A1.2 Nucleic Acids
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
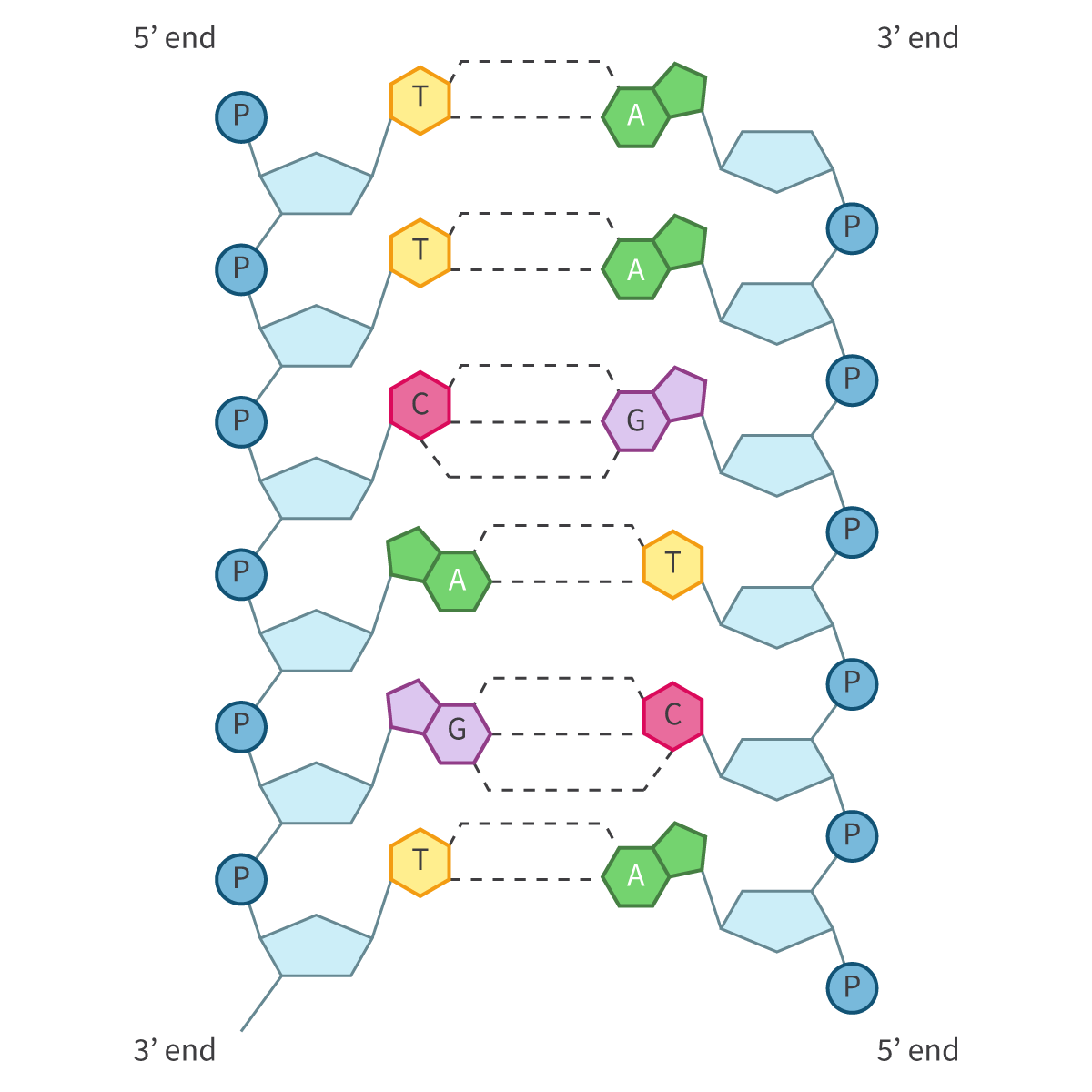
DNA + diagram
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
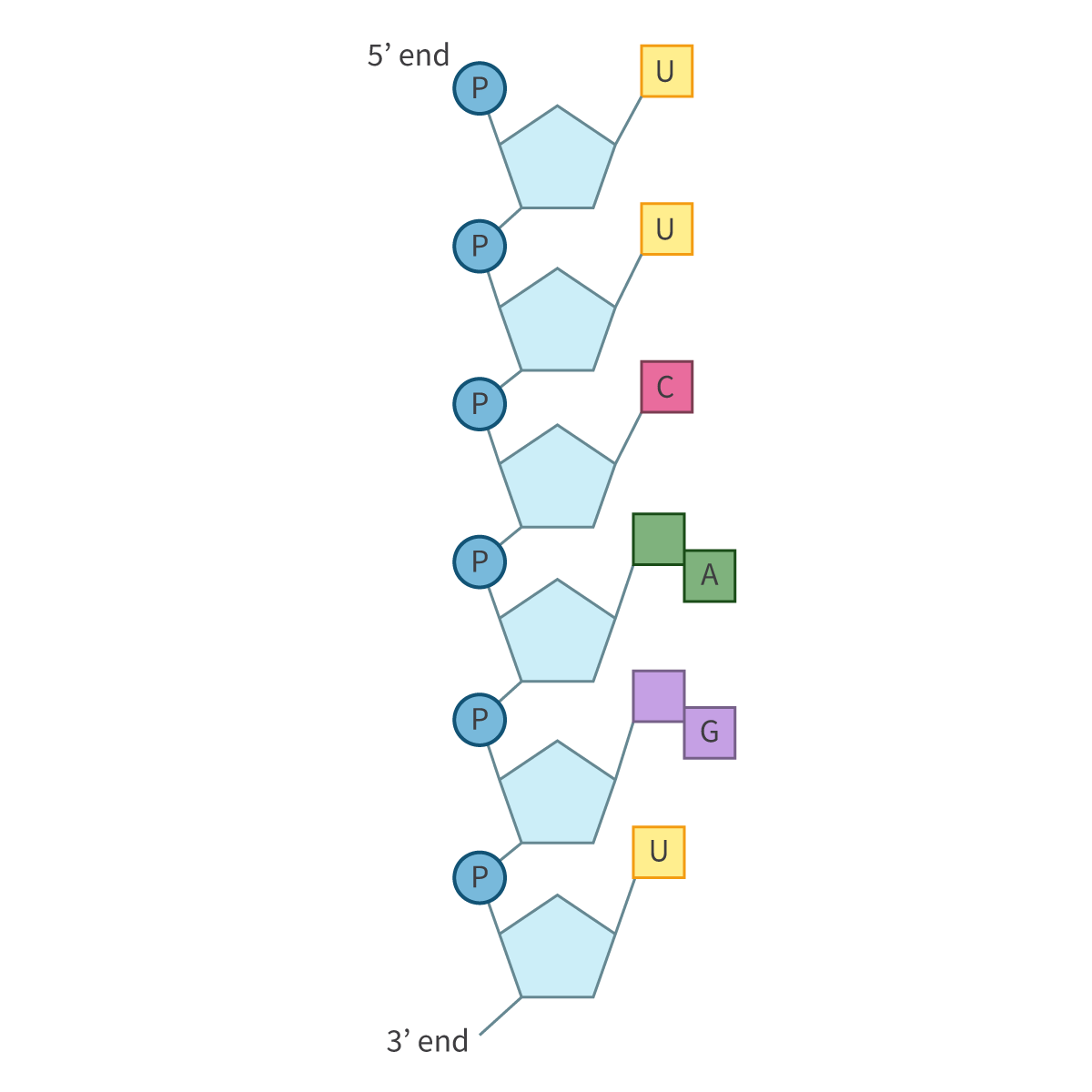
RNA + diagram + mnemonic to remember order
Ribonucleic acid
GUACA (MOLE)
4 majoir types of biological molecules
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Nucleic acids
Functions of nucleic acids
Pass info between generations
Code for protein production
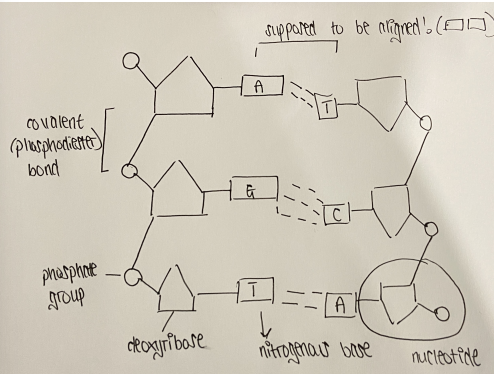
Components of a nucleotide
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
Pentose sugar

How are nucleotides linked together
By covalent bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of another
When drawing covalent bonds, use:
Solid lines
When drawing hydrogen bonds, use:
Dashed lines
Bases in DNA
Adenine
Thymine
Cytosine
Guanine
Bases in RNA
Adenine
Uracil
Guanine
Cytosine
Purines
Adenine
Guanine
Pyrimidines
Cytosine
Uracil
Thymine
Condensation reactions
Removal of water to create a covalent bond
Similarities of DNA and RNA
Both are polymers of nucleotides
Cytosine pairs with guanine
Differences between DNA and RNA
DNA | RNA |
Double-stranded | Single-stranded |
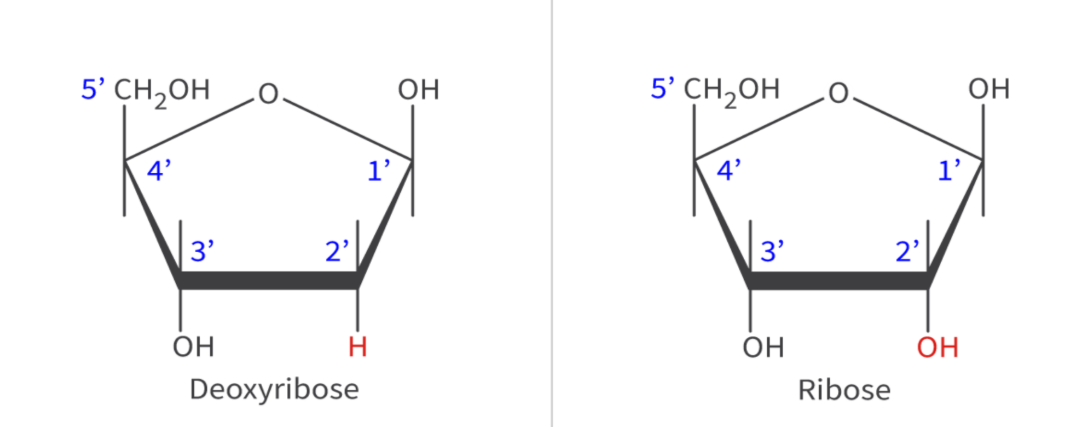
Deoxyribose | Ribose sugar |
