Forensic Pathology First Quiz
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sept. 25th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Forensic Pathology:
A branch of forensics that examines death and the investigation of the body
Egyptians:
first of the removal of organs
Religious reasons
Remove the heart and weigh it to the feather or truth
Autopsy:
derives from the Ancient Greek
“To see for oneself”
“Sight, view”
Around 3000 BC, ancient Egyptians were one of the first civilizations to practice the removal and examination of the internal organs of humans.
More for religious reasons and not so much to determine the cause of death
In 44 B.C., Julius Caesar was stabbed to death by at least 60 rival senatorCaesar’s’s personal physician, Antistius, performed an autopsy and issued an official “autopsy report” (the first in history”
He found that Caesar had been stabbed 23 times. None was fatal except the second wound in the breast, which pierced his aorta. a
This was declared a fatal wound, although it was noted that the amount of blood loss from the other wounds would also have been fatal. Al.
Antistius delivered his results to a Roman forum (the first expert witness), leading to the development of the term “forensic,” meaning “before the forum.”
1888:
in the London area known as White Chapel, five women were brutally murdered and mutilated
Jack the Ripper’s social media campaign
“Dear Boss” letter was postmarked and received on 27 September 1888 by the Central News Agency of London and forwarded to Scotland Yard.d
Taunting police
Some feel that the letters were a hoax perpetrated by a local journalist to sell newspapers.s
Yet, the legend of the Ripper taunting the police has held on
The name “Jack the Ripper” comes from these letters
Media attention
Luka Magnotta:
Born Eric Clinton Kirk New, July 24, 1982, in Canada
Appeared in multiple pornographic videos and worked as a stripper and male model
Was a pin-up model in a 2005 issue of Toronto’s “fab” magazine
OUTtv’s readily show COVERguy
Many claims about his personal life and celebrity, including being involved with Karla Homolka
Initially came to the attention of law enforcement for uploading videos of himself killing a kitten
1 Lunatic 1 Icepick
On May 25, 2012, an 11-minute video titled 1 Lunatic 1 Ice Pick was uploaded to a best gore website, depicting a naked male tied to a bed frame being repeatedly stabbed with an ice pick and a kitchen knife, then dismembered, followed by acts of necrophilia
Body parts were sent to the Conservative Party of Canada, the Liberal Party of Canada, and an elementary school.
The body was identified as that of Lib Jun, a Chinese international student.
Magnotta was identified from surveillance video showing him disposing of the body part.s
Apprehended at an Internet cafe in Berlin while reading news about himself in June 2012
Convicted of first-degree murder on December 23, 2014
The public receives exposure to death and autopsy largely through the media and pop culture.
Sex and death have always been the biggest sellers of media outlets
One could argue that as sex becomes more mainstream, death is now the biggest seller
The death of a famous celebrity frequently gets prominent media attention
This is even more so if the death is felt to be “unnatural” or the result of some foul play
The autopsy report garners great interest
Conspiracy theory is rife
True Crime:
Public interest in “True Crime”
TV shows
Books
Documentaries
Podcasts
“in these fictional programs, sexy, charismatic, and highly astute crime scene investigators recover covert evidence from the crime scene, analyze the evidence with exceedingly sophisticated scientific testing procedures (often to the beat of a stylish soundtrack), make absolute conclusions about the perpetrator’s identity and involvement in the crime, and often extract a confession from the perpetrator, all within an hour”
2006 Nielsen Rating
30 million people watched CSI on one night
70 million people watched at least one of the CSI shows
40 million people watched one of two other forensic dramas: Without a Trace and Cold Case
5 of the top 10 television programs were about scientific evidence in a criminal trial
The “CSI effect”
Portrayal of forensic science (especially on TV) influences public perception and ideas.
More people are interested in forensic careers.
Some studies implied that jurors expected more from forensic evidence, and the burden of proof placed on the prosecution was higher.r
Criminals could “get ideas”
Police investigations
What does the CSI effect mean for courtrooms?
Do jurors expect more from forensic science
Are they more likely to convict or acquit?
Shelton et al. 2007
Study at Eastern Michigan University
Presented potential jurors with various scenarios regarding differing levels of forensic evidence in different cases
These higher expectations of having forensic evidence did not have an effect on the chance of conviction..
The CSI effect doesn’t have a real-life effect on juries.
Julianna Redding:
On March 16, 2008, 21-year-old Julianna Redding was discovered deceased in her Santa Monica, CA apartment.
