GCSE PE Edexcel Paper 1 (Component 1)
1/150
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Functions of the skeletal system
1) Protection of vital organs
2) Muscle attachment
3) Movement (joints)
4) Blood Cell Production
5) Mineral Storage (calcium & phosphorous)
Minerals in bones
Calcium and phosphorus
All bones in arm and hand from top
Humerus
Ulna
Radius
Carpals
Metacarpals
Phalanges
All bones from head, neck, vertebral column, and top of legs. In order
Cranium
Atlas, axis
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacrum
Coccyx
Pelvic girdle
Ribs
Sternum
All bones in leg and foot
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Tarsals
Meta tarsals
Phalanges
All bones in shoulder
Clavical
Scapula
Different types of bones. Examples of each
1) Long bones (Fémur, humérus)
2) Short bones (Carpals, tarsals)
3) Irregular bones. (Vertebra)
4) Flat bones. (Cranium, ribs, scapula)
Structure of the Vertebral Column
1) Cervical
2) Thoracic
3) Lumbar
4) Sacrum
5) Coccyx
8 types of joint movement
1) Flexion
2) Extension
3) Adduction
4) Abduction
5) Rotation
6) Circumduction
7) Plantar-flexion
8) Dorsi-flexion
Three types of connective tissue
1) Cartilage
2) Ligaments
3) Tendons
Cartilage
Acts as a cushion between bones to prevent damage during joint movement.
Ligaments
-Connect bone to bone
- Maintain skeleton stability during movement
- Made of tough and fibrous tissue
Tendons
Attach muscle to bone, to allow bones to move when muscles contract.
3 types of muscle
1) Voluntary
2) Involuntary
3) cardiac
Function of involuntary muscle. Example
Digestive system
Vasodilation and vasoconstriction
Not under our conscious control
Function of voluntary muscle. Example
Under our conscious control
We decide when to use them and how explosively
Quadriceps
Biceps
Function of cardiac muscle. Example
Heart
Continuously contracts and relaxes to pump blood around the body for delivery of oxygen and nutrients to working muscles. Removal of waste products.
List all components in right side of the heart
Vena cava
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Tricuspid valve
Semi lunar valve
List all components in left side of the heart
Aorta
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Bicuspid valve
Semi lunar valve
Four examples of antagonistic pairs
1) KNEE - Hamstrings & Quadriceps
2) ELBOW - Bicep & Triceps
3) HIP - Hip Flexors & Gluteus Maximus
4) ANKLE - Gastrocnemius & Tibialis Anterior
Antagonistic muscles
Pairs of muscles that work against each other, one contracts the other relaxes.
Agonist
The muscle that's contracting to produce the movement
Antagonist
The muscle that's relaxing
Two types of muscle fibres
Slow twitch & Fast twitch
Type I muscle fibres
- Low intensity aerobic work
- Marathon running
- Used for a long time without fatiguing.
Type IIA muscle fibres
- Anaerobic work
- Can be improved through endurance training to increase their resistance to fatigue.
