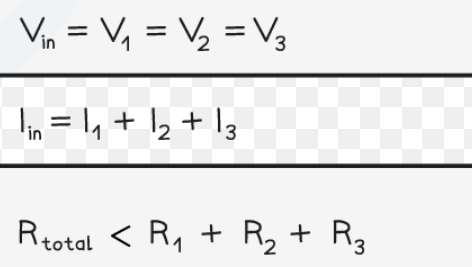P4 electric circuits
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
atom charge
none because has equal numbers of +ive protons and -tive electrons
atom charge when electrons removed/added
becomes positively charged when removed
becomes negatively charged when added
insulating materials
become charged when rubbed with other insulating material because electrons are transferred from one material to another
positive charges do NOT usually transfer between materials
electric charge measured in coulombs
electric field
around a charged object
electrostatic force
experienced when a charged object is placed in electric field of another charged object
THIS MEANS two charged objects exert a non-contact force on each other
what happens when electrostatic force..
like charges repel each other
opposite charges attract each other
electric field and force between two charged objects
gets stronger
distance between them decrease
strong electrostatic field
electrons in air molecules strongly attract the +tive charged object and if field is strong enough, electrons pulled away from air molecules causing flow of electrons between the objects (a spark)
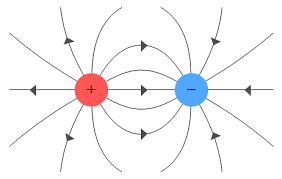
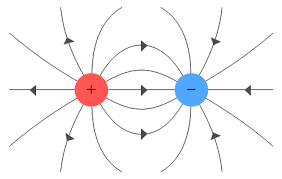
electric field diagram
drawn with field lines to show direction of force that a small positive charge would experience when placed in electrical field
drawing electric field diagram
field lines meet the surface of charged object at 90°
arrows always point away from +tive charge and towards -tive charge
electric current
when charge flows
the charge in an electric circuit is carried by electrons
unit of current
AMPERE (A)
1 ampere=1 coulomb of charge flow per second
conventional current
in circuit diagrams when charge flows from the positive terminal of a cell or battery to the negative terminal
single closed loop
current has the same value at any point in the circuit
metals
good conductors of electricity because they contain delocalised electrons which are free to flow through the structure
potential difference
measure of how much energy is transferred between two points in a circuit (V)
across a component is the work done on it by each coulomb of charge that passes through it
across a power supply/battery energy transferred to each coulomb of charge that passes through it
resistance
opposition in an electrical component to the movement of electrical charge through it. Resistance is measured in ohms.
series
one loop; all electrons in that loop form one current
static
electric charge that accumulates on an insulated object
what causes resistance
when electrons move through a circuit they collide w ions and atoms of the wires and components in te circuit
long vs short wire
long has more resistance bc electrons collide w more ions as they pass through