She had been beaten to death
The smell of natural gas pervaded the apartment
A lit candle was discovered burning on the coffee table
Ms. Redding was a transplant from Arizona who had come to California to try to break into the movie industry
She had appeared in several ads, both print and on television
She was working as a hostess at a local restaurant
It was there that it is theorized she met Dr. Munir Uwaydah
Dr. Munirn Uwaydah was a surgeon who operated multiple clinics in the Los Angeles and Santa Monica area
He was reportedly a multimillionaire
He hired Ms. Redding to work in one of his clinics, and he presented her with a lavish gift.s
There is evidence that they had a romantic relationship
Dr. Uwaydah also pursued Greg Redding, Ms. Redding’s father, who was a pharmacist
Greg Redding backed out of a supposed business deal after hearing rumors of Uwaydah’s shady business deals and discovering that Uwaydah was married with several children overseas
Five days later, Julianna Redding was found dead
No forced entry
A neighbor reported hearing screams around 9:53 on March 15th
An aborted call to 911 was placed around 9:53
Ms. Redding had been strangled to death, and defensive wounds were identified on her throat.
A large amount of DNA was detected at the current scene
On the victim's skin, clothes, and cell phone
On the stove knob
A bloody fingerprint was found on a plate in the sink
All of the DNA at the crime scene (as well as the fingerprint) belonged to a woman named Kelly Soo Park
Kelly was employed by Uwaydah
Many assert that she was an “enforcer” for Uwaydah, but this was not admitted at trial
The defense claimed that her DNA had been deposited by secondary transfer
Secondary transfer occurred because Julianna was taking paper towels from the job to clean her house, and Kelly was the one supplying the paper towels in the job
After three hours, the jury acquitted Kelly Soo Park for the murder of Julianna Redding
As it turns out:
The defense used a “jury profiler”
Potential jurors were questioned about their television-watching habits
Jurors were preferentially selected based on those who preferred television shows that favored the defense and defendants.
Don’t be fooled by the DNA
Lee Miles
Trial partners
Our biggest challenge is that for most people, DNA is DNA, and it tells the truth. Everybody gets that from TV.”
“We were only allowed twenty minutes to question the prospective jurors, so I felt that I had to rely on as much of the art of what I do as the science.”
“I’m looking for, sometimes, a contrarian. Someone who, no matter what you say, they’re going to start challenging you.”
“Probably our most favorite juror, who ended up being the foreperson, one of his favorite shows was The Good Wife. They’re openly confronting the fact that they are often working for clients that they think look guilty, and yet they give them the very best defense possible.”
“Criminal Minds and Blue Bloods, if those were a juror's favorite show, they might be more prosecution-oriented oriented”
“The verdict really showed that DNA alone is not enough to convict someone.”
Medical Examiners interrogate suspects:
No. They do work closely with the police and investigators to obtain information.
Time of death is an exact science:
Time of death is very hard to determine, and no method is foolproof
Liver temperature can be affected by many things
Vitreous fluid
General determinations can be made, but “the patient died between 7 and 7:15 am” isn’t really a thing (unless the bullet also broke a clock)
Technology:
Most labs are in the state budget
A lot of the technology you see on TV doesn’t actually exist
Usually no windows in the morgue either
DNA is analyzed in ten minutes
Another big NCIS offender
DNA analysis is painstaking work and can take weeks
Many labs are backlogged and can take months to issue a report
Many forensic pathologists do not have a DNA lab on-site
Only involved with murders
Actually, most cases that involve forensic pathology are not murders or suicides.
Many more natural and accidental deaths
These cases can also require the skills of a forensic team to determine the cause and circumstances of death.
Careers in Forensics
Medical Examiner
Job Description
Perform autopsy, investigate cause and manner of death, testify in court
Education
Medical degree (MD)
Pathologist, residency in Anatomic Pathology
Fellowship in forensic pathology
Board-certified by the American Board of Pathology in Forensic Pathology
9 years post-graduate education
Average salary
$200,000
Coroner:
Job description
Investigate cause and manner of death, may perform autopsy, may testify in court
Education
No definitive education required
Elected public office
Average salary
$70,000
Pathologist Assistant:
Job Description
Eviscerate during autopsy, write preliminary report, perform surgical pathology duties (grossing, etc)
Education
Graduation from a national accrediting agency for clinical laboratory sciences (NAACLS) accredited education program
Successfully passing the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) certification exam
Average salary
$100,000
Diener
Job description
Eviscerate during autopsy
Education
High school diploma or associate's degreeOn-the-jobb training
Average salary
$35,000
Forensic Investigator
Job description
Go to the scene, preliminary investigation, interview, and work closely with the medical examiner
