Integumentary System
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Organs of the Integumentary System
Skin and its accessory structures (hair, nails, glands)
Blood vessels
Muscles
Nerves
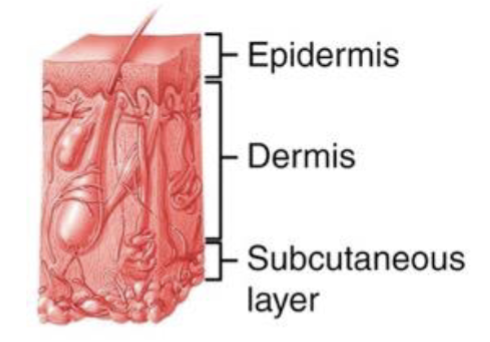
2 major levels of the skin (cutaneous membrane)
Epidermis and dermis
Epidermis
Outer layer of the skin made of 4 main cell types
Composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Avascular
Dermis
Made of connective tissue (2 layers)
Binds the epidermis to the underlying tissues
Vascular
Hypodermis (aka subcutaneous layer)
Deep to the dermis and functions to attach the skin to underlying tissues and organs
Not part of the skin
Composed of areolar and adipose (mostly) tissues
Contains large blood vessels and nerves that feed superficial layers
Thin skin
In most areas of the body the epidermis is made up of 4 distinct strata; Hairy
Thick skin
Epidermis in areas where exposure to friction is the greatest (ex/ fingertips, palms, and soles) contains an extra layer; Hair-less (typically with a thicker stratum corneum due to increased layers)
Keratinocytes
Produces keratin (hard protein) to protect underlying tissues from abrasion, heat, microbes, and chemicals
Melanocytes
Produce melanin pigment (which functions to absorb UV light and prevent DNA damage)
Langerhans cells
Intraepidermal macrophages involved in immunity
Tactile epithelial (Merkel) cells
Special touch receptors that contact sensory neurons
Stratum basale
Deepest layer of skin
Single row of keratinocytes (along with melanocytes and Merkel cells)
Some cells undergo mitosis
As new cells are formed older cells are “pushed” toward the surface and become keratinized (cytoplasm is replaced with keratin)
Stratum spinosum
8-10 layers of keratinocytes
Contain organelles and produce coarser bundle of keratin
Rounded in living tissue but appear shrunk and covered in spines when prepared for microscopic examination
Stratum granulosum
3-5 layers of flattened keratinocytes that undergoing apoptosis
Cells contain keratohyalin (dark staining protein granules that help organize keratin filaments)
Contain lamellar granules that secrete a lipid-filled product that acts as a water repellant
Stratum lucidum
Present only in thick skin
4-6 layers of flattened, clear, dead keratinocytes
Provides additional toughness to these regions of the skin
Stratum corneum
Most superficial layer
25-30 layers of flattened, dead, keratinocytes
Membrane enclosed packages of keratin
No nucleus or organelles
Keratinization
Cells accumulate more keratin as they move from one epidermal layer to the next (cells are moving further away from blood supply and start to die)
As new keratinocytes are formed in the stratum basale (closest to blood supply and receive nutrients)…
Older cells are pushed to the surface and eventually undergo apoptosis and are sloughed off; Entire process takes 7-10 weeks
Dandruff
An excessive number of keratinized cells that shed from the skin of the scalp
Psoriasis
A disorder in which keratinocytes divide and move more quickly than normal & results in flaky, silvery, scales that form on the skins surface
2 regions the dermis contains
Papillary region and reticular region
Papillary region
Superficial portion of the dermis that lies just below the epidermis
Composed of lose areolar connective tissue (contains thin collagen and fine elastic fibers)
Contains dermal papille
Dermal papille
Ridges that project into the undersurface of the epidermis and anchor the epidermis to the dermis
Contains blood vessels that feed epidermis
Contain touch receptors
More pronounced on fingertips and toes
Make fingerprined
Reticular region
Deepest portion of the dermis
Composed of dense irregular connective tissue (resists stretching because it contains thick collagen fibers and coarse elastic fibers arranged in net-like manner)
Contain hair follicles, nerves, and skin glands
Tears or excessive stretching in this region can cause stretch marks (striae)
A combination of genetic, environmental, and physiological factors
Skin color results from
Melanin, hemoglobin, carotene
Certain pigments can impart a variety of colors to skin
Melanin
A pigment protein produced by melanocytes in the stratum basale
Everyone has about the same number of melanocytes
Hemoglobin
Circulation of dermal blood affects skin color
Well oxygenated gives pinkish color and poor oxygen gives bluish color (cyanosis)
Carotene
Diet may affect skin color
Egg yolks and yellow vegetables contain this pigment that may turn skin orange-yellow
Melanocytes
Image
Anatomy of hair
Parts of hair include the shaft, the follicle. and the root
Hair shaft
Above the skin surface
Hair follicle
Epithelium that surrounds the hair root and bulb
Root