resistance of electrical component equation
PD (V)= current(A) x resistance (Ω)
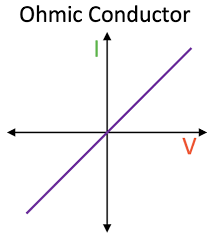
ohmic conductor graph
current directly proportional to PD in an ohmic conductor at a constant temp
resistance constant
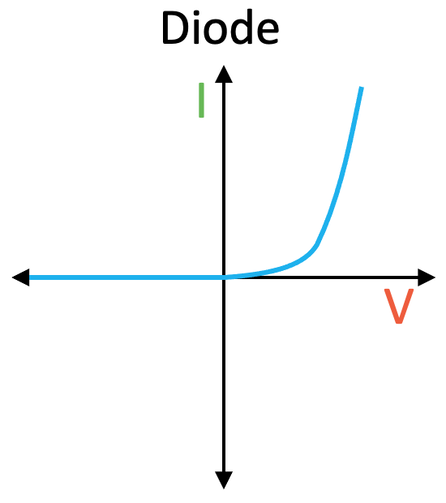
diode graph
current through diode only flows in one direction(forward direction)
needs minimum voltage before any current will flow
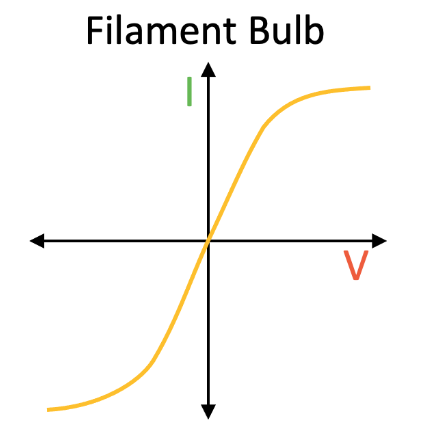
filament lamp graph
more current through filament=temp increase
atoms in wire vibrate more, collide more w electrons flowing through
resistance increase as temp increase
resistance of ohmic conductor
calculate gradient at that point and take inverse
resistance =
1
gradient
cell
electrical power supply
battery
main source of energy that provides a voltage which allows the current to flow through
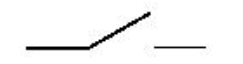
switch
enables the flow of electricity to be turned on and off
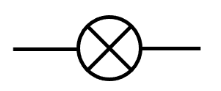
bulb

fixed resistor
resistance that remains the same
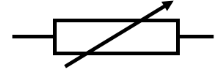
variable resistor
resistance that is used in some dimmer switches and volume controls
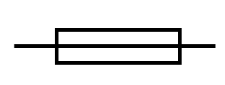
fuse
in an appliance causes too much current to flowbreaks the circuit if a fault
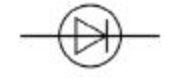
diode
allows current to flow in one direction but not in the reverse direction
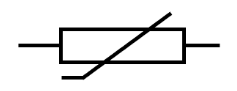
thermistor
temperature sensor
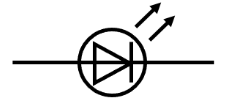
LED (light emitting diode)
transfer a greater proportion of electrical energy as light energy
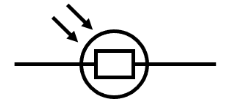
LDR (light dependant resistor)
used to detect light levels
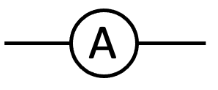
ammeter
measure the current flowing through a circuit
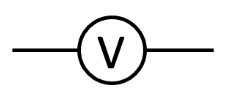
voltmeter
measure the potential difference (voltage) between two points in a circuit
series circuit
components are connected in a single loop
if one component stops working, the whole circuit stops working
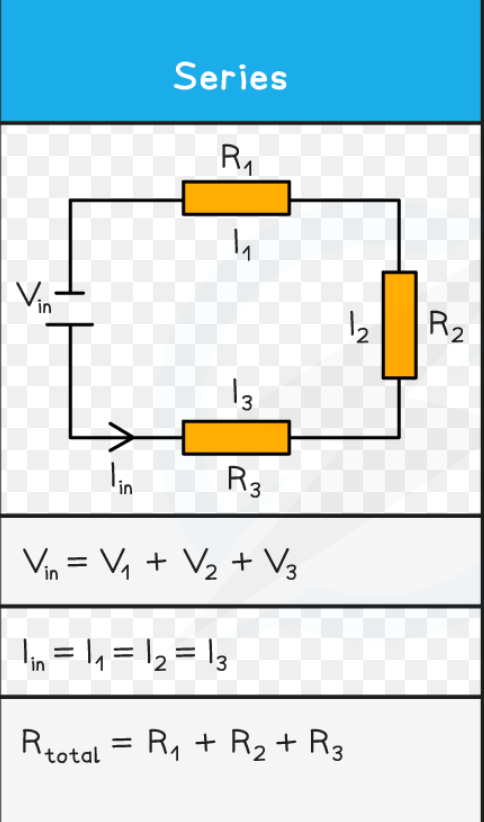
components in a series circuit
components w a higher resistance will transfer a larger share of total PD because V=IR (and current is the same through all components)

parallel circuits
made up of two or more loops through which current can flow
if one branch of parallel stops working, other branches not affected
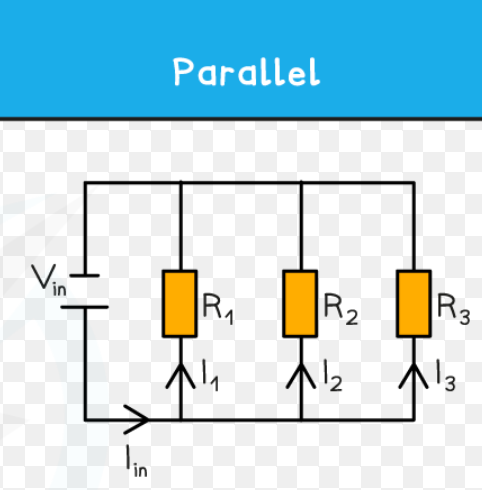
total resistance of 2 or more components in parallel
always less than smallest resistance of any branch bc adding a loop to the circuit provides another loop for the current to flow so more current can flow in total even though PD hasn’t changed.
adding more resistors to parallel
decreases total resistance of circuit