Brief the medical examiner on use
Education
Usually a bachelor's or an associate's degree
Degree in a forensic-related field preferred
Knowledge of the manner and cause of death
On-the-job training
Average salary
$50,000
Crime Scene Technician
Job description
Go to the scene, collect evidence
Work closely with the police and the office of Forensic Science
Education
Usually a bachelor's or an associate's degree
Degree in a forensic-related field preferred
Knowledge of the manner and cause of death
On-the-job training
Average salary
$50,000
3 American serial killers are generally considered to have more than 30 victims.
Ted Bundy
American serial killer known for his charisma and good looks
Confessed to 30 homicides, but has confessed to killing 35-36 women in the past, and some estimates run upwards of 100 or more
Infamous for escaping from prison twice and murdering multiple victims in one day, sometimes abducting women from the same location within hours of one another
He was executed in the electric chair in 1989
John Wayne Gacy
Known to have murdered a minimum of 33 teenage boys and young men between 1972 and 1978, 26 of whom he buried in the crawl space of his Chicago home
Gacy was known as the “Killer Clown” due to the fact that he often entertained children at social events dressed in a self-devised clown costume.
Gacy was executed in 1994
Gary Ridgeway
Also known as The Green River Killer
Truck painter who confessed to killing 71 women
Almost exclusively targeted sex workers from Seattle
Suspected of killing over 90 victims, confessed to 7, convicted of 49
Sentenced to life without parole
Forensic Pathology
The BA branch of pathology that applies medical knowledge to the court of law
Forensic pathologists are physicians (MD, DO) who are trained in pathology and specialize in forensics
Perform medicolegal autopsies
Issue the death certificate and report
Cause and manner of death
Offer expert opinion in court
Team members
Forensic pathologists
Investigators
Autopsy technicians
Toxicologists
DNA lab
Anthropologists
Forensic dentist
Forensic autopsy
Examination of a dead body to determine the cause and manner of death
Identity needs to be established
Cases of sudden, unexplained, suspicious, or violent death
Delaware code title 29, chapter 47
How does the ME office get involved?
Death is reported by:
Hospitals, mostly ER
Police
Nursing homes
Hospice
Correctional facilities
Fire Marshal's office
Gift of Life
Attorney General's Office
Skins, bones, cornea
Bones: Material will be used for replacement
Skin will go to burn victims
Cornea
Who needs a forensic autopsy?
Person dies → police (other) → suspected foul play (csi, detectives, AG) → ME, autopsy performed.
You have to be careful when issuing the time of death
Disposition of cases: Natural Death
Inquiry:
No doctor to sign DC
Extensive medical problems
Released from the scene due to extensive medical problems
Inspection (external examination)
Elderly, with no doctor
Autopsy:
Descendants with no known medical problems
Scene Investigation
The most important part of the investigation
Crucial to be observant of small details
Does anything look out of place?
Suspicious circumstances
Staged scene, postmortem manipulation
Signs of forced entry
Drug paraphernalia
Death investigators/ME have jurisdiction over the body, and law enforcement has jurisdiction over the scene.e
Professionalism and good interdepartmental communication are key
Death scene investigation
Forensic investigator goes to the scene (depending on the case and state)
Investigators must wear protective equipment (shoe covers, mask, gloves, etc.)
Scene and body must be photographed
Conducts interviews of family, friends, witnesses
Transports the body to the morgue
Obtains medical information
Maintains close contact with the police if needed
N.b,. policdepartmentpt, all of the scene investigation in homicides
Collect evidence (e, weapons, bullets, blood, fingerprints, etc.)
Scenes must be attended (pathologist or forensic investigator) in homicides, suspected homicides, mass fatalities, and all pediatric deaths.
Positions of the body are not described in relation to nearby objects, presence of weapons, blood spatter, wounds (if visible), suicide note(s), medications
The body is placed in a body bag, which is sealed to maintain the chain of custody.
