Phylogeny and Genetivs
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Parent Offspring Conflict
Investment per offspring depends on lifetime cost and benefit to parent
Agriculture
Planting certain cultivars in particular substrates to improve crop production
Leaf Cutting Ants Farming
Bring leaves into climate controlled rooms to cultivate it, remove weeds and use antibiotics to suppress pests
Evolution of Ant Farming
A single event caused farming in ants, and three independent origins for fungi to become ant crop
Evolution of Termite Farming
A single event causes farming in termites, and single origins for fungi to become termite crop
Evolution of Farming Beetles
7 event causes farming in beetles, and 2 origins for fungi to become beetle crop
How did fungi and ant phylogeny converge at the same time?
Giant asteroid killed photosynthesizing plants, which fungi fed on its decaying and ants that fed on fungi survived
1 mm into m
10-3m
1 micron into mm
10-3mm
1 nanometre into um
10-3um
Chemotaxis
Ability of organisms and cells to move up and down a chemical gradient
Sperm with Chemotaxis and Thermotaxis
Cells use thermotaxis to get into the fallopian tube, then use chemotaxis to reach the egg
Phototaxis
Moving in response to light either towards or away
Geotaxis
Movement of cell in response to force of gravity
Successive Comparisons
Using one-step memory to compare
Bacteria uses of chemotaxis
Compares chemical gradients for higher concentration of food using successive comparison
Simultaneous Comparison
Comparing stimuli at the same
Who uses and doesn’t use simultaneous comparions
Humans use simultaneous for hearing and seeing
Bacteria are too simple, and chemical gradients are really small
Chemotaxis in E. Coli
Receptors detect chemicals
Transmit information to nucleus with electrical communication
Nucleus sends information to flagellum
Chemotaxis isn’t learning because
Lacks internal representation but decisions are affected by new information
Behaviour from Sydney Brenner
Behaviour is from genetic code of the nervous system and how it works to make behaviour
Biomimicry
Copying mechanisms of animals for new gadgets
Innate Behaviour/Fixed Action Pattern
Pattern that’s fully functional from the first time it’s performed
Advantages of Innate Behaviour
Rapid response to stimulus, and if it’s the first time
Village Weaverbird Males
Innate behaviour to build a nest to impress females starting from a forked branch, and weave it in a sphere, if the female likes it, the male will finish with a large opening downwards to protect against predators

Nest building adapts based on
Context, colour of material and needs
Geese recovering egg instinct
Will recover any smooth object near the nest because it ensures a real egg is never ignored
Chivers Experiment Set Up
Lets 3 groups of pikes feed on minnows, dameselfies, or mealworms in different tanks for 3 days, then place dameselfies in the tanks that had the pikes containing pike’s predatory chemicals
Subspecies of A. aegypti
A. eformosus native to Africa, which feeds on nonhumans and lives in the forest
A. e aegypti non-native, which feeds on humans
Introduction of A.e aegypti
Accidentally introduced and entered houses to lay their eggs
Both Subspecies are attracted to different odors for food from
Nonnative OR genes were more sensitive to sulcatone in human odor, causing them to express it more
What happens when a termite queen dies?
Workers get aggressive between each other and eventually one of them becomes queen
Neofem 2 Gene
Expresses pheromones that suppresses butting behaviours in workers, which leads to stopping reproduction
Principle of Segregation
Individual of two copies of each genes stays distinct and segregated fairly in sex cell formation
Independent Assortment
Whichever allele passed down at locus is independent of other alleles passed down (only for unlinked loci)
Ruffs Mating Behaviours
Independent males guarding a small mating area
