Life science - All units flash cards
1/197
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all teach quizlets combined as one
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
strand of DNA
two DNA polymers twisted around each other in a double helix shape, with each polymer made of four types of nucleotide monomers.
replication
process occurring before cell division in which DNA is copied
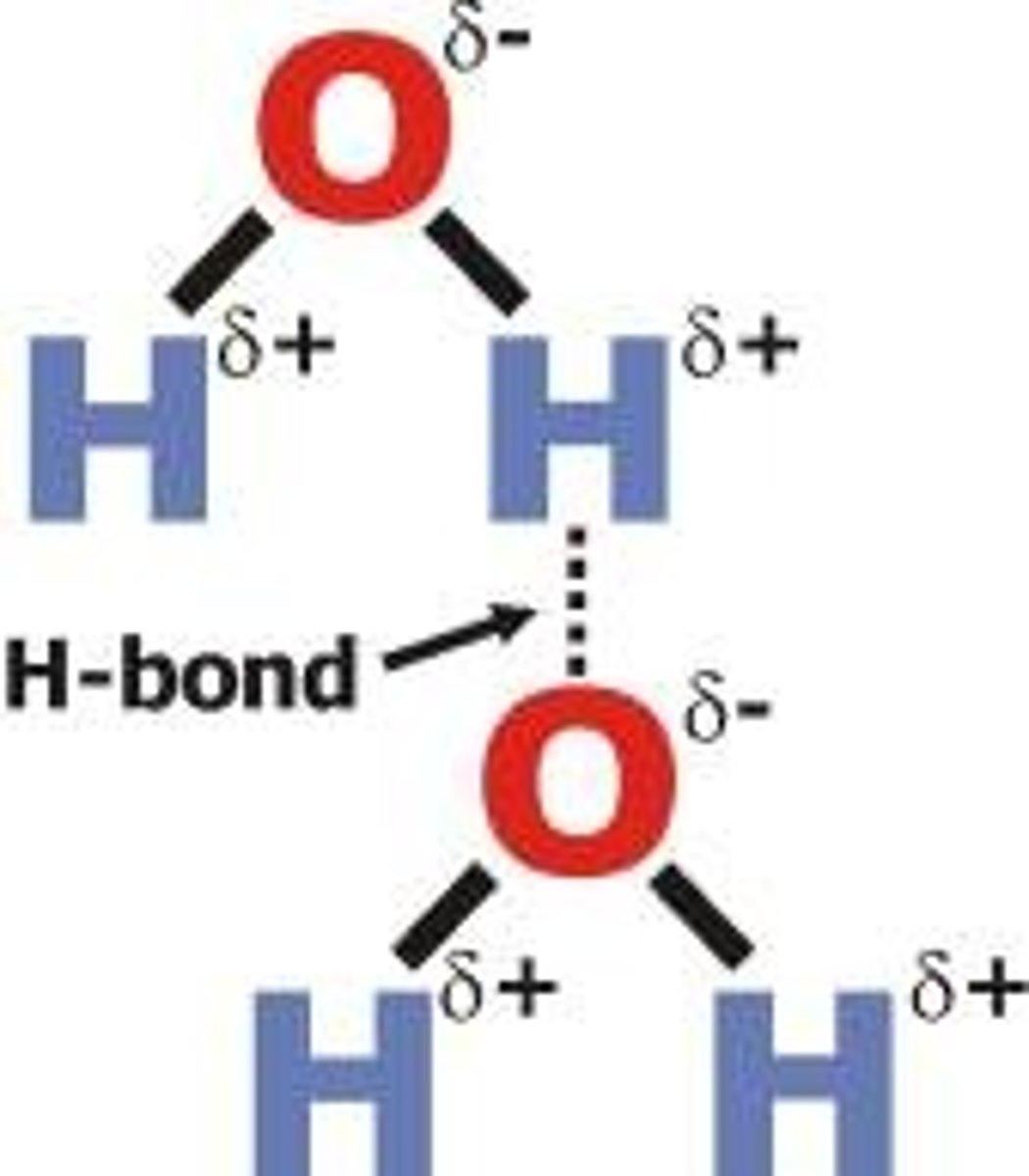
complimentary base pairs
pair of nucleotide bases that are attracted to each other by hydrogen bond forces—either adenine (A) and thymine (T) (or uracil, U) or cytosine (C) and guanine (G).
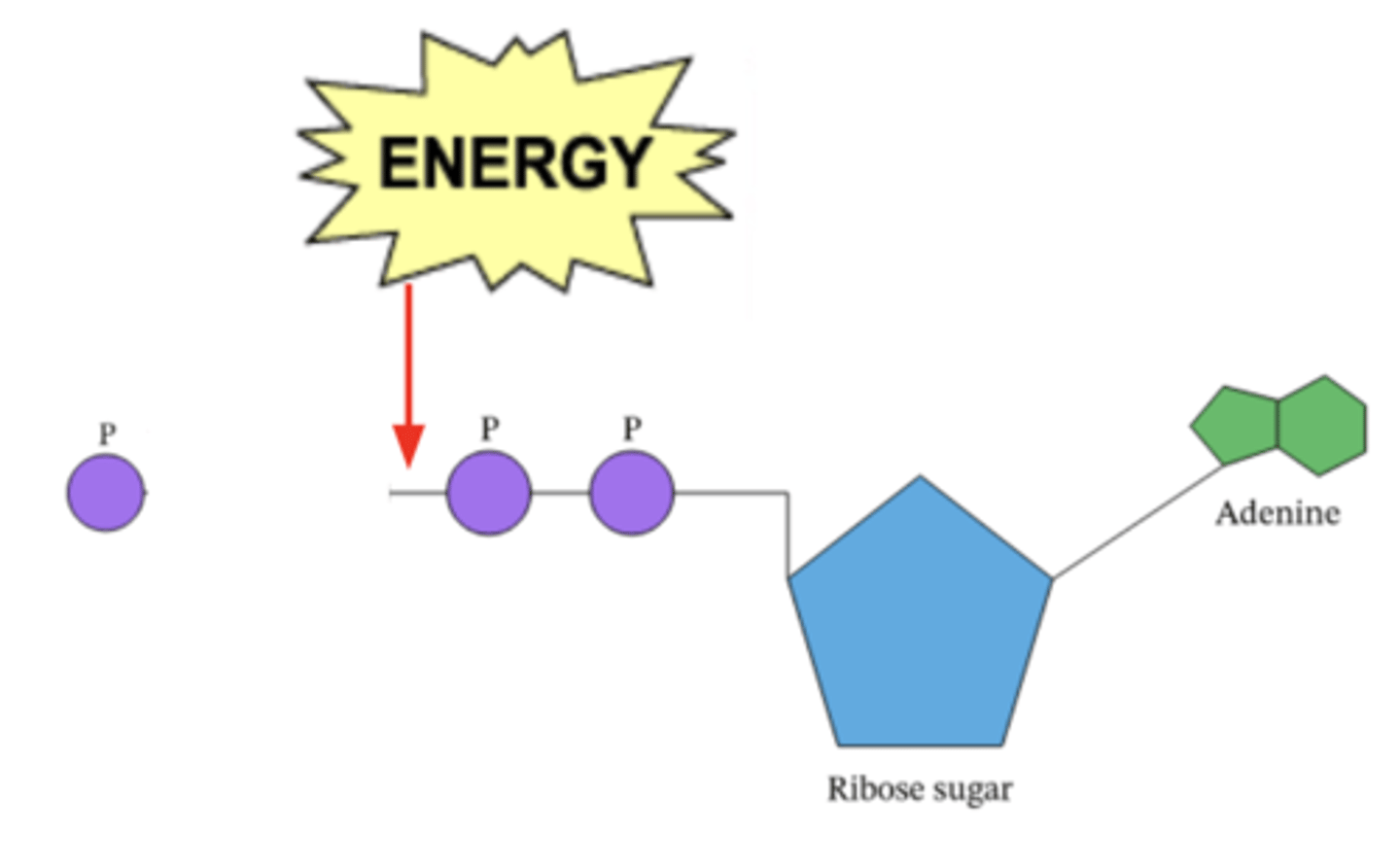
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate - an immediately available source of energy cells use to do work
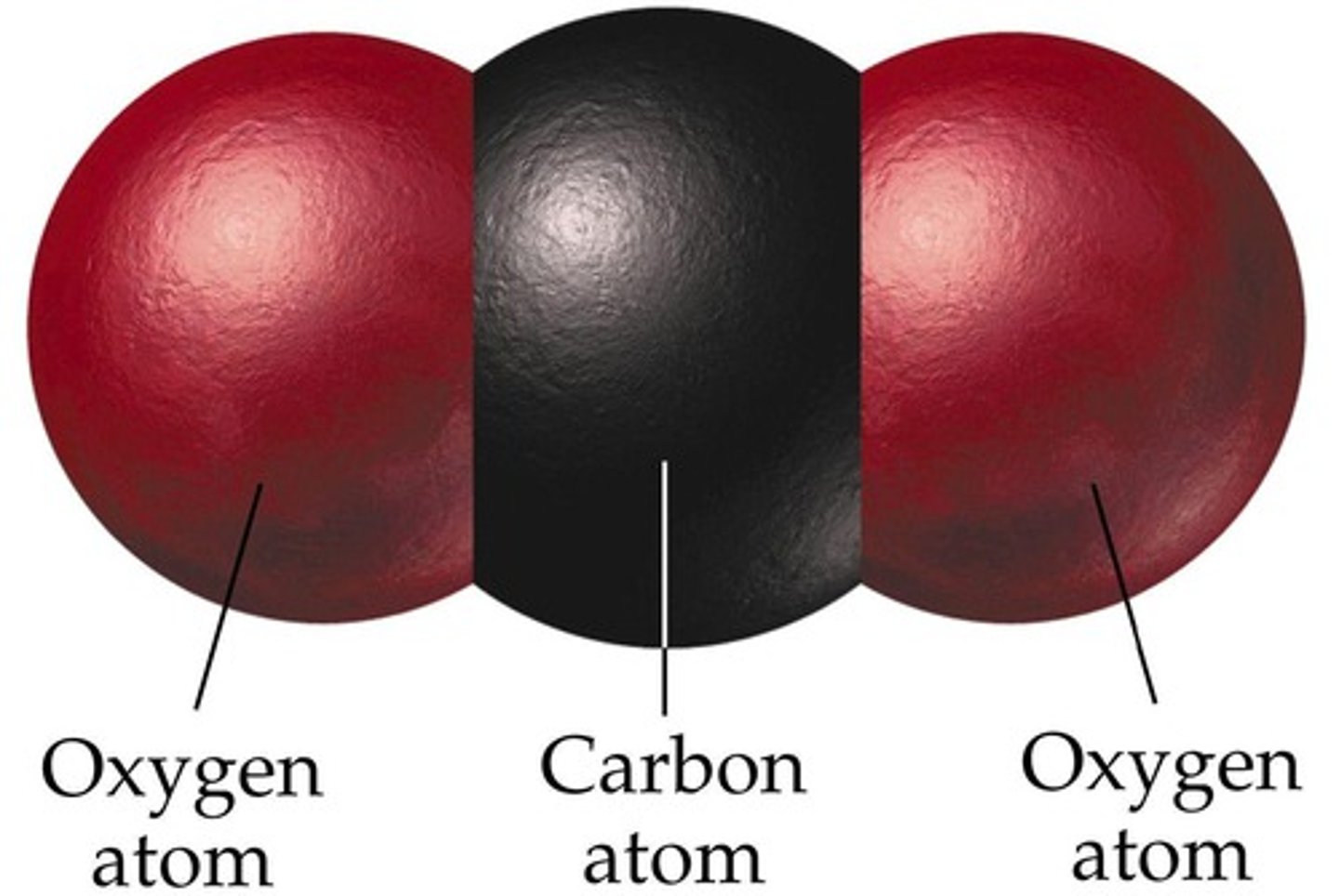
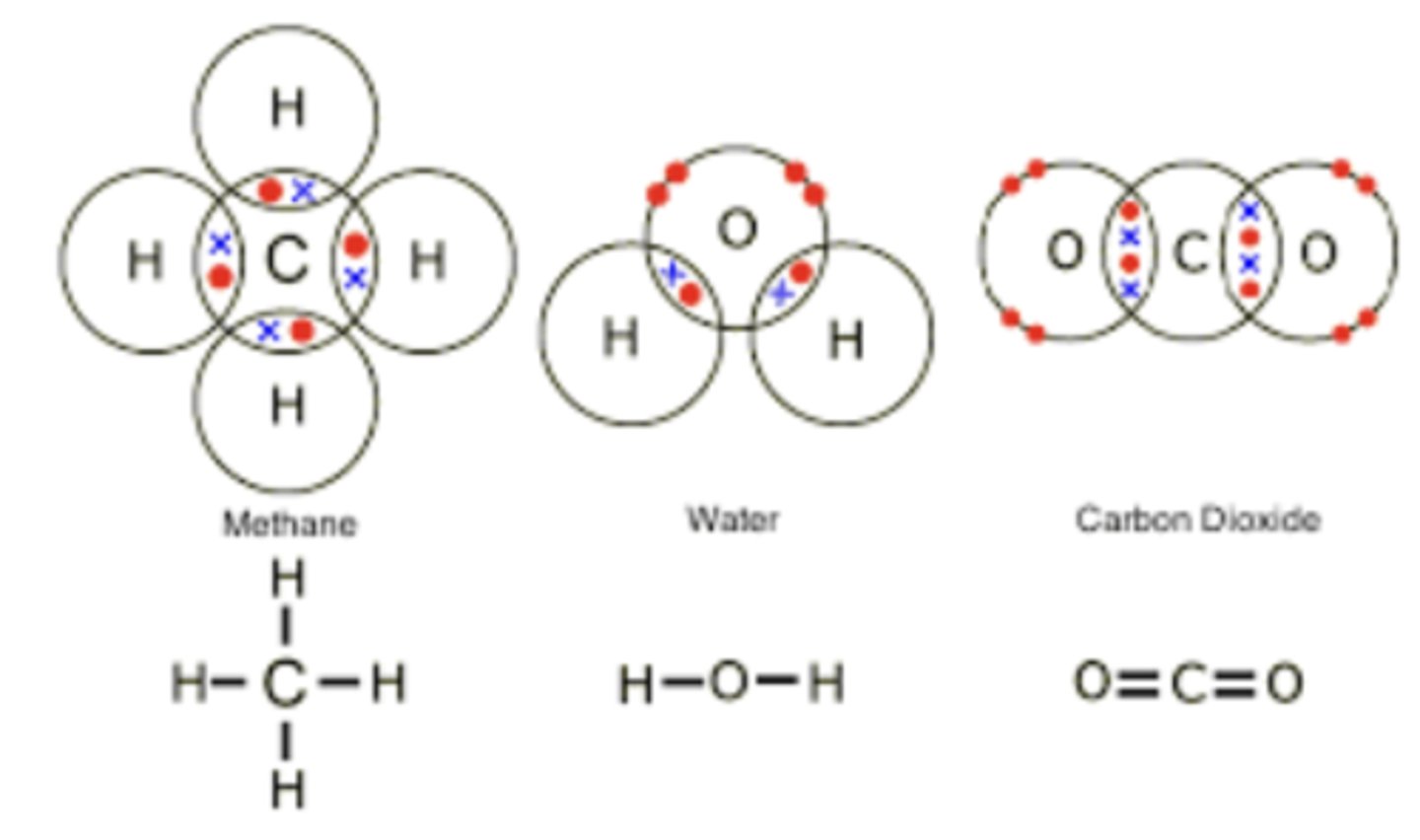
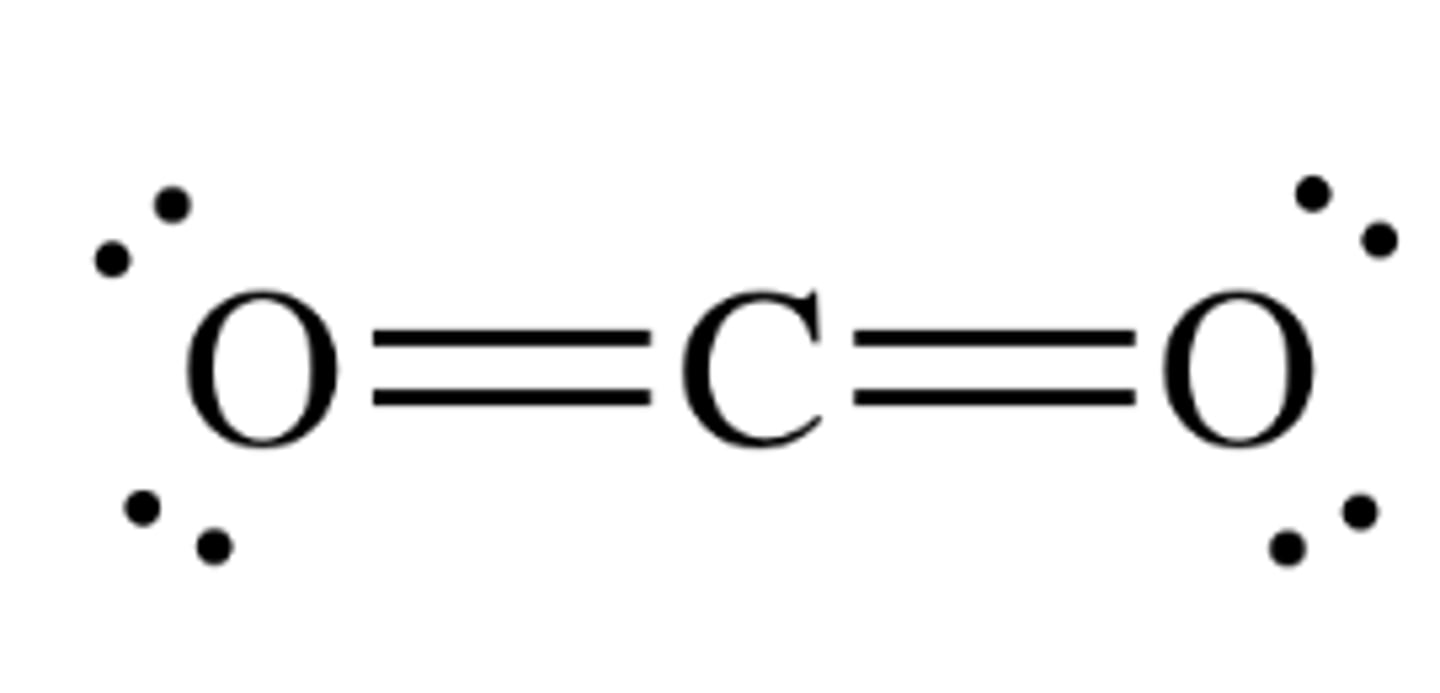
Carbon dioxide
CO2 - Plants use carbon dioxide to make glucose during photosynthesis.
cellular respiration
the process of breaking glucose to create ATP
Chemical energy
energy stored in chemical bonds
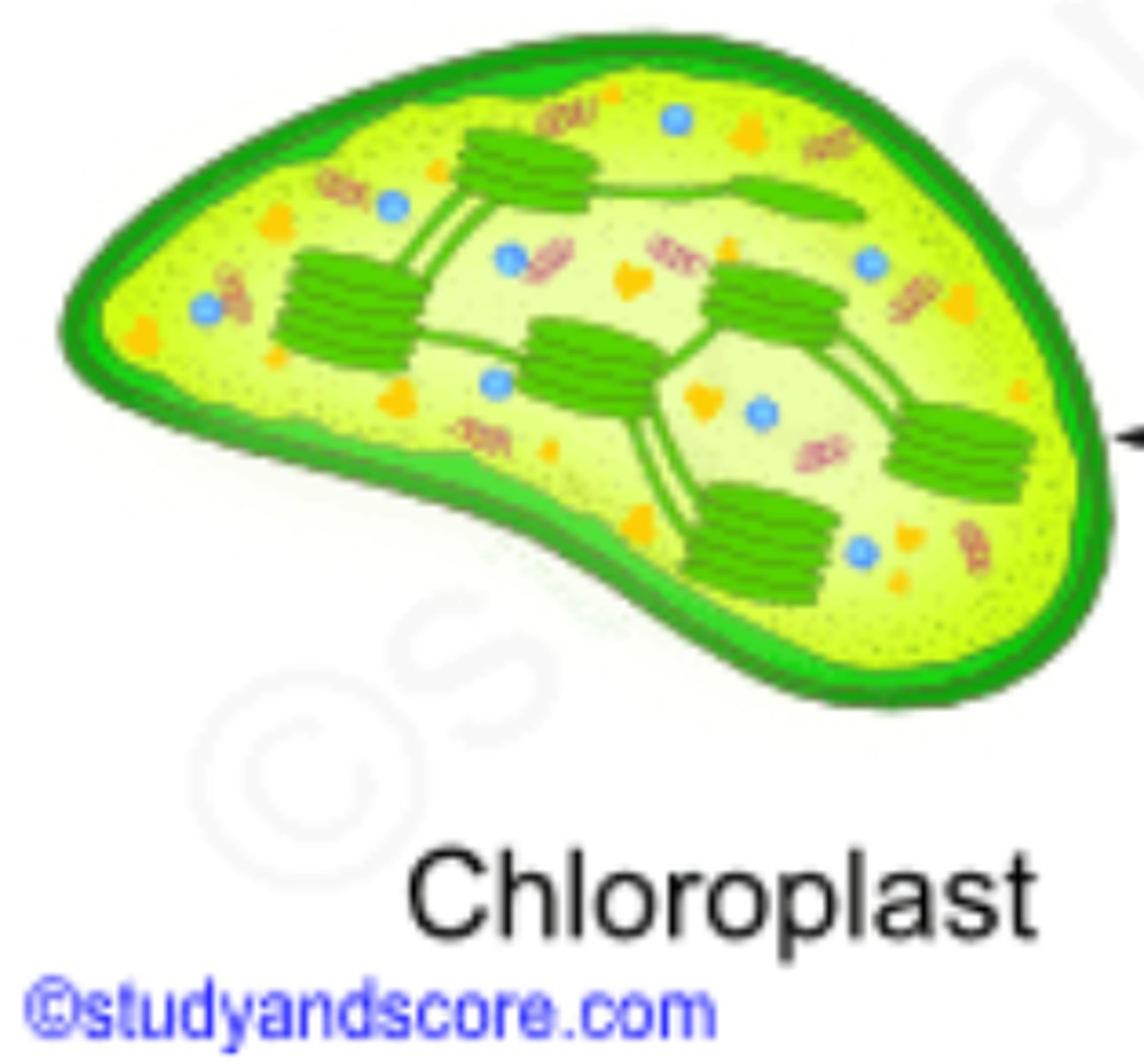
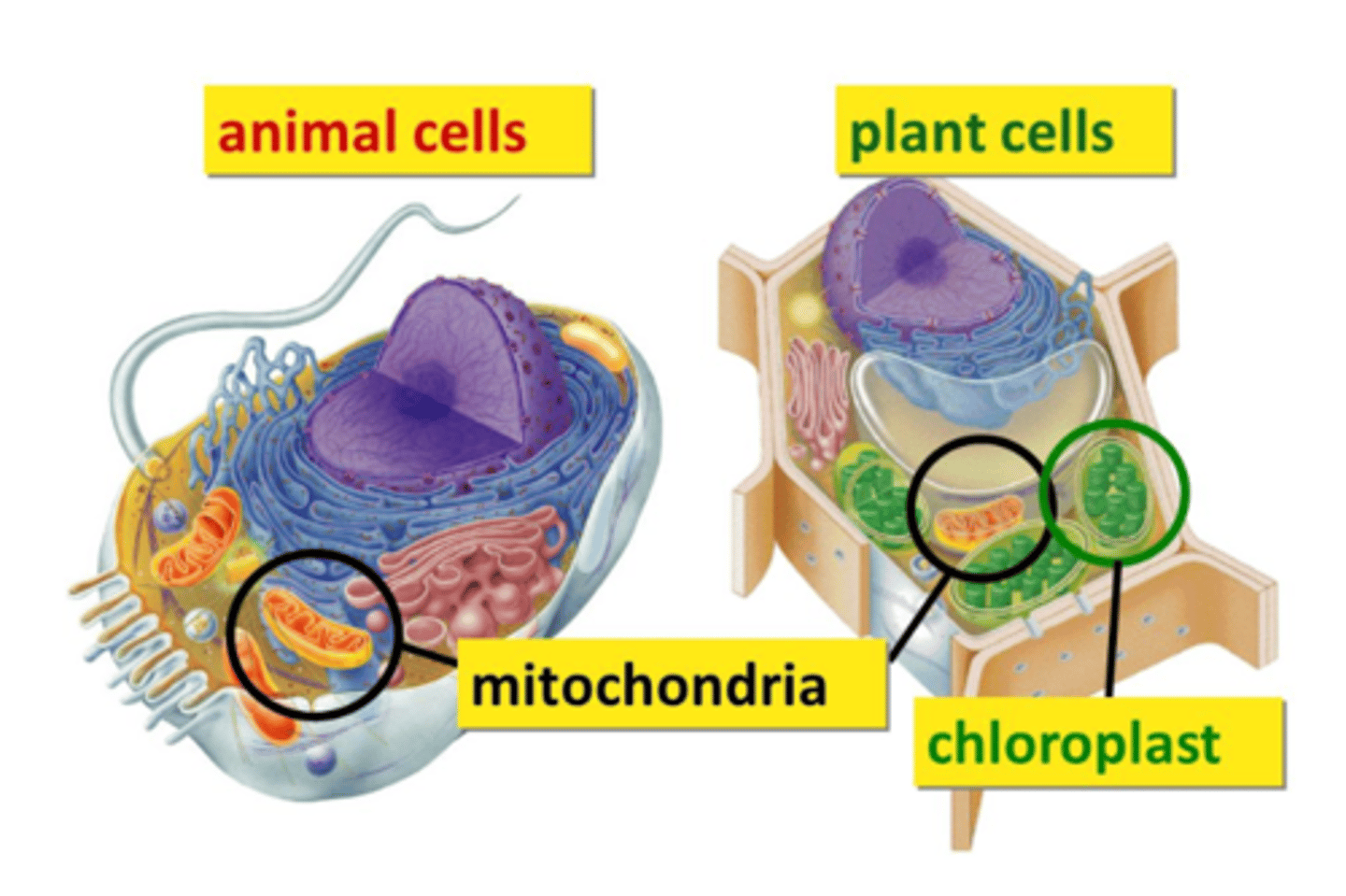
Chloroplast
an organelle in the plant cell that converts light energy into chemical energy via the photosynthetic process.
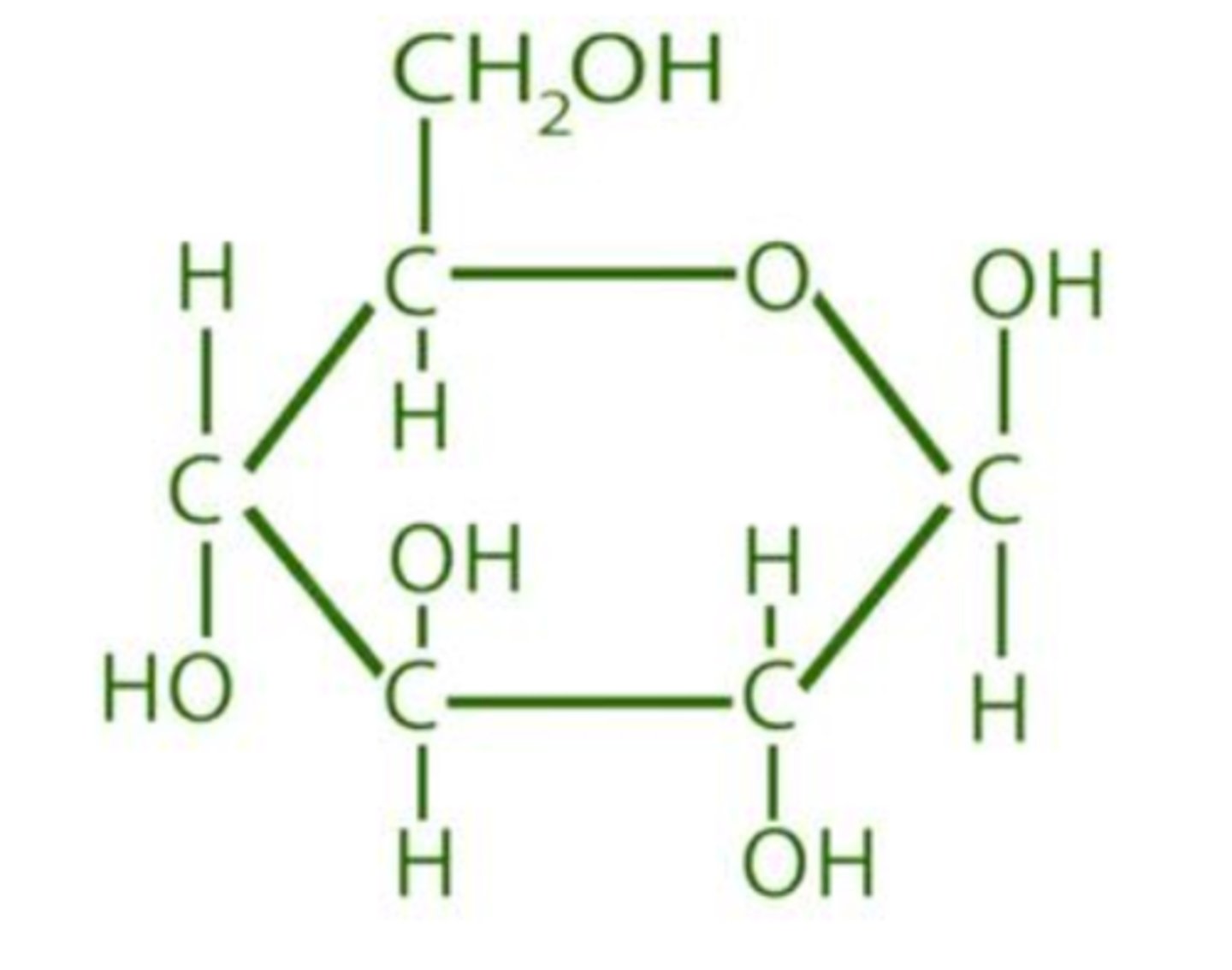
glucose
sugar molecule made of: 6 Carbons, 12 Hydrogens, and 6 Oxygens
Glucose = stored chemical energy
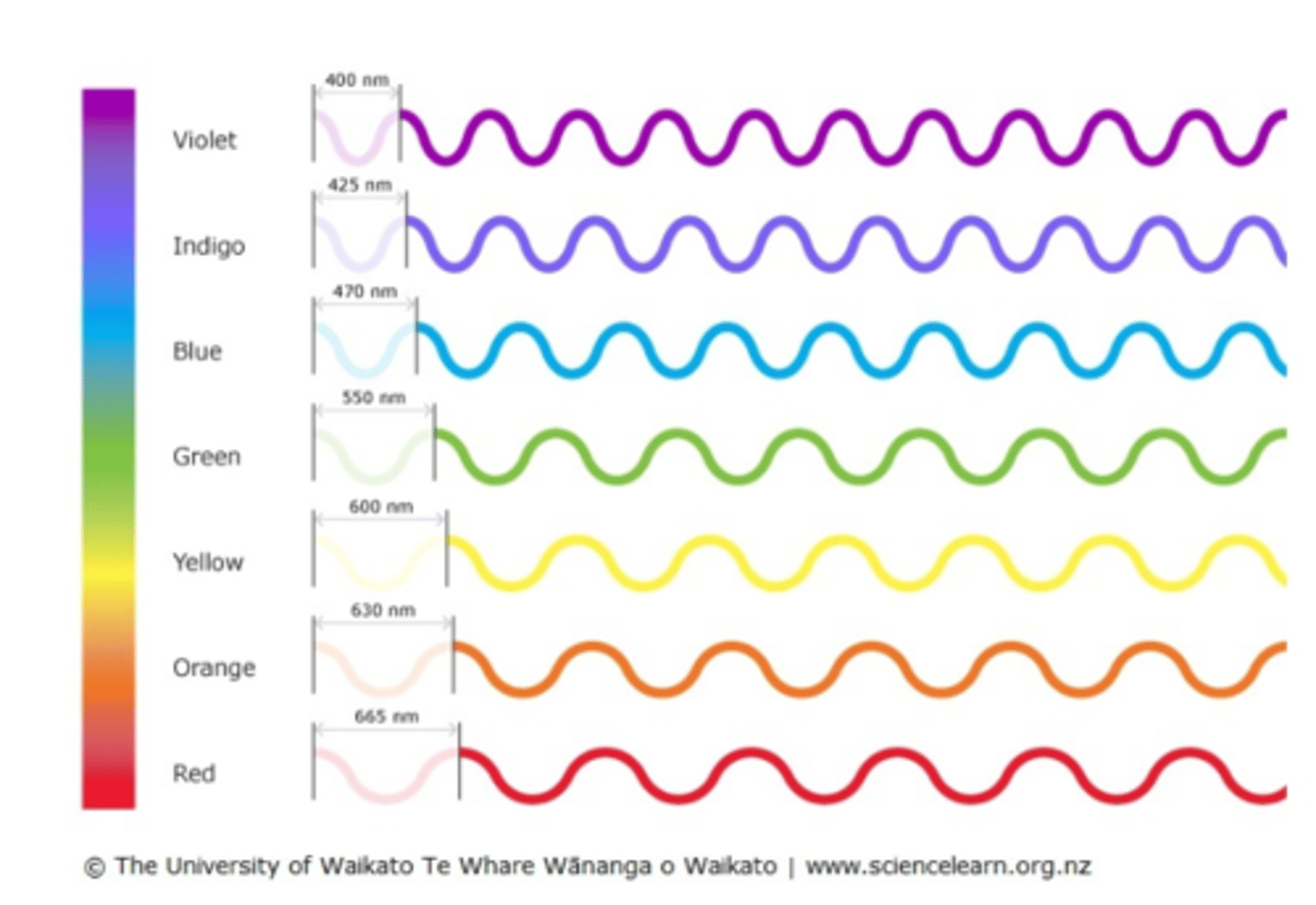
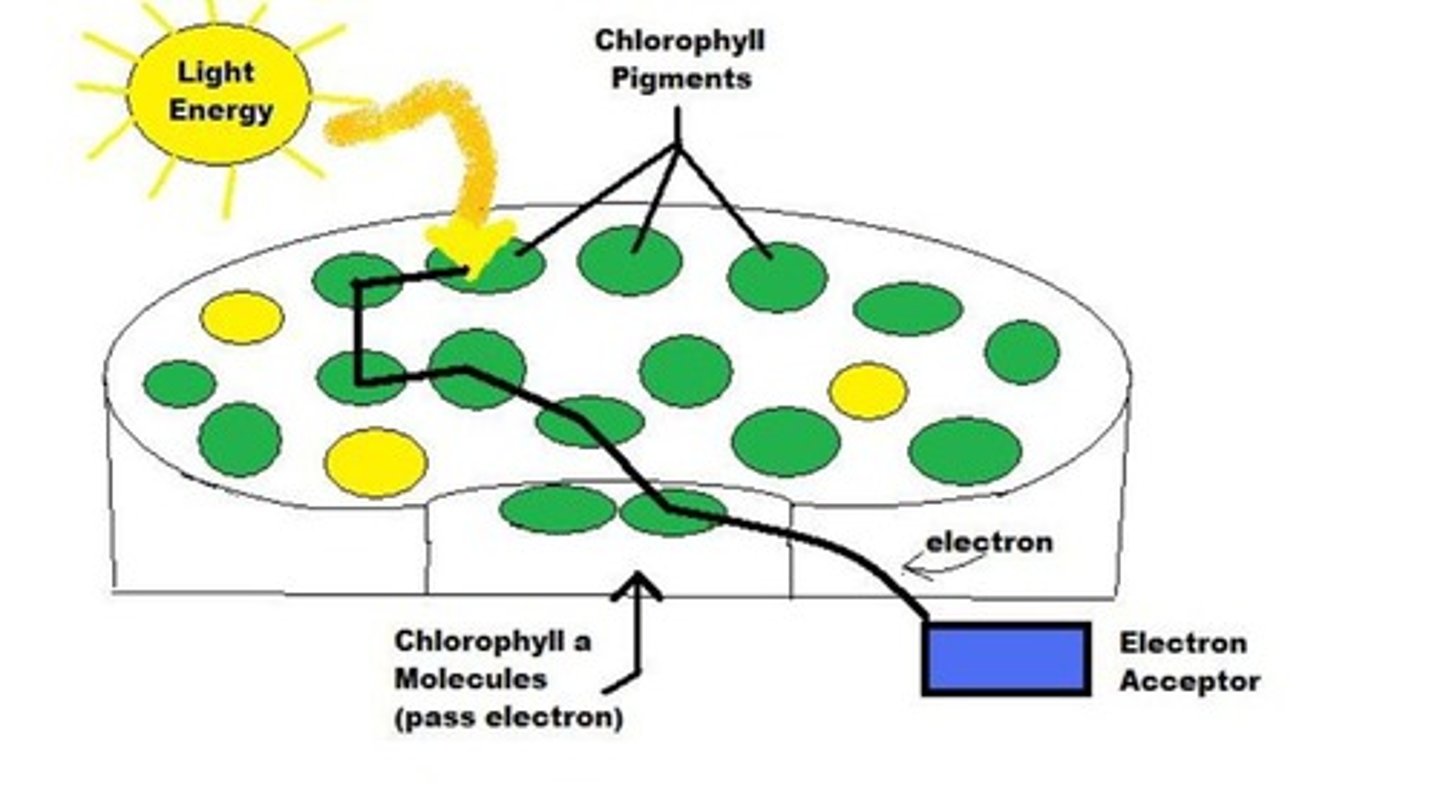
Light energy
A form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves and can be seen by the human eye. Light is made of many photons ("particles") moving in different waves of energy (seen as different colours)
mitochondria
an organelle in a cell that produces ATP. This is where cellular respiration takes place.
