aqa a level biology
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
What is covalent bonding?
When atoms share a pair of electrons in their outer shells
What is ionic bonding?
When ions with opposite charges attract one another
Describe hydrogen bonding
When a polarised molecule negatively charged area attracts a positively charged area of another molecule forming a weak electrostatic bond
What type of sub-unit makes up a polymer?
A monomer
What is the process of how monomers are joined?
Polymerisation
The monomers of a polymer are usually based on which element?
Carbon
What is the basic sub unit for a polysaccharide?
A monosaccharide
What are the three monosaccharides you need to know?
Glucose, galactose and fructose
What reaction joins molecules together?
Condensation reactions
What is released during a condensation reaction?
Water
Hydrolysis happens because of the addition of what molecule?
Water
What is hydrolysis?
The splitting of molecules via the addition of water
Define metabolism
ALL the chemical processes that take place in a living organism
What feature of carbon atoms allows for life?
Carbon can easily form bonds with other carbon molecules, forming a backbone
Molecules containing carbon are know as what?
Organic molecules
What is the general formula for a monosaccharide?
(CH2O)n
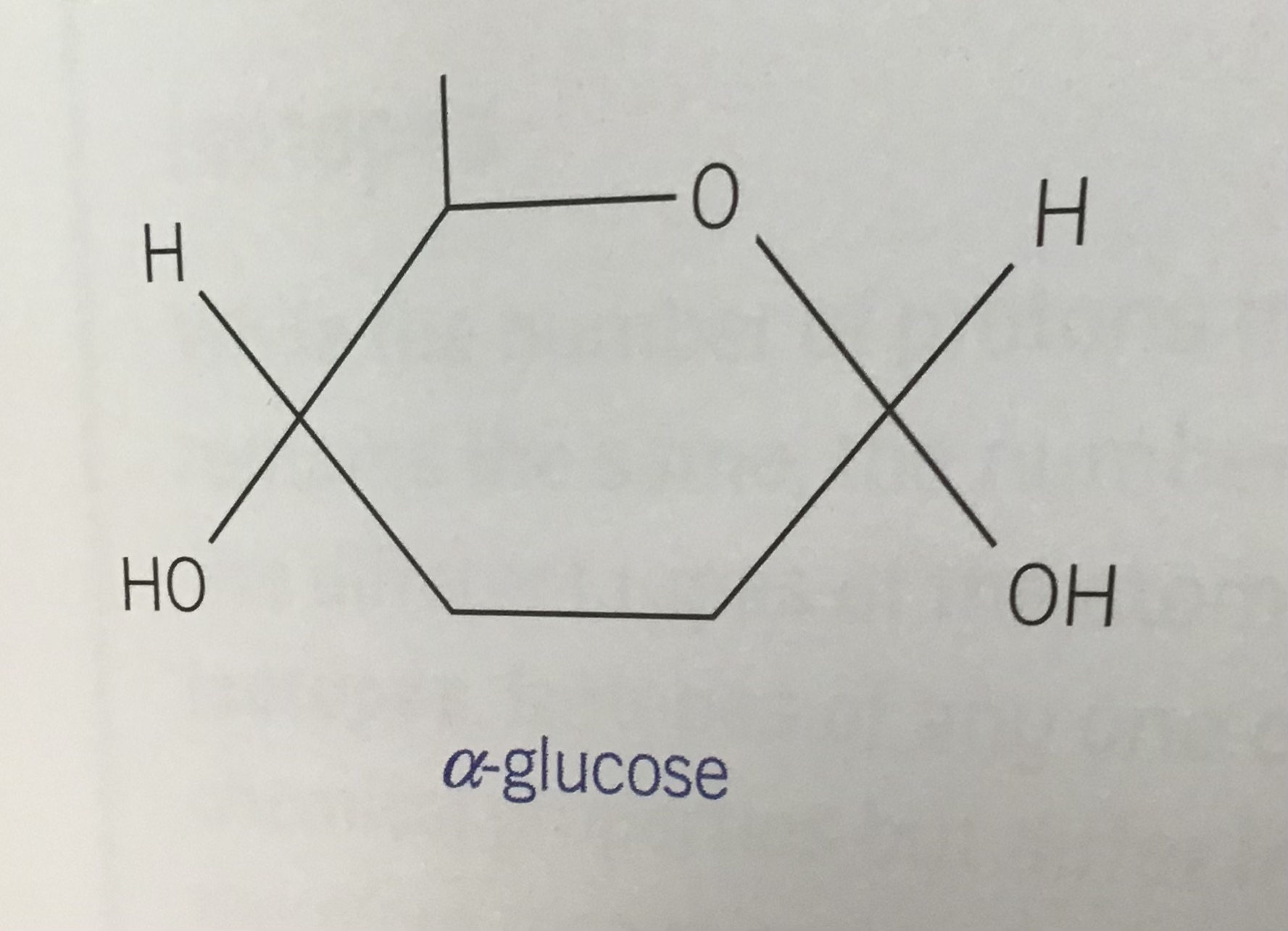
Draw the structure of alpha glucose
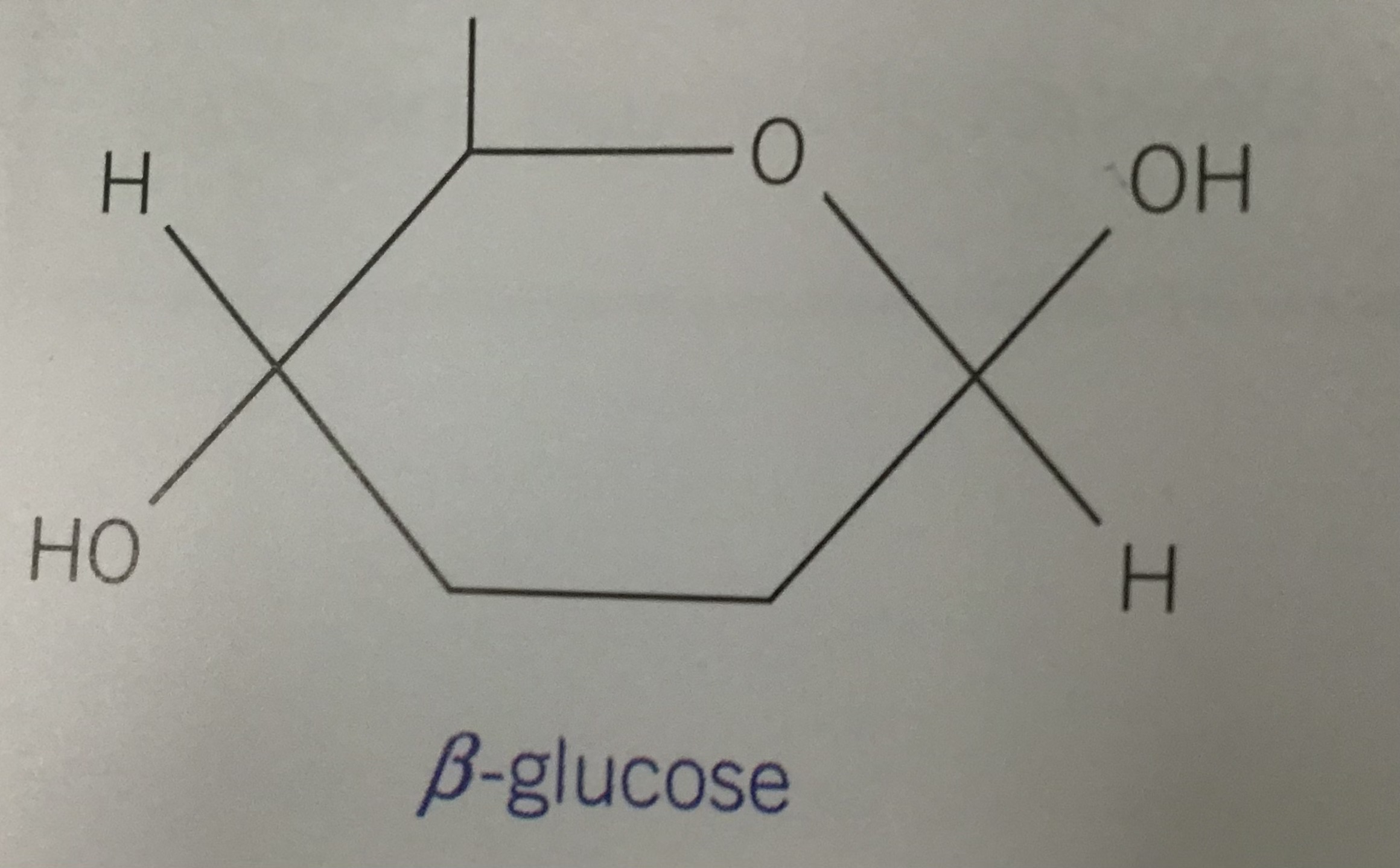
Draw the structure for beta glucose
Glucose is a hexose sugar. What does this mean?