The scene may be visited or revisited after an autopsy is performed if new information is unearthed.d
Requires police presence
The report about the scene investigation needs to be completed promptly:
Where, when, who reported, when arrived at scene, circumstances, medical history, medications, scene description, disposition of the body
Examination of clothing
Needs to be examined at the scene and during autopsy
Examine for blood, semen, and other body fluids
Check pockets for personal belongings, drug/paraphernalia, medications
Injuries should match damage to the clothing (cuts, holes from a gunshot wound)
Tearing, grease marks, broken glass, and paint chips can assist in reconstruction for a motor vehicle accident
Determining CoD and MoD
42-year-old female, history of alcohol abuse, found dead at the bottom of the steps
Interview of neighbors: allegedly involved in an altercation the previous night
Medical records reveal an ER visit for a broken nose and laceration repair on the cheek 2 months ago
On autopsy: numerous bruises, head trauma, and cirrhotic liver30-year-oldd male, history of depression, found at his residence, numerous pill bottles with missing pills. On the day found was the first anniversary of his mother's death
No foul play at the scene
Autopsy: negative findings
Toxicology positive for zoloft, Benadryl, Tylenol
25-year-old female, found dead by her friend, heroin packets at the scene, tourniquet on the arm
Family reports several rehab admissions in the last 2 years and an abusive boyfriend
Autopsy reveals scattered bruises, but no severe trauma
Toxicology positive for heroin metabolites
65 year 65-year-old male with dementia and chronic pain was found dead in bed, with numerous opened pill bottles
Lives by himself, has a caretaker who comes every day
Autopsy: negative findings, no trauma
Toxicology: high levels of antidepressants and oxycodone
Identification of the body
Known:
Family identifies the body
Documents (ex: drivers license)
Unknown:
No family/identification documents
Due to decomposition/skeleton remains
Missing person
Found in remote area
Burned or mutilated bodies
Identification of the Body
Known
Family identifies the body
Documents, e.g, driver's license
Unknown
No family/identification documents
Due to decomposition/skeletal remains
Missing person
Found an iemote area
Burned or mutilated bodies
Postmortem interval (PMI)
Time elapsed since death
Livor mortis
Rigor mortis
Core body temperature
Degree of decomposition
Insect activity
Animal activity
Scene investigation
Lividity
Reddish-purple discoloration in dependent areas of the body due to gravity
Areas resting against a firm surface will be pale
Evidence within 30 minutes to 2 hours after death
Not fixed
Reaches a maximum of 8-12 hr
Fixed
Not helpful for PMI, but to determine if the body was moved
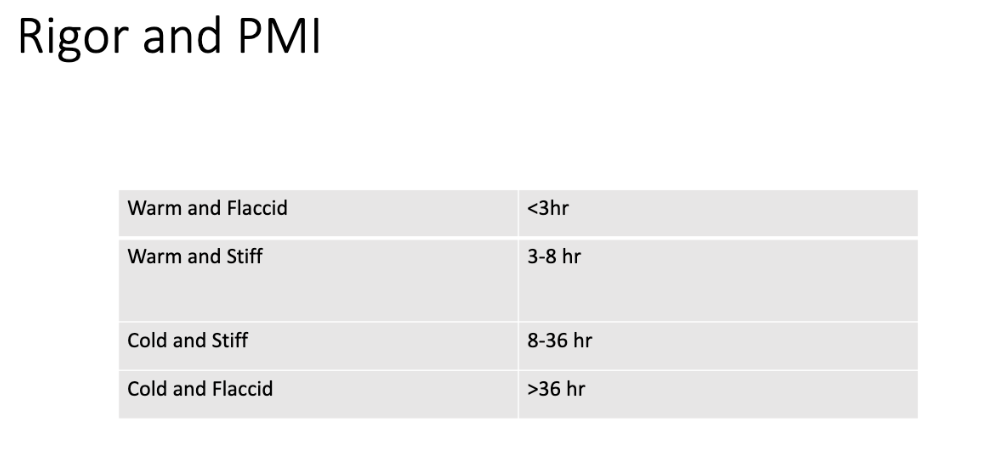
Rigor Mortis
Stiffening of muscles due to the disappearance of the metabolic energy source within cells (ATP) and the accumulation of lactic acid
Appears 3-6 hr after death, fully developed by 12 hr
First in small muscles: face, jaw
May last 18-36 hr
Influenced by
Activity before death
Temperature
Clothing
Preexisting conditions
Rapid:
Heavy exercise
Seizures
fever/infection
Poisons
Strychnine
Electrocution
Delayed:
Cold temperature
Thin
Chronic disease
Temperature
PMI = 37 degree celsius - rectal temp + 3 degree celsius
Imperfect
The environment around the body
Cooling not uniform
AC or heating
Wet, dry conditions
Sun, shade
Extremes of age
Other techniques
Vitreous fluid potassium levels
Gastric emptying
Invalidated
Types of food, protein vs fatty meal
Affected by comorbid conditions, ex, diabetes
Death Scene Investigation
These clues are the most helpful in determining PMI if the person was not seen for an extended period of time.