Oxygen
O2
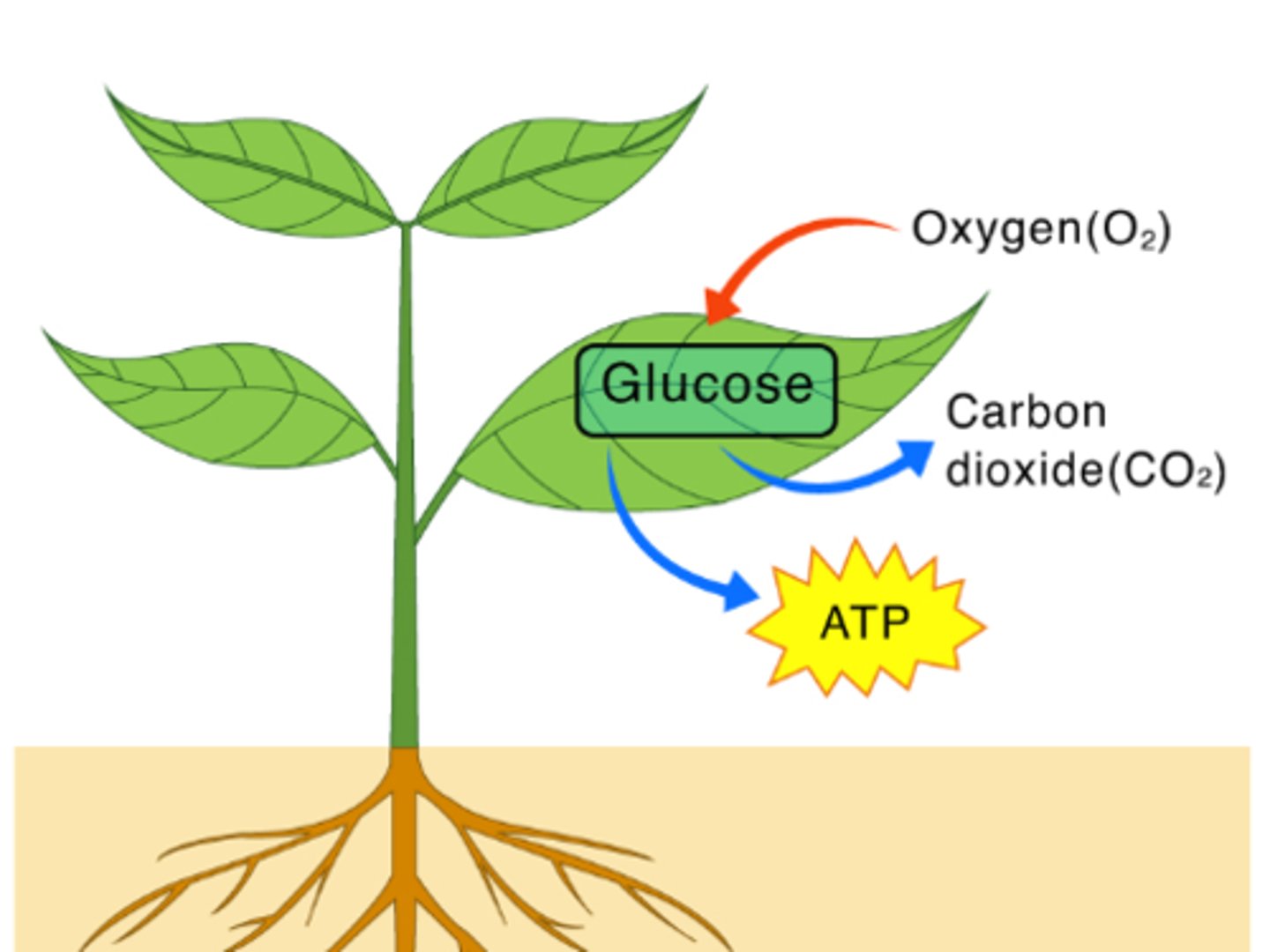
Photosynthesis
the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy.
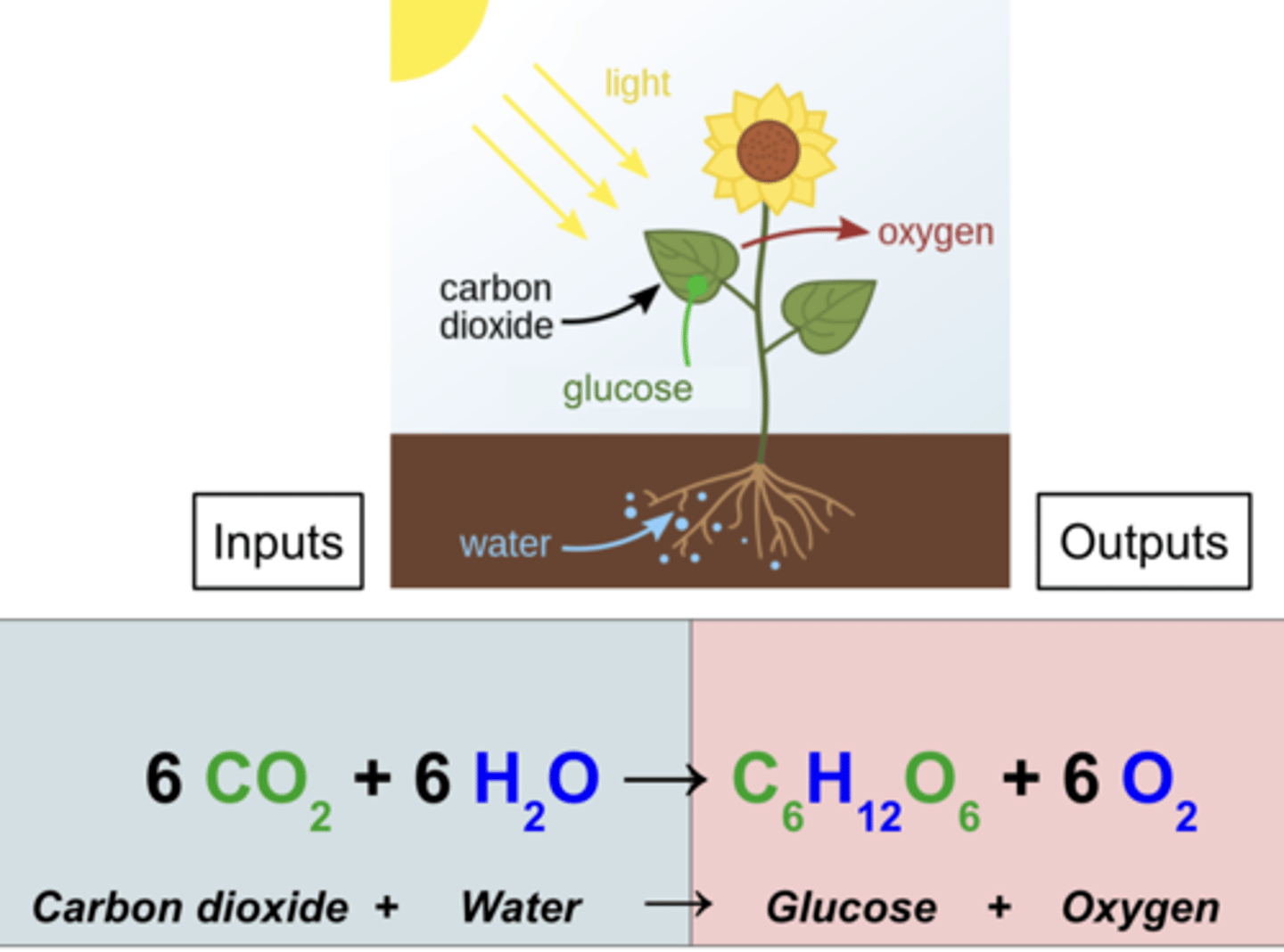
Water
H20
Chlorophyll
green pigment in a chloroplast that absorbs light energy during the light reactions of photosynthesis
Organic compound
a compound made by living organisms that contains carbon - hydrogen bonds
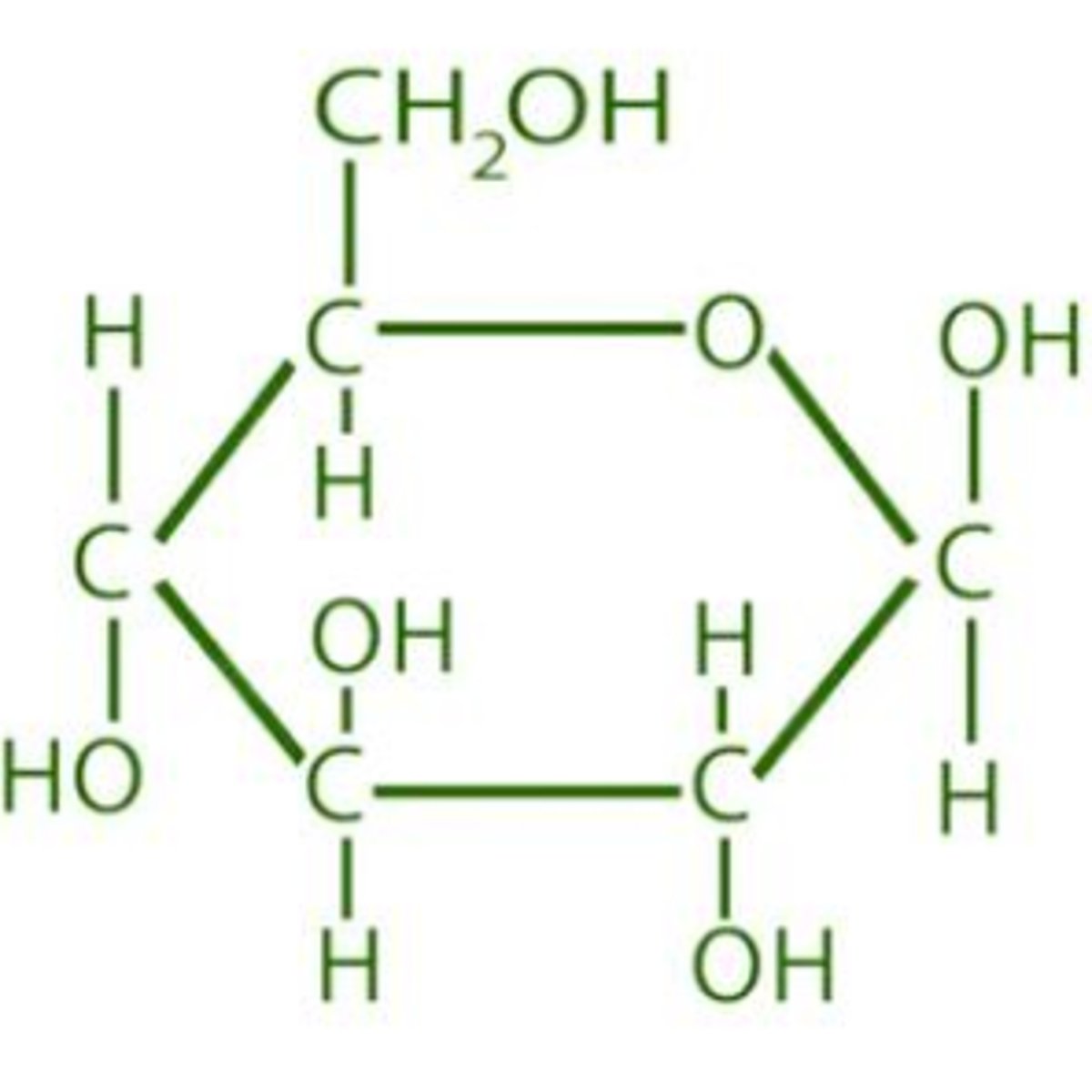
Inorganic compound
a compound that exists separately from living organisms and does not contain a carbon - hydrogen bond
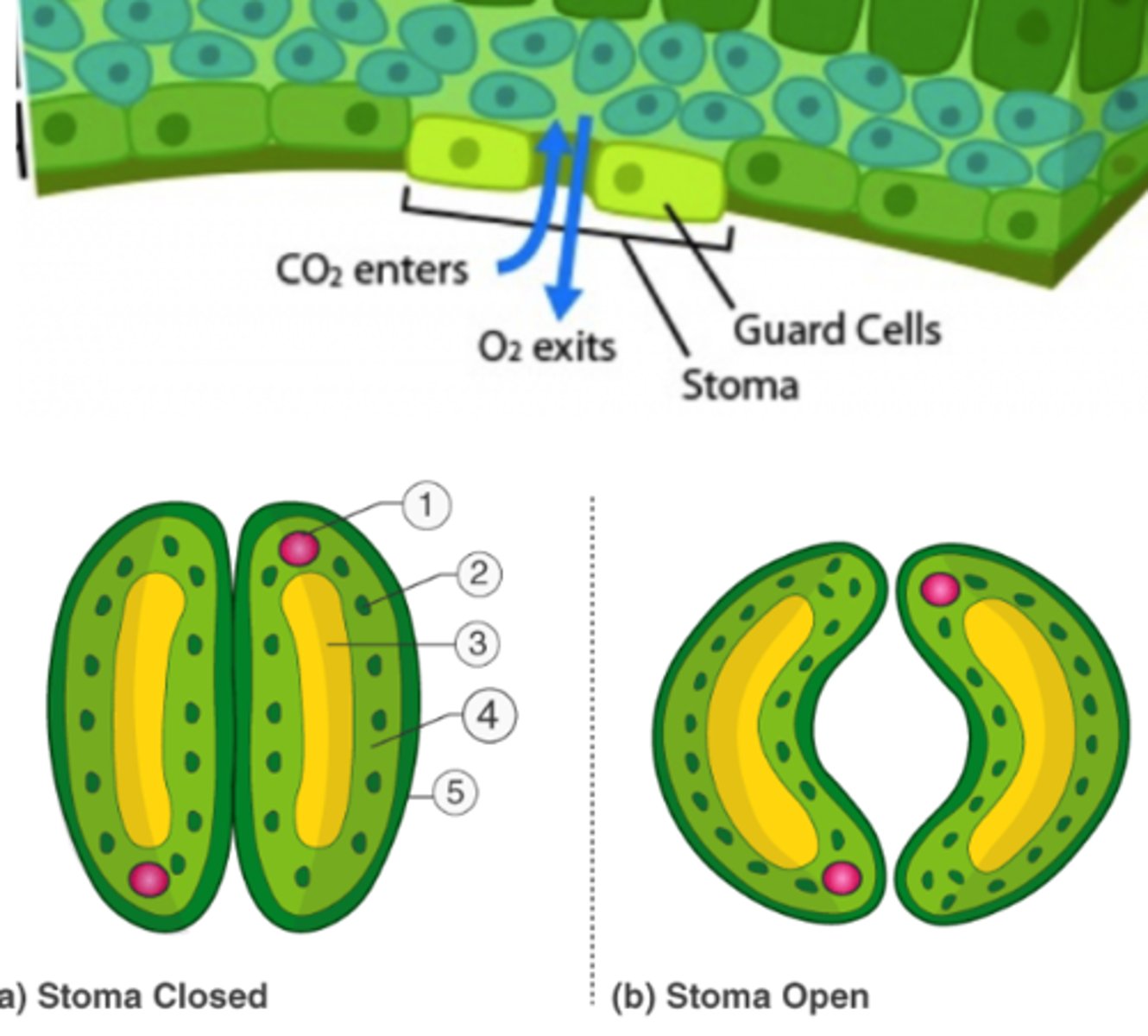
Stoma (stomata)
a hole-like structure found in leaves and stems of plants. Stomata control the rate of gas exchange between the plant and the atmosphere by opening and closing.
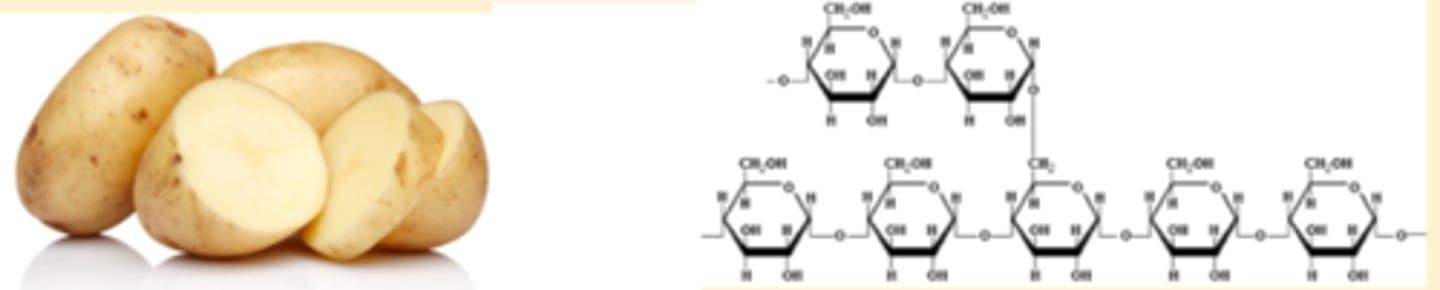
starch
a string (polymer) of glucose molecules
carbohydrate
a biomolecule (organic compound) made of simple or complex sugars. Carbohydrates supply energy to the body, such as sugar and starch.

biomolecule
a chemical compound found in living organisms
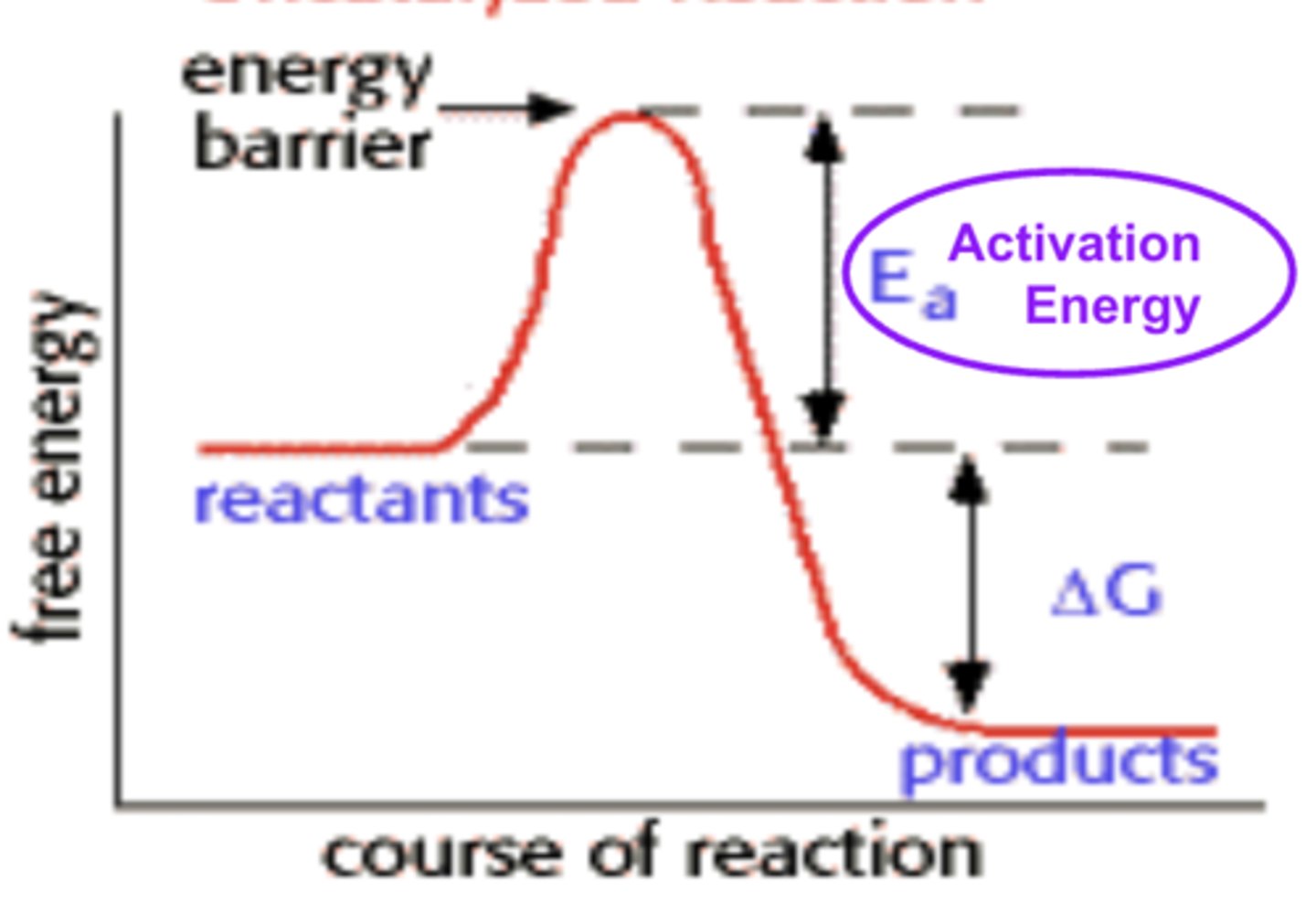
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy that must be provided to break covalent bonds in reactants so that a chemical reaction occurs.
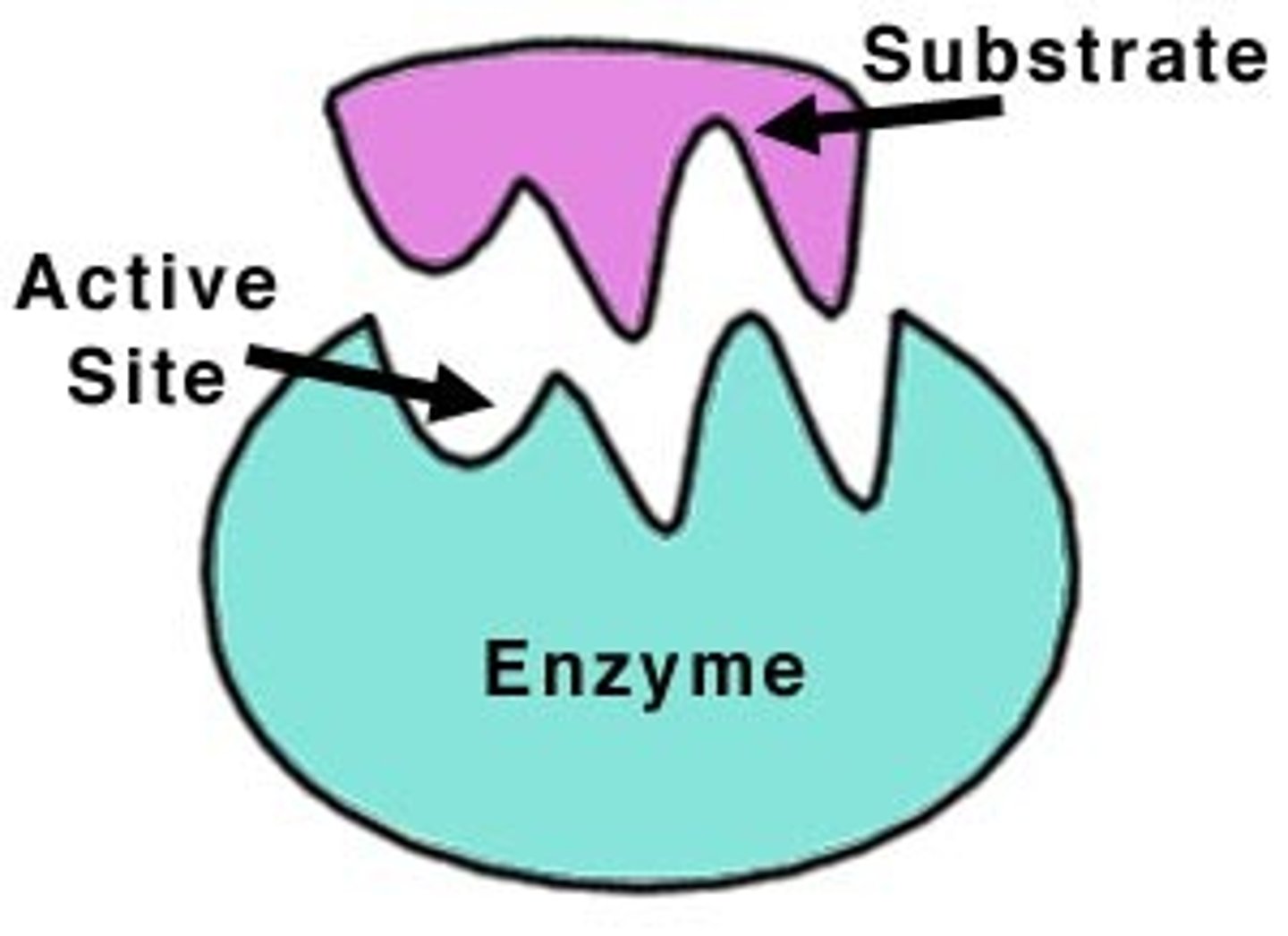
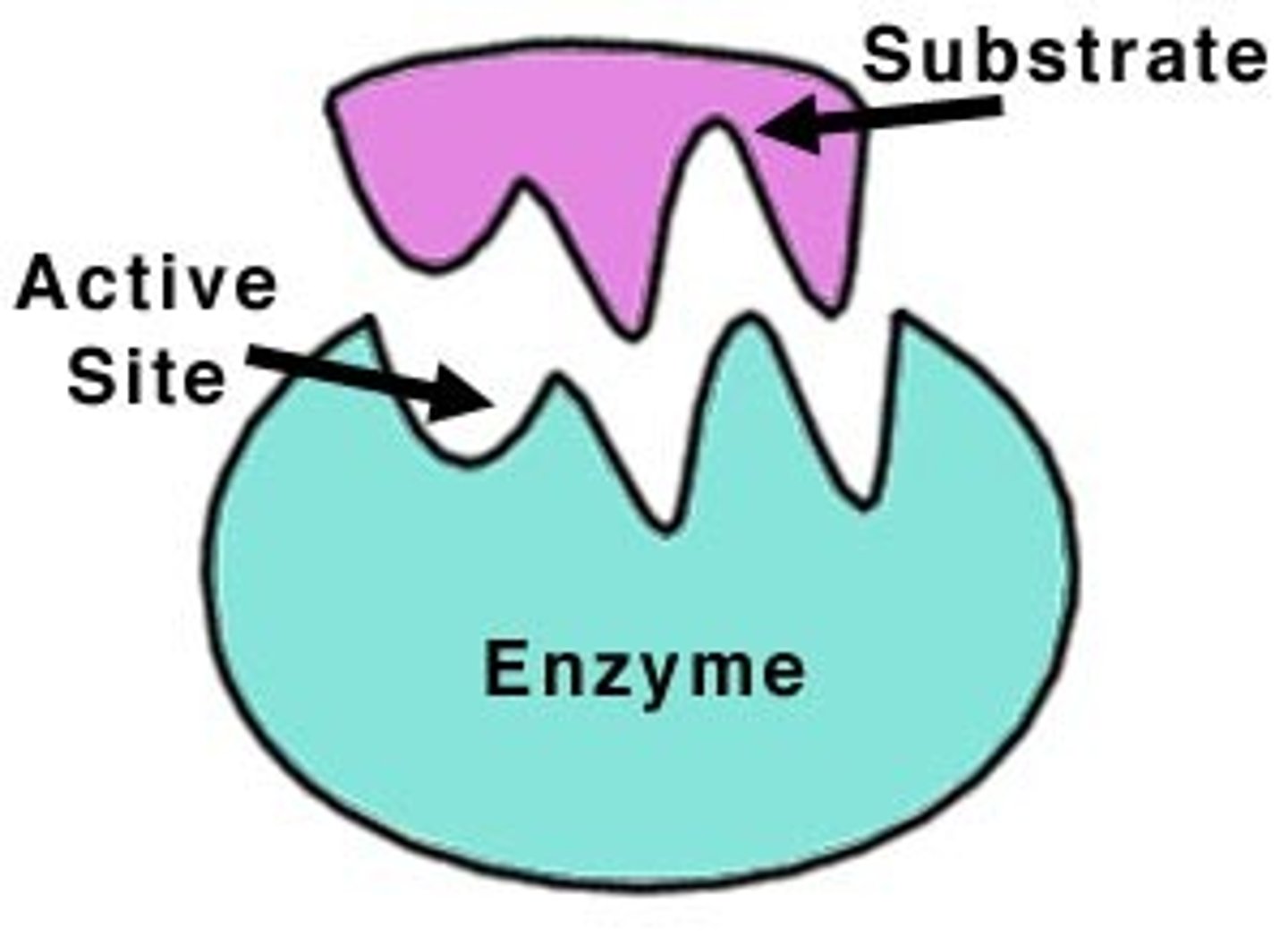
active site
a space in the enzyme that fits the substrate shape exactly. Or: the part of the enzyme where substrate molecules bind and a chemical reaction takes place
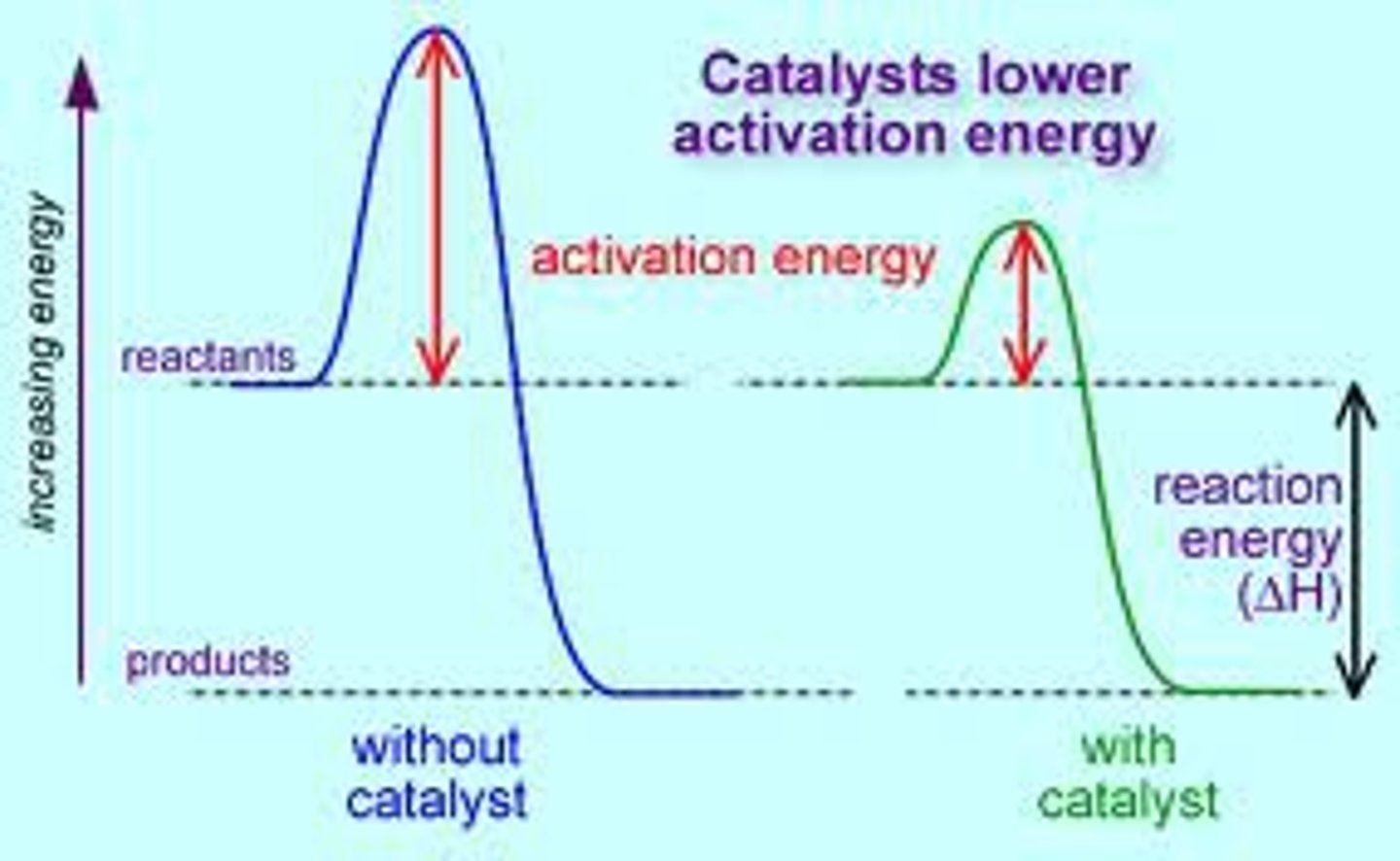
catalyst
a molecule that lowers the activation energy required for reactions
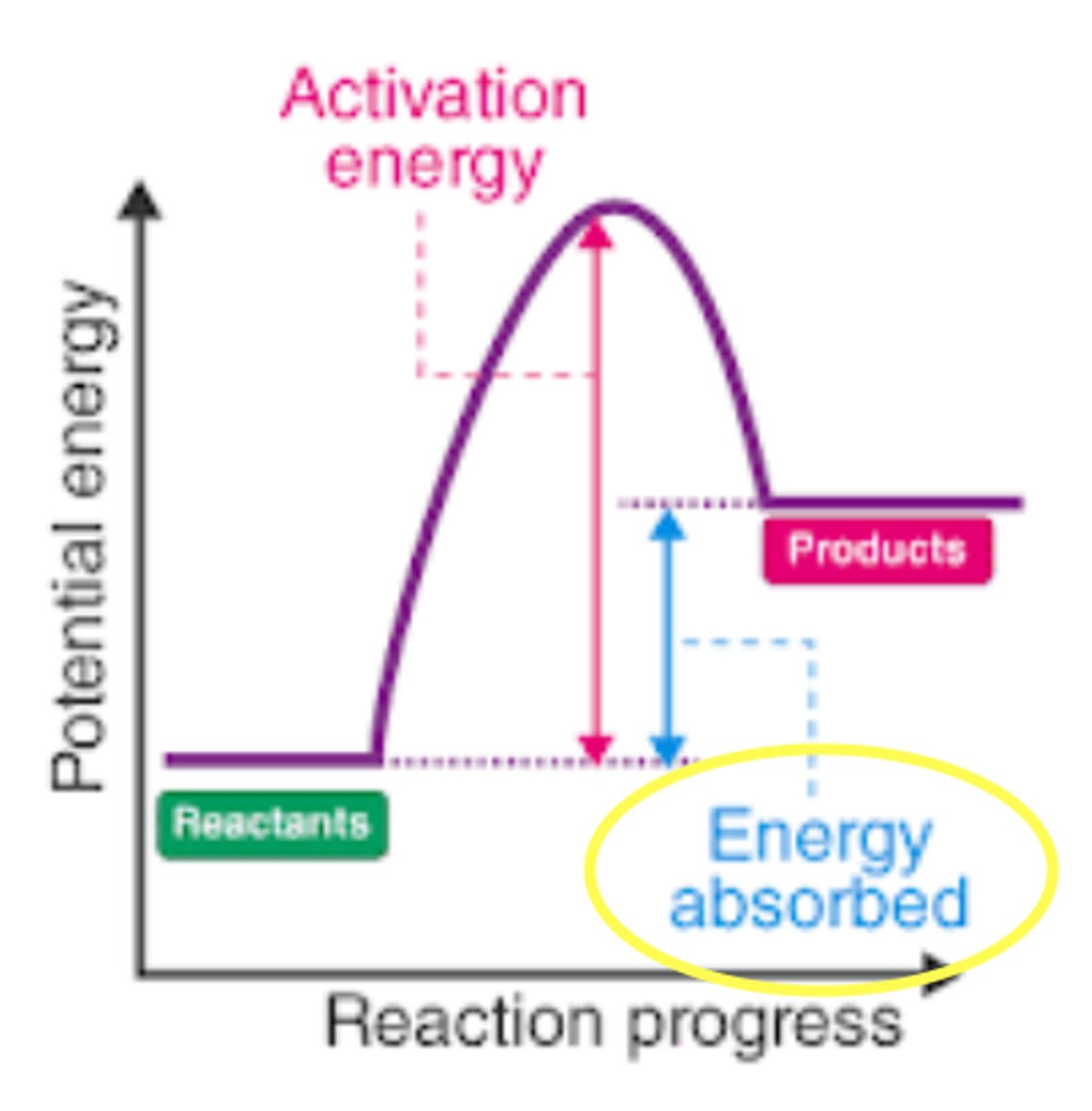
endothermic