Type IIX muscle fibres
- Used in anaerobic work
- Generate much greater force
- But fatigue quickly
- Short bursts of exercise: 100m sprint
Three main functions of cardiovascular system
1) Transport of substances
2) Temperature control
3) Clotting of wounds
3 types of blood vessels
1) Arteries
2) Veins
3) Capillaries
Arteries
- Away from the heart
- Oxygenated blood (except pulmonary arteries)
- Thick muscular walls
- High pressure
Veins
- Towards the heart
- Deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary veins)
- Low pressure
- Thinner walls & less muslce
Capillaries
- Carry blood to exchange: oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients
- Very thin walls
- Gaseous exchange, substances can pass through
Make up of blood
- Red blood cells (RBC)
- White blood cells (WBC)
- Platelets
- Plasma
Purpose of red blood cells
Carry oxygen, to release energy needed by working muscles
Purpose of white blood cells
Fight against disease: stay healthy and perform well
Platelets
Help blood clot at wounds, preventing infection
Plasma
Carries everything in bloodstream;
- Blood cells
- Digested food (e.g glucose)
- Waste (e.g carbon dioxide)
Structure of the respiratory system
1) Trachea
2) Bronchi
3) Bronchioles
4) Alveoli
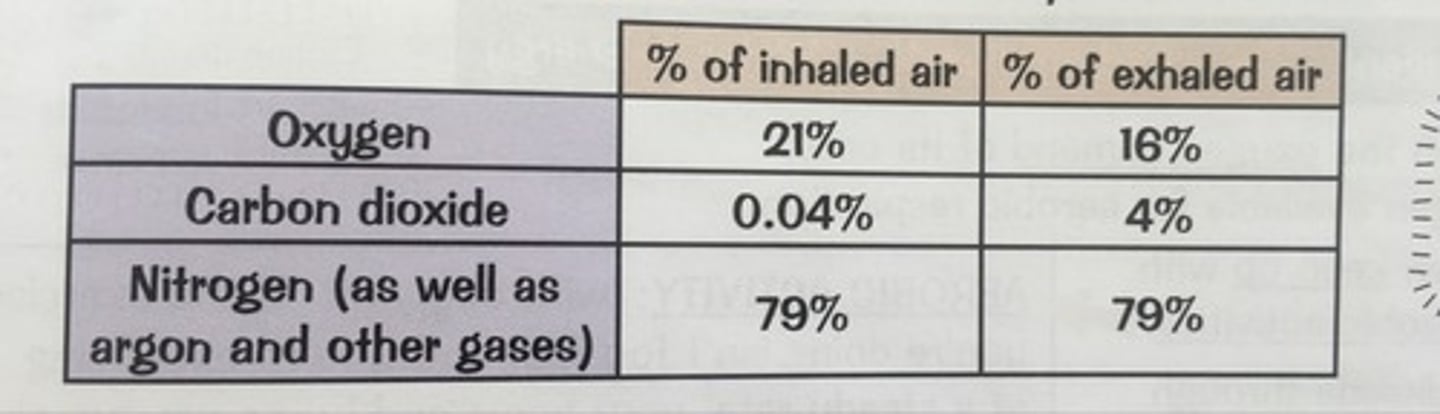
Make up of inhaled & exhaled air (%)
Inhaled: 21% - Oxygen
0.04% Carbon dioxide
78% nitrogen
Exhaled: 16% Oxygen
Carbon dioxide - 4 %
Nitrogen - 78%
Actions of respiratory system as breath in
Diaphragm flattens
Intercostal muscles contract
Thoracic cavity increases
Lung pressure decreases
Air sucked into the lungs
Actions of respiratory system in exhalation
Inter coastal muscles relax
Diaphragm relaxes
Thoracic cavity decreases
Lung pressure increases
Air forced out
Stroke volume
Amount of blood pumped out of heart per beat
Cardiac output
Volume of blood pumped in and out of heart per min (SVXHR)
Cardiac output equation
Heart rate x stroke volume = cardiac output
Tidal volume
Amount of air inhaled and exhaled in a normal breath
Vital capacity
The maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after taking the deepest breath.
Aerobic Respiration Formula
(Carbohydrates>) Glucose + Oxygen ➡️ Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
Fat > fatty acids + oxygen —> carbon dioxide + water
Anaerobic Respiration Formula
Glucose ➡️ Lactic acid + Energy
Two sources of fuel in the body
1) Carbohydrates
2) Fats
Carbohydrates used as fuel
- Main source of fuel
- During aerobic activities (moderate intensity)
- Anaerobic activities (high intensity)
Effect of exercise on the musculo-skeletal system?
- Muscle hypertrophy
- Increased bone density
- Stronger ligaments & tendons
Effect of exercise on the cardio-respiratory system?