Satellite males temporarily sharing independent male’s area and forms an alliance where both court at the same time
Satellite Birds Difference
Smaller and lighter plumage
Satellite and Independent Mating Controlled by
Single gene, S = satellite (dominant), and s = independent
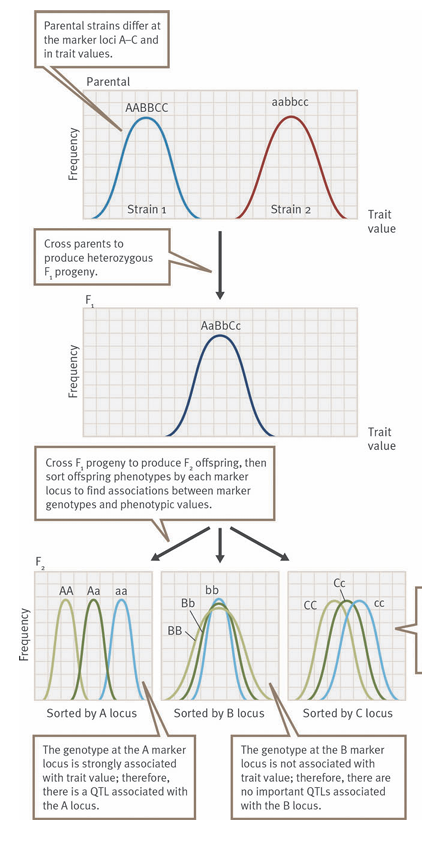
QTL Mapping
Finding general region where QTL is
QTL Mapping Procedure
Choosing 2 strains where 1 has lower trait values, and the other has higher trait values
Cross to make F1, if strains were homozygous at marker loci, F1 is intermediate
Cross F1 for F2 to measure genotype at marker and value of trait, using that, it can be inferred which marker is most associated for QTL
QTL associated with fear in mice are in
14 chromosomes
QTL for emotionality (fear and anxiety) is on
20 chromosomes
Period Gene
Influences circadian rhythms, development in bees
mRNA levels in bees
Higher in foraging bees than nurse ones
QTL of Genes associated with age at 1st foraging on
Chromosome 4 and 5
Gene Malvolio
Effects of manganese transport to bee brain
Pollen foragers are more responsive to
Sucrose than nectar foragers, but both stronger than nurse bees
Manganese levels and mvl mRNA high in
Pollen foragers > nectar foragers > nurses
FOXP2 Gene
Associated with song perception in birds, and language acquisition in humans
Young Zebra Finches with deactivated FOXP2 gene
Can’t copy song
mRNA levels from zenj gene increases
When birds heard zebra finch songs, which increase number of neurons in neostriatum
mRNA level from zenk gene increased less from
Other species songs, and no change from no songs or tone bursts
Zebra Finch Habituate
Same song, zenk mRNA will decrease
AVPR1A Gene
Controls vasopresson receptors
Long AVPR1A Allele
Associated with more prosocial behaviour, and males with two displays more care and positive to familiar females
Ratio of nonsynonymous and synonymous fixation indicates
Strength natural selection has acted on traits, with higher ratio meaning positive natural selection
Selection on ECR1 and FOXP2 Gene
Strong positive selection for learning and memory in great tits
GPCR
Involved in hormonal and neurobiological processes with behaviour
Transcription Factor
Guide development by binding to regulatory enhancers
Regulatory Enhancers
Non coding sequences that regulate expression of nearby genes
Mouse, Spined Stickleback and Honeybee all have
Similar gene expression/differentiation in response to territorial expression and 7 transcription factors apart from responses to intrusions
Temperature effects
Development of smell in insects
Female Parasitoid Wasps raised in Colder Areas were
Worse at learning a paritized hosts using external cues and affected number of eggs laid
Ballooning Behaviour
Uses thread to sail long distances
Rappeling
Make silk thread bridge for short distance
E. Atra Migration in Fall
Migrate using ballooning to noncrop area where habitats are scarce
E. Atra Migration in pring
Migrate using rappelling from abundant habitats
E. Atra Temperatures
Spides raised at higher temperatures were likely to rappel, and low temperatures ballooned
Pups raised by single mom got
More alone time than BP pups who were groomed more overall, but both moms groom the same time
SM Offspring Females
Groomed less and took longer to find a mate to bond with than BP
Cichlid babies raised by
Adults and siblings to defend the nest from predators and remove parasites from eggs
Taborsky Expereiment
Raised group 1 with no adult, group 2 with adults, group 3 adults + helpers
Taborsky Results
Group 2 and 3 displayed behaviours less energy costly but efficient in defending territories
Oldfield Mouse Females that have experience from babysitting other litters have
Offsprings that have higher probability of surviving from better nest building
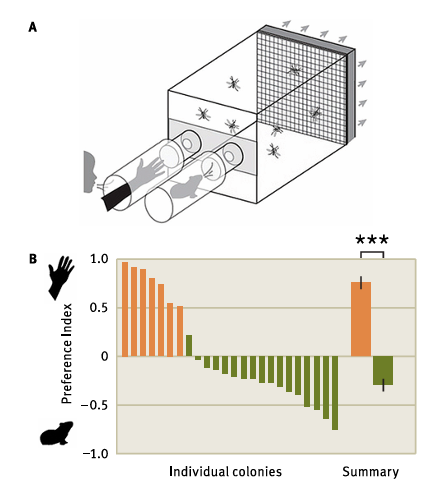
What’s the Main Message?
Odor preference for humans in nonnative mosquitos
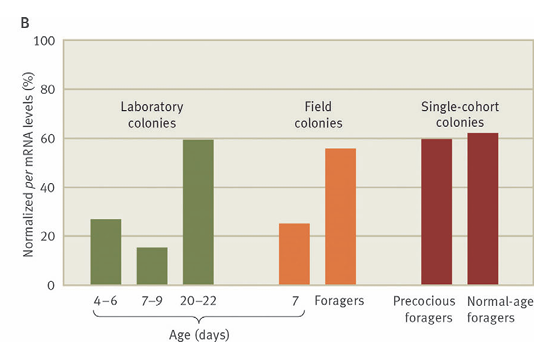
What’s the main message?