a chemical reaction where the reactants absorb heat energy from the surroundings to form products. (it 'sucks up' heat from the area around it)
enzyme
a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions
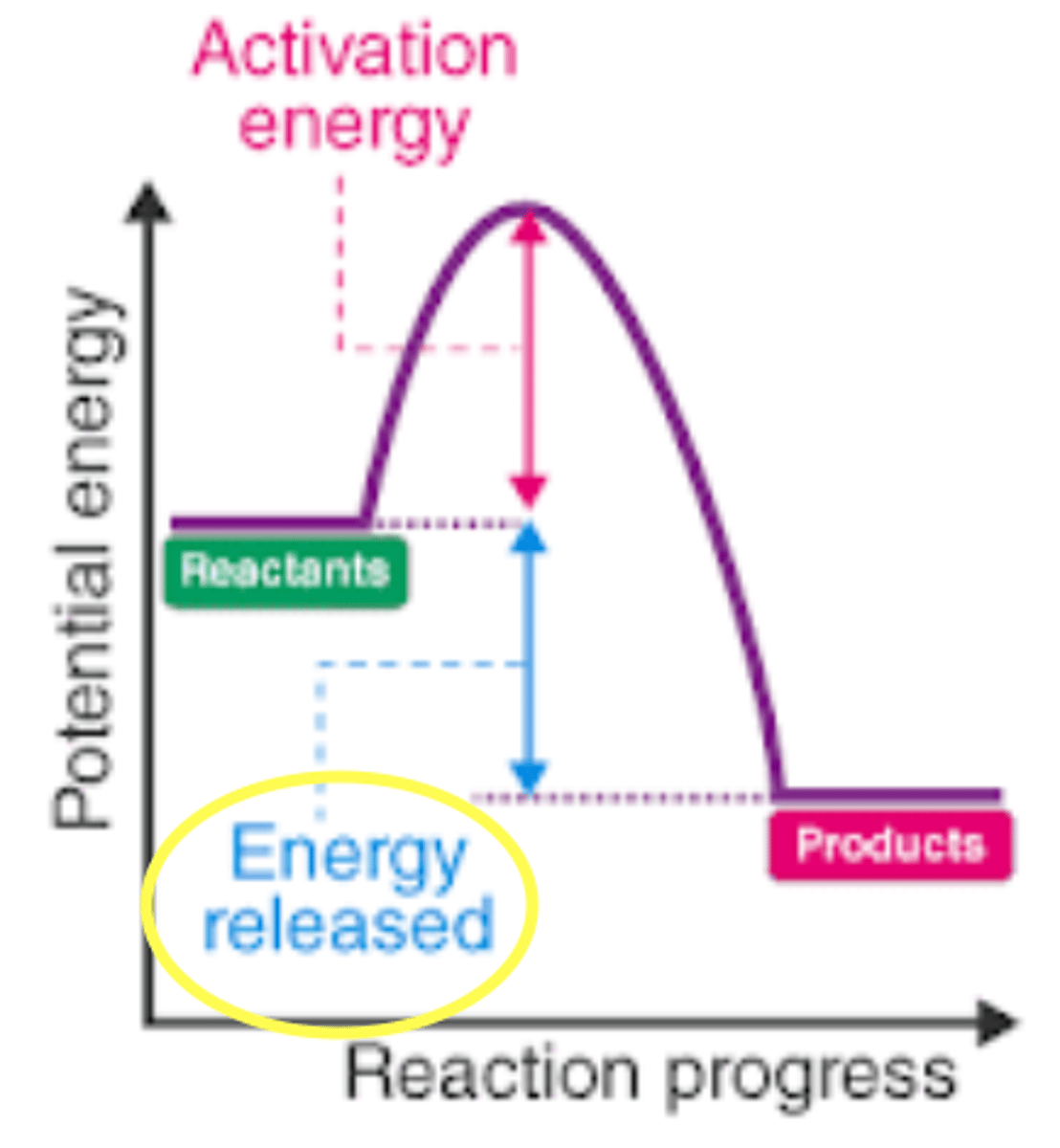
exothermic
a chemical reaction where the reactants releases energy (heat) to the surroundings (it gives off heat to the area around it)
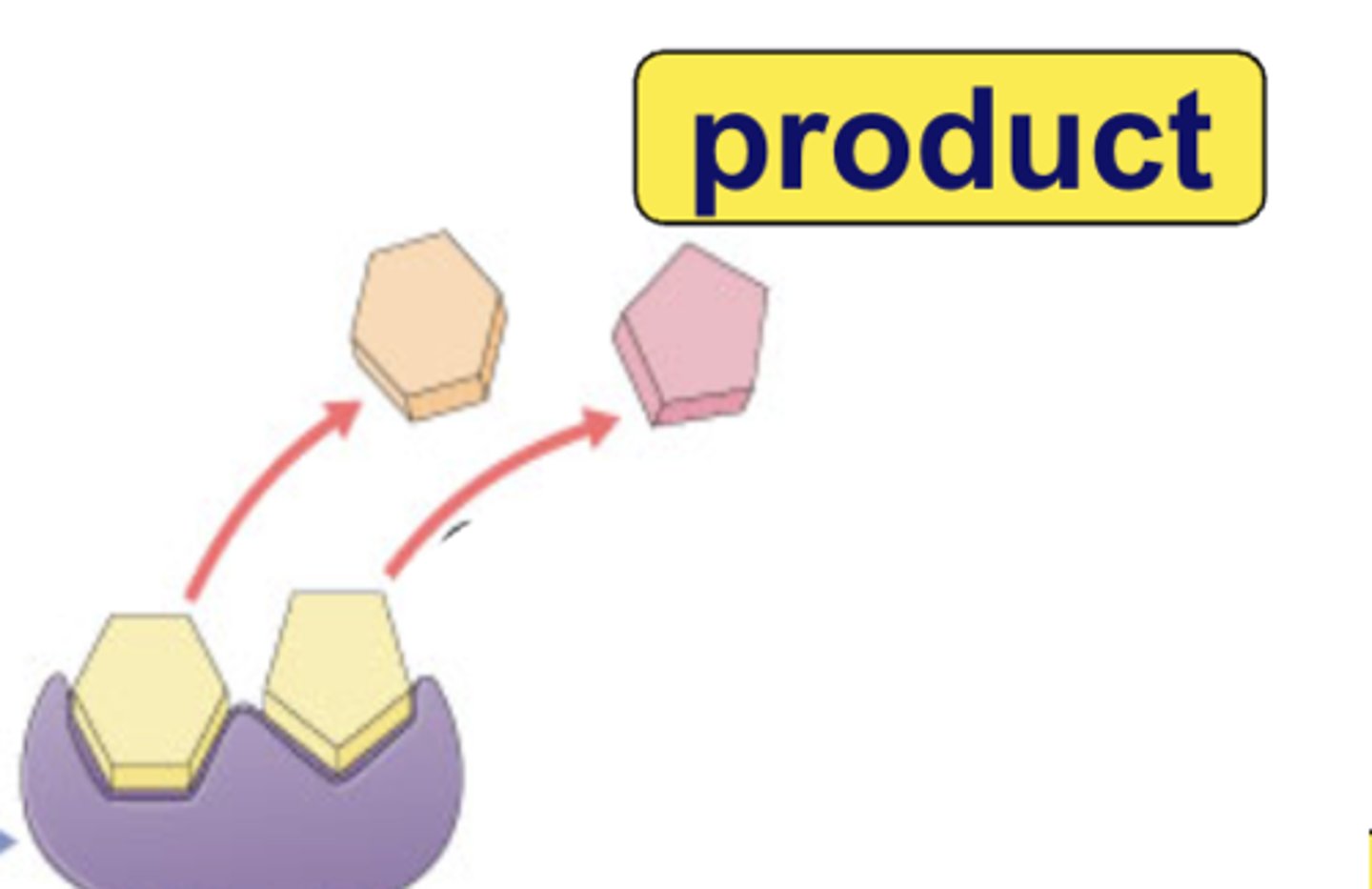
product
a substance that is formed from a chemical reaction
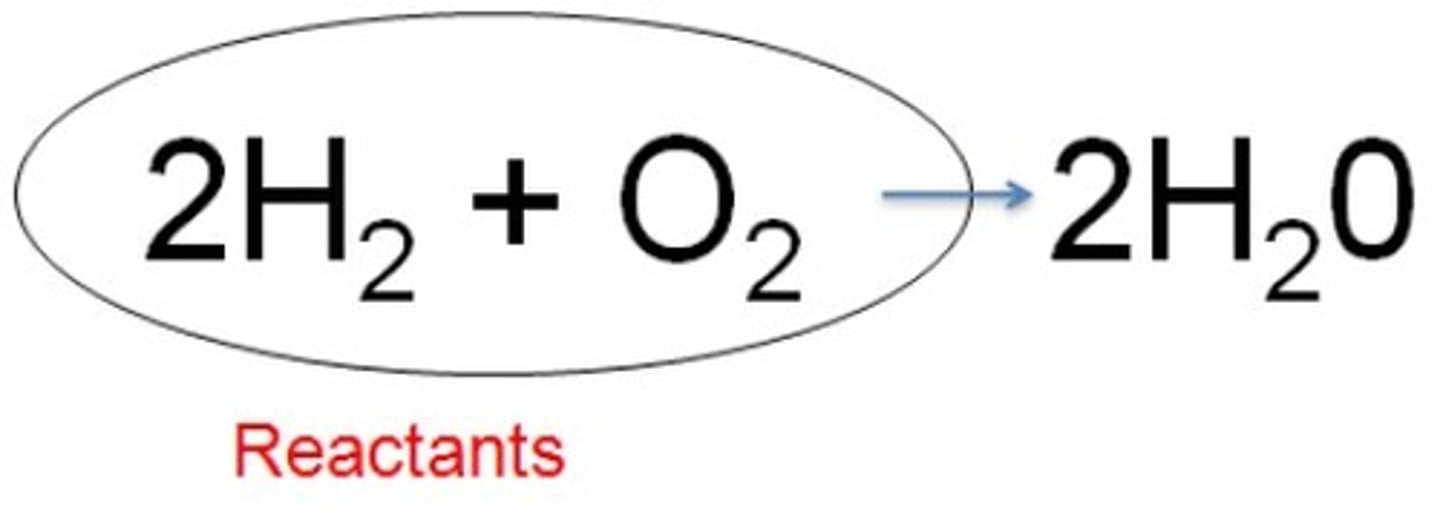
reactant
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction
substrate
a molecule that an enzyme reacts with (the reactant in the reaction the enzyme helps)
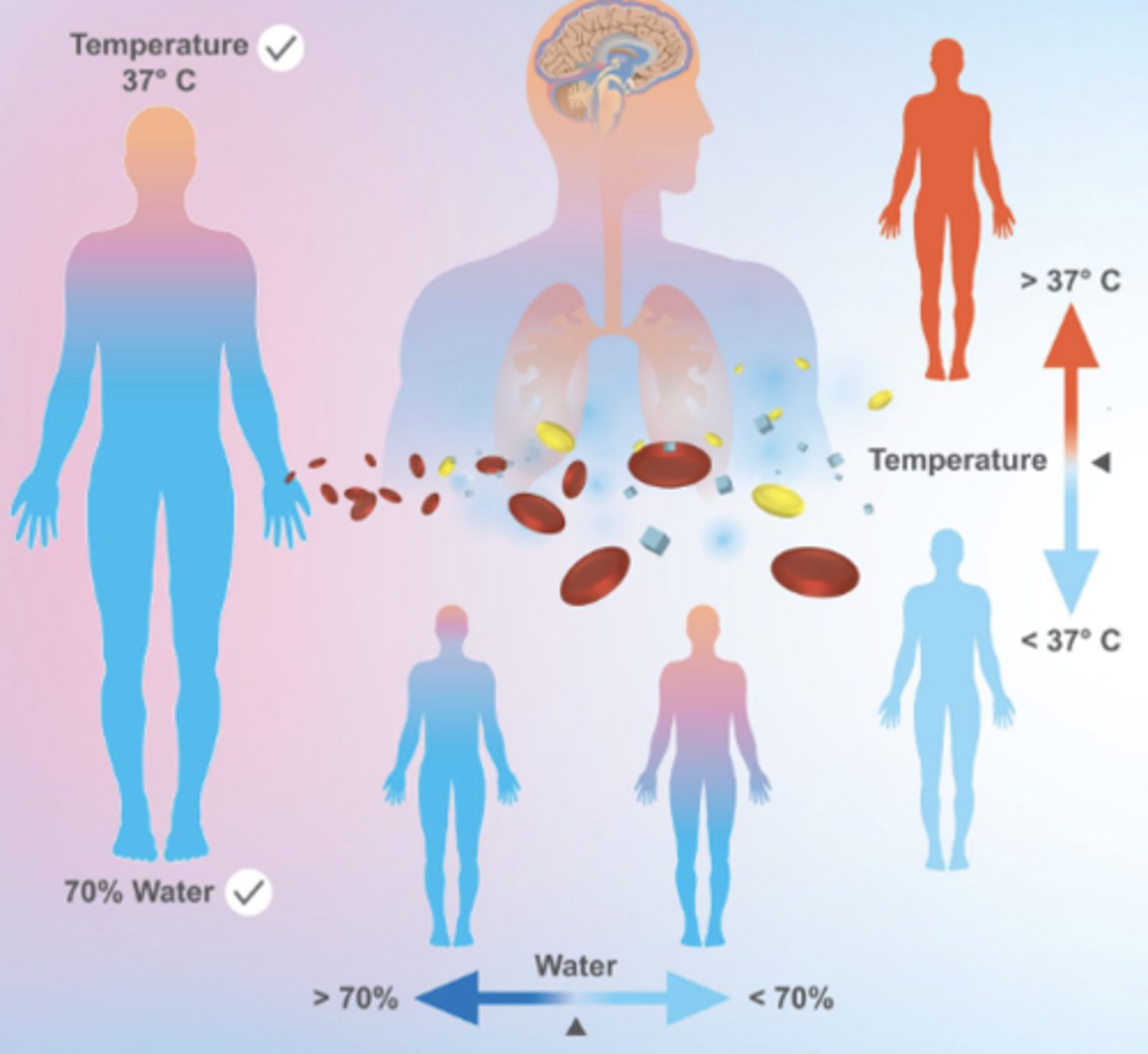
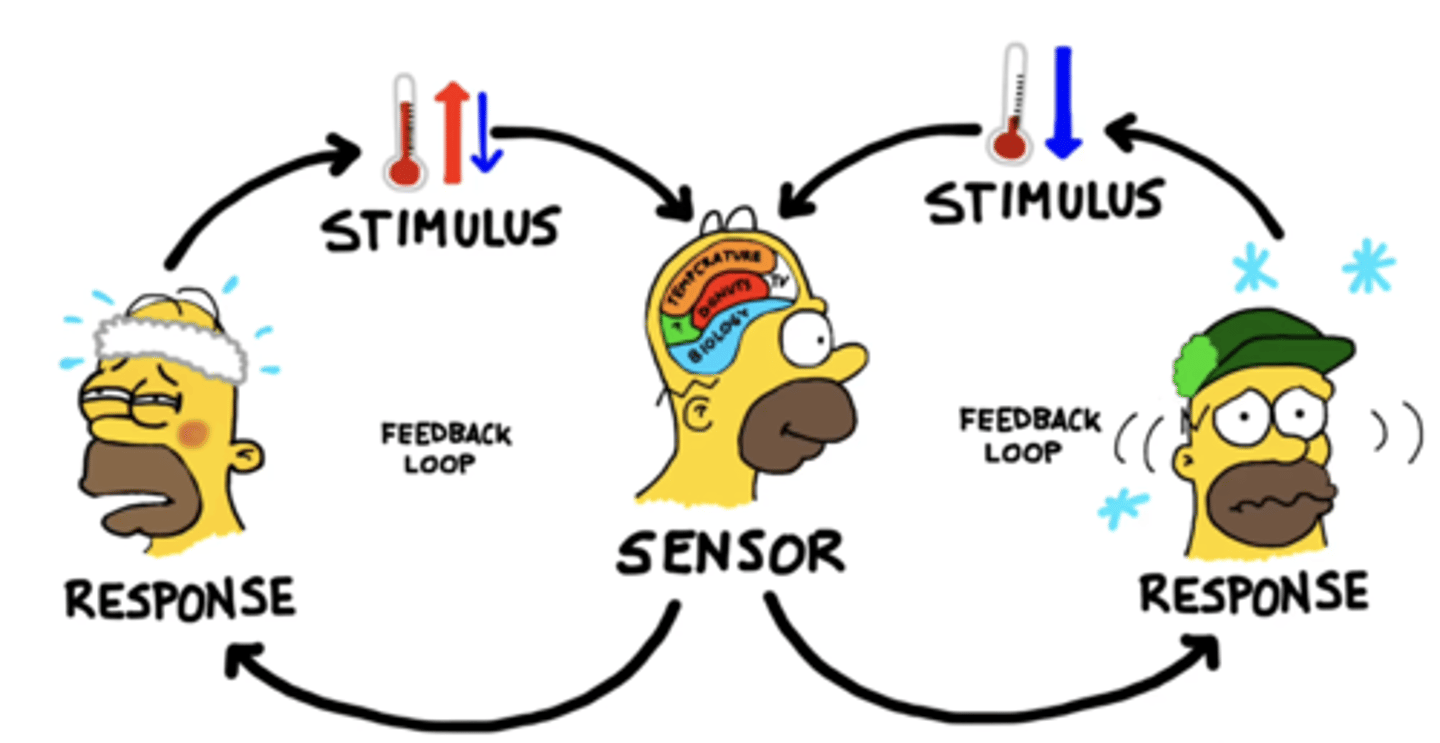
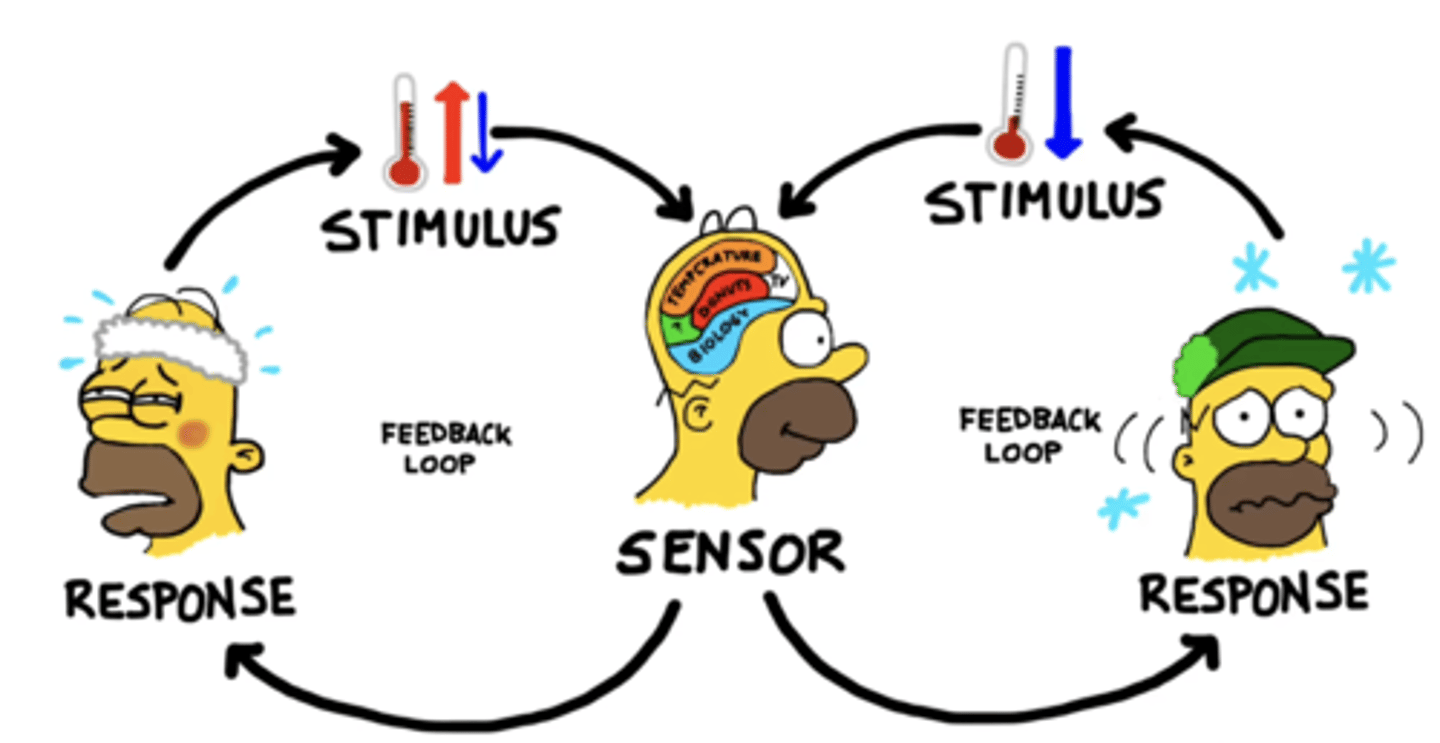
homeostasis
the process where organ systems work to maintain (keep) a stable internal environment.
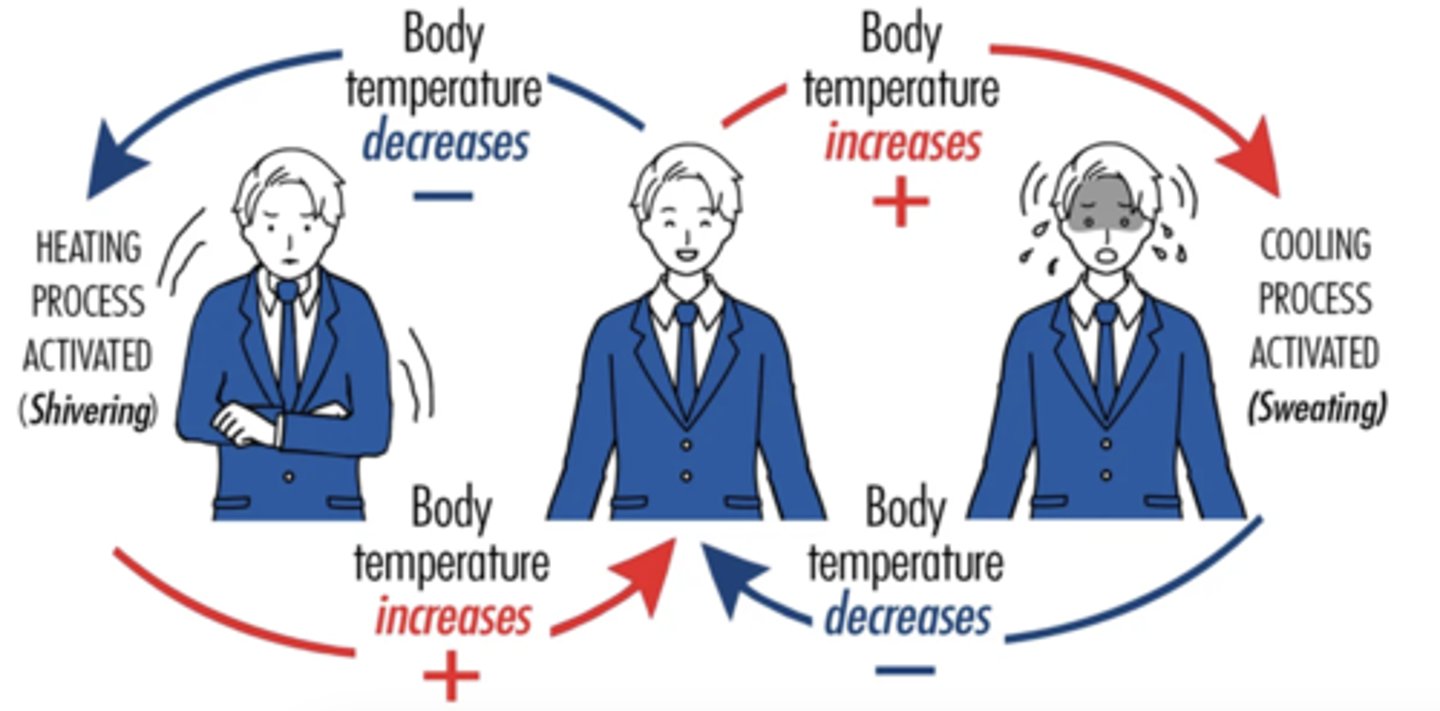
negative feedback
a response to a stimulus that keeps a variable close to a set value (it "shuts off" or "turns on" a system when it varies from a set value)
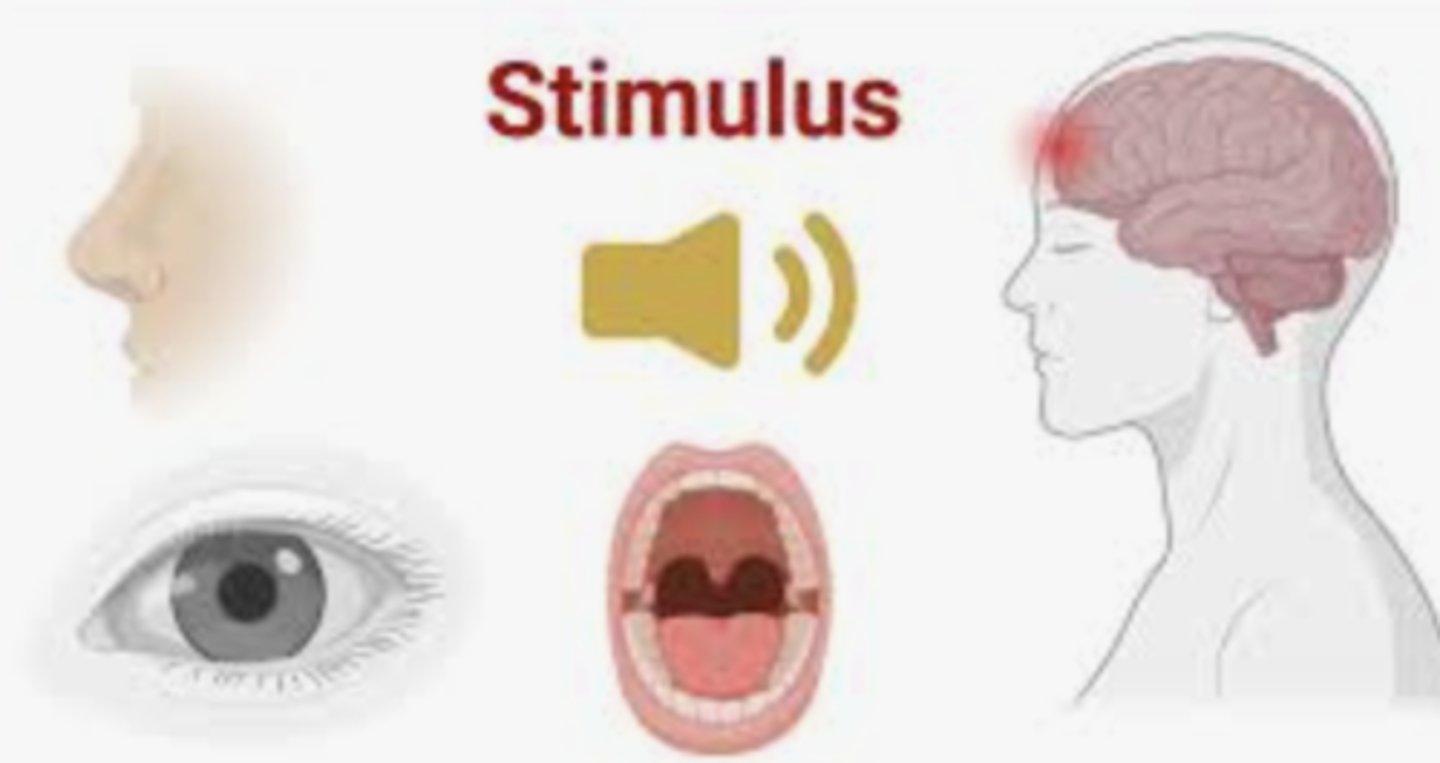
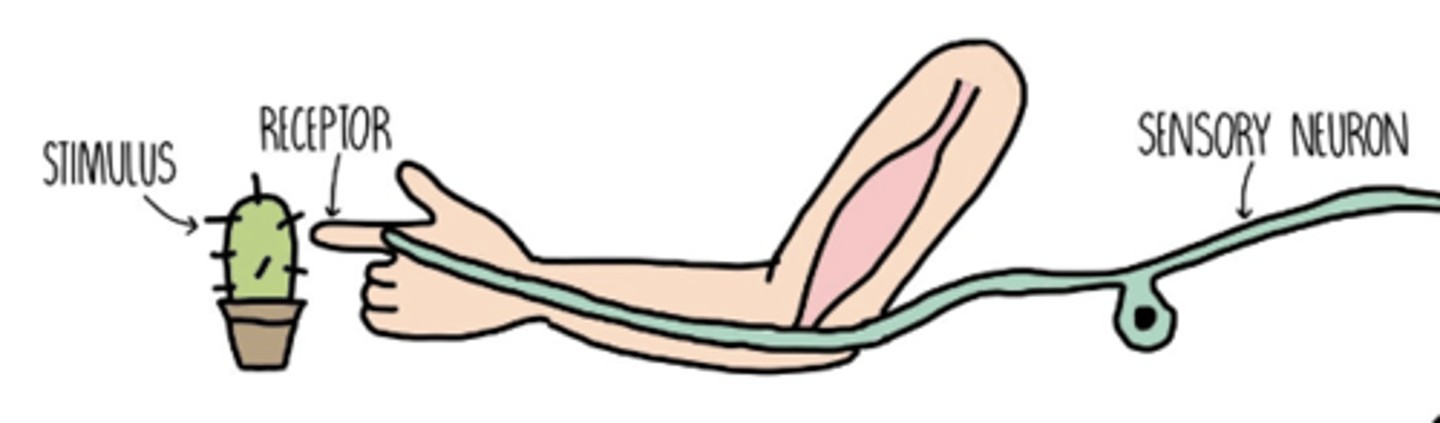
stimulus (plural: stimuli)
something that triggers a behavior or causes a reaction in an organism.
receptor
a cell or group of cells that receives stimuli
signal
a message that is sent between cells
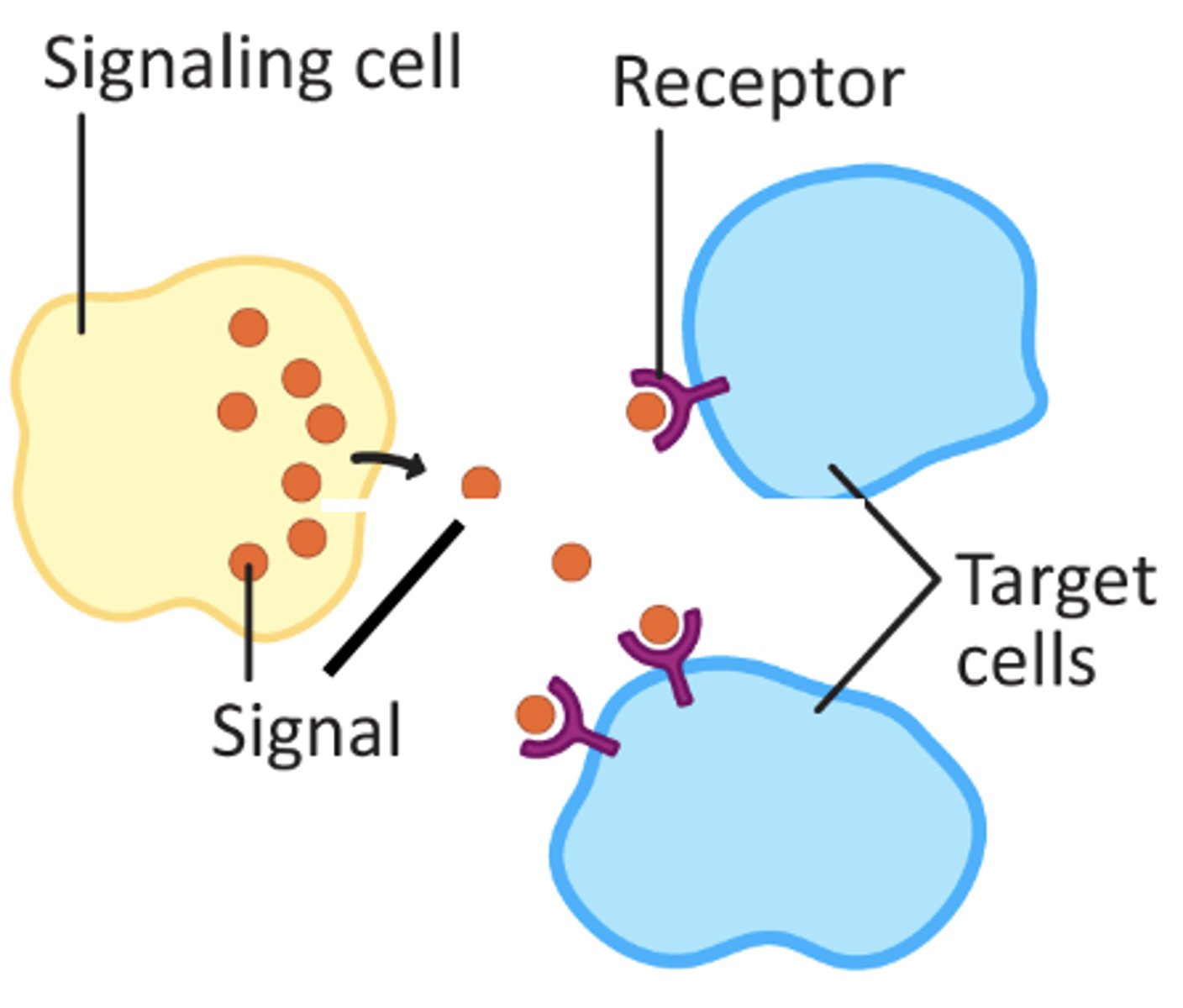
response
an action or message as a result of a signal
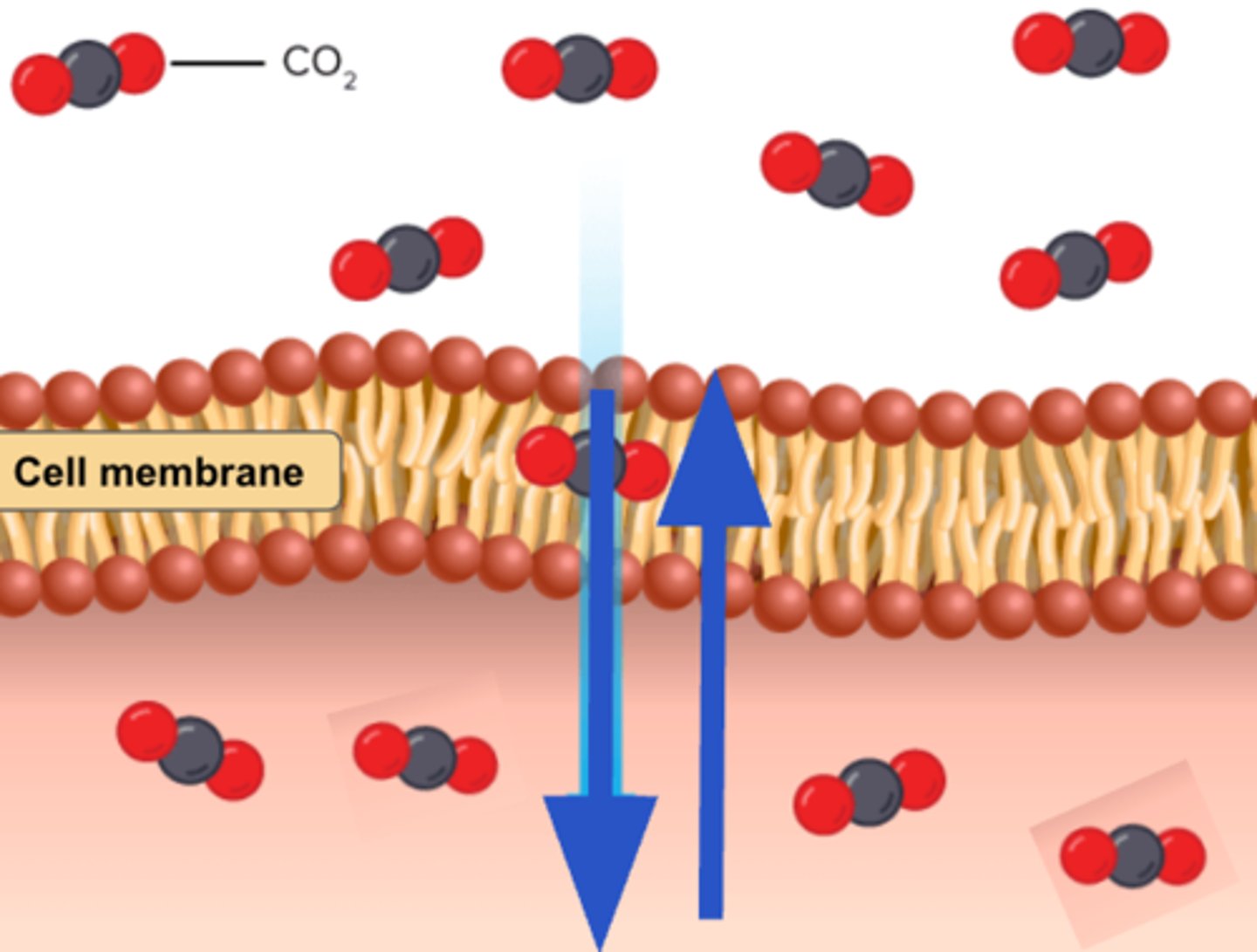
diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration of the molecules to an area with a lower concentration
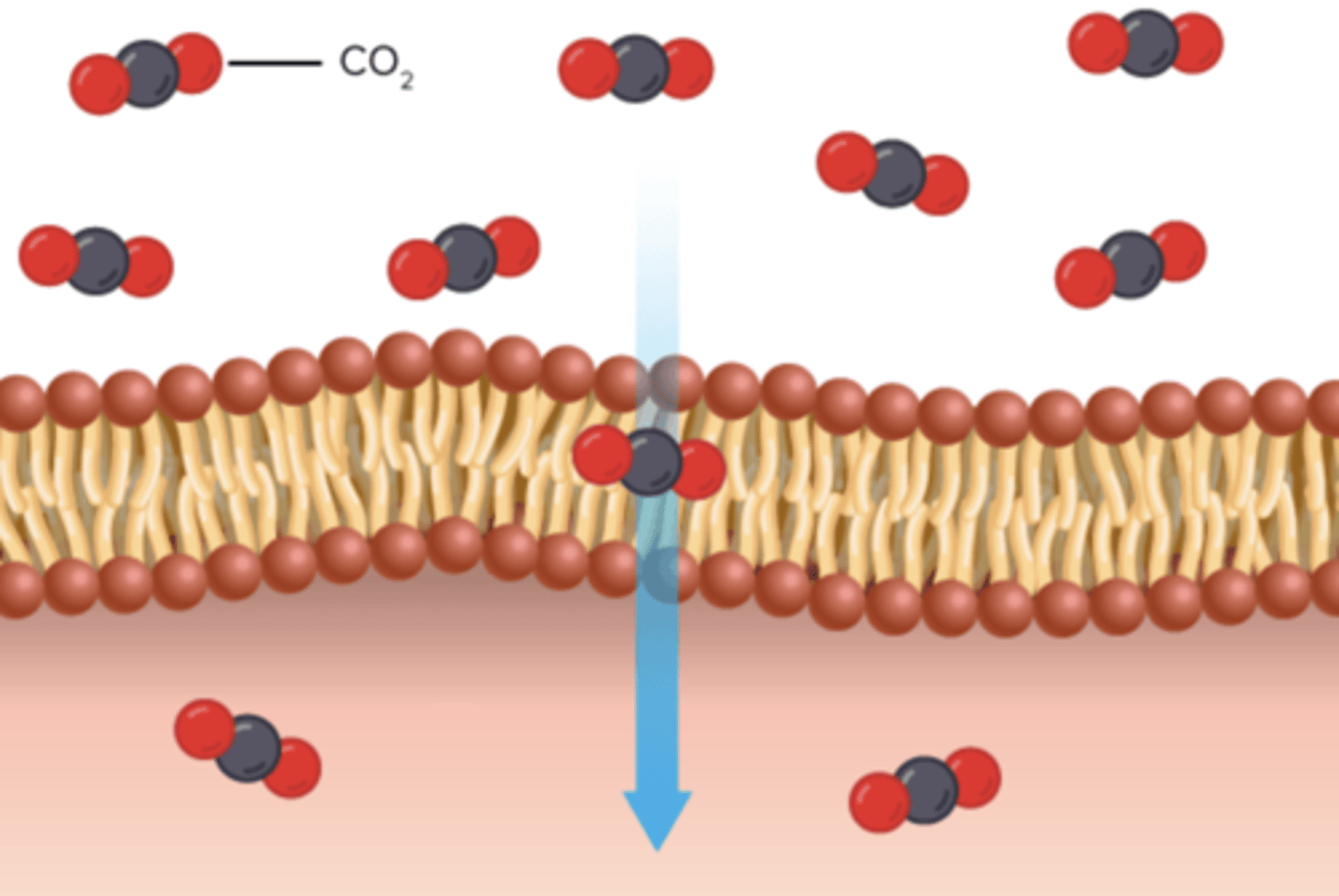
membrane
a thin sheet of tissue or layer of cells acting as a boundary, lining, or partition in an organism.
