Comprehensive Taxation and Business Law Review for CPA Exam
1/230
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
231 Terms
What is the filing requirement for individuals regarding gross income?
Individuals must file if their income is equal to or greater than the sum of their gross income and the regular standard deduction amount.
What is the definition of a qualifying child under the CARES criteria?
A qualifying child must be a close relative (son, daughter, stepchild, sibling, stepsibling, or their descendants), must obtain an SSN, and must be younger than the taxpayer and under 19 (or 24 for full-time students).
What is the adjusted gross income (AGI) requirement for filing?
Taxpayers must file if their self-employment income is $400 or more.
What is the deadline for filing individual income tax returns?
Taxpayers must file by April 15th, with an extension available until October 15th.
What is the requirement for a full-time student to be considered a qualifying child?
A full-time student must attend an educational institution for at least part of 5 months of the taxable year.
What is the residency requirement for a qualifying child?
The child must have the same principal place of abode as the taxpayer for more than half of the tax year.
What is the citizenship requirement for a qualifying child?
The child must be a citizen of the US or a resident of the US, Canada, or Mexico.
What does the Support Test entail for a qualifying relative?
The taxpayer must have supplied more than half of the support for a person to claim them as a relative.
What is the significance of the Under Gross Income Limitation for qualifying relatives?
The gross income test does not apply to a qualifying child, meaning they can still be claimed even if they have some income.
What is the filing status for single taxpayers?
Single status is based on the taxpayer's status at the end of the year; they must be unmarried or legally separated.
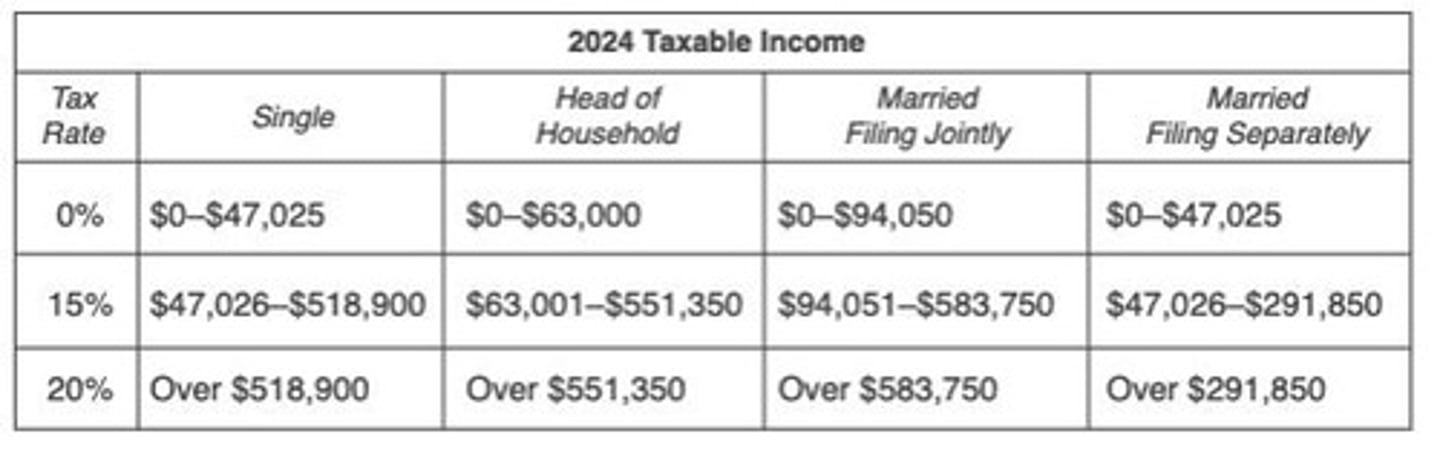
What are the conditions for filing a joint return for married couples?
Married couples can file jointly if they are married at year-end or living together in a common law marriage.
What happens if parents have equal custody of a child?
The parent with the higher adjusted gross income qualifies to claim the child as a dependent.
What is the impact of divorce on filing a joint return?
If divorced during the year, a joint return may not be filed; if a spouse dies during the year, a joint return may be filed.
What form is used to request an extension to file taxes?
Form 4868 is used to request a 6-month extension to file.
What is the additional standard deduction for taxpayers aged 65 and older?
Taxpayers aged 65 and older are eligible for an additional standard deduction amount.
What is the significance of the term 'Qualifying Relative' in tax filing?