Bank activity
Unopened mail
Missed appointments
Receipts
Text messages, phone calls, emails
Social media
Postmortem Changes
Autolysis
Self-digestion of cells due to enzymes
Putrefaction
Breakdown of tissue due to anaerobic bacterial activity intestines
Influenced primarily by moisture and temperature
Decomposition
A corpse progresses through five stages of decomposition
Fresh
Bloat (autolysis)
Active decay (putrefaction)
Advanced decay
Skeletonisation
Manifestations of decomposition
Marbling
Due to the breakdown of hemoglobin within blood vessels
Skin slippage and blistering
Green discoloration
Gas formation
Scrotal swelling
Maggot infestation
insect/animal activity
Can occur rapidly, <24hr in hot climates
The degree of decomposition may help to establish
Post mortem interval
Place of death
To help advance this research, several body farms have been established
Mummification
Body dehydrated
Often, a dry and hot environment
Adiopcere
Gray, whit, waxy material from the breakdown of fat to acids
Body immersed in water or in a damp, warm environment
Months to appear
Body Farm
Bill Bass established the Forensic Anthropology Center in 1987
Observe body decomposition in different conditions for training and medicolegal purposes
Bodies donated to medicine
4000 registered future donors
Entomology
Studying the mature flies, pupal casings and maggots can help determine PMI
Correlated against weather patterns
Each state of decomposition attracts a different species of insect
Identification
Fingerprints are the fastest way to identify
Although it is hard because not everybody’s fingerprints are in a system
Tattoo
Surgery scars
Dental
DNA
Medical equipment
Skeletal Remains
Requires consultation of a forensic anthropologist
Determine sex, age, stature, race
PMI estimation is difficult
DNA
Forensic anthropology
Helps to determine if there was pre-, peri, post post-mortem trauma
Helps to identify if the deceased had a predisposing joint/bone disease
Help to determine if the deceased had procedures/surgeries with implants
External Examination
X-ray
Performed on cases with gunshot wounds, sharp force injuries, and pediatric death
Localizes and identifies the presence of metal objects
Identifies bone fractures
Also may be used for ID purposes
UV light
Evidence collection
Photography
Examination of clothing
Documentation
Washing
Photography
Tardieu spots
Small hemorrhages due to rupture of small vessels
Postmortem drying of sclera
Collection of rape kit
Fingernail scrapings
Vaginal swab
Oral swab
Rectal swab
Pubic hair
Head hair
Underwear
Rape kit
Two cotton tip swabs used for collection of vaginal, oral, and rectal specimens
Smears on glass slides and then air-dried
Slides are stained to identify sperm
Failure to demonstrate sperm does not preclude intercourse
Evidence Collection
In cases of homicide and suspicious death, the body has to be examined for trace evidence
Hair
Fibers
Paint
Foreign material
Labeled, sealed, and submitted to police, maintaining the chain of custody
Bite marks
Should be swabbed for recovery of saliva for DNA testing
Forensic dentist consultation
Internal Exam
An essential part of autopsy
Requires knowledge of anatomy and pathology
Examination of all internal organs
Different pathological conditions can be diagnosed during gross exam
Congenital anomalies
Trauma
Cancer
Infection
For centuries, internal examination was the only tool available to determine the cause of death
Changes in organs lead to the discovery of pathological processes
Most pathology books use knowledge of autopsy findings in diagnosing the disease
In the 18th century, the idea of matching autopsy findings with pre-death diagnosis was introduced
During the first half of the 20th century, postmortem examinations demonstrated that clinical diagnoses were often wrong
Through autopsies, doctors were better able to understand and correct trends in misdiagnosis and to identify mistakes
Autopsy was critical to improvement of joint prostheses, new heart valves, and heart transplants
Y-shaped incision is performed
Skin and soft tissue is reflected
Chest plate is removed
Examination of 3 cavities
Chest
Heart and lungs
Abdomen
Liver, spleen, kidneys, intestines, adrenal glands, pancreas
Cranial
Brain
Methods of Examination
Virchov’s: organ by organ
Rokitansky: en block removal and dissection
All organs are weighed, examined, and sections and cultures are taken if needed
Scalp incised
Skull cap removed
Dura opened
Brain removed and examined
Small pieces of tissues are saved in formalin
Microscopic analysis
Chest Cavity
Heart
Lungs
Thoracic aorta
Rib cage
Heart
Normally weighs 250-400 grams
Pumps blood rich in oxygen to all organs
Located inside pericardial sac
Heart disease is leading cause of death
Myocardial infarction
Hypertension
Atherosclerosis
Aortic dissection
Sudden Cardiac Death
May be due to atherosclerosis, ie, narrowing of coronary arteries due to cholesterol plaques
Myocardial infarctions are more rare among forensic autopsies
Seen more in a hospital setting
Mechanism is the sudden onset of ventricular fibrillation
Often seen after strenuous physical or emotional activity eg, snow shoveling, grass cutting, running
Hypertension
Can lead to cardiomegaly (enlarged heart) or left ventricular hypertrophy (thick left ventricle)
Predisposes to sudden death due to
Ruptured aortic aneurysm
Sudden arrhythmia
Stroke
Lungs
Paired, sponge-like organs
Right lung is larger
Normally weigh 350-450 grams
Oxygenate blood and eliminate carbon monoxide
Damaged by tobacco smoke, leading to COPD
Light and air filled in asthma
Heavy and congested in heart disease
Filled with fluid in drug overdose
Pulmonary embolism
Blood clot in the pulmonary artery(ies) which occludes flow through lungs, cutting off oxygenated blood back to the heart
Who is at risk?
