14.1-14.3 Quiz
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What factors affect rates of reactions?
reactant concentration, temperature, action of catalysts, physical state (surface temperature)
Rate of Reaction
change in concentration over time
rate of reaction of appearance equation
(change in moles)/(change in time)
rate of reaction of disappearance equation
-(change in moles)/(change in time)
What is the most useful unit for rate?
molarity; V is constant; M and mol are directly proportional
units for average rate
mol/L*s or M/s
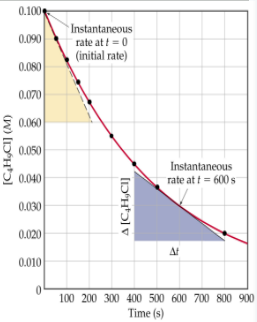
Average rate of disappearance of reactant _____ over time
decreases
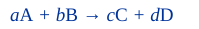
General Rule for Reaction Rate Stoichiometry
*don’t have coefficients in the denominator for the notable one
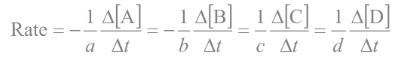
In general, rates increase as concentrations
increase
![<p>as [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] doubles with [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] constant, the rate</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/61e557fe-b106-44ec-a286-99f1f18103b3.png)
as [NH4+] doubles with [NO2-] constant, the rate
doubles
![<p>as [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] doubles with [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] constant, the rate </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4d0b135e-6fc2-4ed4-8eda-ffc1df9ba762.png)
as [NO2-] doubles with [NH4+] constant, the rate
doubles
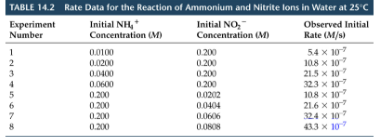
Rate Law for the reaction
Rate = k[NH4+][NO2-]
k in rate law
rate constant; specific reaction, units based on overall order of reaction, not change with concentration or time, refers to temperature (changes with temp), depends on catalyst presence, determined experimentally
Rate Law
Rate = k[reactant 1]m[reactant 2]n
Overall order of reaction
m+n+…
m and n mean in Rate Law
order in the specific reactant
when m or n =1, the rate is _______ _________ to the concentration of the reactant
directly proportional
when m or n =2, the rate is _________ __________ to the square of the concentration of that reactant
directly proportional; a reaction is xth order if doubling the concentration causes a 2x increase in rate
when m or n = 0, the rate _______ depend on the concentration of that reactant
does not
Units of rate constant general formula
units of rate/ units of concentration
1st order overall, k =
time-1
2nd order overall, k =
M-1time-1
3rd order overall, k =
M-2time-1
How do you interpret a rate expression?
make a relationship; the rate of disappearance of reactant is equal to _____ (ex. twice) the rate of appearance of product
Orders
0,1,2,3,etc.; come from experimental data; not related to Stoichiometry; usually variable m or n; exponent of substance concentration