It has 6 carbon atoms in its structure
What is the general formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. What does this mean?
A sugar that can donate electrons/reduce another chemical
What is the used to test for a reducing sugar?
Benedict’s Reagent
The test for reducing sugars is called what?
The Benedict’s test
What is Benedict’s reagent?
An alkaline solution of copper(II) sulphate
What colour is copper (II) sulphate?
Blue
When a reducing sugar is present what is formed during the Benedict’s test?
The insoluble, red precipitate of copper (I) sulphate
Describe the steps to the Benedict’s test
Add 2cm³ of the food sample, if this is not in liquids form grind it in water
Add an equal volume of Benedict’s reagent
Heat the mixture gently for 5 minutes
How is the Benedict’s test semi-quantitative?
The closer the colour of the final precipitate is to red the more reducing sugars are present
When combined in pairs, monosaccharides form what?
Disaccharides
Name three disaccharides and the monosaccharides that make them
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
Which disaccharide is a reducing sugar?
Maltose
What type of bond joins monosaccharides together?
A glycosidic bond
List the steps required in the test for non-reducing sugars
If the sample is not already in water it must be ground up into water
Add 2cm³ of the food sample being tested to 2cm³ of Benedict’s reagents in a test tube and filter
Place the test tube in gently boiling water for 5 minutes, if the colour of the Benedict’s reagent stays the same then a reducing sugar is not present
Add another 2cm³ of the food sample to 2cm³ of dilute hydrochloric acid in a test tube and place in the gently boiling water for another five minutes
The hydrochloric acid will hydrolyse the disaccharides leaving monosaccharides behind
Slowly add sodium hydrogen carbonate solution to the test tube to neutralise the hydrochloric acid and then test with pH paper to make sure the solution is alkaline
Re-test the resulting solution by heating gently with 2cm³ of Benedict’s solution for 5 minutes
If a non-reducing sugar was present the original sample will now turn orange-brown due to the reducing sugars that were produced by the hydrolysis of non-reducing sugars
Polysaccharides are large, insoluble molecules this makes them good for what?
Storage
What type of glucose is starch made out of?
Alpha glucose
What is cellulose used for in plants?
Structural support
Describe the test for starch?
Place 2cm³ of the sample being tested into a test tube
Add two drops of iodine solution and shake
The presence of starch is indicated when the iodine turns from an orangey yellow to a blue black
Where is starch found?
In many parts of a plant such as the seeds and storage organs
Starch acts as what for plants?
A major energy source
An unbranched chain of alpha glucose molecules that form starch can be wound up into a tight coil, why is this useful?
It makes the molecule very compact and therefore take up less space
Are starch chains branched or unbanched?
They can be both
Why is starch being branched an advantage for the plant?
It has many ends that enzymes can act on simultaneously meaning that glucose is readily available for respiration
Why is starch being insoluble good for the plant?
It does not affect water potential so too much water isn’t drawn into the plant
It cannot diffuse out of cells
Where is starch never found?
In animal cells
What is the animal equivalent of starch?
Glycogen
Why is the mass off carbohydrates stored in glycogen low?
Because fats are the main storage molecule in animals
What three features of glycogen make it suited to its role?
It’s insoluble, compact and highly branched
Why is glycogen more highly branched than starch?
Because animals are more metabolically active and therefore need energy faster than plants
What is the main difference between cellulose and starch?
Cellulose is made of beta glucose and starch is made of alpha glucose
Rather than forming a coiled chain what structure does cellulose form?
It forms a straight, unbranched chain
What does the straight structure of cellulose allow it to do?
It allows it to run parallel to each other and form hydrogen bonds which create cross linkages between adjacent chains.
Cellulose molecules are grouped together to form what?
Microfibrils
Microfibrils are arranged are arranged in parallel groups called what?
Fibres
What is cellulose used for in plants?