Recent injury or surgery
Cancer
Contraceptive medications
Immobilization for a prolonged time
Genetic factors
Can present as sudden death
Abdominal Cavity
Liver
Kidneys
Stomach
Intestines
Spleen
Pancreas
Adrenal glands
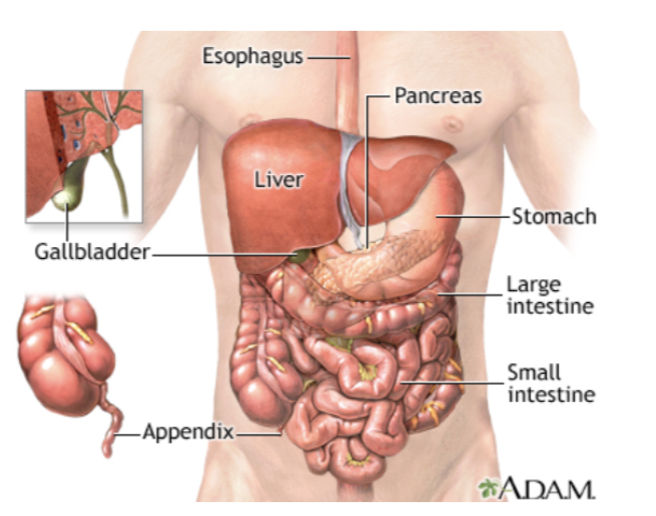
Abdomen
Ischemic bowel
Peritonitis
GI bleeding
Cirrhosis
Ruptured abdominal aneurysm
Acute pancreatitis
Spleen laceration with bleeding
Kidneys
Paired, bean-shaped smooth surface organs
Normally weigh 100-160 grams
Filter waste products from blood and produce urine
Regulate blood pressure and electrolyte balance
Granular surface
Hypertension
Small and atrophied
Diabetes
Liver
Largest organ in the body
Normally weighs 1200-1600g
Primary function is to produce bile, break down fats, remove toxins, and produce proteins important for clotting
Brown and smooth surface
Alcohol abuse and hepatitis C are two common causes of liver failure due to cirrhosis
Spleen
Located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen
It recycles red blood cells and plays an important role within the immune system by storing white blood cells
Extremely rich blood supply
After trauma, it can lead to massive hemorrhage, causing hemoperitoneum (blood in abdominal cavity)
Can be affected in viral infections
Mono
Stomach
Acidic environment allows for first part of digestion, eg. the breakdown of food
Stomach lining can be irritated by alcohol and tobacco, leading to ulcers, which can bleed
Intestines
Small intestine: about 20 feet long
Large intestines: about 5 feet long
Digestion of food, absorption of nutrients and water, and production of waste
Commonly found postmortem pathologies
cancer
Diverticulitis
Ischemic bowel
Ruptured appendicitis
Pancreas
Produces enzymes to help digest fat
Produces insulin, controls blood sugar
Acute pancreatitis
Commonly seen with alcohol abuse
Cranial cavity
The brain normally weighs 1200-1450 grams
Very important for examinations in the cases of trauma, especially child abuse
Can identify changes if meningitis or encephalitis
Diagnoses of Alzheimer’s, Lewy Body dementia, etc., are made only postmortem
White matter shrinking
Amyloid plaques
Brain
Controls all functions of the body
Interprets information from the outside world
Hearing, smell, taste, touch, sight
Essence of mind and soul
Intelligence, creativity, emotion, and memory are a few things governed by the brain
3 parts: cerebrum, brain stem, cerebellum
Protected by dura and skull
Natural Death
Sudden and unexpected
Cardiovascular disease is the most common and leading cause in men
Atherosclerosis
Myocardial infarction
Aortic dissection
Stroke
Ruptured cerebral aneurysm
Diabetes mellitus, obesity, smoking, and ethanol abuse are important contributory factors to morbidity
Medical history is essential
Recent ER/doctor’s visits
Review of prescription medications
Testing
Preliminary: ELISA, detects commonly used and abused drugs
Confirmatory: GC/MS, LC?MS
Will confirm and give concentrations
Gas Chromatography
Separation of multiple compounds in a mixture appears as peaks
Mass Spectroscopy
Detects the fingerprint of each compound
Drug Testing
Hundreds of different drug compounds
Antidepressants
Antipsychotics
Stimulants
Pain killers
Sedatives
Tylenol
What is pathology?