- Cardiac hypertrophy - Decrease in resting HR, increase in SV, increase in max. Q
- Increased lung capacity
- Decreased blood pressure (BP)
- Capillarisation
- More red blood cells (RBC)
Lever arm
Body part being moved about a point
Effort
Force applied by the muscles to the levee arm
Fulcrum
Joint where lever arm pivots
Load
The resistance against the pull of the muscles on the lever arm (e.g dumbbell)
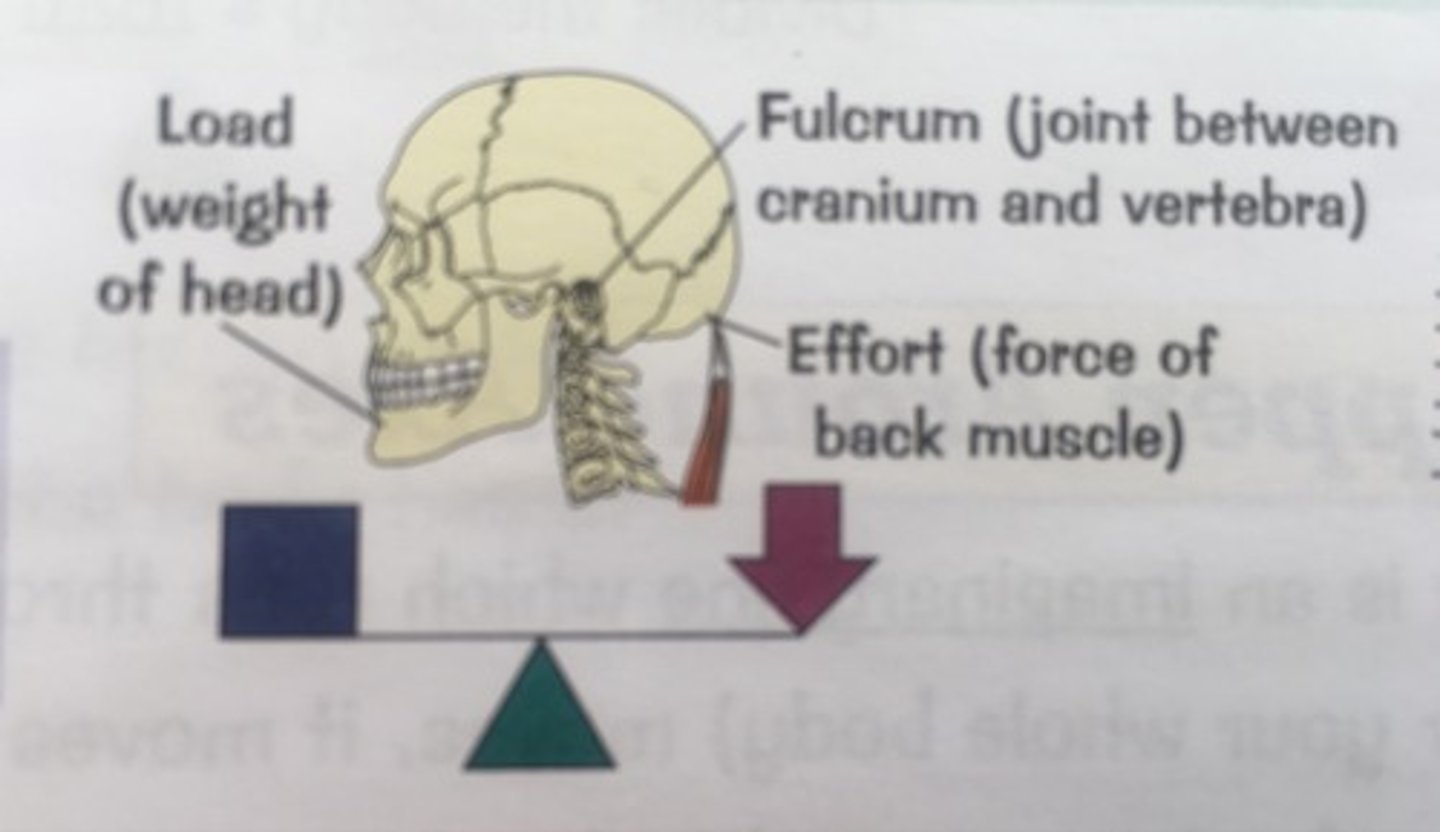
1st class lever system
- Fulcrum in the middle
- Load & effort at opposite ends
- Mechanical advantage or disadvantage
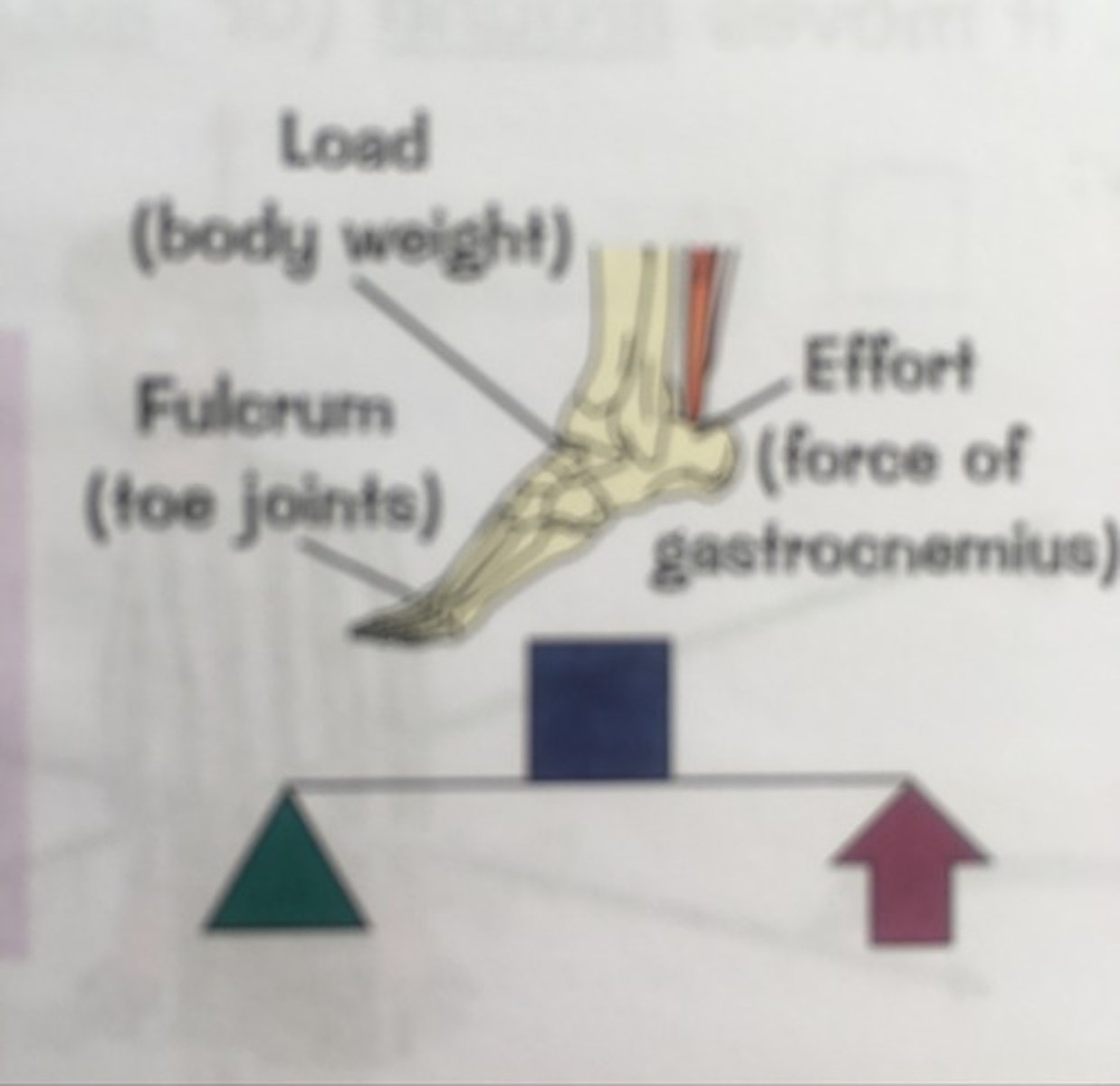
2nd class lever system
- Load in the middle
- Always mechanical advantage
- Fulcrum and effort at opposite ends
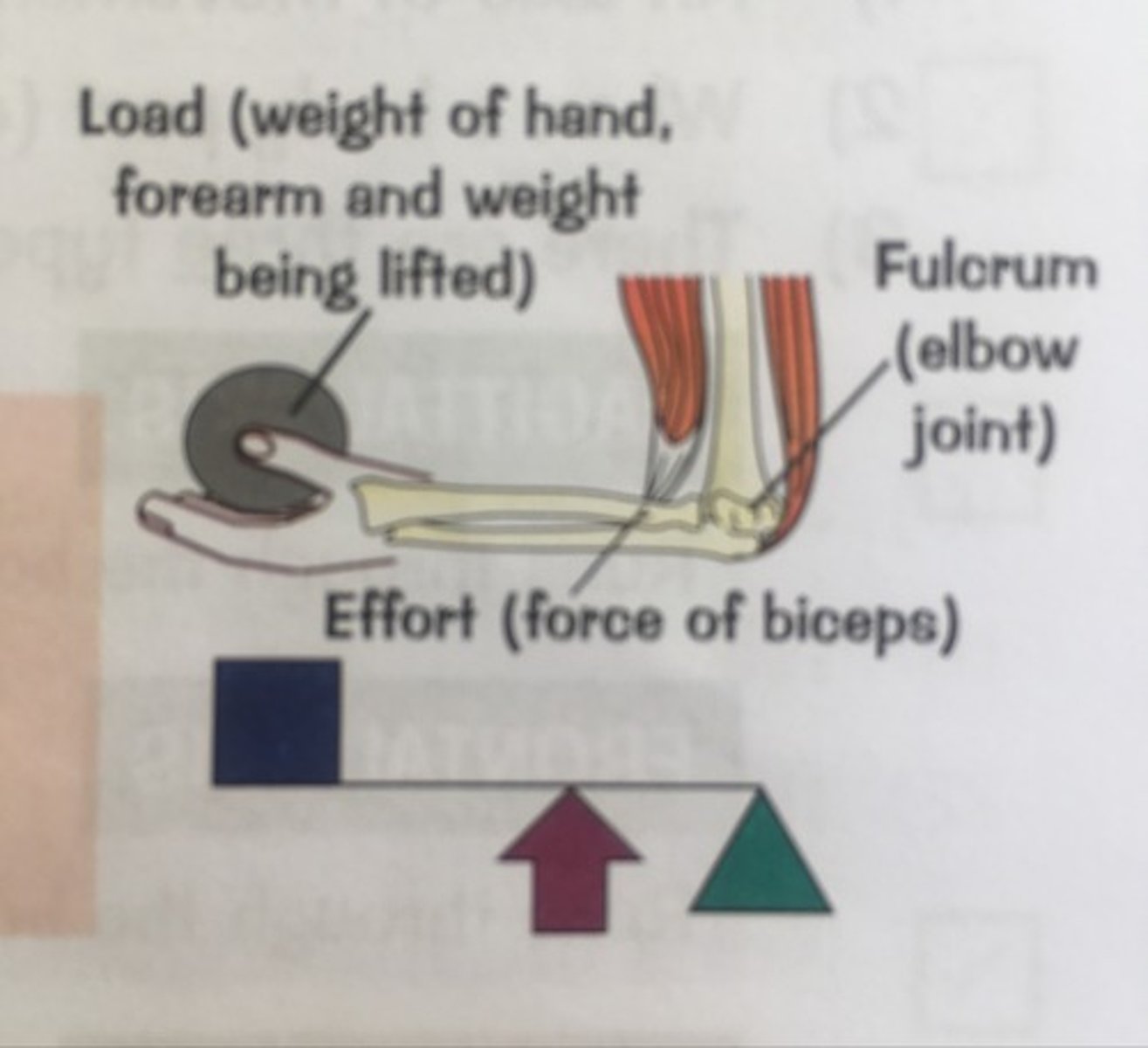
3rd class level system
- Effort in the middle
- Fulcrum and load at opposite ends
- Always mechanical disadvantage
When does a 1st class lever system have mechanical advantage?
If the fulcrum is closer to the load than it is to the effort.
When does a 1st class lever system have mechanical disadvantage?
If the fulcrum is closer to the effort than it is to the load.