A qualifying relative must meet the Support Test, meaning the taxpayer must provide more than half of their support.
What is the requirement for a child to be considered a qualifying child in terms of support?
A qualifying child must not have contributed more than half of their own support.
What is the tax filing requirement for individuals with self-employment income?
Individuals must file if their self-employment income is $400 or more.
What is the income threshold for a qualifying relative in a separate property state?
The gross income must be less than $5,050.
How is income treated in a community property state?
Most incomes are split 50/50, and only taxable income is included.
What is the definition of a qualifying widower with a dependent child?
A taxpayer who can use the joint tax deduction for two years following the death of their spouse.
What is the accrual method of income recognition?
Recognition occurs when income is earned, similar to GAAP with exceptions.
What are the requirements for a qualifying child?
Must be a child, stepchild, legally adopted child, or sibling.
What is the cash method of income recognition?
Recognition occurs in the period the revenue is actually or constructively received.
What are the conditions to qualify as Head of Household?
Must be unmarried, not a qualifying widower, and maintain a home for more than half the year.
What is included in gross income under dividend income?
Includes taxable dividends from earnings and profits (E&P).
What are qualified dividends?
Dividends paid by domestic or certain qualified foreign corporations.
What is the tax treatment of employer contributions to a Roth 401k?
Contributions made by the employer are included in income.
What are nontaxable fringe benefits?
Benefits like employer-paid health insurance premiums that are excludable from income.
What is tax-exempt interest income?
Interest from state and local government bonds, which is reportable but not taxable.
What is the exclusion limit for employee educational expenses?
Up to $5,250 may be excluded from gross income for payments on behalf of student loans.
What is the tax treatment of stock dividends?
Stock dividends are nontaxable.
What is the maximum exclusion for adoption expenses paid by an employer?
$16,810 can be excluded from taxable income.
What is the tax treatment of rental income?
Net rental income is calculated as rental income minus total rental expenses.
What is the tax treatment of unemployment compensation?
All of unemployment compensation is taxable.
What are the income thresholds for Social Security benefits to be taxable?
Up to 50% of benefits are taxable for middle-income earners.
What is the tax treatment of gifts and inheritances?
Not taxable unless the property is sold in future terms.
What is the tax treatment of life insurance proceeds?
Excluded from the gross income of the beneficiary.
What is the treatment of payments made pursuant to a divorce before December 2018?
Alimony received is not included in gross income.
What is the tax treatment of cancellation of debt?
Cancellation of debt is taxable and included in gross income.
What is the maximum exclusion for first-time homebuyer distributions?
$10,000 can be excluded for first-time homebuyer distributions.
What is the tax treatment of personal injury awards?
Compensation for lost profit is taxable, but wrongful death awards are not.
What is the treatment of rental income for properties rented less than 15 days?
Not required to report rental income.
What is the Bona Fide Residence Test for foreign-earned income exclusion?
The filer must have been a bona fide resident of the country for an entire taxable year.
What is the Physical Presence Test for foreign-earned income exclusion?
The filer must be present in the country for 330 full days.
What is the tax treatment of gambling winnings?
Winnings are included in gross income, and losses are deductible only to the extent of winnings.
What is the tax treatment of prizes and awards?
FMV of prizes and awards is taxable unless selected without entering a contest.
What are the tax implications of qualified tuition reductions?
Exclusions apply for undergraduate and graduate level tuition reductions.
What is the treatment of payments for medical expenses under FSAs?
Must be used within the plan year; forfeited if not used within 2.5 months after year-end.
What is the exclusion limit for dependent care assistance benefits?
$5,000 of benefits can be excluded from gross income.
What is the treatment of rental income in taxation?
Rental income is excluded from gross income, but depreciation of business assets and employee benefits are deductible.
What is the Nine Factor Test used for?
It determines if an activity is engaged in for profit, considering factors like business-like manner, expert advice, and personal time devoted.
What are hobby losses in tax terms?
Hobby losses are limited deductions for activities not engaged in for profit; income must be included but expenses cannot be deducted.
What is the maximum deduction for self-employment tax?
50% of self-employment tax is deductible to arrive at AGI.
What is the standard deduction for married taxpayers?
$1,550 per issue per taxpayer.
What is the standard deduction for unmarried taxpayers?
$1,950 per issue per taxpayer.
What is the maximum contribution to an IRA for individuals under 50?
$7,000.
What is the maximum contribution to an IRA for individuals over 50?
$8,000.
What is the maximum allowable deduction for organization costs?