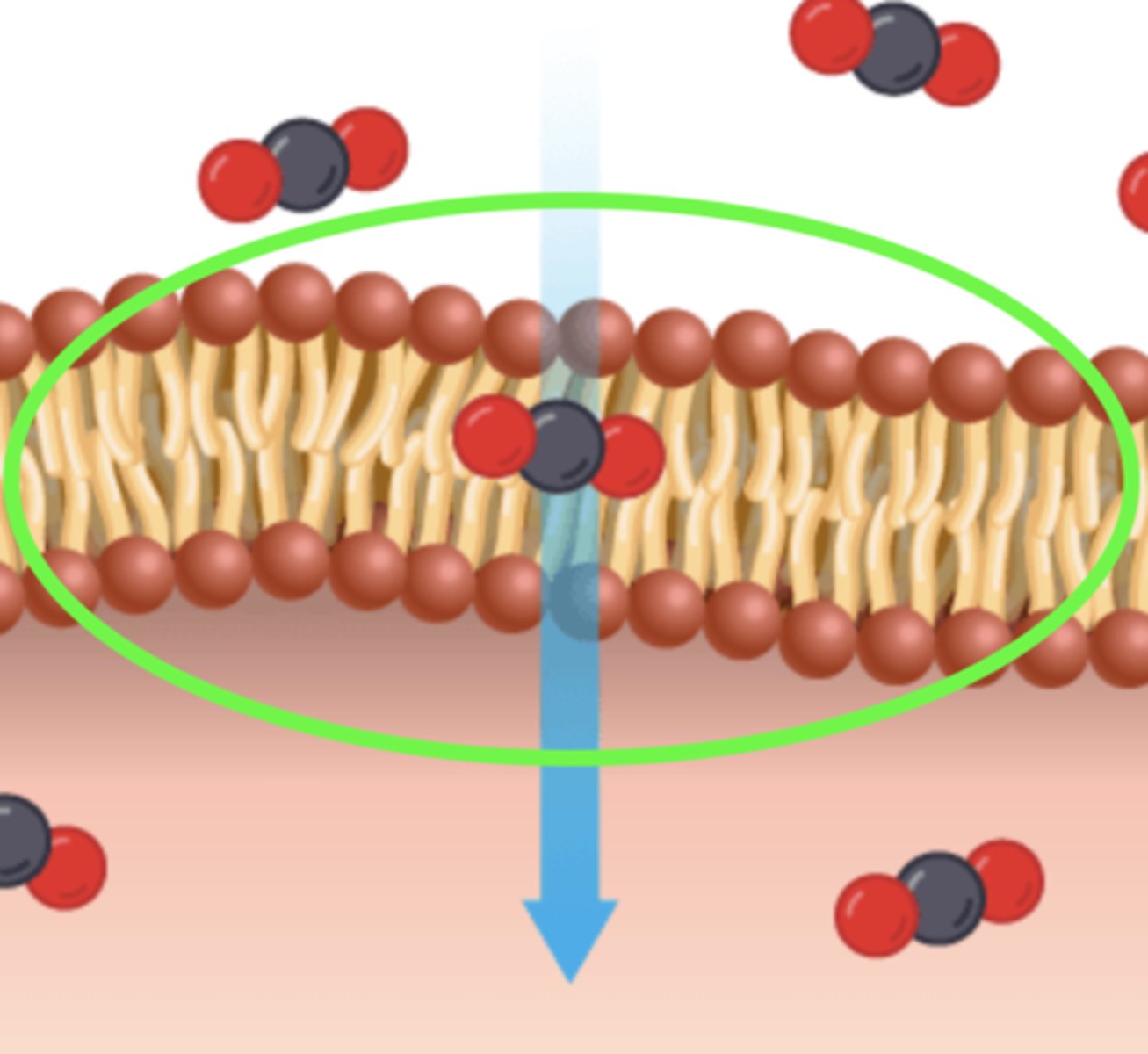
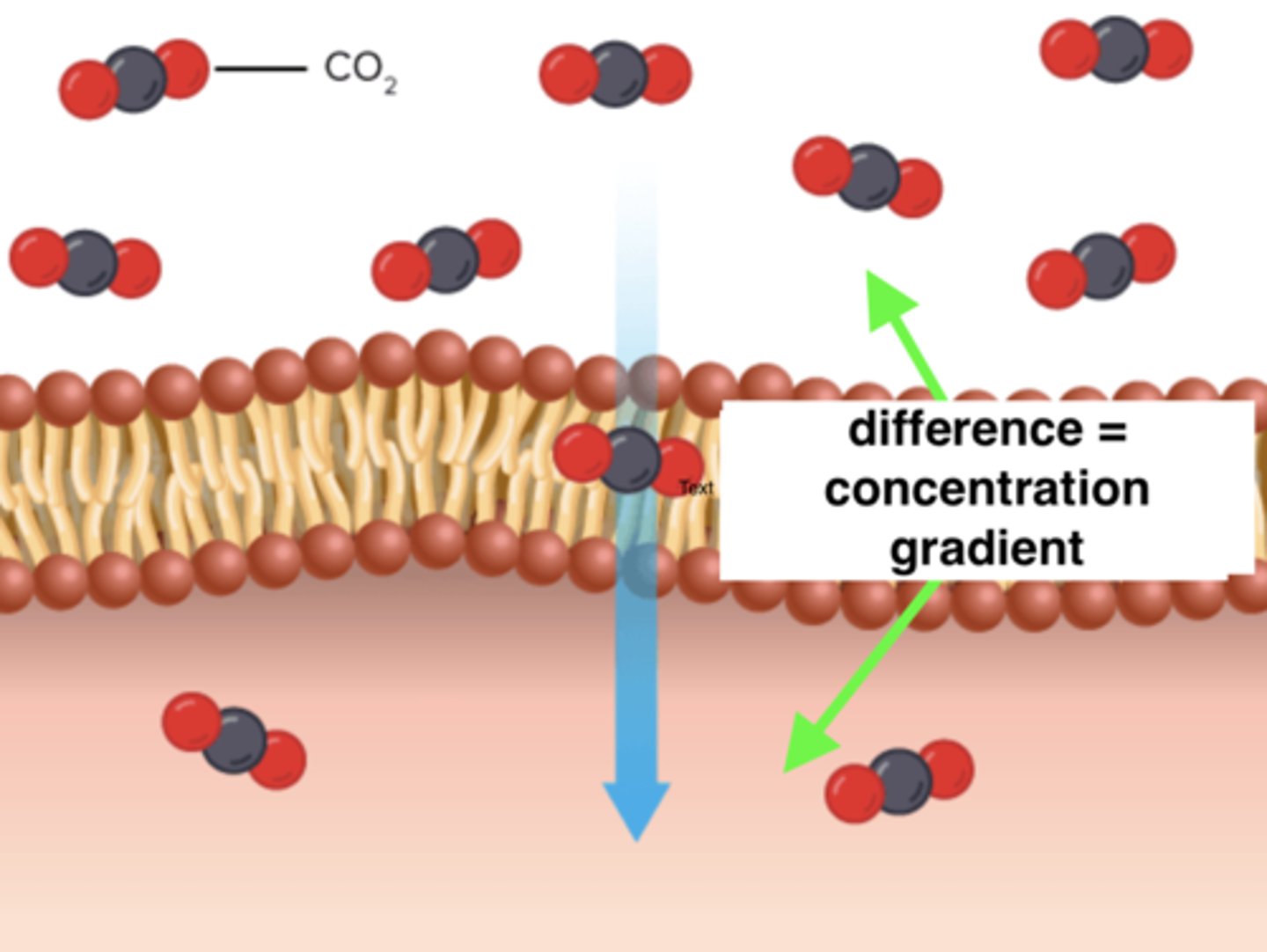
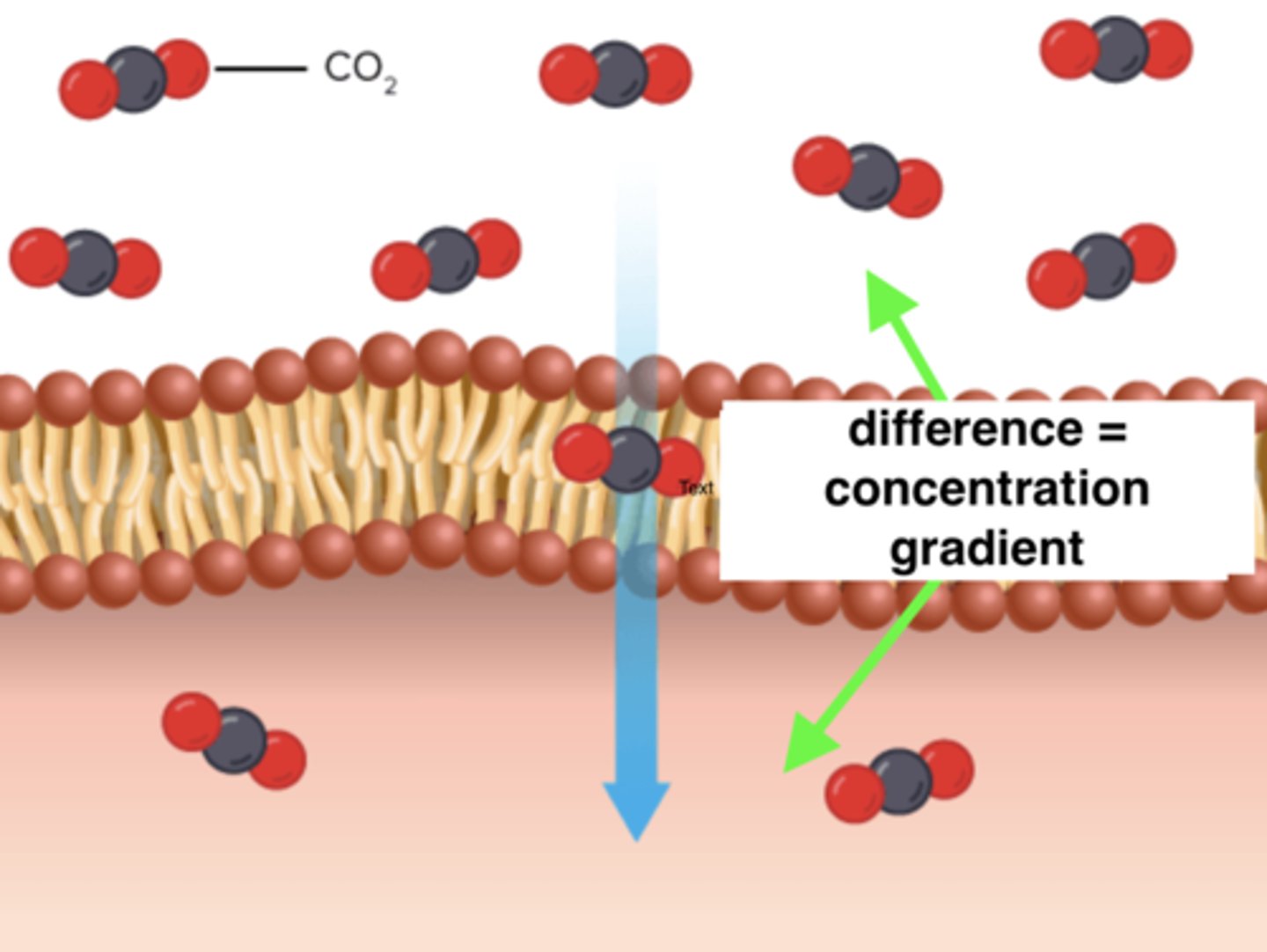
concentration gradient
The difference in the concentrations of molecules in two areas
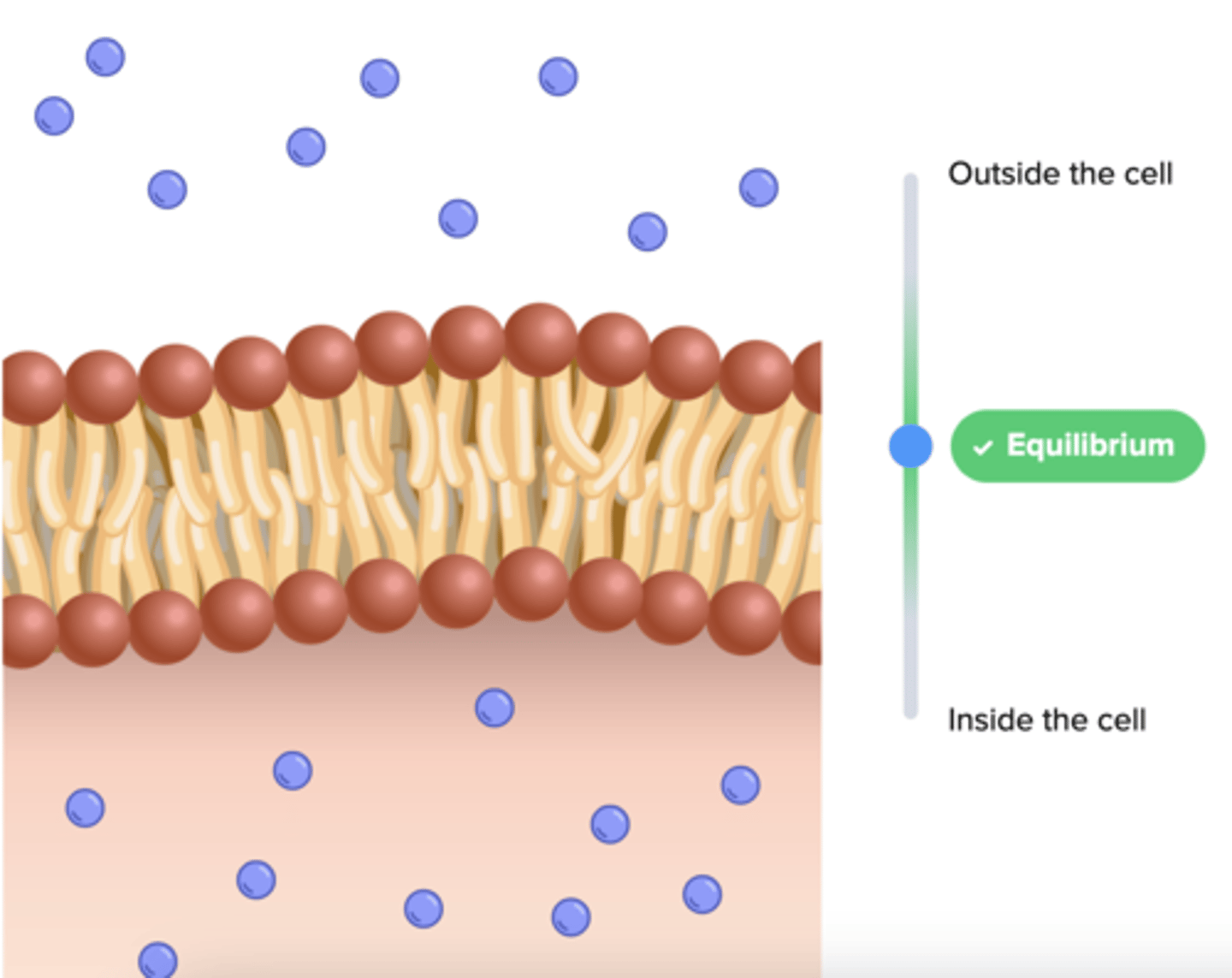
equilibrium
the process where organ systems work to maintain (keep) a stable internal environment
Cell
basic unit of structure and function of living things.
Specialized Cell
a cell that has a specific shape (structure) and function
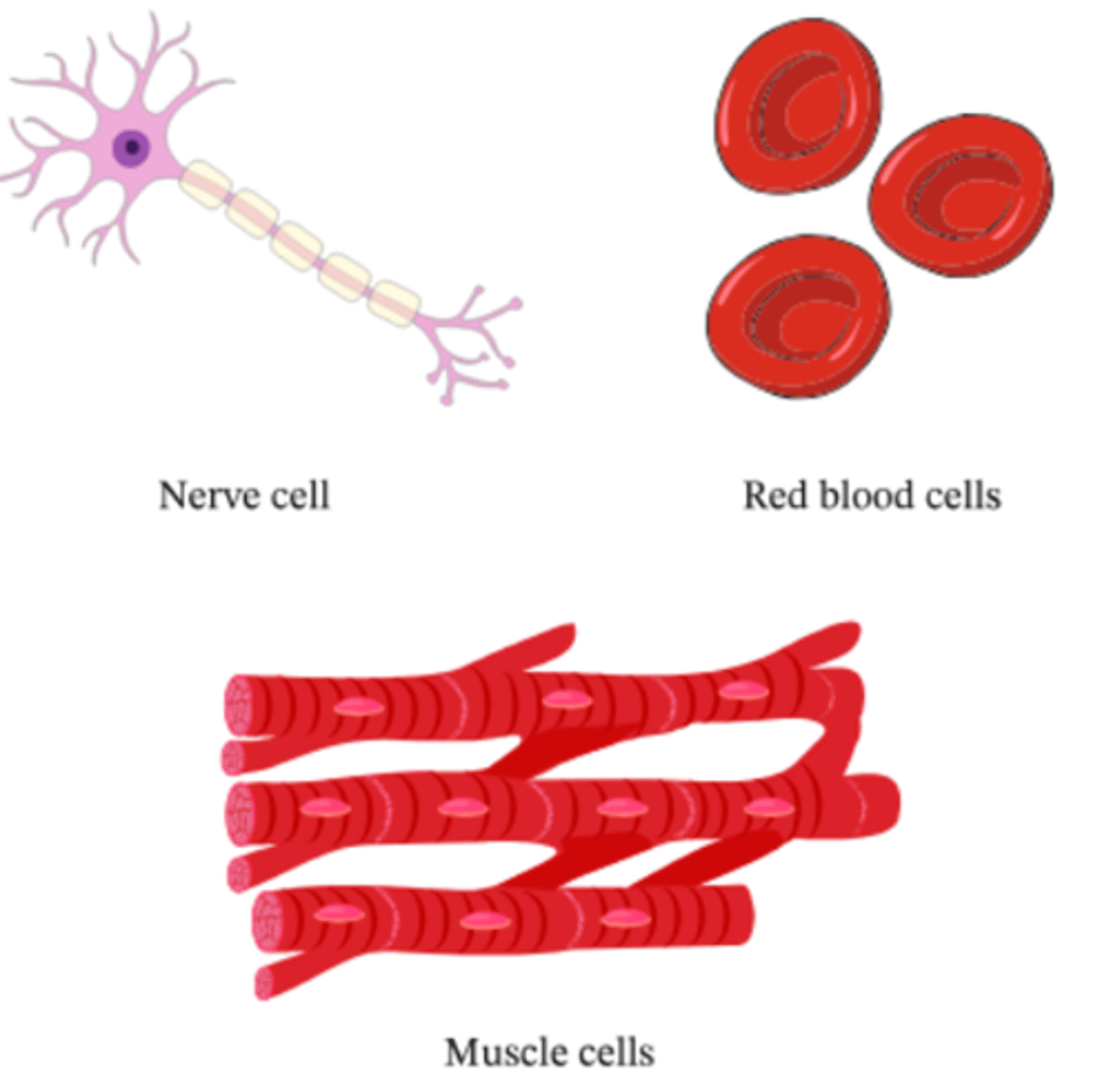
Tissue
group of specialized cells of the same kind that work together to perform the same function.
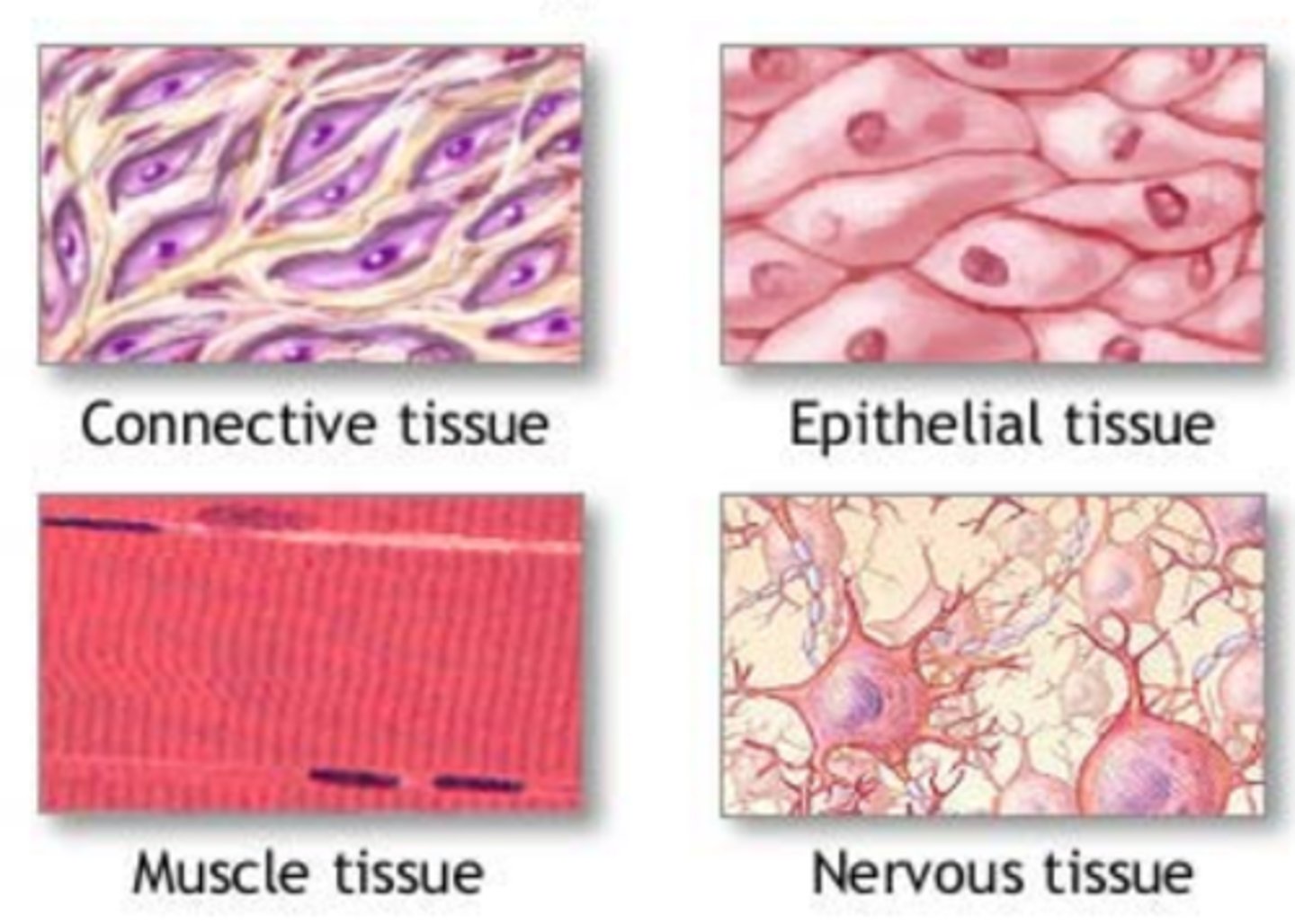
Organ
structure composed of two or more types of tissues that work together to perform a particular function.
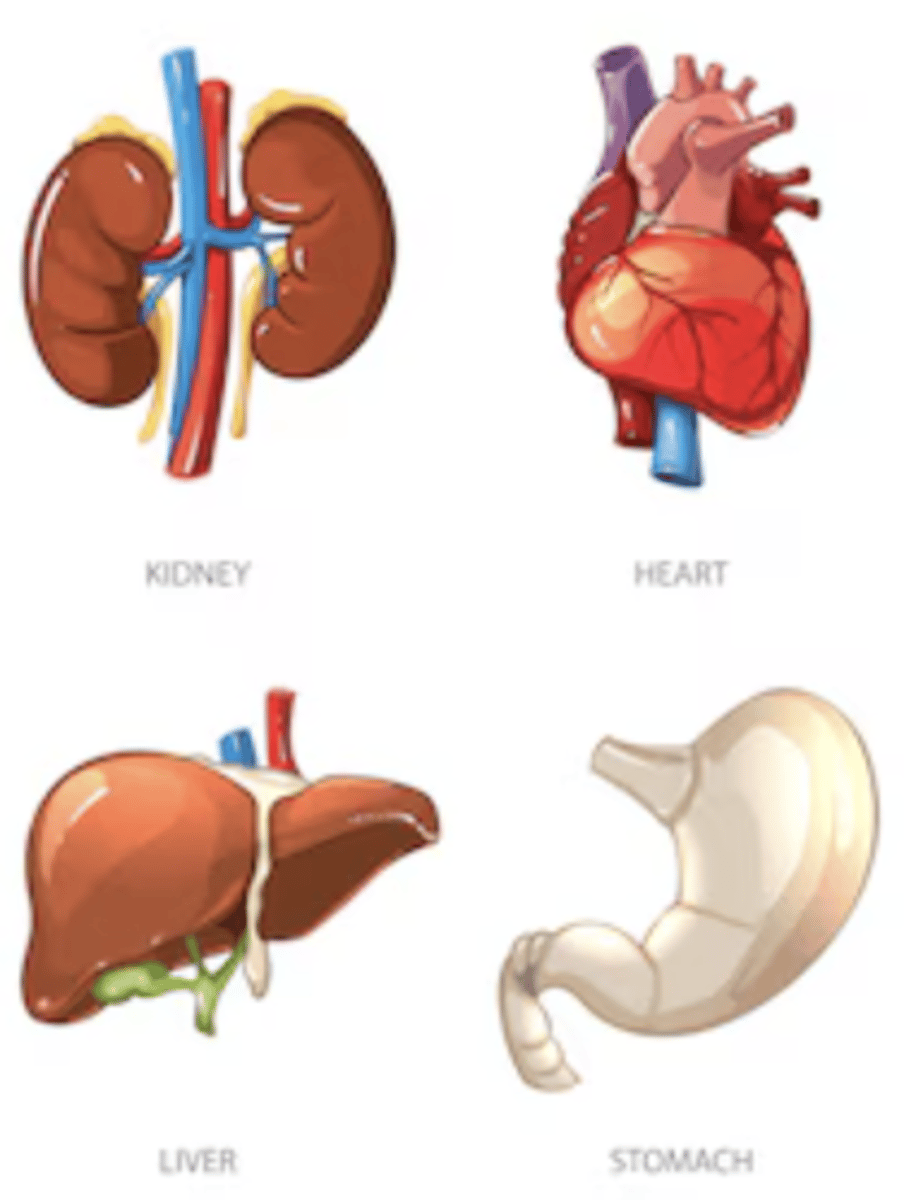
Organ System
group of organs that work together to perform a particular function for the organism.
Nervous System
organ system that consists of the brain, spinal cord, and a complex network of nerves that carries electrical messages throughout the body.
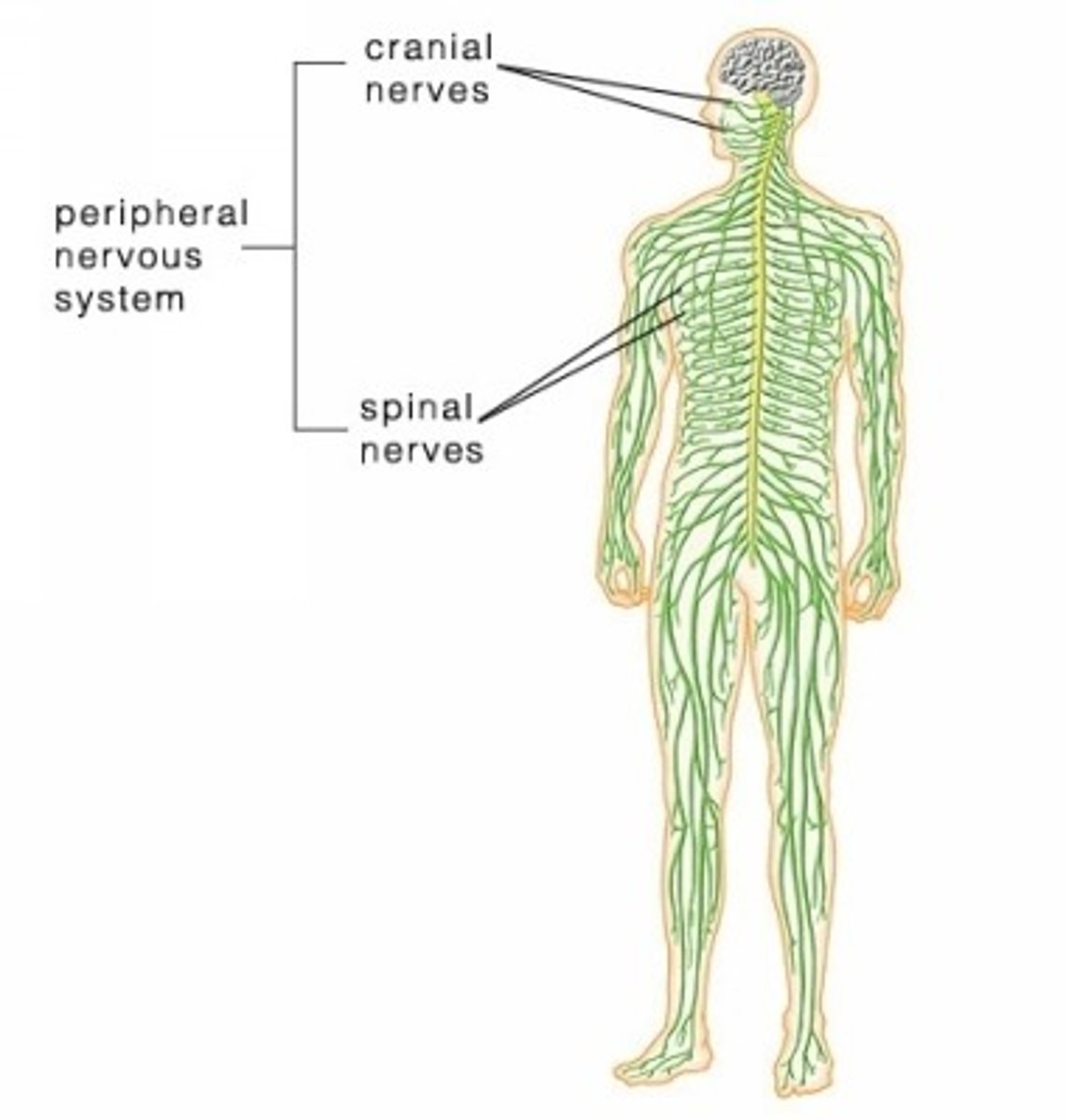
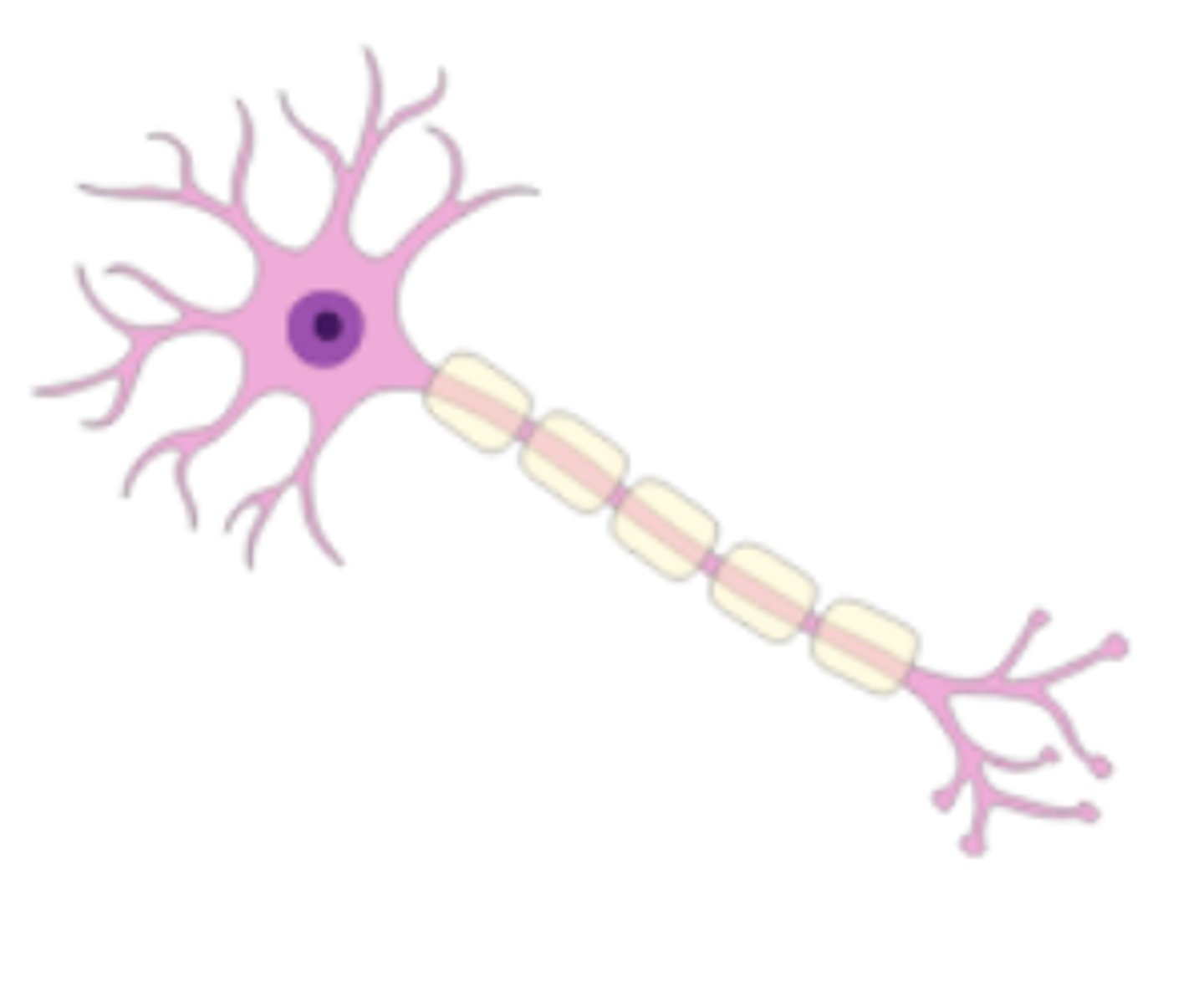
Neuron
a nerve cell, is the basic unit of the nervous system and is responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information through the body
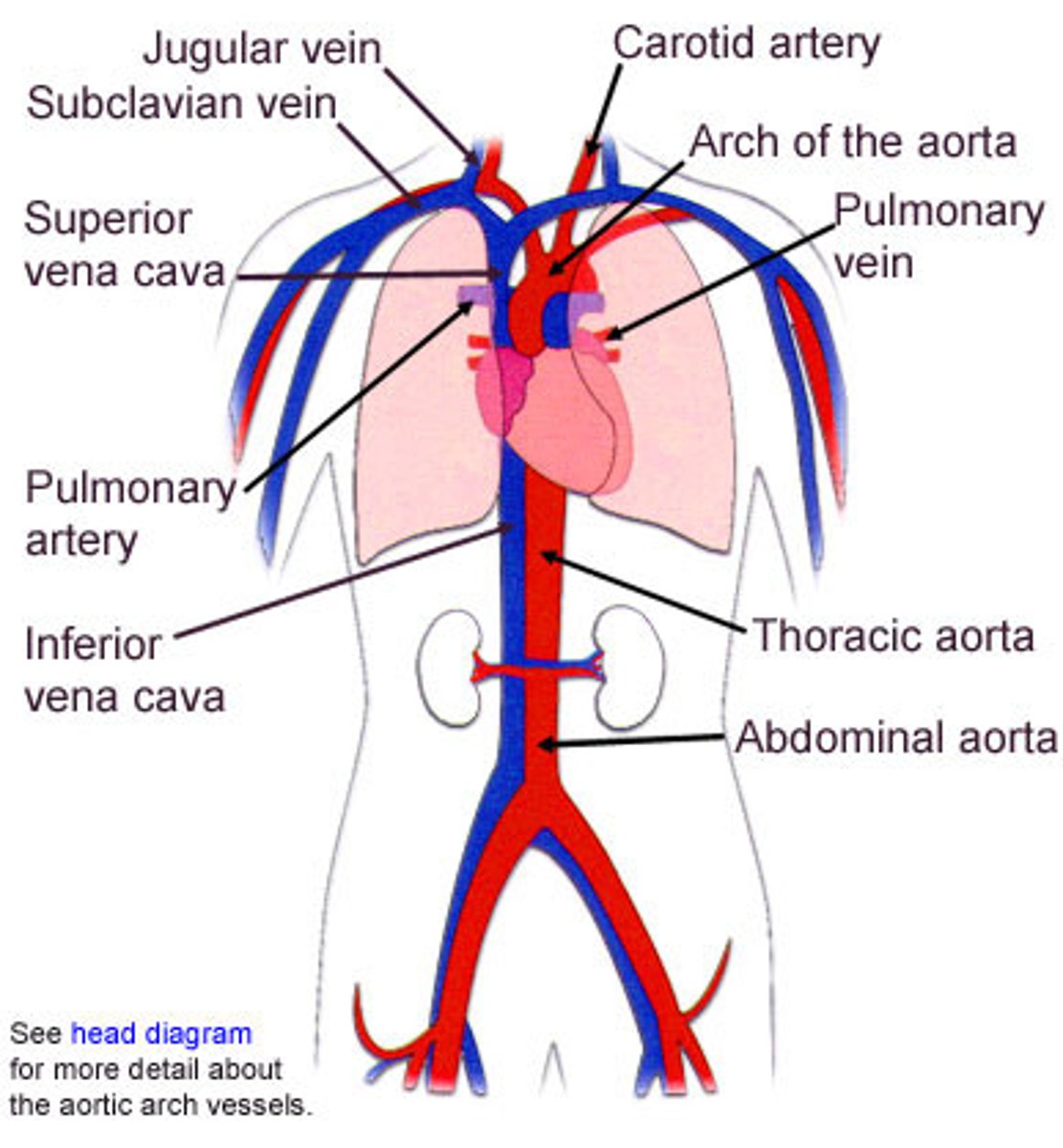
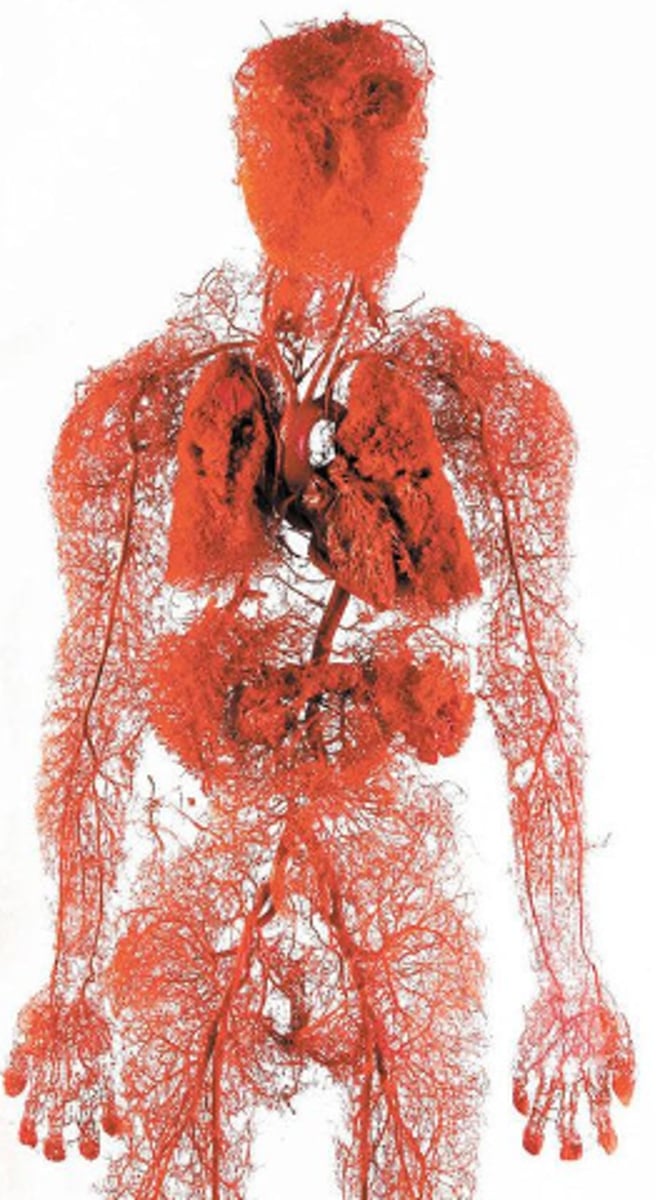
circulatory system
a system made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart.
circuit
a loop / track within your body that has a specific function
artery
carries blood away from the heart to capillaries, has a thick layer of muscle tissue
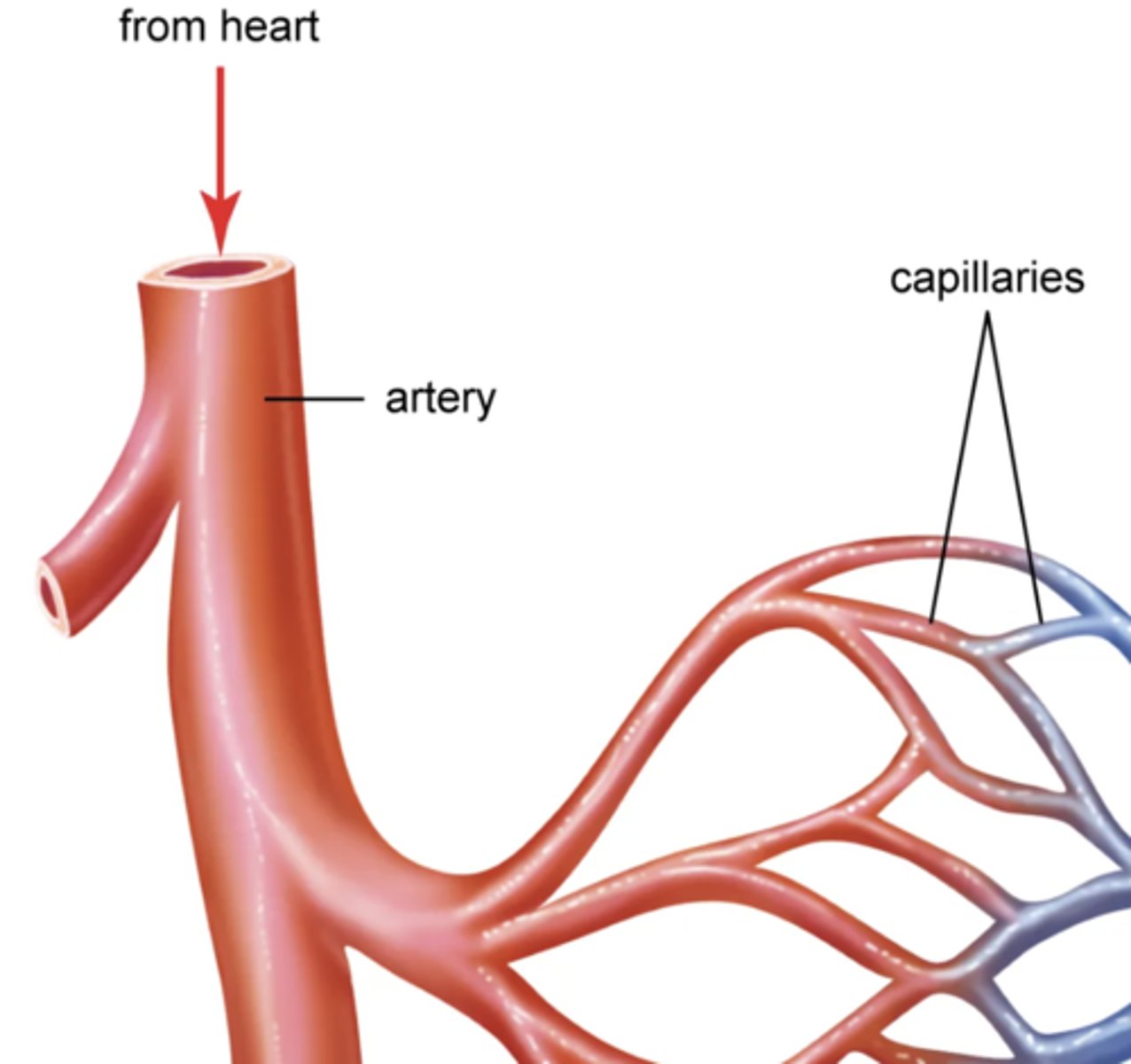
capillary
a very thin blood vessel, only 1 cell thick, that allows the exchange of molecules between tissues and blood.