Adenine pairs with thymine | Adenine pairs with uracil |
Sketch of ribose and deoxyribose
(draw and label)
Examples of nucleic acids
DNA
RNA
tRNA
mRNA
Semiconservative
Each resulting copy is made of one parent strand and one new strand
What is complementarity based on
Hydrogen bonding
Gene expression
Using DNA code for protein synthesis
Simple steps of gene expression
DNA is used as a template to make RNA
RNA is “translated” into a protein
DNA to RNA follows rules of CBP
Complementary base pairing during transcription
RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand
Reads the DNA template
Adds complementary RNA nucleotide
Complementary base pairing during translation
Ribosome builds polypeptide by reading mRNA template
Binds coded amino acid to polypeptide chain
Outline why there are limitless diversity of DNA base sequences
There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA (A, T, C and G). These 4 bases are components of nucleotides that can form a DNA molecule in any order and of any length
Directionality of RNA and DNA
5’ with a phosphate
3’ with a pentose
DNA has antiparallel directionality
5’ to 3’ on one side
3’ to 5’ on other side
What do complentary pairs consist of
One purine
One pyrimidine
Nucleosome + diagram
DNA wrapped twice around a core of 8 histone proteins
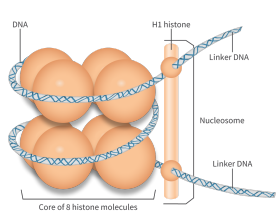
Structure of nucleosomes
DNA molecule wrapped
8 histone proteins
Additional histone protein
Linker DNA attached
Hershey–Chase experiment blurt
This was an experiment in the 1950s, Hershey-Chase knew chromosomes were made of DNA and protein and that they carried genetic info, but didn’t know which one was responsible for transmitting hereditary information: DNA or Protein?!
Viruses were made up of DNA and protein, so they grew two different groups of bacteriophage viruses in different radioactive mediums; Sulphur, Phosphorous and allowed each of these to infect others, they spun them through a centrifuge, this separates things based on weight, heavier things goes down
A pellet; the cell’s genetic material at the bottom of the centrifuge. The ones that were grown in radioactive sulphur was the supernatant and in phosphorus, it was the pellet. They concluded that it was DNA that carried the genetic material NOT the protein!!
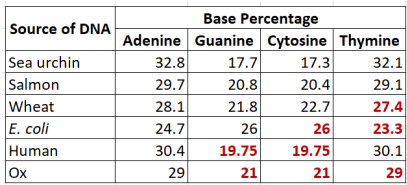
Tetranucleotide hypothesis
DNA consisted of a repeating sequence of 4 nucleotides in equal amounts and proteins were the genetic material
Falsification of the tetranucleotide hypothesis
Through Chargaff’s data
Table shows that organisms infact DO NOT have equal amounts of A, T, G, and Cs