the forelimb, hindlimb is more fore propulsion
HOW does the stay apparatus work?
• Requirements:
• Maintenance of all joints in weight- bearing extension
• Proximal limb joints:
Prevention of flexion in shoulder and elbow
• Carpus:
Prevention of flexion
Prevention of hyperextension
• Distal limbs joints:
Prevention of hyperextension
What key muscles are important parts of the equine stay apparatus and what actions or purpose does each have?
Thoracic (Forelimb) Stay Apparatus
Purpose: prevents shoulder/elbow/fetlock collapse
Serratus ventralis (supports trunk between forelimbs - acting like a sling)
Biceps brachii + lacertus fibrosus (locks shoulder, preventing flexion, and carpus in extension)
Collateral Ligaments maintain alignment in the elbow
Suspensory apparatus of the fetlock: → Prevent fetlock overextension (dropping too low)
Suspensory ligament
Proximal sesamoid bones
Inter, Collateral & Distal sesamoidean ligaments
Check ligaments (accessory ligaments of DDFT & SDFT)
→ prevent excessive stretching of the flexor tendons
Flexor tendons (SDFT, DDFT)
SDFT- acts as a major support against fetlock overextension.
DDFT - Adds additional support to the distal limb and helps resist flexion/buckling of the coffin joint.
Annular ligaments
Hold the flexor tendons close to the bones, preventing them from bowstringing.
This stabilizes the tendons so they can efficiently counteract the forces that would otherwise hyperextend the fetlock.
How do the carpus and distal limb joints prevent hyperextension in the equine stay apparatus?
• Carpus:
Palmar fibrocartilage joint reinforcement at level of the carpus
SDFT and check ligament
Retinaculum
MCP, PIP & DIP joints:
DDFT & SDFT
Check ligaments
Annular ligaments
• MCP / Fetlock joint :
Suspensory ligament
Common digital extensor
Proximal sesamoids
Distal sesamoidean ligaments
(short, cruciate, oblique & straight)