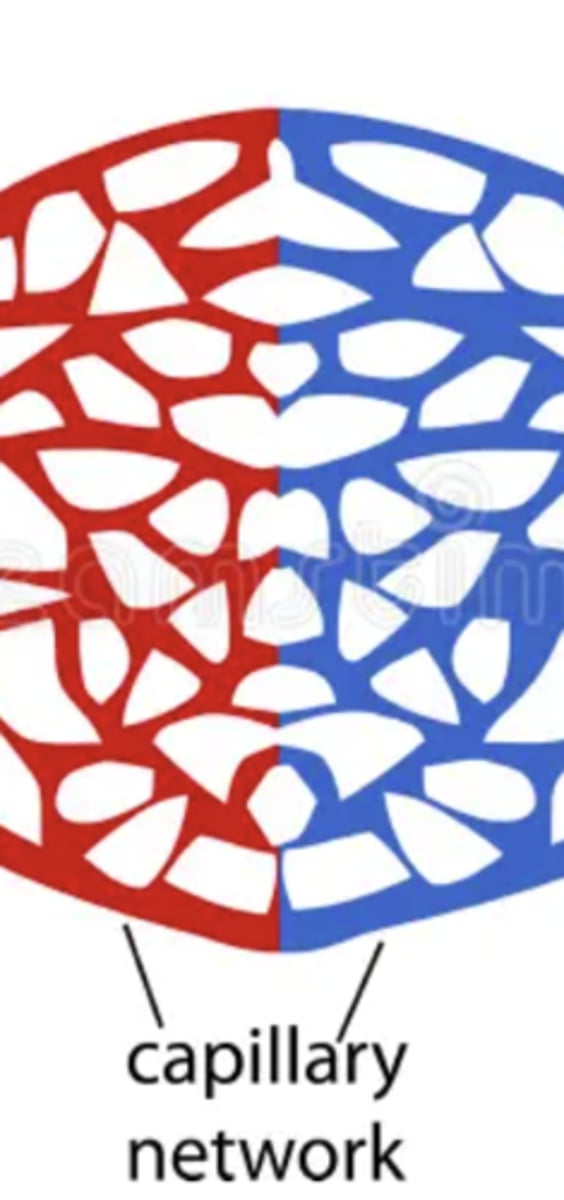

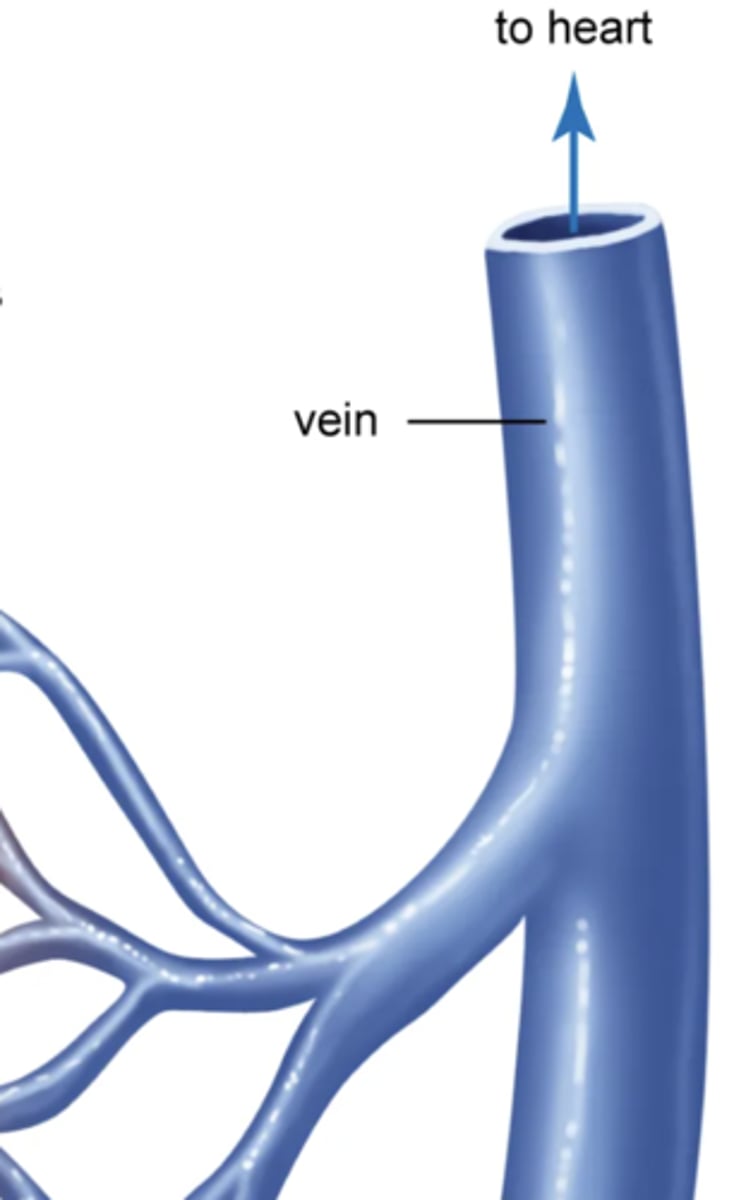
vein
carries blood from capillaries back to your heart, has a thin muscle tissue layer and valves
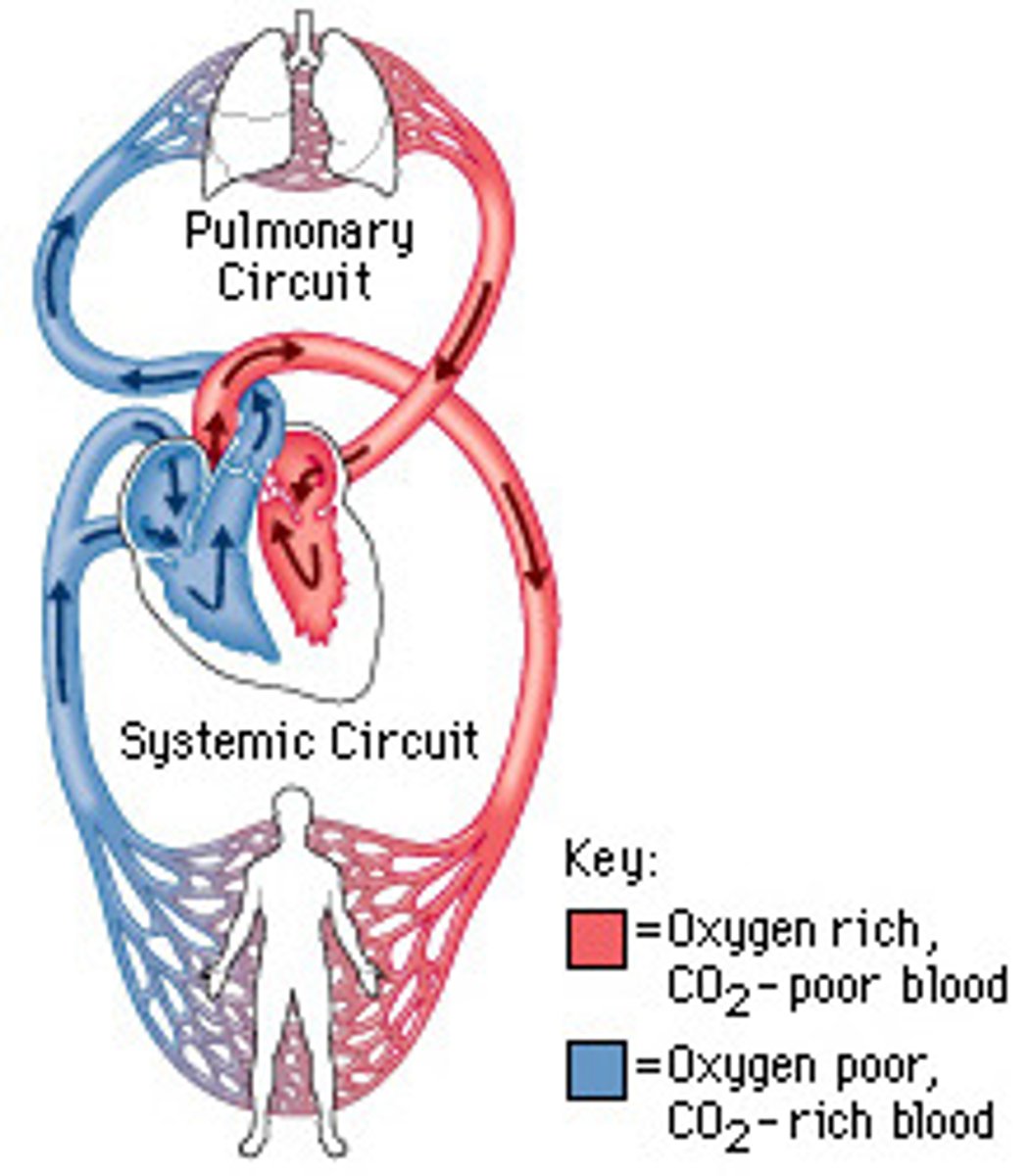
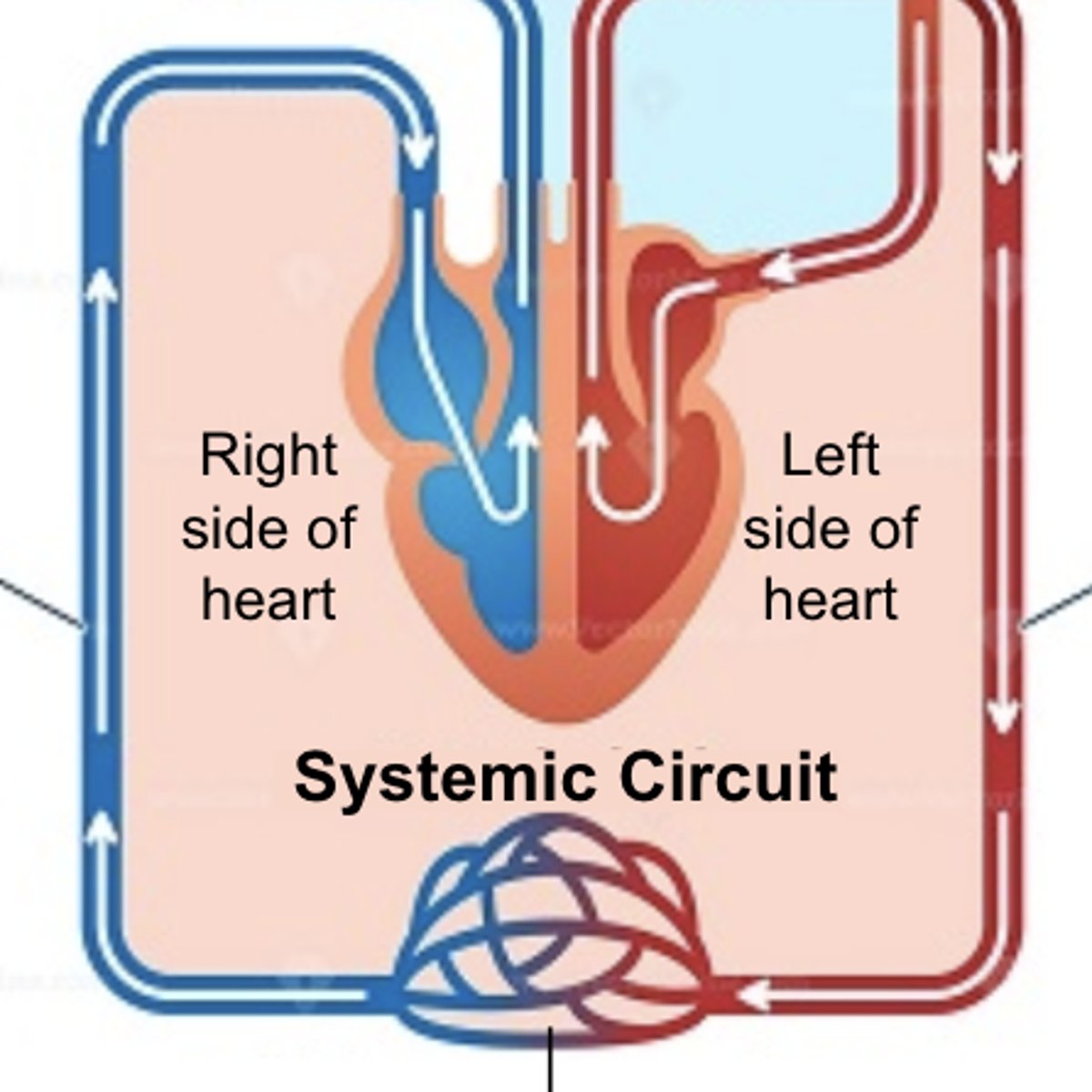
systemic circuit
the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and body
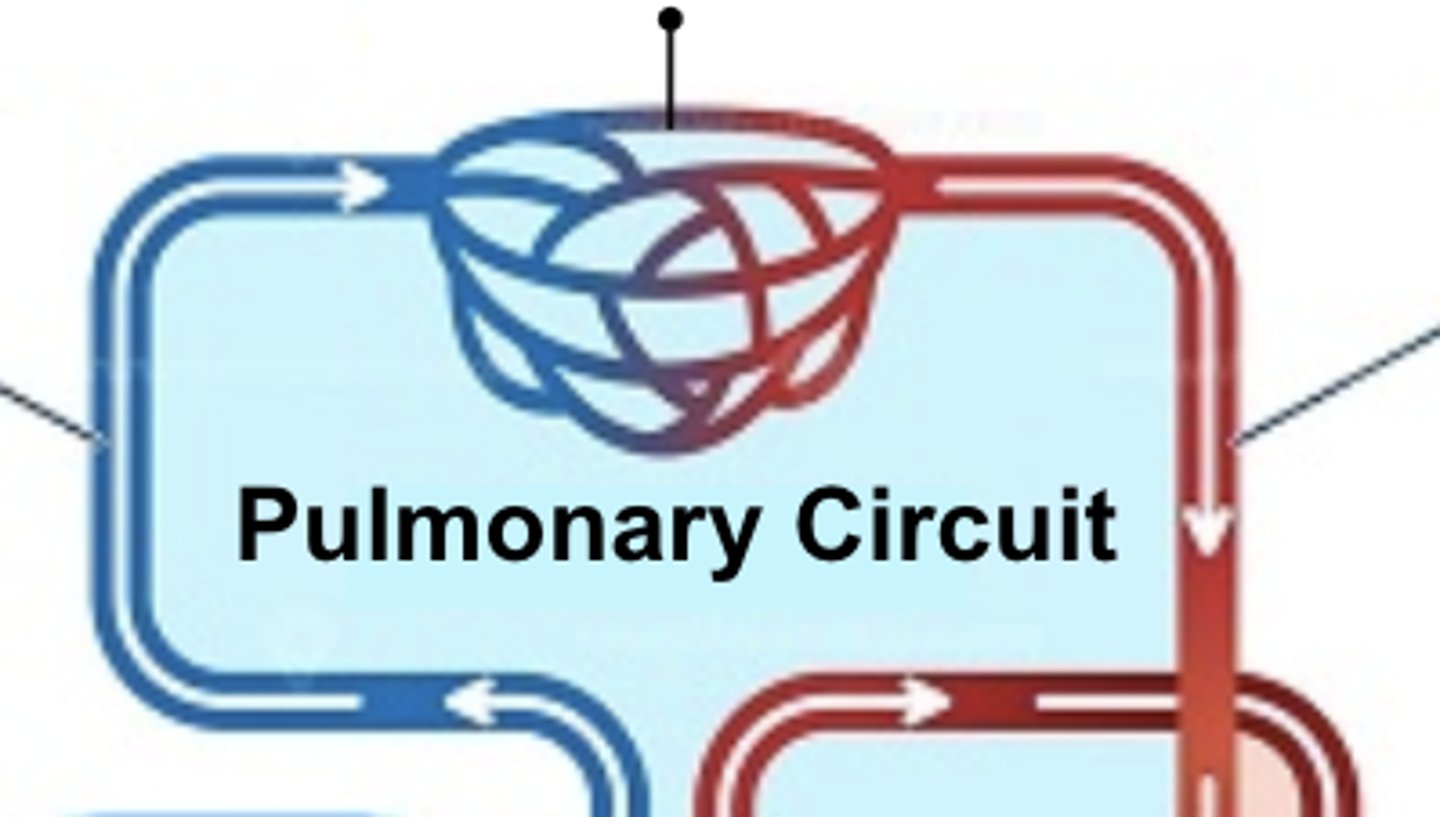
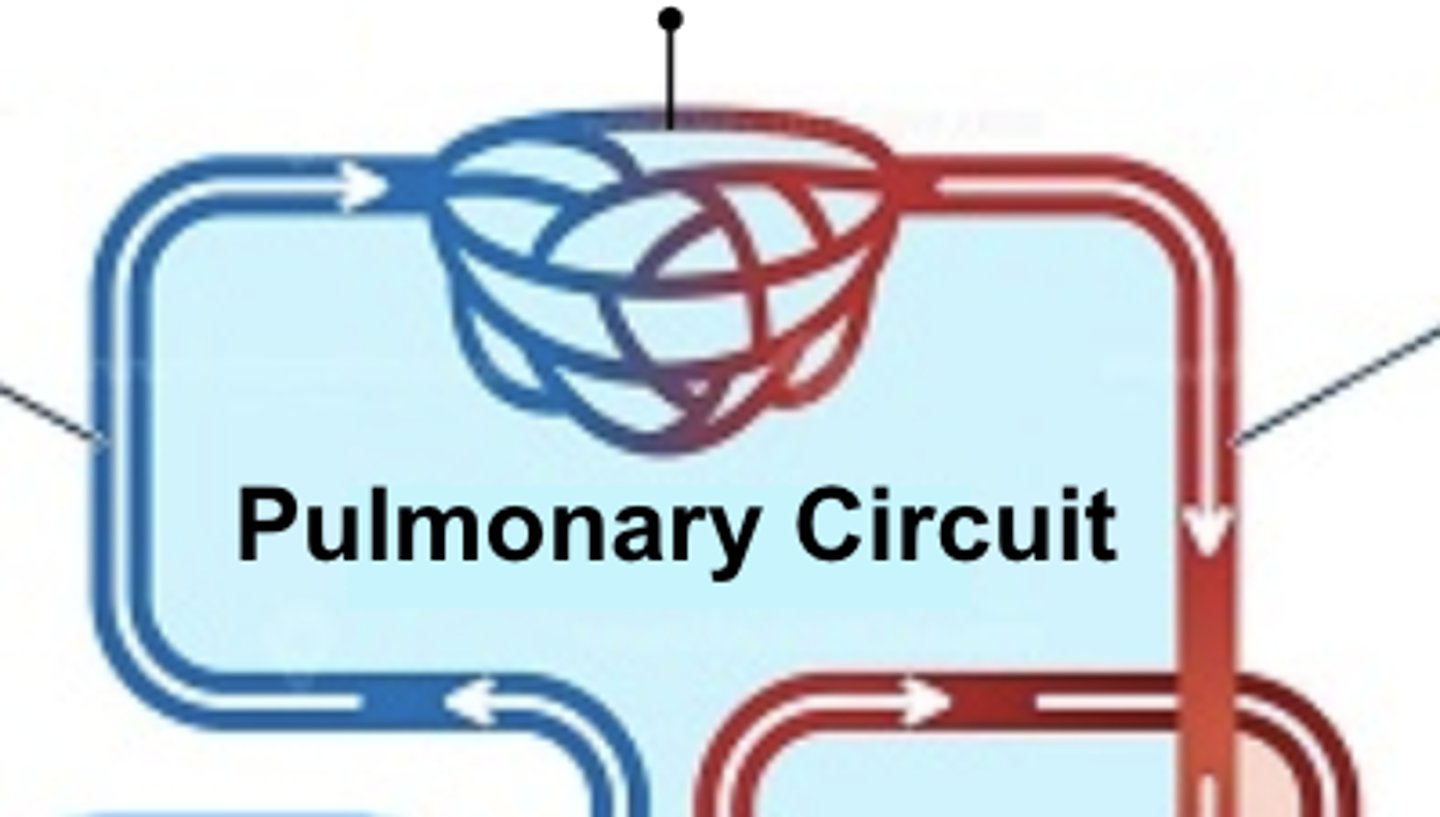
pulmonary circuit
the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and lungs
diffusion
the movement of anything generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
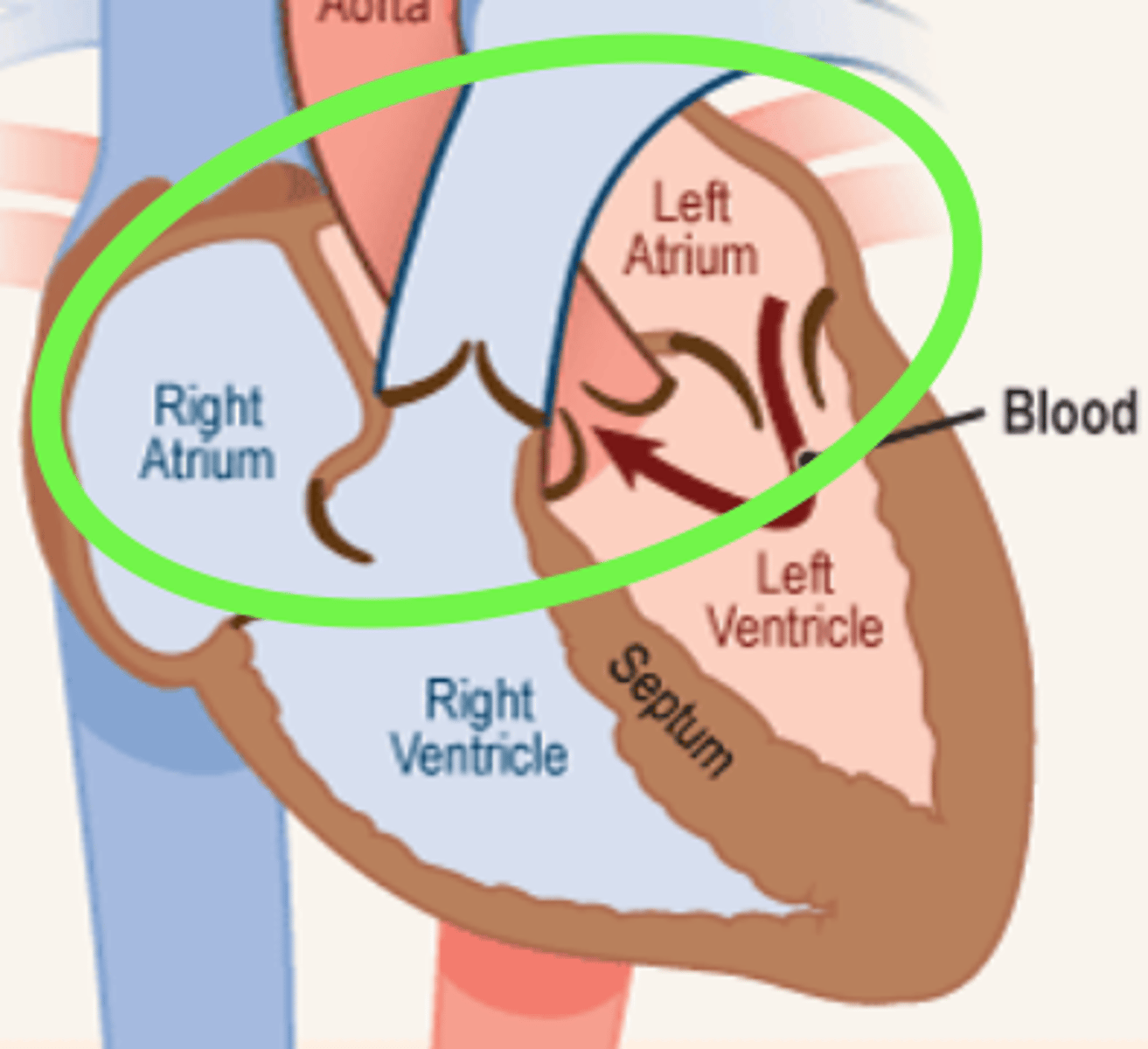
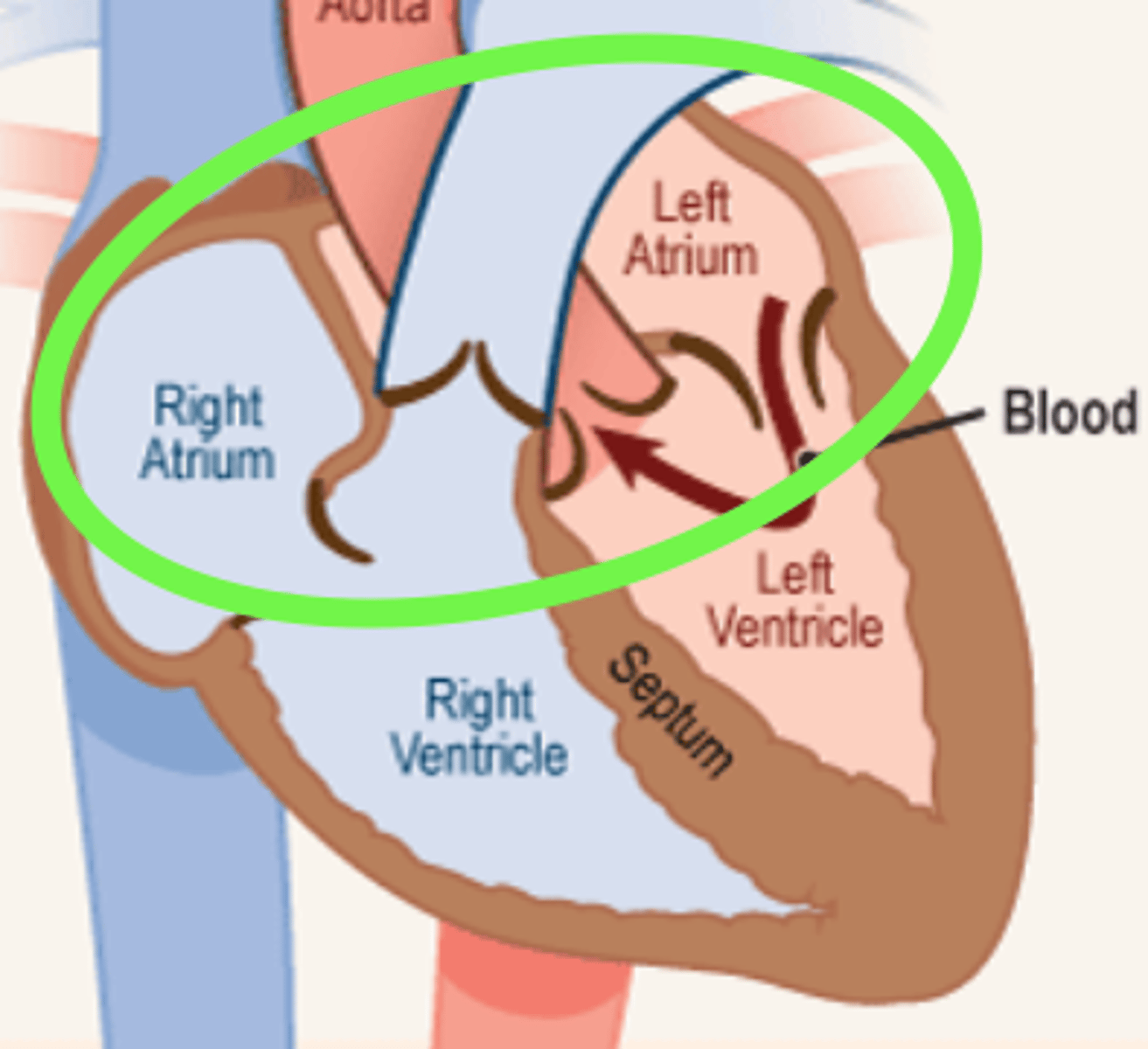
atrium (plural = atria)
heart chamber (at the top of the heart) that receives blood into the heart and drives it into a ventricle
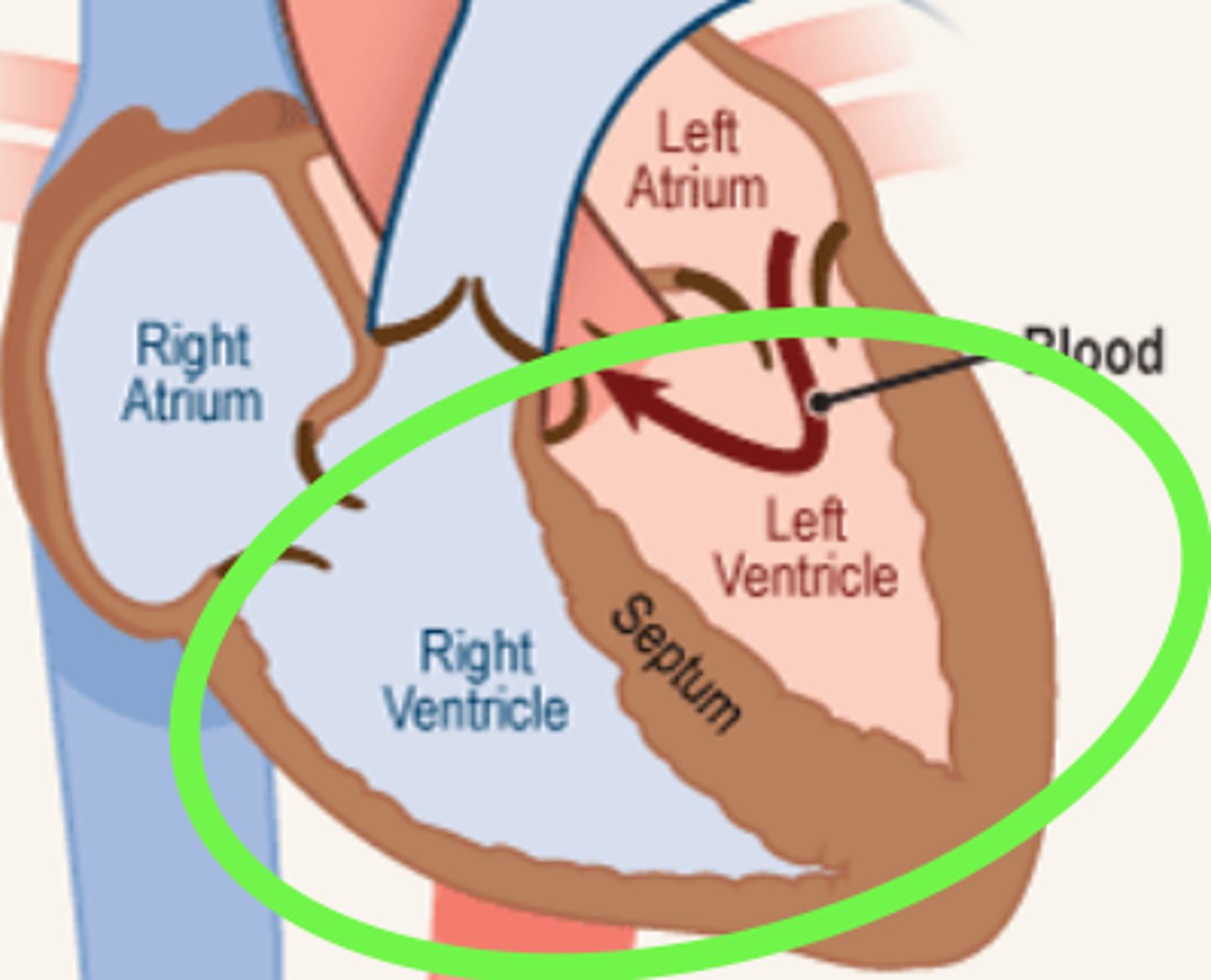
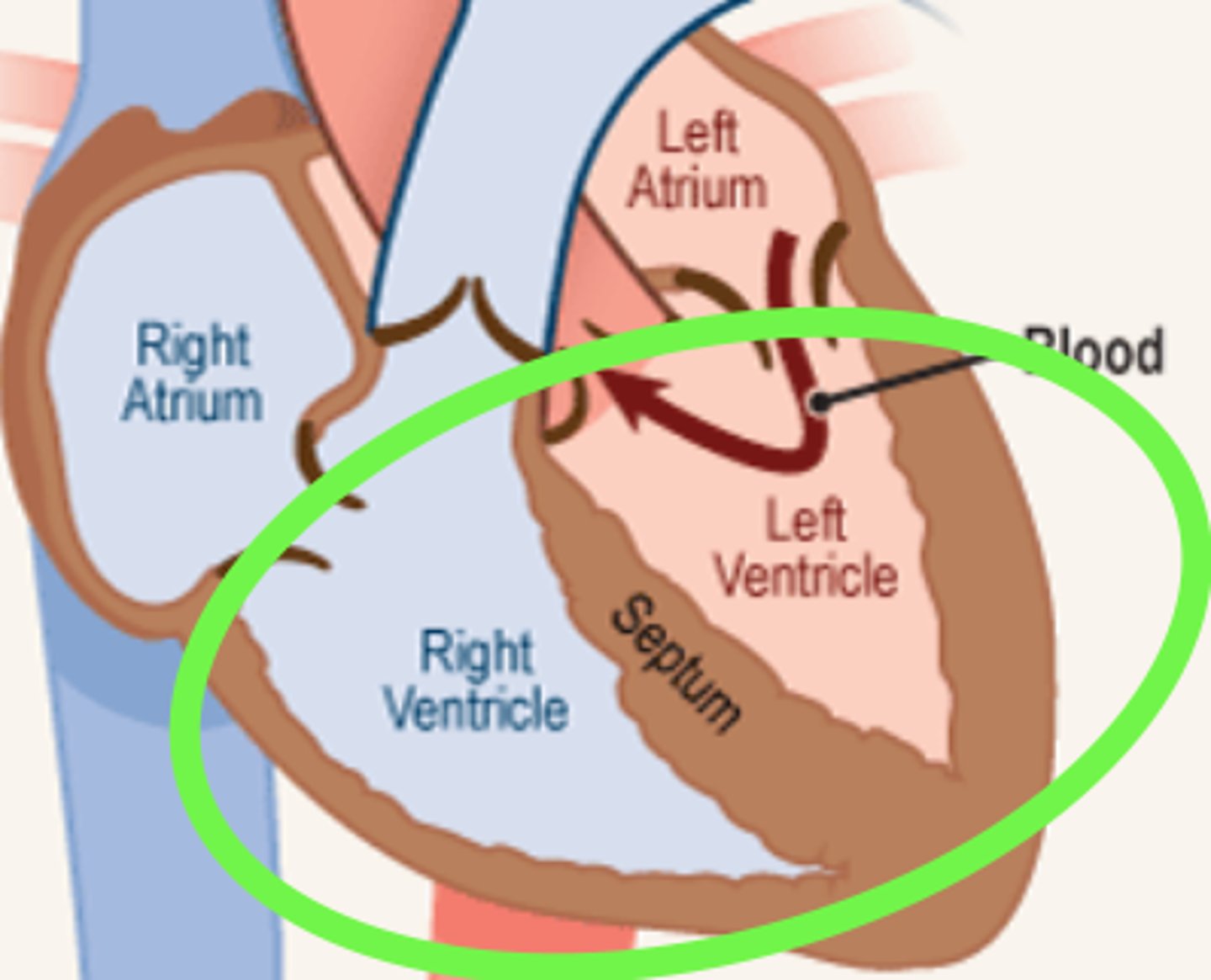
ventricle
heart chamber (at the bottom of the heart) that pumps blood out of the heart and into the circulatory system
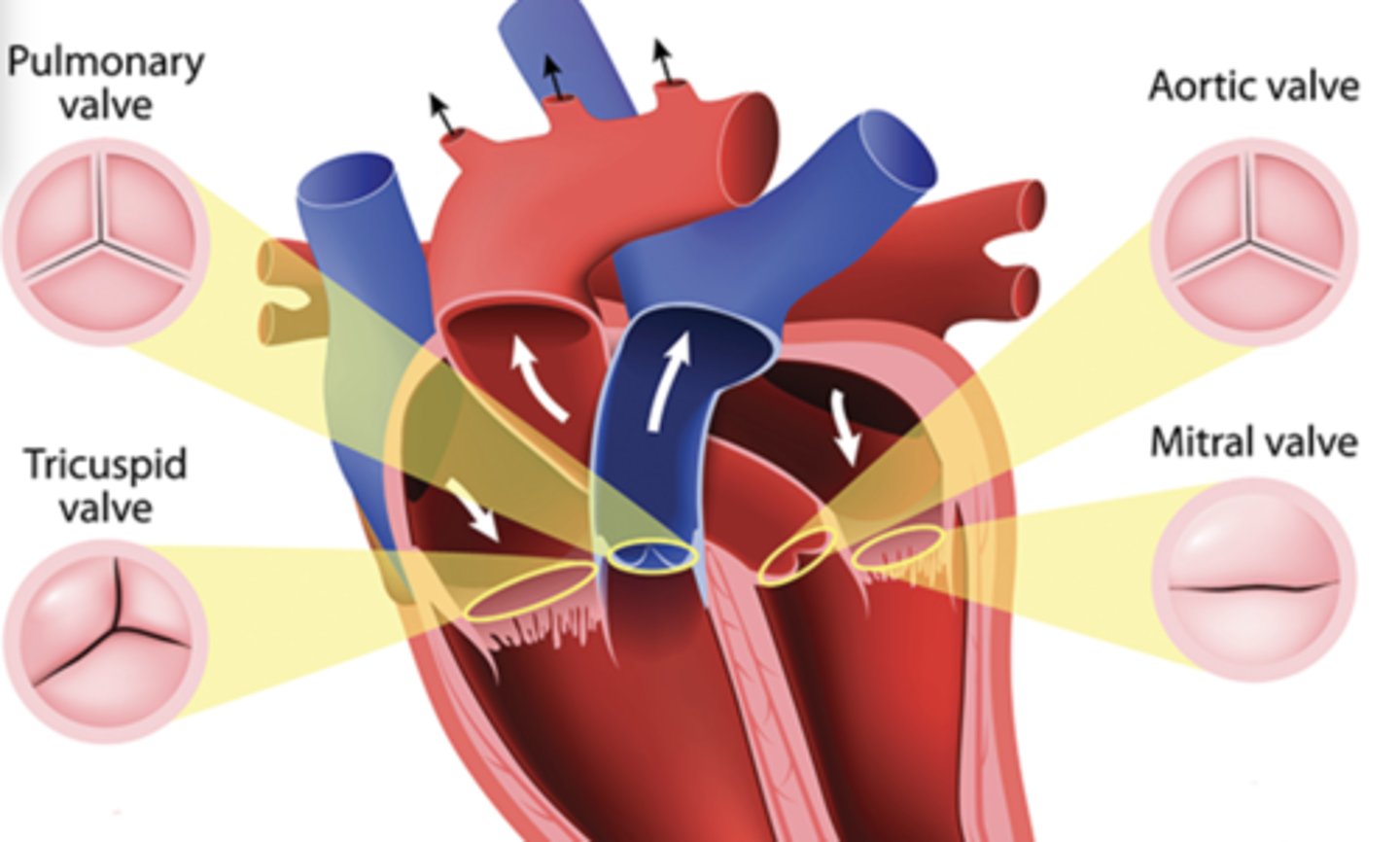
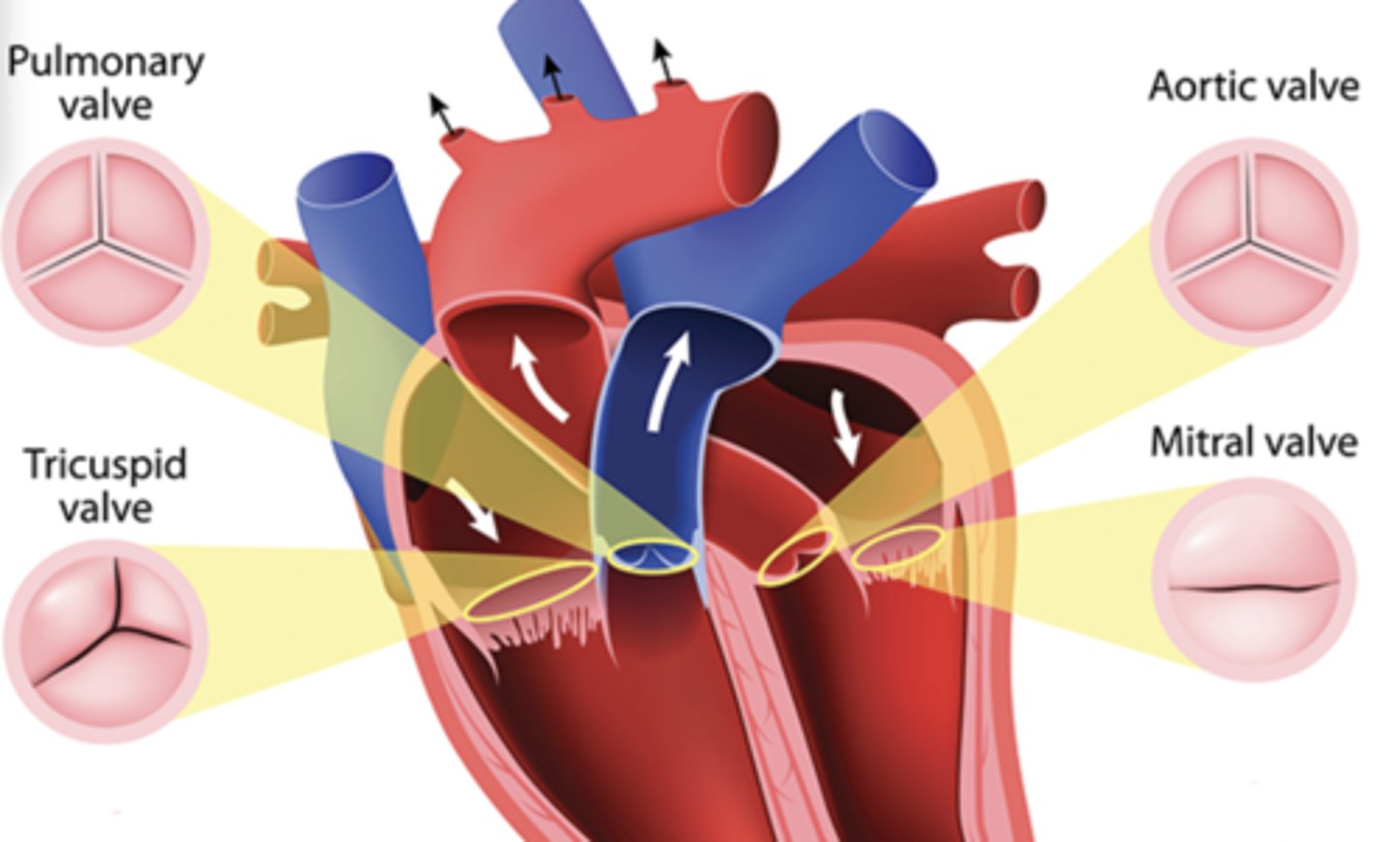
valve
a type of flap that act as one-way inlets for blood coming into a ventricle and one-way outlets for blood leaving a ventricle.