Mechanical advantage
- Move large load with small effort
- But only short distances at low speeds
Mechanical disadvantage
- Requires large effort to move small load
- Move quickly through a large range of movement
Plane
An imaginary flat surface running through the body dividing it into sections
Axis
An imaginary line running through the body, which an body/object rotates around.
Sagittal plane
Divides body into left + right sides.
Transverse plane
Divides body into top and bottom.
Frontal plane
Divides body into front and back.
Sagittal axis
Runs from front to back
Frontal axis
Runs from left to right
Vertical axis
Runs from top to bottom
Example of plane & axis pairs
1) Sagittal plane & frontal axis
2) Frontal plane & sagittal axis
3) Transverse plane & vertical axis
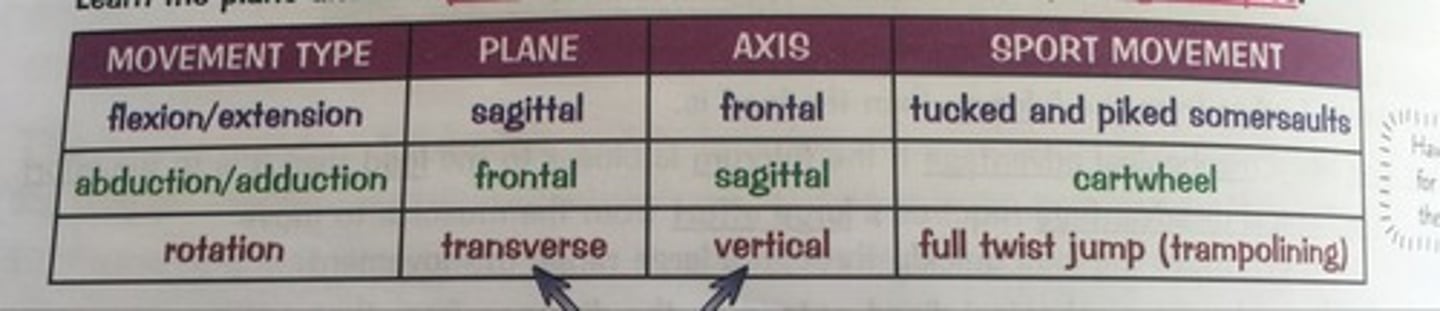
Movement allowed at sagittal plane
Flexion and extension
Movement allowed around frontal plane
Abduction and adduction
Movement allowed around a transverse plane
Rotation
What movement do all axis allow around each of their planes
Rotation
Health
A state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Fitness
Ability to meet the demands of the environment.
Exercise
A form of physical activity done to maintain or improve health and/or fitness. Not a competitive sport
Performance
The actions of preforming s task including a sporting performance
Name 11 components of fitness
Strength
Body composition
cardiovascular fitness
Balance
Flexibility
Muscular endurance
Power
Agility
Coordination
Speed
reaction time
Cardiovascular fitness
The ability to exercise your entire body for long periods of time without getting tired.
Strength
Amount of force that a muscle can apply against a resistance.
Muscular endurance
Ability to repeatedly use the voluntary muscles over a long time, without fatigue.
Flexibility
Amount of movement possible at a joint.
Body Composition
Percentage of body weight made up by fat, muscle, and bone.
Speed
Rate at which someone is able to cover a distance in a given amount of time.
Agility
Ability to change direction quickly and under control
Balance
Ability to keep the body's centre of mass over a base of support.
Coordination
Ability that use two or more body parts together, efficiently and accurately.
Reaction time
Time taken to move to respond to a stimulus.
Power
Combination of speed and strength
Health related fitness components
BEEFS
Body Composition
Endurance (muscular)
Endurance (cardiovascular)
Flexibility
Strength
Skill-related components of fitness
CRABPs
Coordination
Reaction Time
Agility
Balance
Speed
Power
Reversibility
Any fitness improvement of body adaptation caused by training will gradually reverse and be lost when you stop training.
Aerobic target zone
60-80% of maximum heart rate
Anaerobic target zone
80-90% of maximum heart rate
Maximum heart rate
220-age
PARQ
Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire
Method of treating soft tissue injuries
RICE
Rest
Ice
Compression
Elevation