$5,000 for both organization and start-up costs.
What is the treatment of personal interest in tax deductions?
Personal interest is not deductible.
What is the maximum deduction for charitable contributions?
Cash contributions are limited to 60% of AGI, while ordinary income property is limited to 50% of AGI.
What is the tax treatment for education loan interest?
Education loan interest is an adjustment to AGI and limited to $2,500.
What is the penalty for early withdrawal of savings?
A penalty is assessed on early withdrawal, which is deductible when arriving at AGI.
What is the tax treatment for moving expenses?
Moving expenses are only allowed for members of the armed services with a permanent change of station.
What is the definition of Qualified Business Income (QBI)?
Qualified Business Income must be generated in the USA and is eligible for a deduction of 20%.
What is the maximum deduction for self-employed health insurance?
All health insurance premiums for dependents are deductible.
What is the tax treatment for casualty losses?
Casualty losses are deductible only for areas in a declared disaster.
What is the maximum credit for the Adoption Credit?
The maximum credit is $16,810 for qualified adoption expenses.
What is the maximum credit for the Child Tax Credit?
Taxpayers may claim a $2,000 credit for each qualified child under 17.
What is the Earned Income Credit?
The Earned Income Credit applies to low-income individuals and families, providing a refundable tax credit.
What is the treatment of alimony payments for tax purposes?
Alimony payments are deductible for divorces finalized before December 2018.
What is the treatment of student loan interest for tax purposes?
Student loan interest is an adjustment for AGI, limited to $2,500.
What is the maximum contribution for a Coverdell Education Savings Account?
The maximum contribution per beneficiary is $2,000 annually.
What is the tax treatment of gifted property?
The donee's basis in gifted property is generally the donor's adjusted basis at the date of the gift.
What is the holding period for gifted property?
The recipient of a gift absorbs the donor's holding period.
What is the maximum allowable deduction for Section 179 depreciation?
$1.22 million.
What is the phase-out amount for Section 179 depreciation?
The phase-out begins when the total cost exceeds $3,050,000.
What is the treatment of bad debts for tax purposes?
Accrual basis taxpayers must write off bad debts when they are uncollectible; cash basis taxpayers cannot deduct bad debts.
What is the maximum deduction for moving expenses?
Moving expenses are only deductible for members of the armed services with a permanent change of station.
What is the treatment of capital gains and losses?
Gains are recognized if sales price exceeds adjusted basis; losses are recognized if sales price is less than FMV.
What is the tax treatment of ordinary and necessary expenses?
Ordinary and necessary expenses are deductible if they are common and accepted in the industry.
What is the tax treatment for energy-efficient home improvements?
The maximum credit for energy-efficient home improvements is 30% of the cost.
What is the treatment of personal losses in tax deductions?
Personal losses are not deductible.
What is the tax treatment of non-deductible medical expenses?
Non-deductible medical expenses include elective procedures and illegal drugs.
What is the maximum deduction for health savings accounts (HSA)?
Individuals can make up to $4,150 of pre-tax contributions, increasing by $1,000 for those 55 and older.
What is the maximum deduction for qualified medical expenses?
Qualified medical expenses are deductible if they exceed 7.5% of AGI.
What is the tax treatment of interest paid on business loans?
Interest paid on business loans is generally deductible unless the firm exceeds the $30 million threshold.
What limits the deduction of interest expenses when average gross receipts exceed the threshold?
The sum of business interest income, 30% of adjusted taxable income, and floor plan financing.
What happens to disallowed business interest expenses?
They can be carried forward indefinitely.
What is the maximum deduction for charitable contributions before considering DRD?
10% of taxable income.
How are installment sales recognized for income tax purposes?
Income is recognized when received.
What is the treatment of state tax refunds for income tax?
State tax refunds are treated as income.
What is the income recognition for rent and royalties received in advance?
Income is recognized when earned.
What is the treatment of life insurance proceeds for key staff?
They are not included in taxable income.
What is the limit on business gifts for tax deductions?
Deductible up to $25 per recipient per year.
What is the limit on deductions for business meals?
50% of the cost is deductible.
What is the maximum deduction for organizational expenditures and start-up costs?
$5,000 for each cost, with excess amortized over 15 years.
What is the depreciation limit under Section 179?
$1,160,000.
What is the treatment of penalties, bribes, and kickbacks in tax deductions?
They are not deductible.
What is the treatment of federal income taxes for corporations?
They are not deductible.