The study of disease
Divided into anatomic pathology and clinical pathology
Anatomic pathology: cytology (cells), histology (tissues), autopsy
Clinical pathology: lab administration, blood bank, chemistry, hematology, molecular pathology, microbiology, urinalysis
Who are pathologists?
Physicians trained in anatomic and/or clinical pathology
We supervise medical laboratories and all lab tests performed in a hospital or clinic
We diagnose diseases looking at cells and tissue under a microscope
We perform hospital autopsies when requested by family members
What is forensic pathology?
The medicolegal investigation of sudden, unexplained deaths, violent deaths, and suspicious deaths
Forensic pathologists are anatomic pathologists additionally trained in special autopsy procedures, collection of evidence, toxicology, injury patterns, would ballistics, forensic serology and DNA
Forensic pathologists testify as expert witnesses in courts of law
What does it take to become a forensic pathologist?
Bachelor degree (4 years)
Medical degree (4 years)
Anatomic pathology (3 years) or anatomic and clinical pathology residency (4 years)
Forensic pathology fellowship (1-2 years)
All forensic pathologists are required to be board certified in anatomic pathology and forensic pathology at a minimum
Why investigate deaths?
To identify the decedent
To determine cause and manner of death
To identify diseases or injuries pertinent to public health
To provide closure to families
To determine if a crime has been comitted, documentation of injuries, and collection of evidence
Coroner Systems
An elected public official whose duty is to determine cause and manner of death
Usually are not physicians and have no medical training
Very minimal forensic training if any
If autopsy is determined to be necessary, a physician or forensic pathologist will perform (non-physician coroners cannot perform autopsies)
May have a conflict of interest if a funeral director, prosecurtor, or law eforcement officail
No accreditation or standarization between jurisdictions
Medical Examiner Systems
Employ physicians (usually board certified forensic pathologists) to investigate deaths and perform autopsies
May be accredited by the National Association of Medical Examiners (NAME)
Usually work independently of law enforcement to prevent bias
Many offices are critically understaffed in 2022
FP Shortages making national headlines
What is an autopsy?
Comes from the Greek word autopsia which means “seen by oneself”
Involves an external examination of a deceased individual, sometimes followed by an internal examination of the organs
There are different types of autopsy
Hospital autopsy vs forensic autopsy
External exam only vs partial autopsy vs virtopsy vs full autopsy
Hospital Autopsy
Perfomed by general pathologist
Requires written permission from next of kin
Is an educational tool
Minimal external examination; focus is on internal examination and correlation of findings with clinical records
Almost never involves examination of neck organs; no collection of evidence or toxicology
Usually can only sign out manner of death as “natural”
Top 10 Causes of Death in the US (2019)
Heart disease, cancer, unintentional injuries, chronic lower respitatory disease, stroke, alzheimer disease, diabetes, kidney disease, influenza and pneumonia, suicide
Accidental Death:
Since 2011, unintential posioning (drug overdoses) have been the leading injury mortality, followed by motor vehicle accidents
The rate of drug overdose deaths is increasing every year
The rate of drug overdose deaths due to synthetic opioids (fentanyl, fentanyl analogs, and tramadol) increased by 45% between 2016 and 2017 and continues to increase every year since
Overdoses due to cocaine and other psychostimulants has also been on the rise since 2012
Although official data is not yet available, it is believed that 2020 was the worst year for drug overdoses and suicides in recent history due to the COVID pandemic
Death Certificates:
There is no standard death certificate, each state has their own version
However, most have the general appearance shown
The death certificate is very important
The source for state and national mortality statistics
Is often required before burial or cremation
Required for insurance payouts
Medical certifier required fields
Date and time of death
Cause of death
Manner of death
Was case referred to ME?
Was an autopsy performed?
Did tobacco use contribute to death?