It provides structure and rigidity to the plants cell wall
What does cellulose prevent the cell from doing during osmosis?
Bursting
Why do adjacent cellulose molecules have so many cross linkages?
To provide more strength to the molecule?
What four characteristics do lipids share with one another?
they all contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
the proportion of oxygen to carbon and hydrogen is smaller than in carbohydrates
they are insoluble in water
they are soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols and acetones
What are the two main groups of lipids?
Triglycerides and phospholipids
What are the main roles of lipids?
a source of energy
waterproofing
Insulation
Protection
Why are lipids a source of energy?
When oxidised lipids provide more than twice the energy as the same mass of carbohydrates
How are lipids waterproofing?
Lipids are insoluble in water, for example plants have a waxy cuticle layer that conserves water.
How do fats insulate the body?
They are slow conductors of heat so help retain body heat. They also act as electrical insulators in the myelin sheath around nerve cells
How do fats offer protection to the body?
It is often stored around delicate organs such as the kidneys, this protects them
Describe the structure of a triglyceride
They have three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule
What type of bond forms between each of the fatty acids and the glycerol in triglycerides
An ester bond
If a fatty acid has a double carbon-carbon bond what is it?
Polyunsaturated
If a fatty acid has a single carbon-carbon bond what is it?
Mono-unsaturated
If a fatty aid has no carbon-carbon bonds what is it?
Saturated
Why are triglycerides a good source of energy?
Carbon-hydrogen bonds store a lot of energy and they have a low mass to energy ratio so lots of energy is stored in a small volume.
Why are triglycerides non-polar?
So that they are insoluble in water and do not affect the water potential of the cell
What is the benefit of triglycerides releasing water when oxidised?
They provide a source of water to organisms such as camels that live in the desert where water is sparse
What is the difference in structure between triglycerides and phospholipids?
Phospholipids have a phosphate molecule in place of one of the fatty acids
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic?
The head
What does hydrophilic mean?
To be attracted to water
Which area of a phospholipid is hydrophobic?
The tail
What does hydrophobic mean?
To repel water
Because one part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic and one is hydrophobic what can a phospholipid be described as?
A polar molecule
Because phospholipids are polar what do they do in the presence of water?
They position themselves so that the hydrophilic heads are as close to the water as possible and the hydrophobic tails are as far away as possible
What are the advantages of phospholipids being polar?
In an aqueous environment they form a bilayer such as in a cell surface membrane. As a result a hydrophobic barrier is created between the inside and outside of the cell
What can phospholipids in the cell-surface membrane form when combined with carbohydrates and what do these structures do?
They form glycolipids which are important in cell recognition
Describe the steps in the emulsion test
Take a completely dry and grease free test tube
Take 2cm³ of the sample and add 5cm³ of ethanol
Shake the tube thoroughly to dissolve any lipid in the sample
Add 5cm³ of water and shake gently
A milky white emulsion forming indicates the presence of a lipid
As a control repeat the process using just water and the final solution should remain clear
How many amino acids occur naturally?
20
Every amino acid has a central what?
Carbon atom
What do is a chain of amino acids called?
A polypeptide
Polypeptides can be combined to form what?
Proteins
What is the amino group of an amino acid?
-NH2
What group makes an amino acid an acid?
The carboxyl group
What is the structure of the carboxyl group?
-COOH
What five things does every amino acid have?
a central carbon atom
an amino group
a carboxyl group
a hydrogen atom
a R group
How are peptide bonds formed?
A condensation reaction between the -OH from a carboxyl group of one amino acid and the -H from the amino group of another amino acid
What is a proteins primary structure?
The sequence of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain
What determines the primary structure of a protein?
The DNA sequence
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
The hydrogen bonds between the amine and carboxyl groups of the amino acids that determine the folded shape of the polypeptide chain
What are the two possible secondary structures of proteins?
Alpha sheets and beta pleats
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The 3D structure of the protein
What three bonds create a proteins tertiary structure?
disulphide bridges
ionic bonds
hydrogen bonds
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
If a protein contains more than one polypeptide chain it has a quaternary structure
What is the test for proteins?
The biurets test
Describe the steps in the biurets test
Place a sample of the solution in a test tube.
Add an equal volume of sodium hydroxide solution
Add a few drops of very dilute copper (II) sulphate solution and mix gently
If the solution turns from blue to purple a protein is present