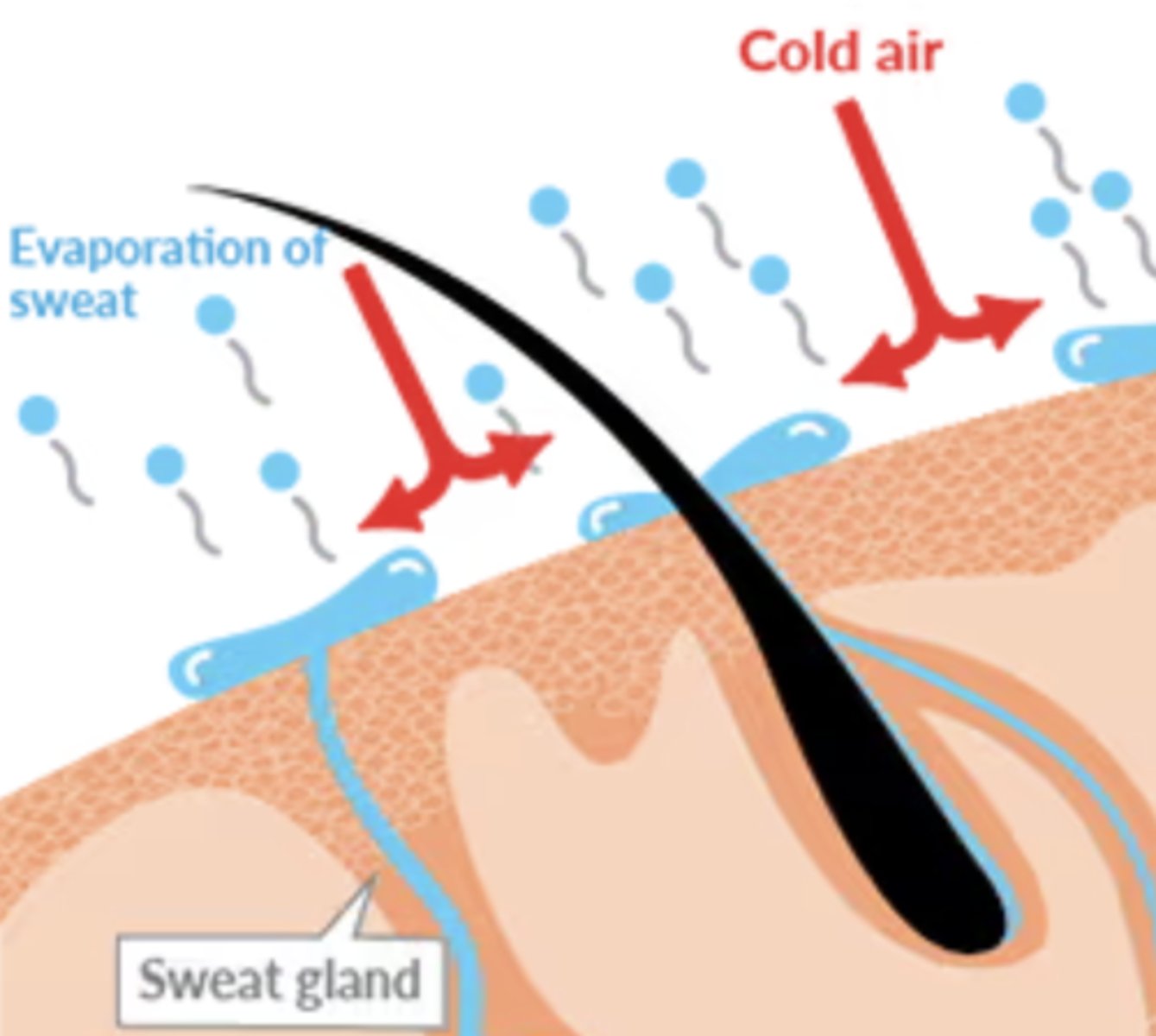
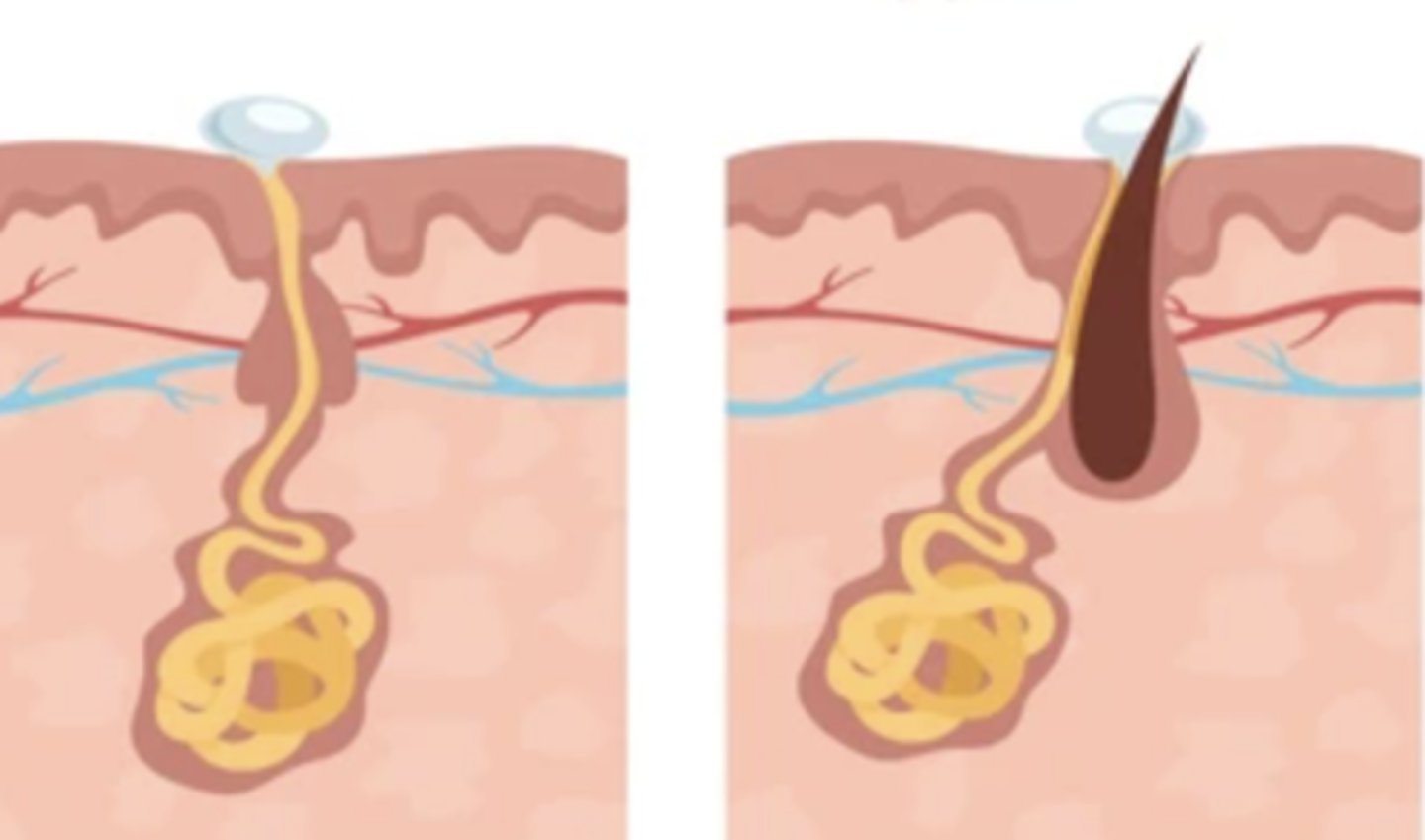
sweat gland
gland in the skin that produces the salty fluid called sweat, which excretes (gets rid of) wastes and helps cool the body
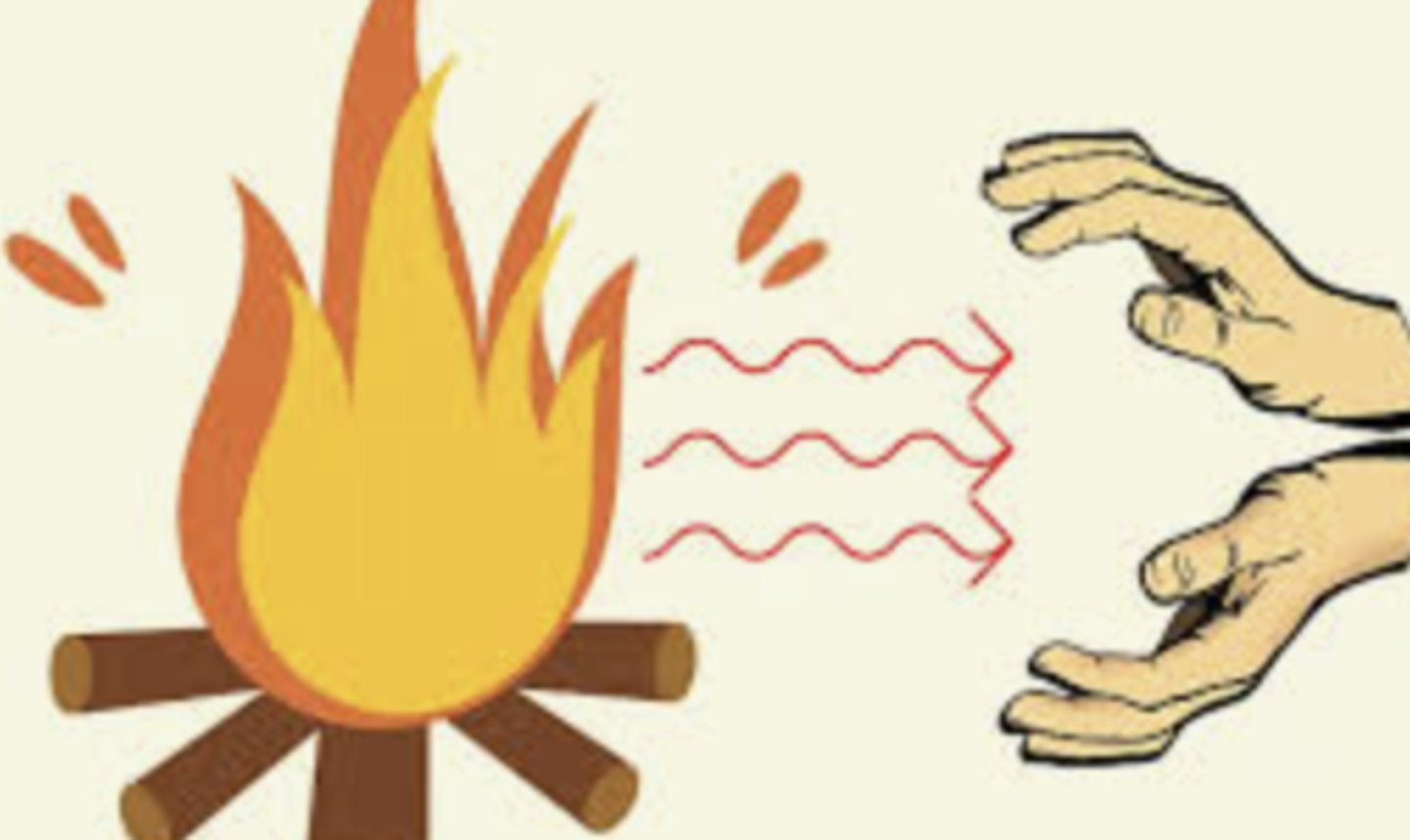
radiation (of heat)
heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves (for instance from your skin to the environment)
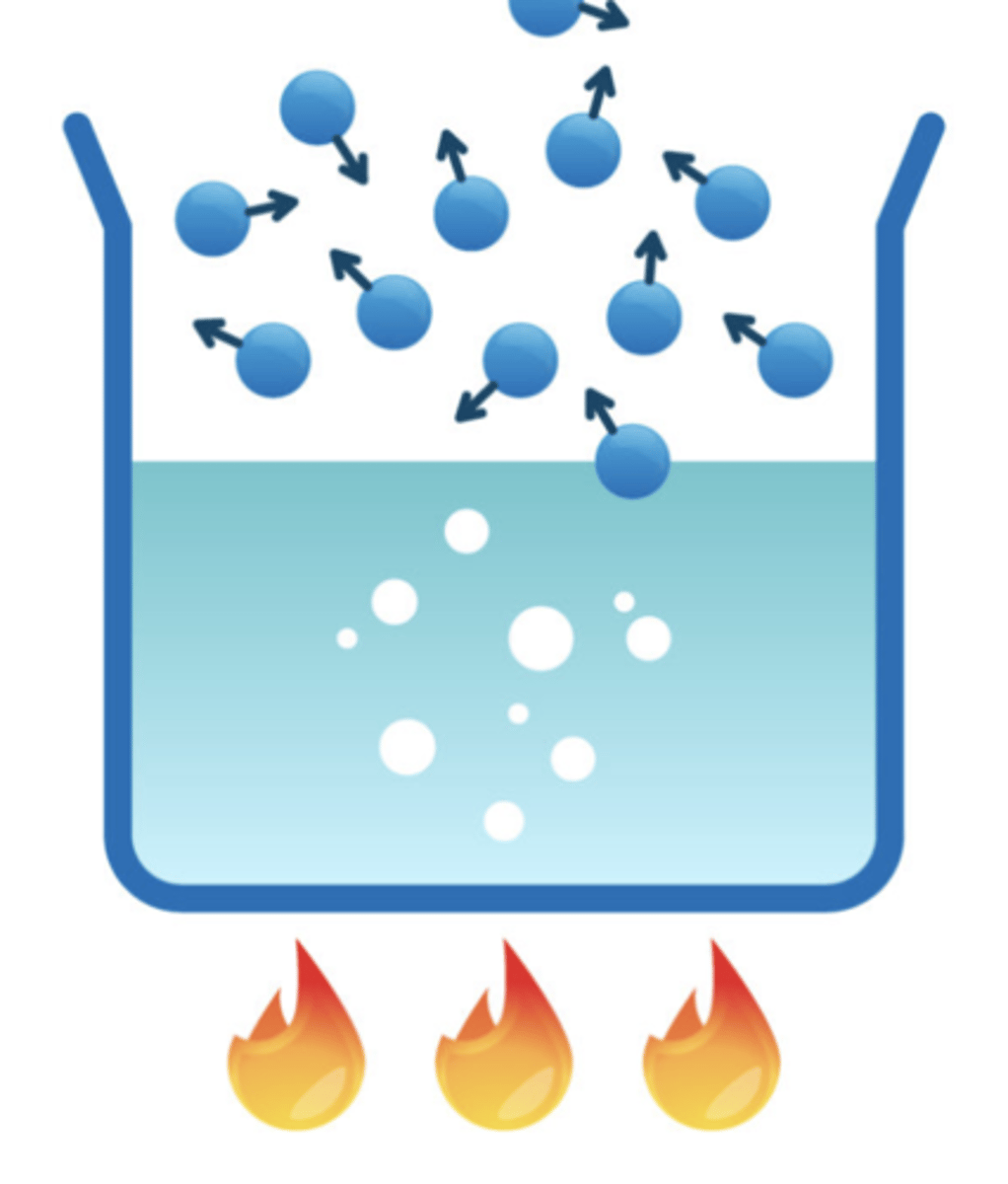
evaporation
the process where a liquid turns into a vapor (gas).; this process requires heat energy
evaporative cooling
reduction in temperature resulting from the evaporation of a liquid
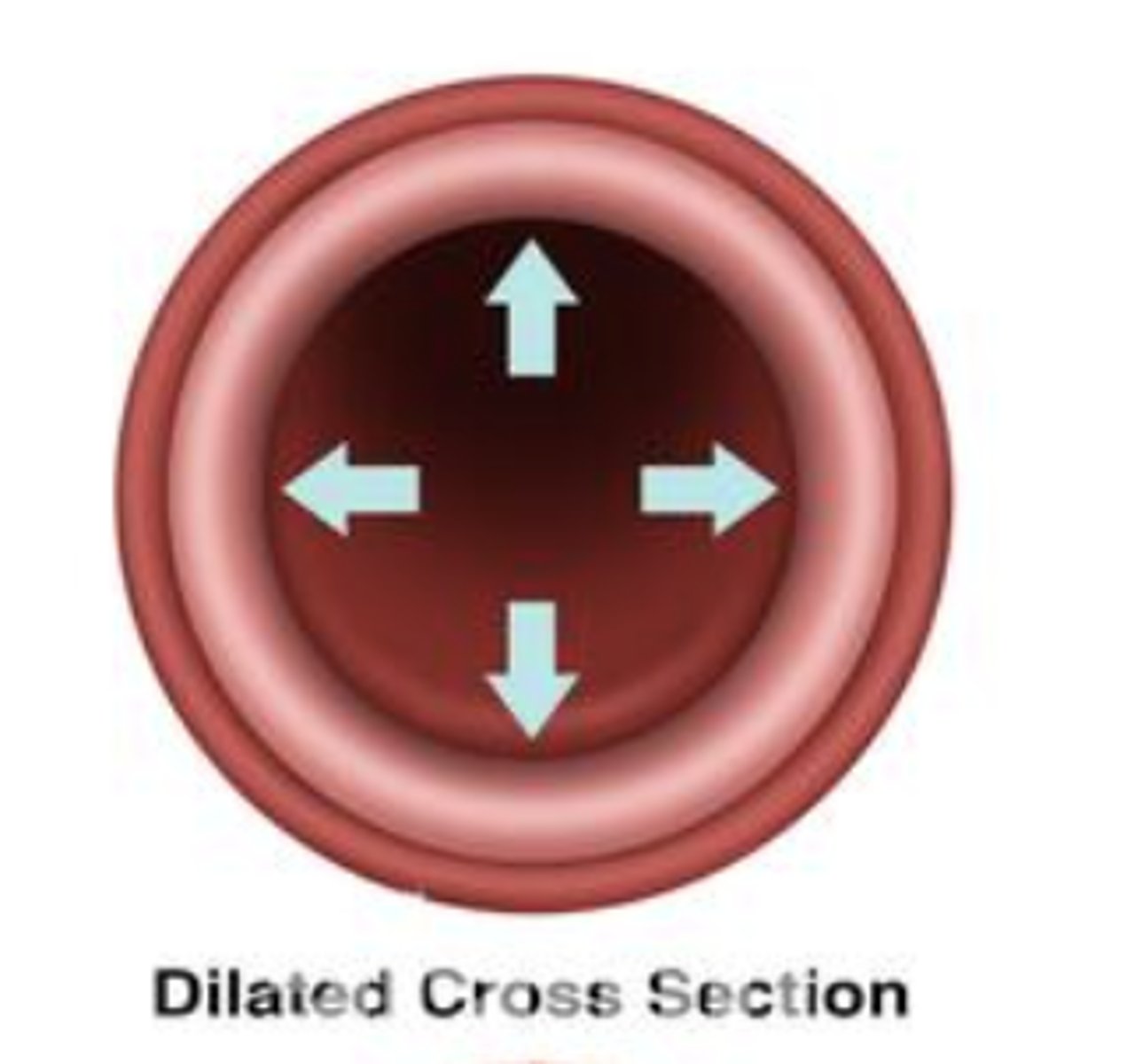
dilate
to relax or make bigger/wider
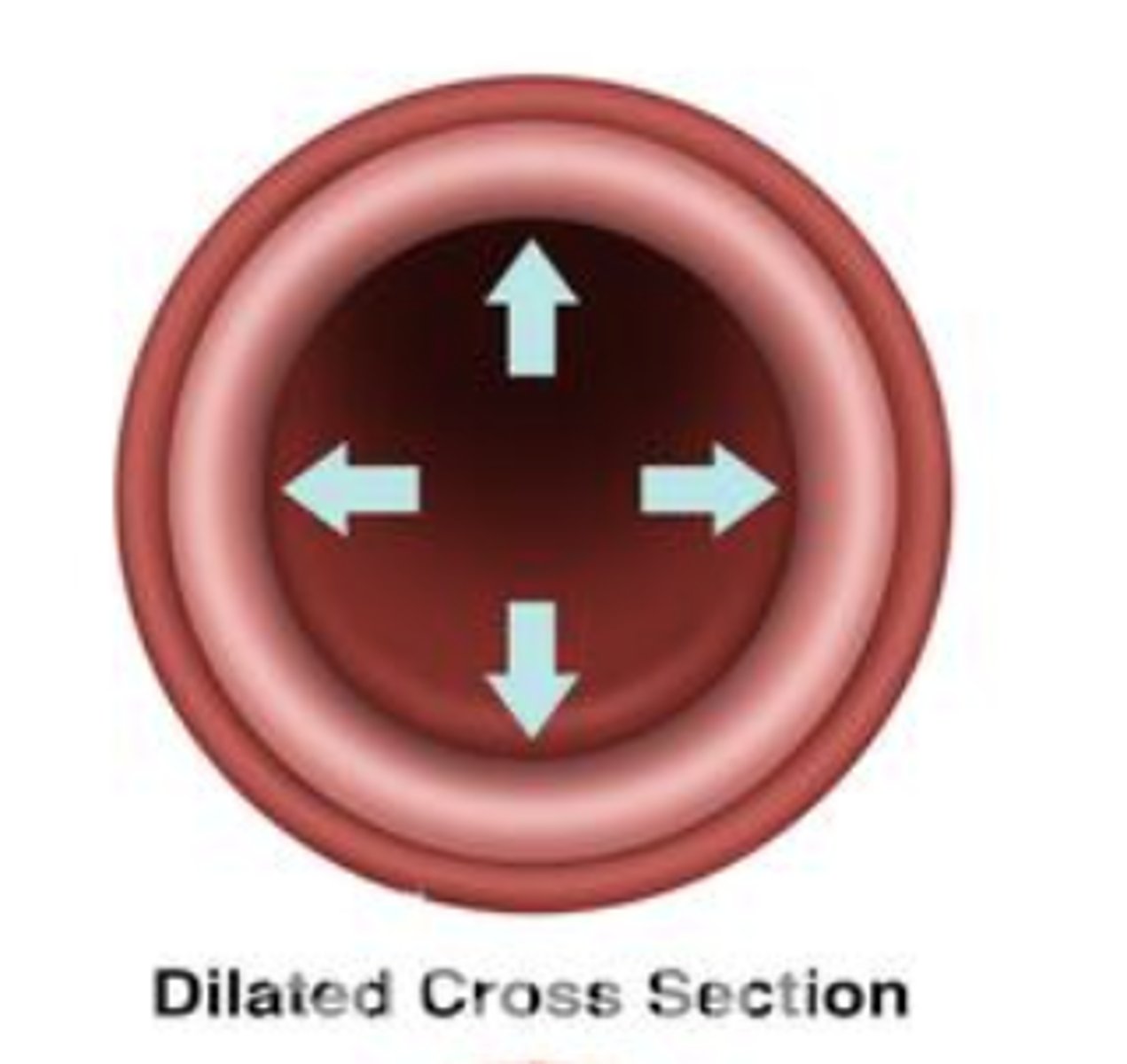
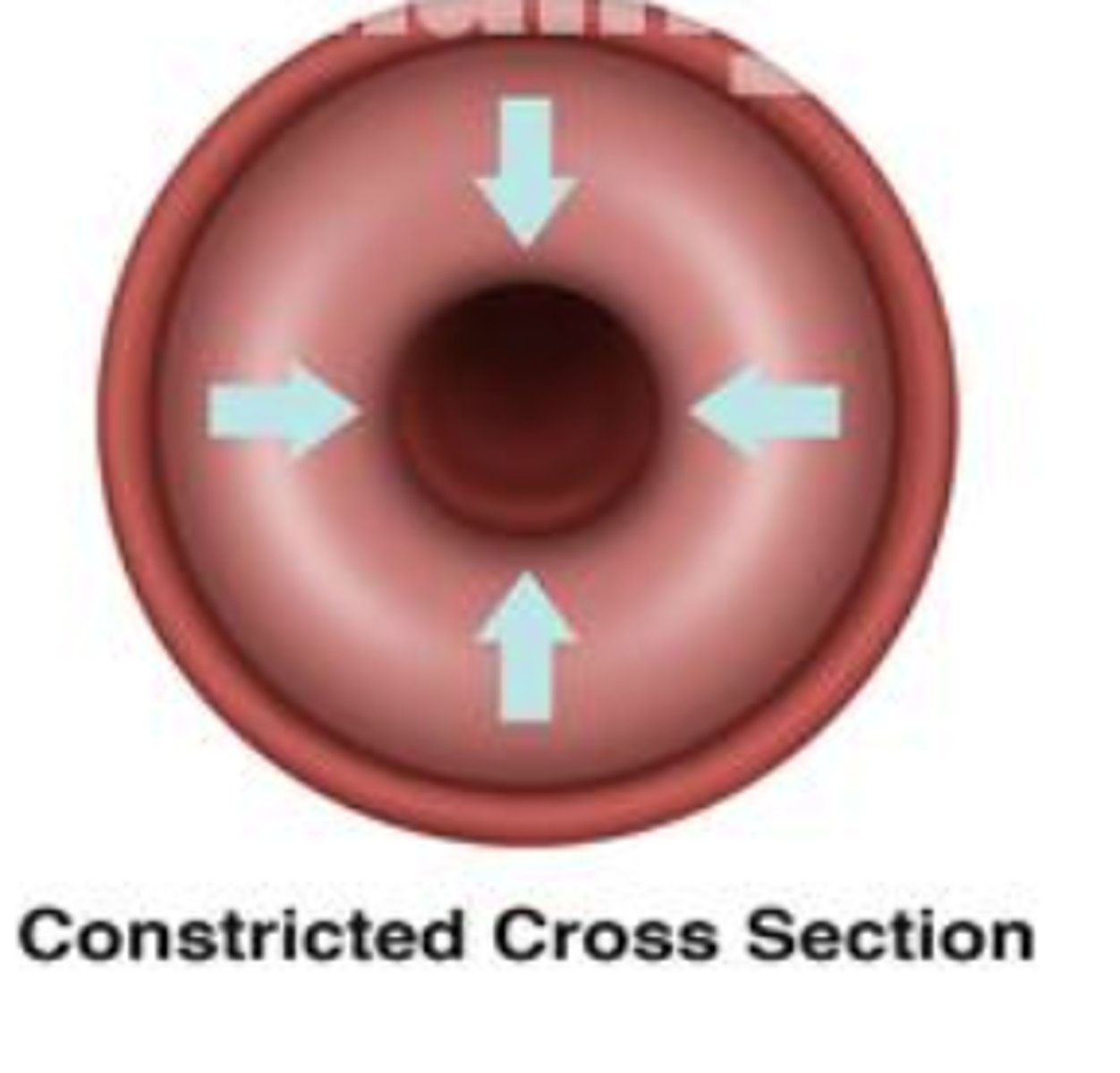
constrict
to squeeze or make smaller/narrower
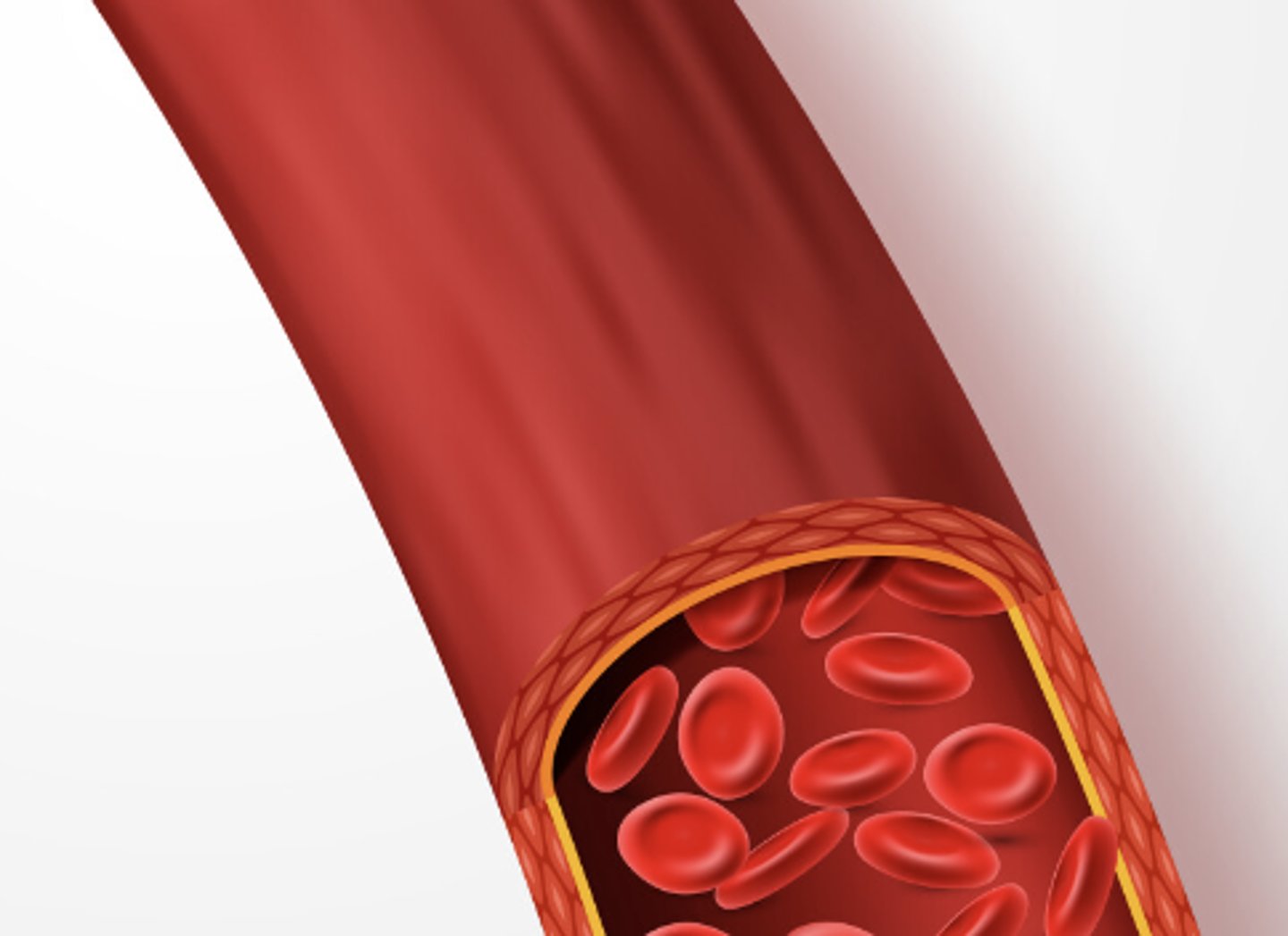
blood vessel
a tubular (pipe-shaped) structure carrying blood that connects the heart to the rest of your body (e.g. a vein, artery, or capillary)
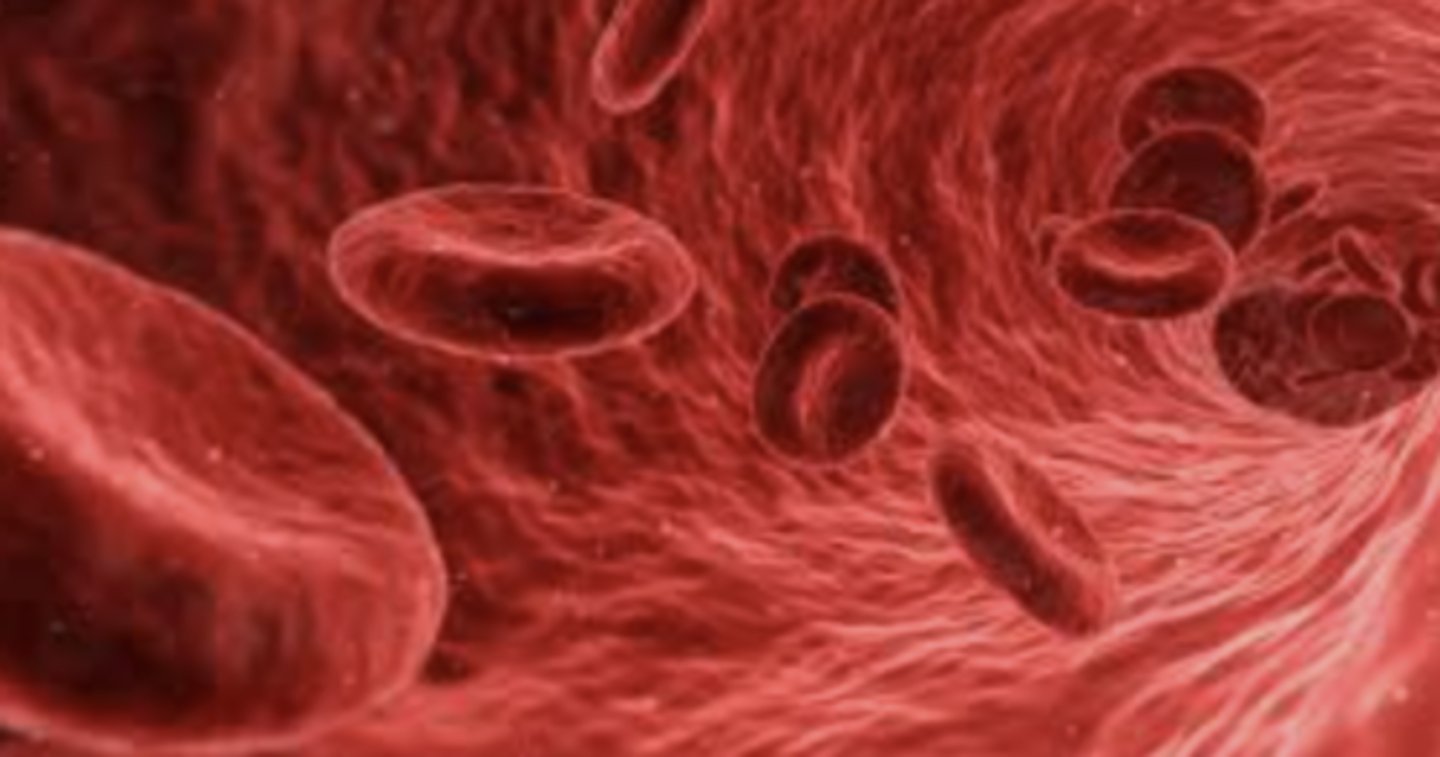
blood
carries gases, nutrients and heat to and from cells in vessels called capillaries
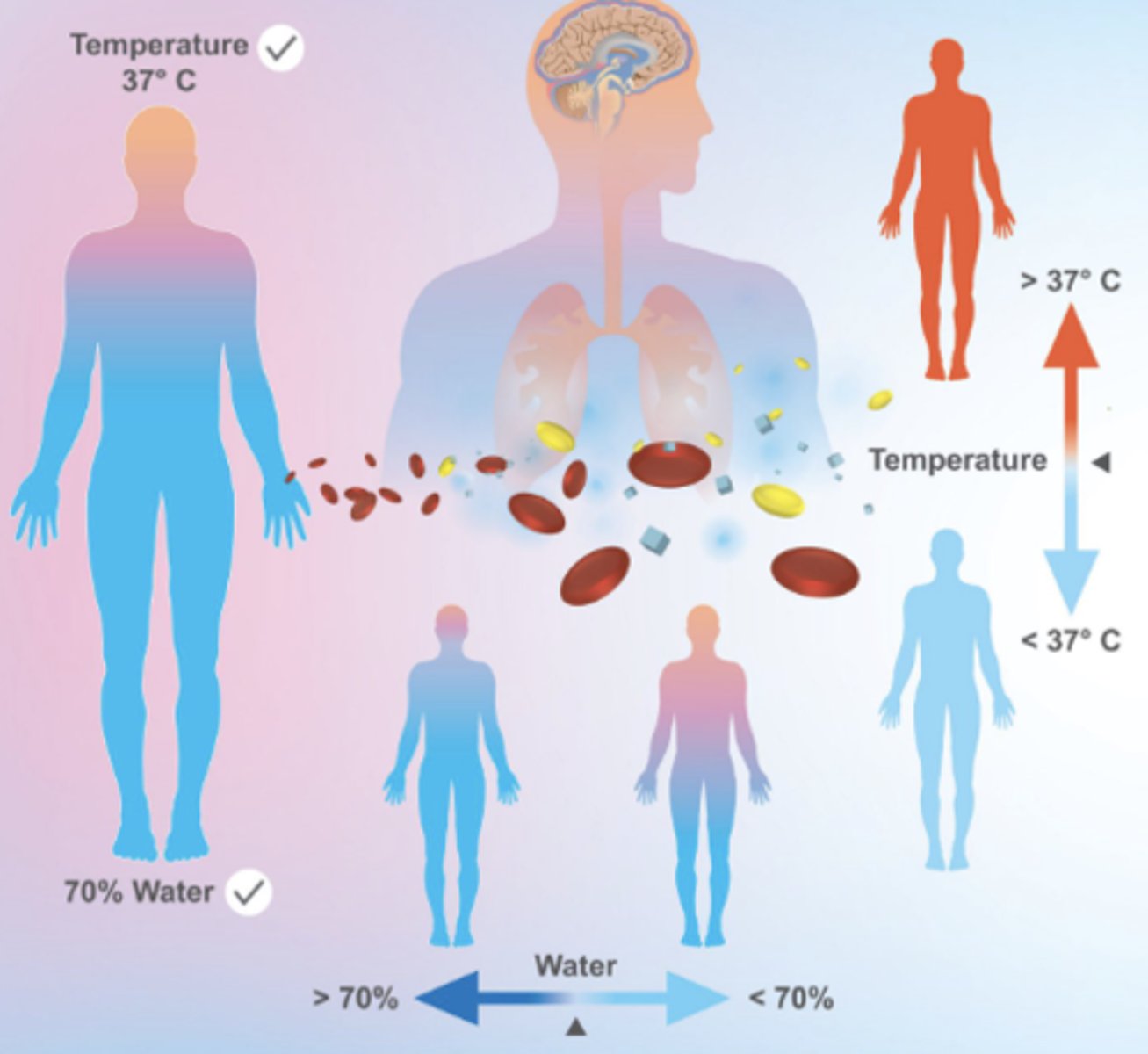
homeostasis
the process where organ systems work to maintain (keep) a stable internal environment.