Pregnancy status of females
Injury section as applicable
Certifier section with signature
Cause of Death
Any injury or disease that produces a physiologic dereangment in the body that results in the death of the individual
Examples:
Gunshot wound of the head
Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
Multiple blunt force injuries
Heroin overdose
Hanging
Immediate COD: occurs just before death
Intermediate COD: intervening steps
Proximate COD: what started the whole process
Examples: pericardial tamponade due to ruptured myocardial infarction due to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Contributing conditions: diabetes mellitus
Multiple blunt force injuries due to motor vehicle collision
Or, most forensic pathologists would just sign cause of death as “gunshot wound of the abdomen”
Undetermined Cause of Death
Rarely, after complete investigation, autopsy, histology, and toxicology, the cause of death cannot be determined
The presumed mechanism in these deaths is a physiologic process, such as a cardiac arrhythmia, that leaves no evidence at autopsy
Genetic testing is becoming more commonplace to assist in these deaths but is not standard at this time
Mechanism of Death:
The physiologic derangement produced by the cause of death that results in death
Many causes of death have similar mechanisms of death
Should NOT be used on a death certificate
Examples:
Hemorrhage
Cardiac arrhythmia
Cardiopulmonary arrest → this is frequently used in appropriately on death certificates by untrained physicians
Manner of Death:
Explains how the cause of death came about
This is determined by investigation, not the autopsy
Five options:
Natural
Due to solely or nearly totally to disease and/or the aging process
Accident
There is no evidence that the injury occurred with intent to harm or cause death
Suicide
An intentional, self-inflicted act committed to do self-harm or cause death of oneself
Homicide
Occurs when death results from an injury from a volitional act committed by another person to cause fear, harm, or death
Classification of death as “homicide” does not indicate or imply criminal intent
Undetermined
Used when the information pointing to one manner of death is no more compelling than one or more other competing manners of death when all information is considered
Some juristions was “undetermined” as a standard manner of death in drug overdose deaths unless the intent of the deceased is known
Law enforcement often cannot close a case with an “Undetermined” manner
Pending Investigation:
Is NOT an appropriate final manner of death but can be used when filling out the initial death certificate if the pathologist is waiting for further investigation and testing
Death certificates signed out as “pending investigation” must be amended when final cause and manner of death is determined
Basic Rules in Determining Manner
The time interval between the injury and death is of little relevance
In delayed deaths, it is important to consider what previous disease process or injury led to an individual’s demise
When death involves a combination of natural processes and external factors such as injury, preference is given to the non-natural manner of death
Consequences of chonric substance abuse, such as alcoholic cirrhosis, alcohol withdrawal seizures, endocardities secondary to chronic IV drug abuse, and emphysema associated with smoking are signed out as “natural” as long as toxicology is negative for a toxic level of the substance
Deaths directly due to the acute toxic effects of a drug or poison are typically classified as “accident”
Russian Roulette is typically classified as “suicide” because the act of placing a loaded firearm to the head and pulling the trigger is inherently dangerous
Motor vehicle fatalities are usually classified as “accident” even if the driver was impaired
Vehicles homicide is a legal term and not used by forensic pathologists
Death due to toxic envenomization, such as spider bites, snake bite, and anaphylactic reactions to bee stings are usually classified as “accident”
Deaths due to positional restraint or choke hold by law enforcement personnel are classified as “homicide”
Deaths due to discharge of a weapon by another person are usually classified as “homicide” unless it can be demonstrated that the weapon discharged without anyone pulling a trigger
A 55 year old male complains of severe chest pain and goes to the ER. he is diagnosed with a myocardial infarction (heart attack) but dies despite treatment.
What is the cause of death?
Myocardial infarction
What is the manner of death?
manner
Would this case require autopsy?
yes
A 20 year old male athlete suddenly collapses and dies during footbal practice. Should this case be referred to a medical examiner? Autopsy shows hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (a genetic type of enlarged heart) and toxicology is negative. What is the manner of death?
Yes shold be referred to a medical examiner.
Autopsy findings: HCM, negative toxicology
Manner of death: natural
Going back to the previous scenario, suppose the autopsy is negative. Investigation reveals that a rectal temperature taken on scene showed a core temperature of 106 degrees Fahrenheit.
What is the cause of death now?
Hyperthermia (heat stroke)
What is the manner of death?
Accident
A 60 year old male is paraplegic due to being shot in the back at age 18. He requires daily bladder catheterization since he is unable to urinate. He dies of sepsis (blood infection) due to a urinary tract infection.
What is the cause of death?
Sepsis due to urinary tract infection
What is the manner of death?
homicide
A 23 year old female is found death in an abndoned warehouse with drug paraphernalia. Toxicology shows a toxic level of fentanyl.
What is the cause of death?
Fentanyl
What is the manner of death?
accident
A 75 year old female is found deceased at home near several empty bottles of prescription medications. Her husband recently passed away. A will and insurance documents are found near her body. Autopsy shows severe heart disease. Toxicology is positive for lethal levels of multiple medications
What is the manner of death?
suicide
A 19 year old male is found deceased on the parking lot adjacent to a 20-story building. He has no known medical history, did not leave a suicide note, and had no recent life stressors. Autopsy shows multiple blunt force injuries and a blood alcohol level of 0.32
What is the cause of death?
Multiple blunt force injuries due to fall from height
What is the manner of death?
accident