Higher mRNA in foraging individuals regardless of age
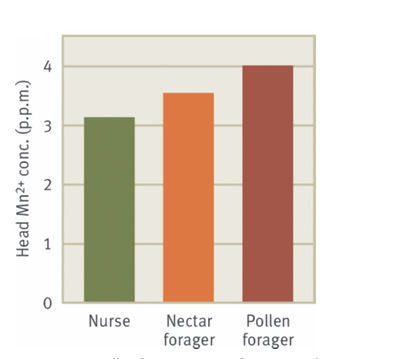
What’s the main message?
Pollen foragers have more manganese than nectar and nurses
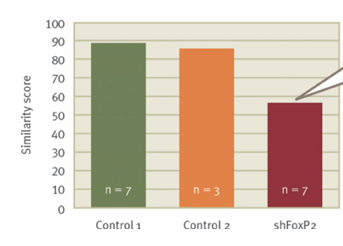
What’s the main message
Songs of birds with deactivated FOXP2 had lower similarity scores to their tutor’s songs
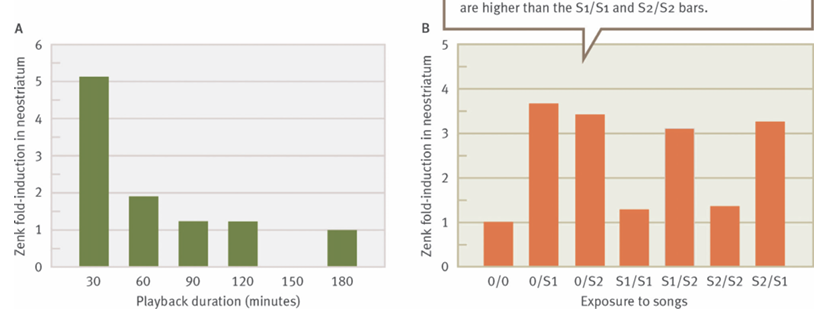
What’s the main message?
zenk mRNA levels decrease with increase exposure to same song, and levels increase when exposed to a new song
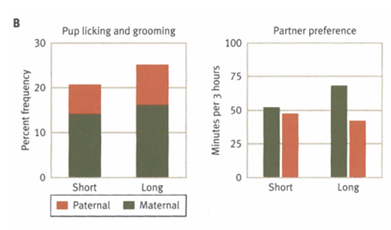
What’s the main message?
Male care and partner preferences greater in males with the long avpr1a allele
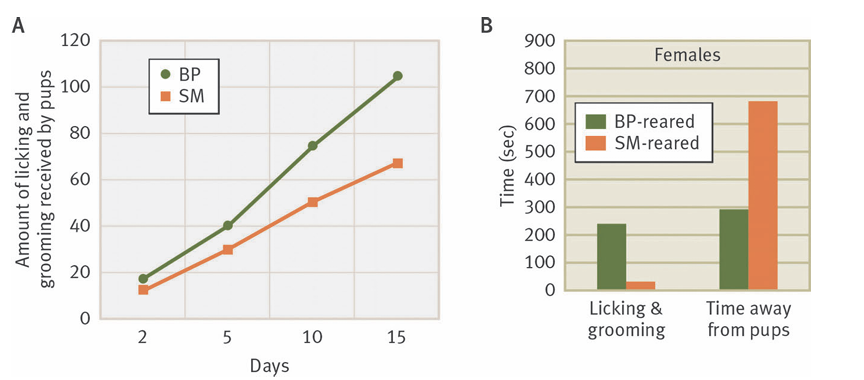
What’s the main message?
Pups in BP got more grooming, and after maturation, displayed more grooming + spent more time with their pups
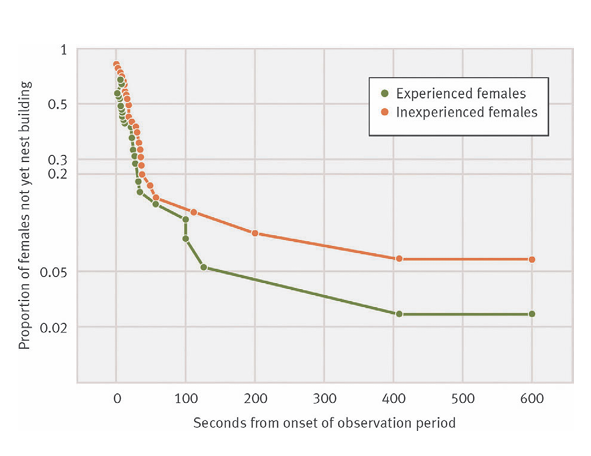
What’s the main message?
EF began building nests sooner than IF females and built them better