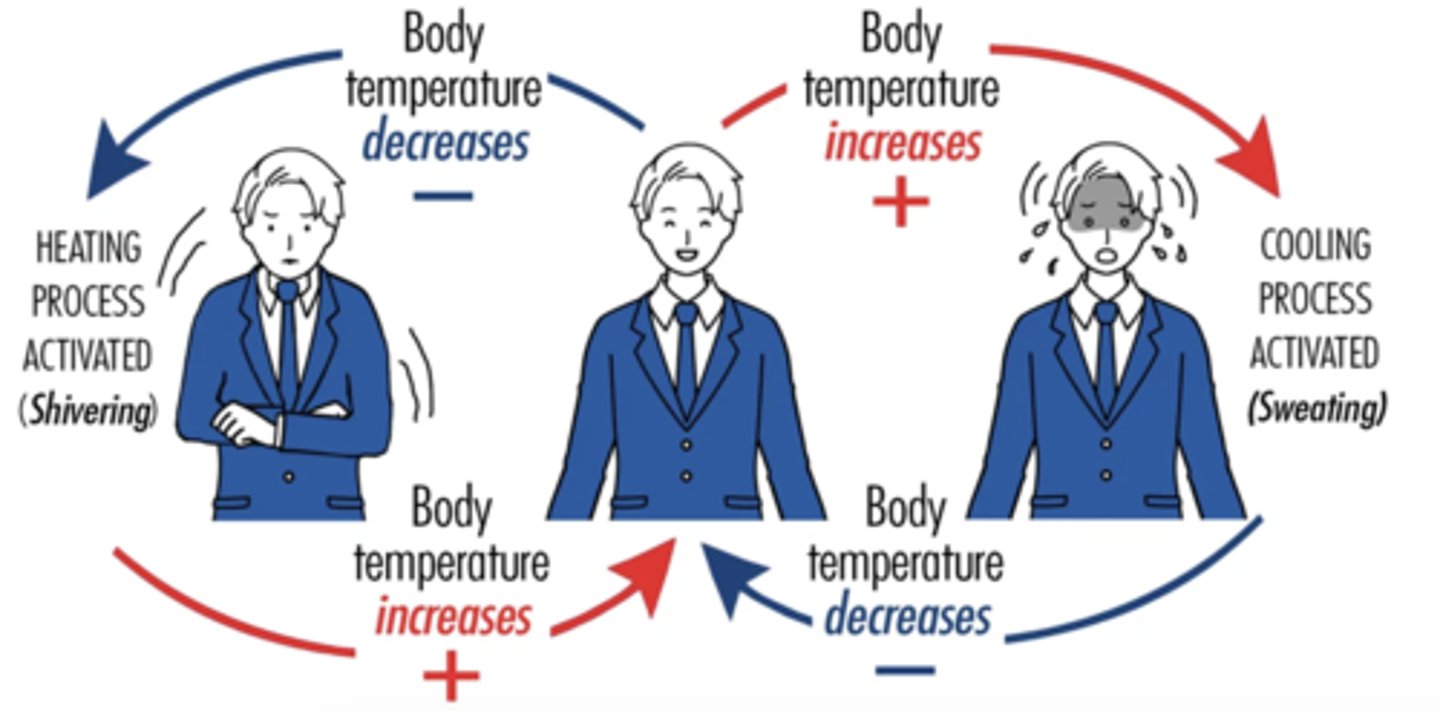
negative feedback
a response to a stimulus that keeps a variable close to a set value (it "shuts off" or "turns on" a system when it varies from a set value)
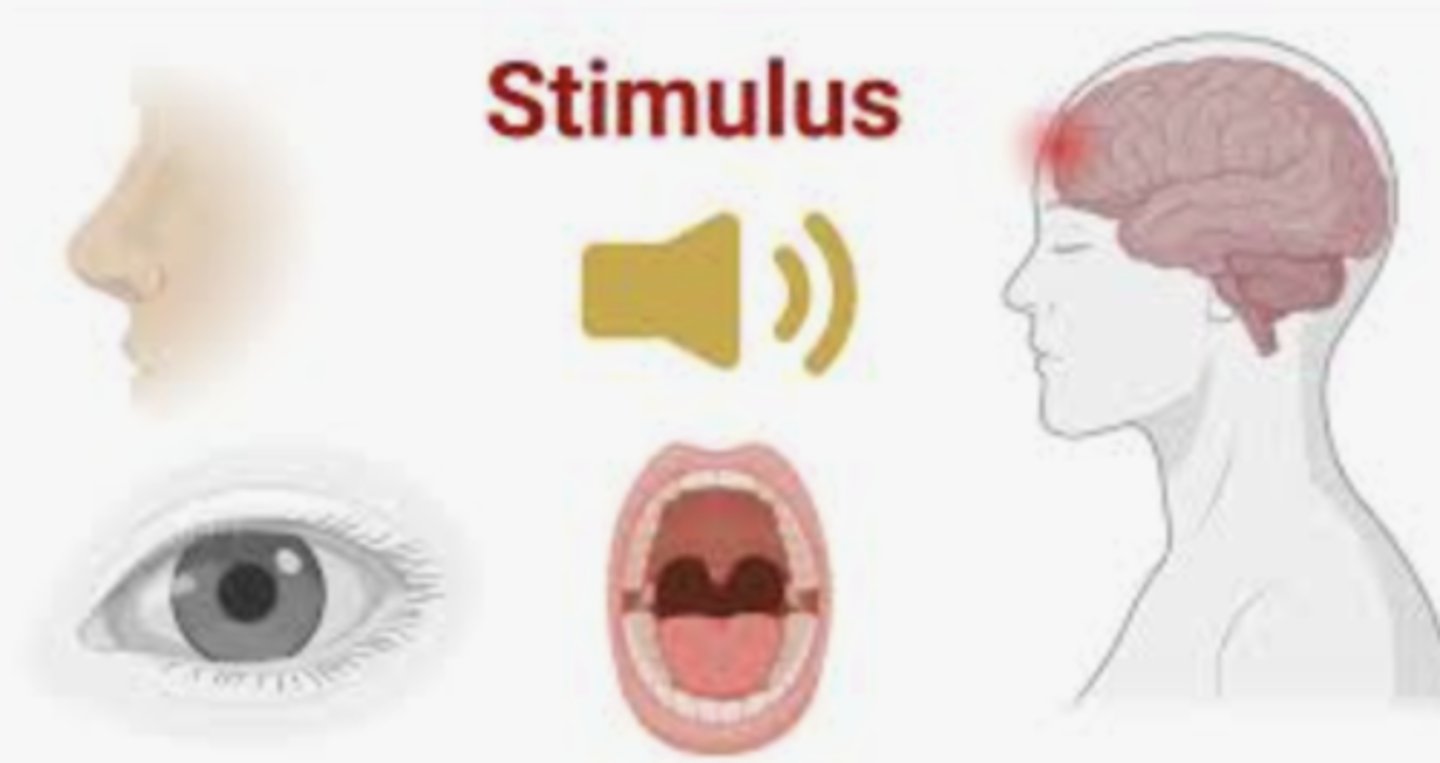
stimulus (plural: stimuli)
something that triggers a behavior or causes a reaction in an organism.
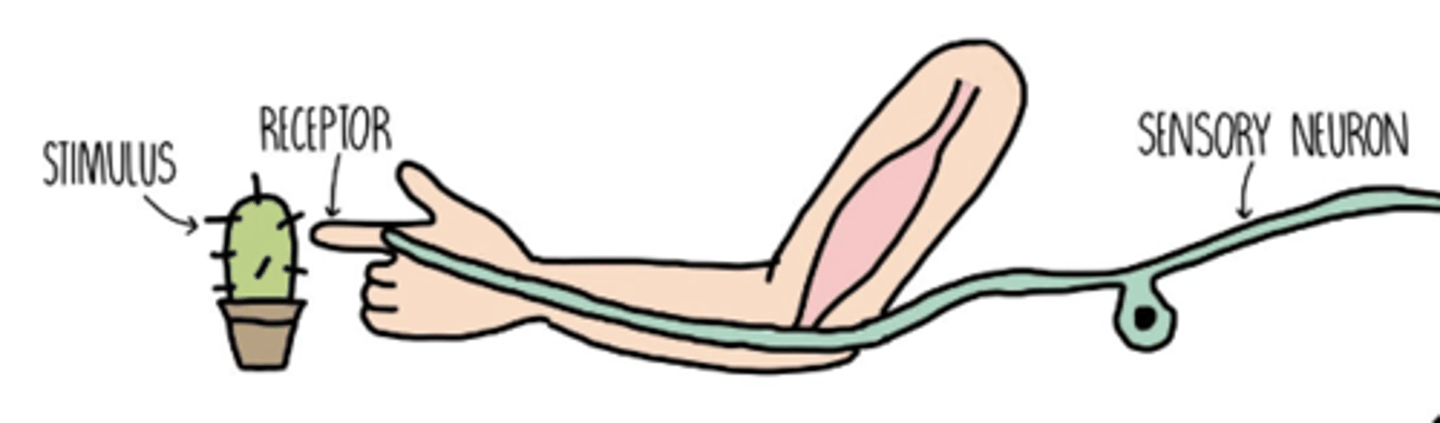
receptor
a cell or group of cells that receives stimuli
signal
a message that is sent between cells
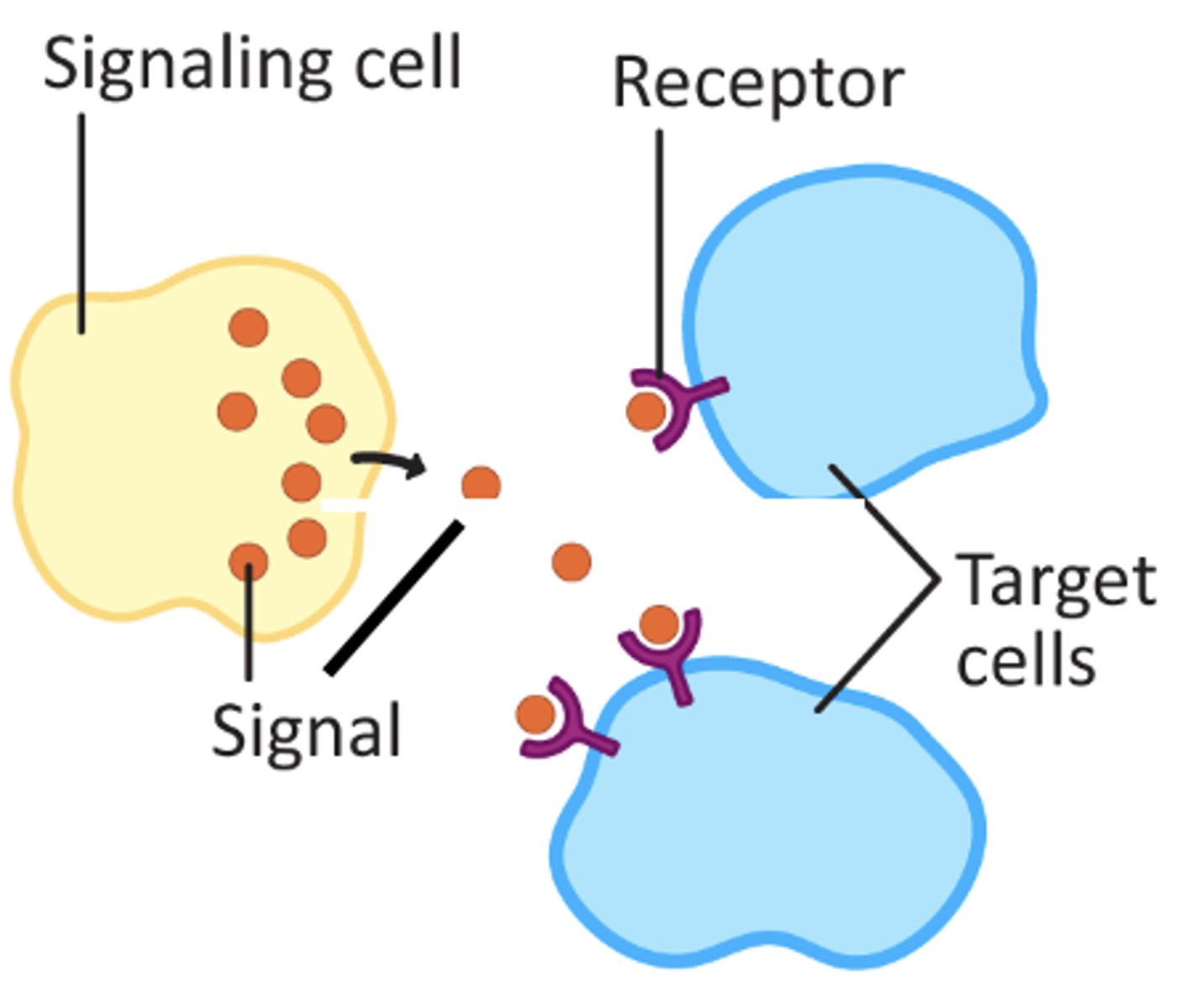
response
an action or message as a result of a signal
diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration of the molecules to an area with a lower concentration
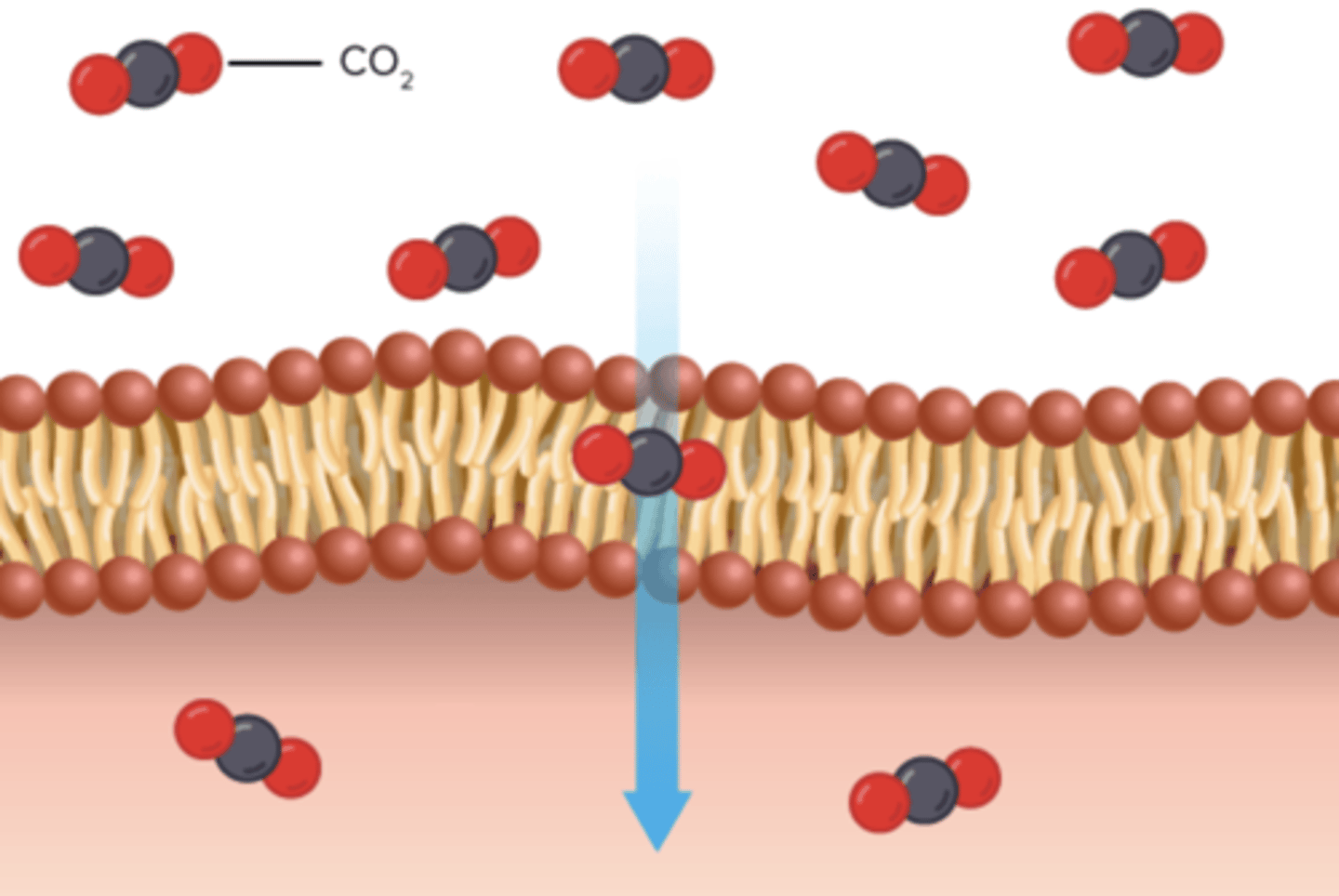
membrane
a thin sheet of tissue or layer of cells acting as a boundary, lining, or partition in an organism.

concentration gradient
The difference in the concentrations of molecules in two areas
equilibrium
the process where organ systems work to maintain (keep) a stable internal environment
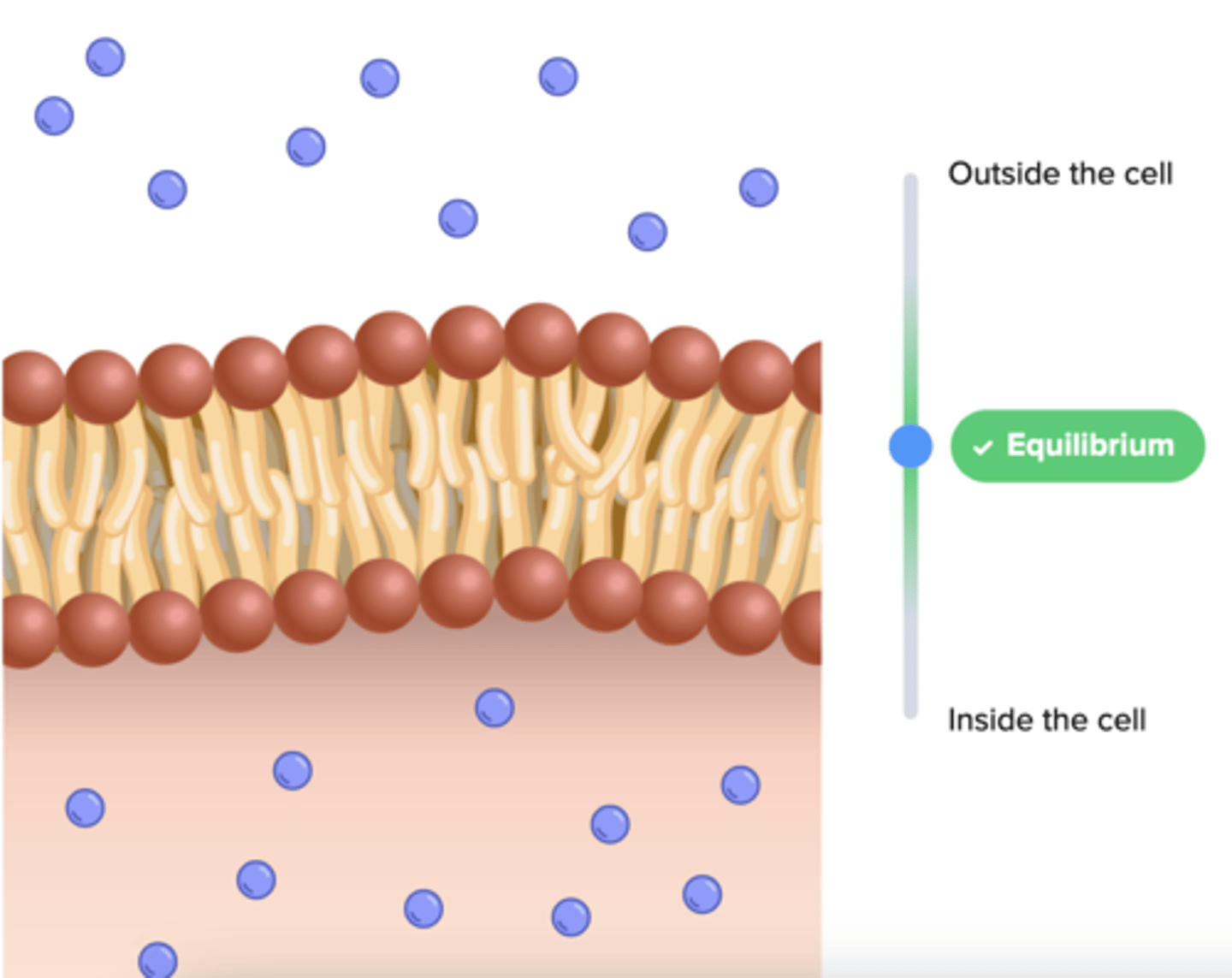
Cell
basic unit of structure and function of living things.
Specialized Cell
a cell that has a specific shape (structure) and function
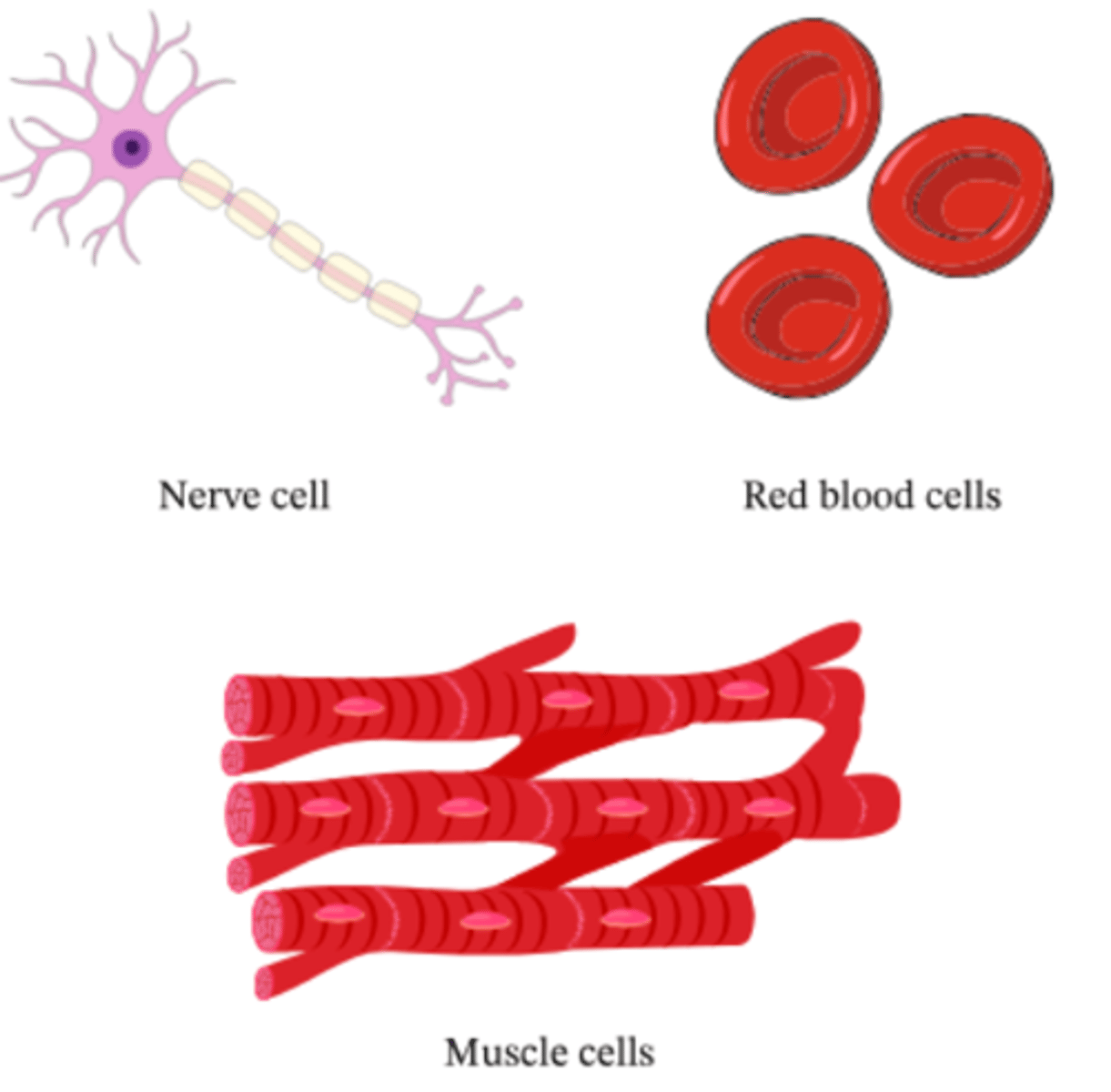
Tissue
group of specialized cells of the same kind that work together to perform the same function.
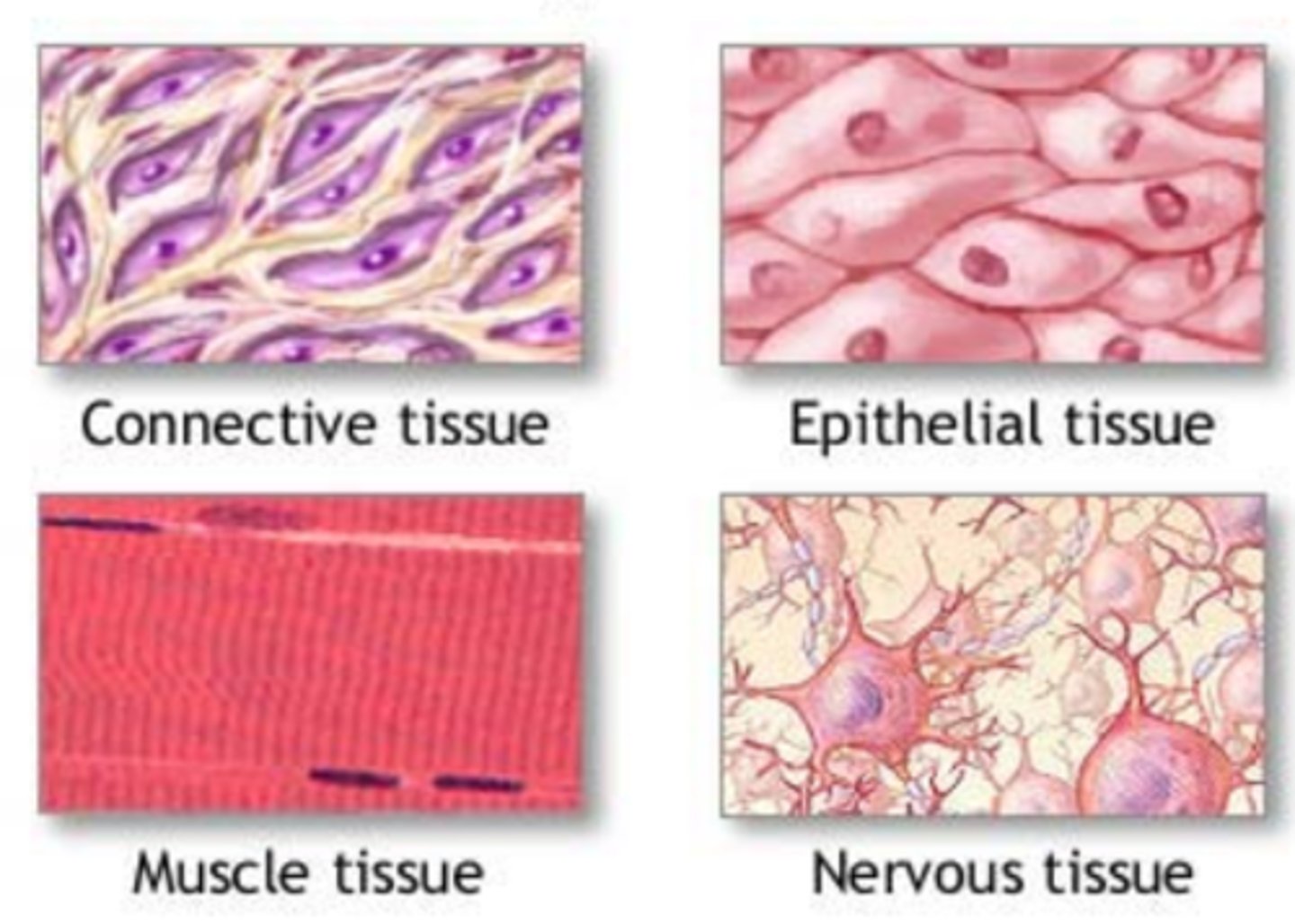
Organ
structure composed of two or more types of tissues that work together to perform a particular function.
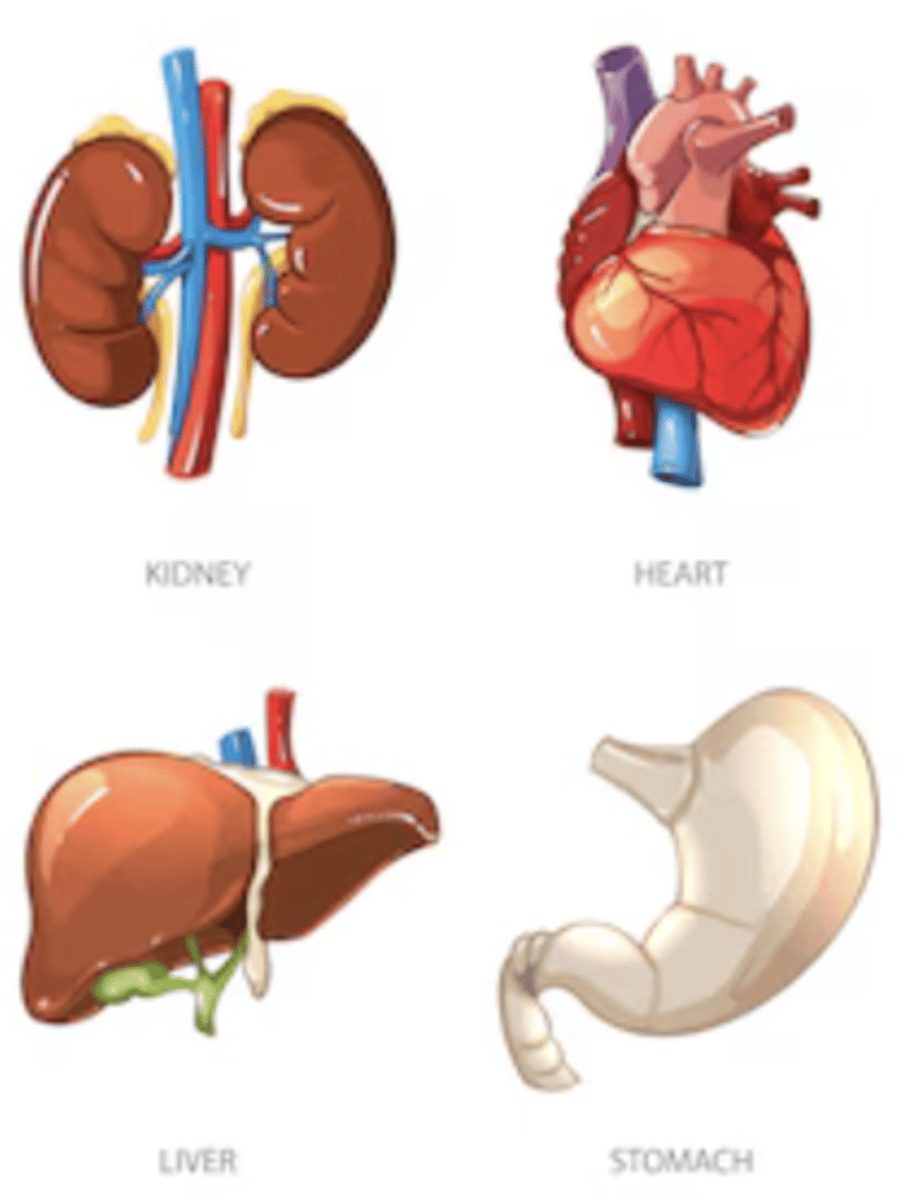
Organ System
group of organs that work together to perform a particular function for the organism.
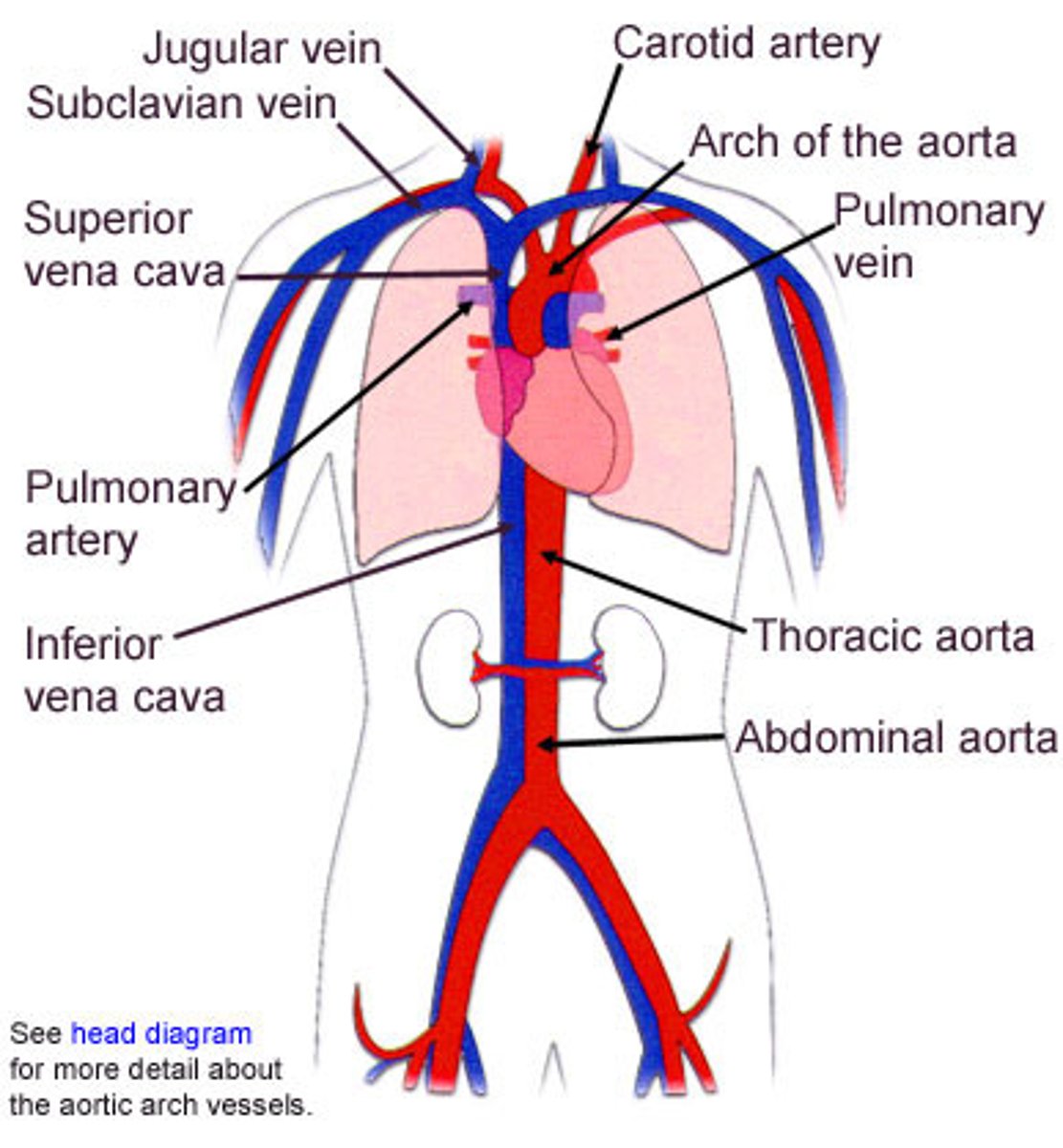
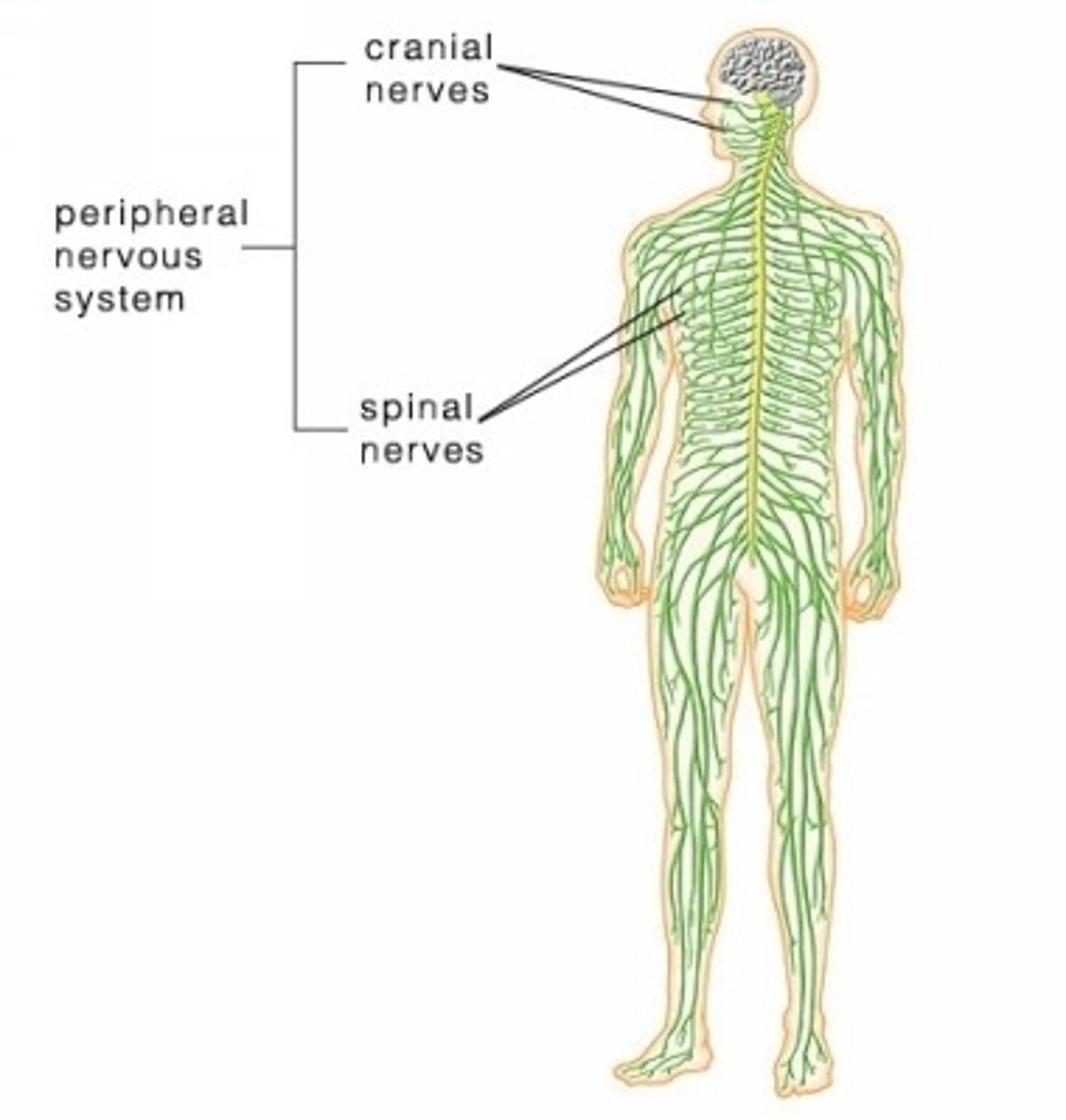
Nervous System
organ system that consists of the brain, spinal cord, and a complex network of nerves that carries electrical messages throughout the body.
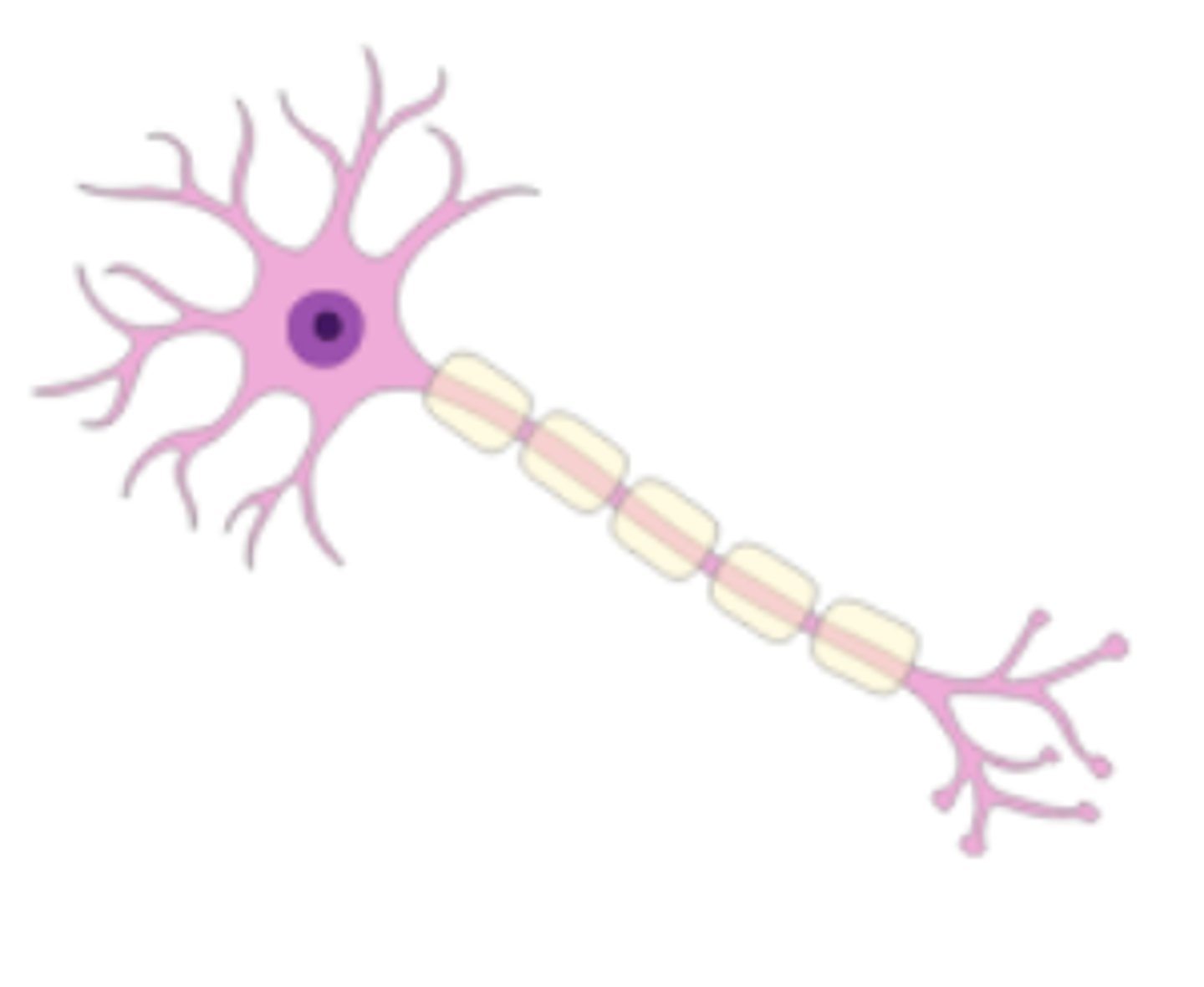
Neuron
a nerve cell, is the basic unit of the nervous system and is responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information through the body
circulatory system
a system made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart.
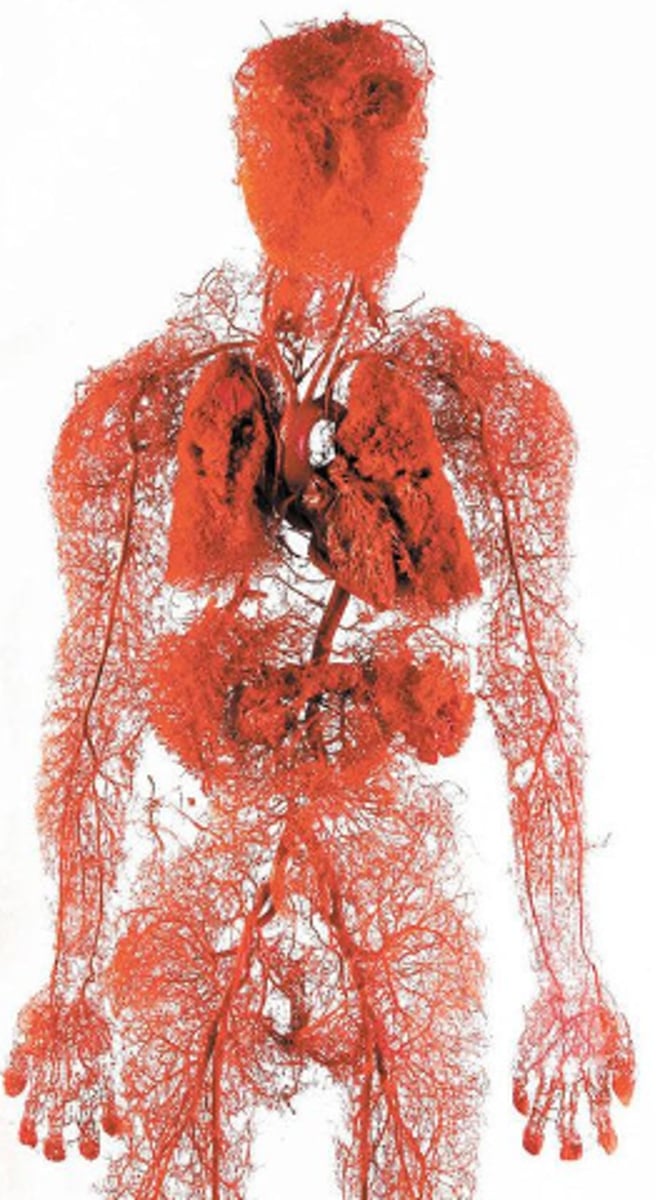
circuit
a loop / track within your body that has a specific function
artery
carries blood away from the heart to capillaries
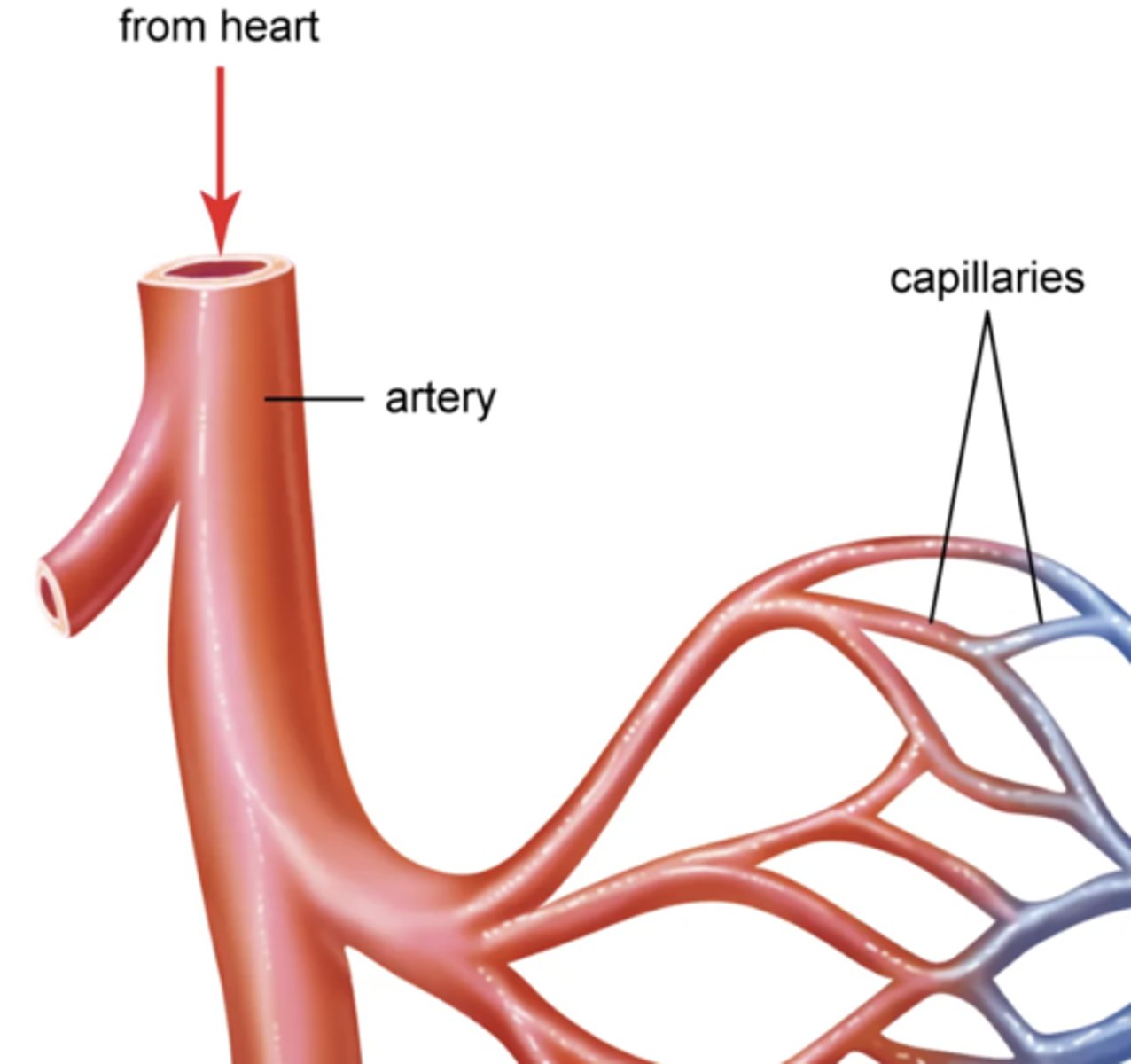
capillary
a very fine (thin) blood vessel that allows the exchange of molecules between tissues and blood.
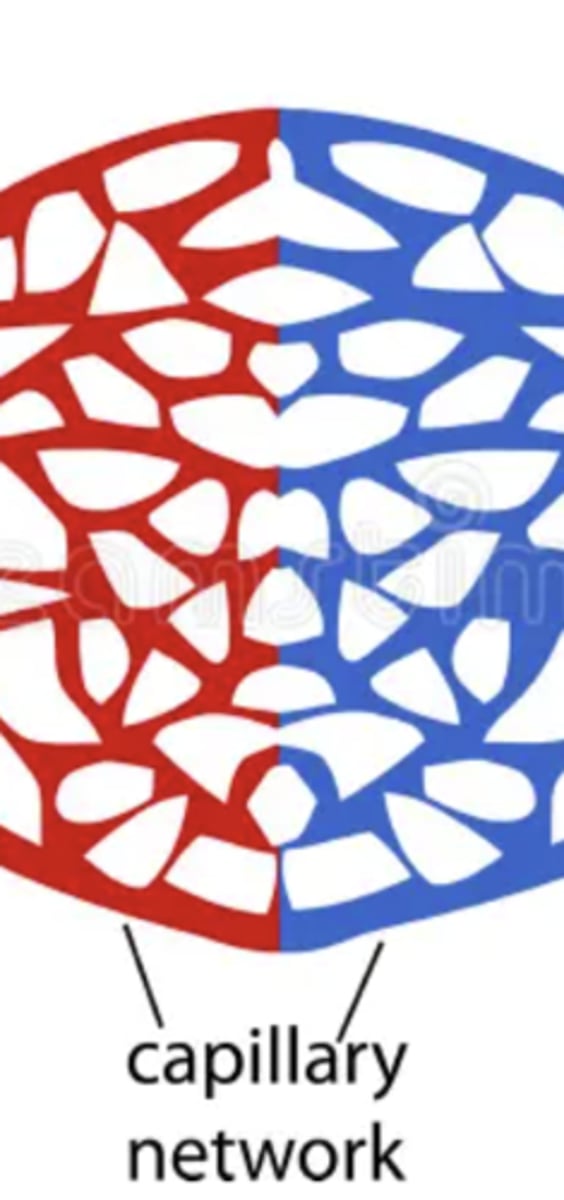

vein
carries blood from capillaries back to your heart

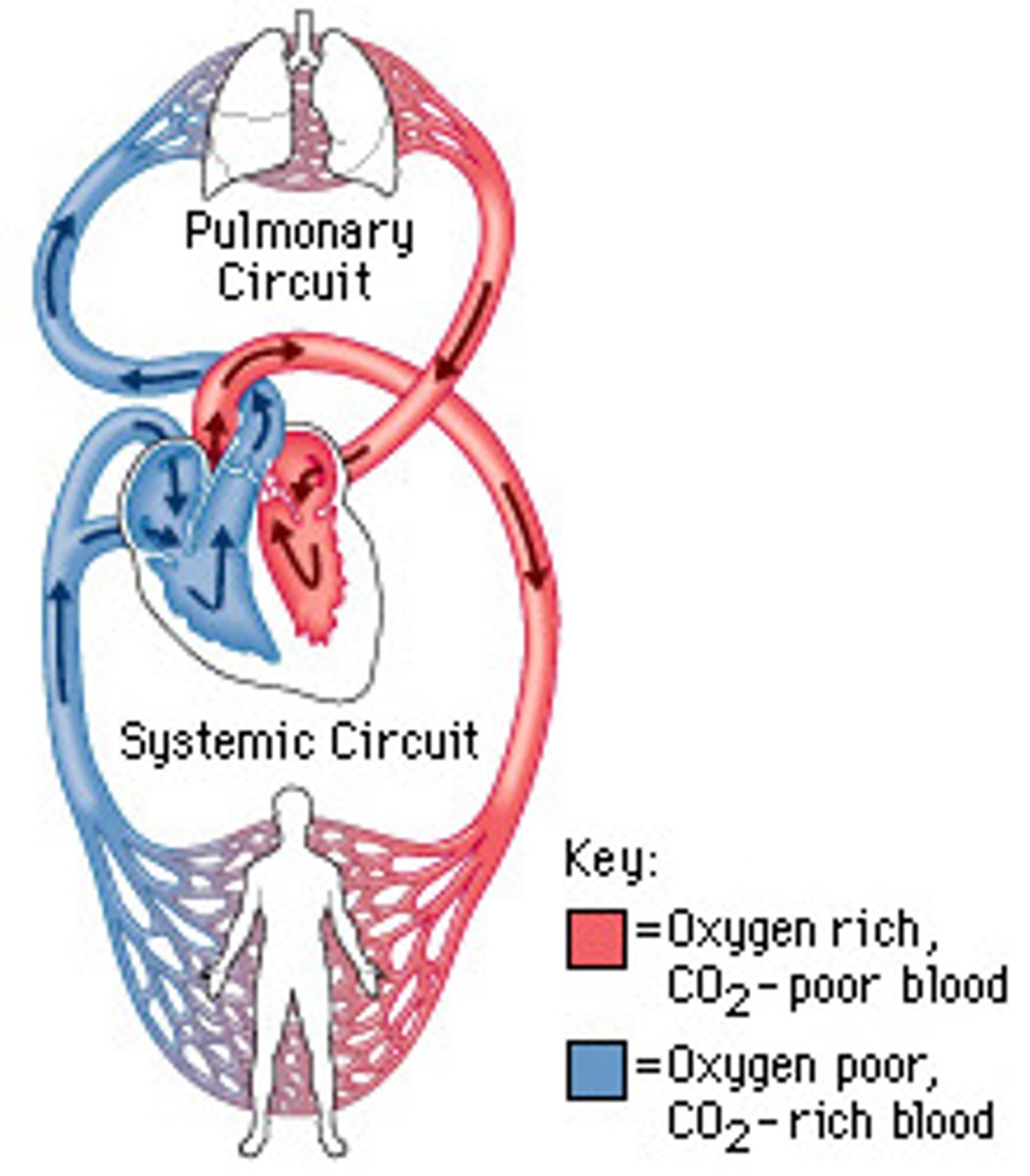
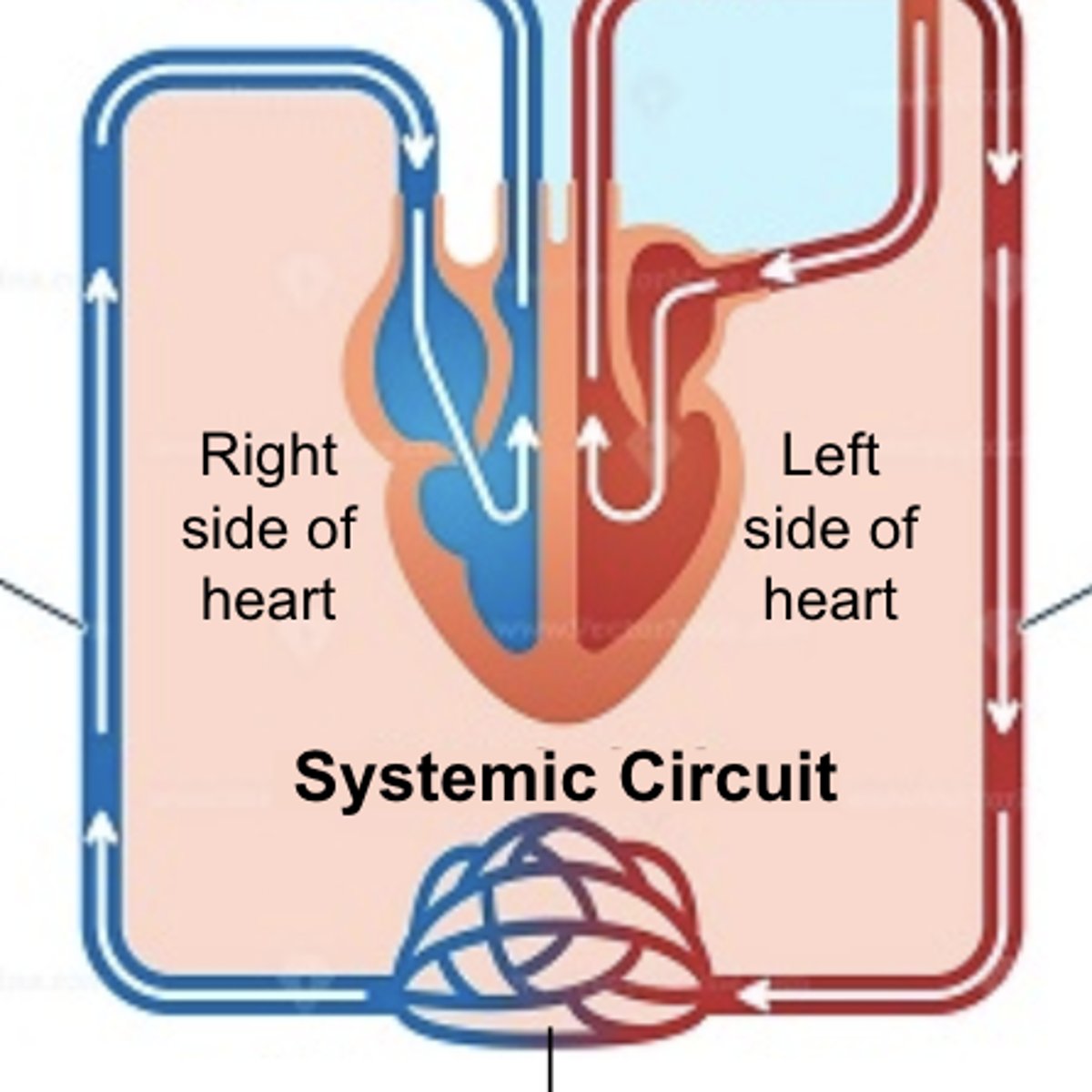
systemic circuit
the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and body
pulmonary circuit
the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and lungs
diffusion
the movement of anything generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
atrium (plural = atria)
heart chamber that receives blood into the heart and drives it into a ventricle
ventricle
heart chamber that pumps blood out of the heart and into the circulatory system
valve
a type of flap that act as one-way inlets for blood coming into a ventricle and one-way outlets for blood leaving a ventricle.
sweat gland
gland in the skin that produces the salty fluid called sweat, which excretes (gets rid of) wastes and helps cool the body
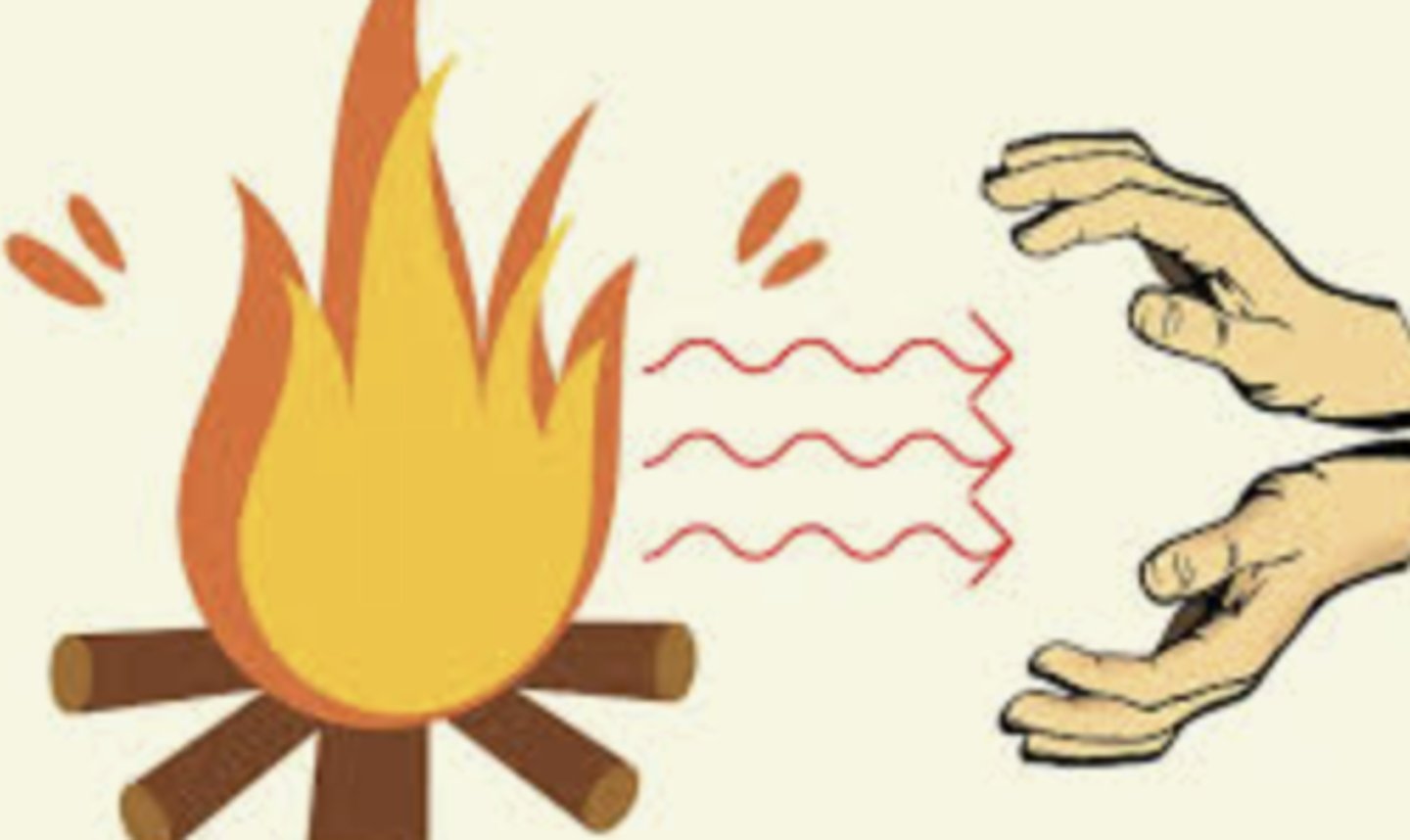
radiation (of heat)
heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves (for instance from your skin to the environment)
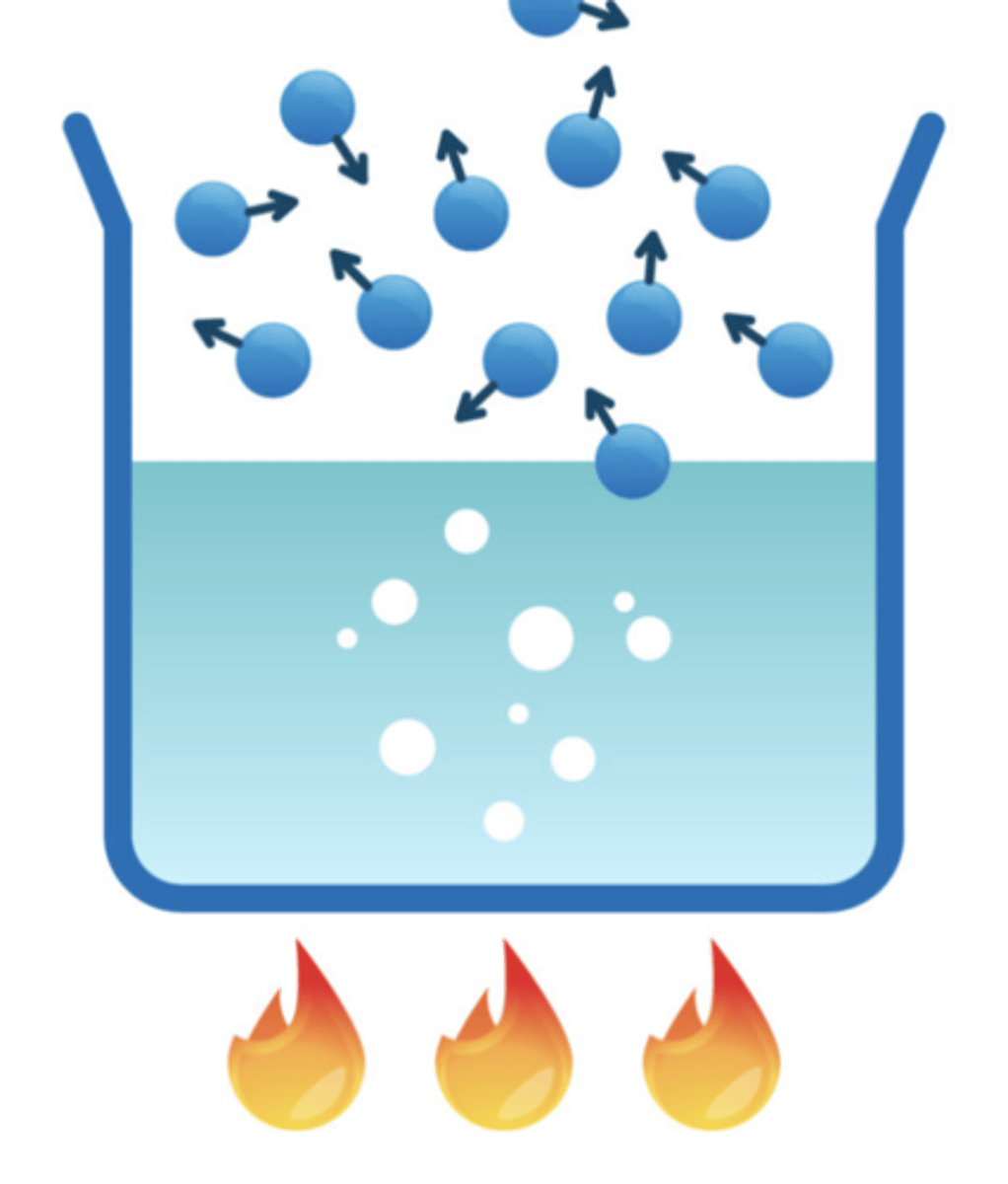
evaporation
the process where a liquid turns into a vapor (gas).; this process requires heat energy
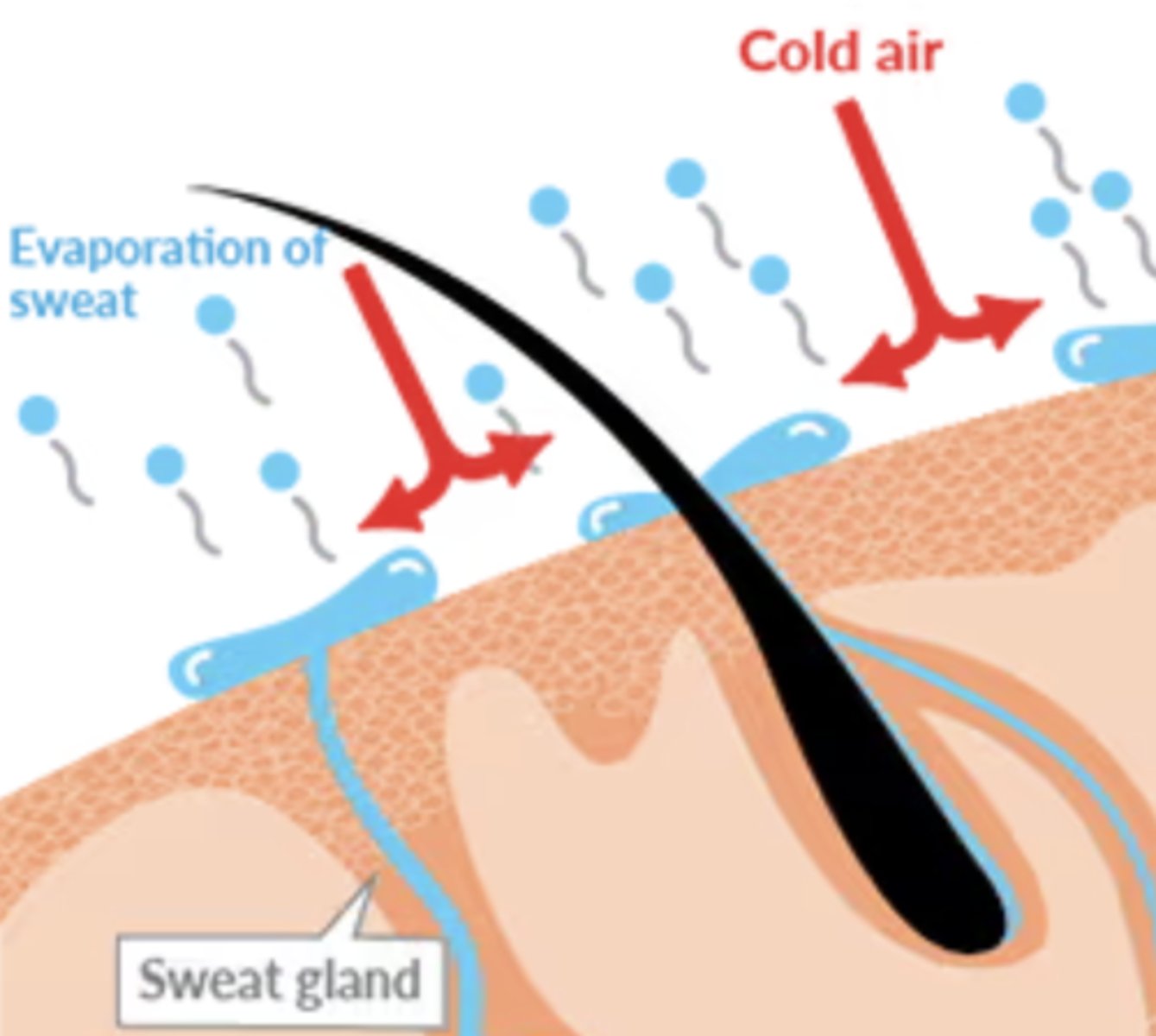
evaporative cooling
reduction in temperature resulting from the evaporation of a liquid
dilate
to relax or make bigger/wider