Below the skin surface; May be called either the epithelial root sheath or a dermal root sheath
Hair related structures
Arrector pili muscles and hair root plexus
Arrector pili muscles
Smooth muscles in the dermis that contract with cold/fear forming “goose bumps”
Hair root plexus
Bundle of nerve endings that detects hair movement
4 types of skin glands
Sebaceous glands, eccrine sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, ceruminous glands
Sebaceous glands
Secrete sebum (oil) into hair follicles
Found in most areas of the body except for this skin
Prevents skin/hair from drying out and inhibits some bacterial growth
Eccrine sweat glands
Secretes watery sweat through ducts that open to pores in the skin
Found in most regions of the body
Helps with thermoregulation as sweat evaporates from skin
Apocrine sweat glands
Secrete a thicker sweat into hair follicles
Become active after puberty and found mainly in the axilla, groin, and areolae
Contents include lipids and proteins that bacteria feed off and gives off a musky scent (body odor)
Ceruminous glands
Secrete cerumin (wax) into the ear anal (only)
Provides a sticky barrier that impedes the entrance of foreign bodies and insects
Waterproofs the ear canal and prevents the growth of bacteria and fungi
Nails
Plates of tightly packed, hard, dead, keratinocytes that form a clear, solid covering over the dorsal surface of the distal portions of the digits
Nail body (plate), free edge, and nail root
3 regions of the nail
Nail body (plate)
Visible part, filled with harder keratin
Contains lunula
Lunula
A crescent-shaped area of the proximal portion of the nail body that appear white-ish because it is the thicker, most actively growing region of the nail
Free edge
Part of nail that extends past the distal end of the digit
Contains hyponychium
Hyponychium
Thickened region of the epidermis that binds the nail to the tip of the digit
Nail root
Part that is not visible and is buried in a fold of the skin (eponychium or cuticle)
Nail matrix
Proximal to the nail root and contains cells that divide mitotically to produce new nail cells
Thickness, strength, flexibility, degree of keratinization, distribution and type of hair, density and types of glands, pigmentation, vascularity, innervation
Variations of skin throughout the entire body (despite the same basic structure)
Thermoregulation, blood reservoir, protection, cutaneous sensations, excretion and absorption, synthesis of vitamin D
Functions of the skin
Skin homeostatic regulation of body temperature
Releases sweat onto the surface
Adjusts the flow of blood in the dermis
How does releasing sweat help with thermoregulation
Evaporation of sweat from the skin helps lower body temperature
How does adjusting blood flow in the dermis help with thermoregulation
Blood vessels in the dermis can dilate allowing more blood to flow closer to the surface of the skin which increases the amount of heat loss through the skin OR in the cold vessels can constrict to decrease the amount of blood flow to decrease heat loss
Dermis houses an extensive network of blood vessels
8-10% of the total volume of blood in an adult
Keratin function in skin
Protects underlying tissues from microbes, abrasion, heat, and chemicals
Tightly packed cells of the epidermis act as a water barrier to
Prevent evaporation
What do macrophages in the epidermis do
Guard against bacteria and viruses
Cutaneous sensations
Touch, pressure, vibration, and thermal sensations that rely on special sensory receptors as well as free nerve ending
Papillary layer (superficial) cutaneous sensations
Free nerve endings - heat, pain, cold, tickle, itch
Meissner’s corpuscles - light touch
Reticular and subcutaneous layer(deep) cutaneous sensations
Pacinian corcupscles
Skin plays a small role in excretion
Small amounts of water is lost through sweat and evaporation while most substances are excreted through the digestive and urinary systems
Skin plays a role in absorption
Water-soluble substances are not absorbed
Lipid-soluble substances (fat-soluble vitamins, certain drugs, gases, some hormones) can be absorbed
Transdermal drugs
A drug contained in a skin patch is released continuously at a controlled rate, normally used for drugs that are quickly eliminated from the body
Skin synthesis of vitamin-D
Requires the activation of a precursor molecule in the skin by UV rays in sunlight then enzymes in the liver/kidneys modify the activated molecule producing calcitriol
Calcitriol
The most active form of vitamin-D, as a hormone that aids in absorption of calcium from foods in the gastrointestinal tract into the blood
Small amount of sun exposure is required for vitamin D synthesis
People who avoid sun exposure or live in northern climates need to supplement their vitamin D
Vitamin D also plays a large role in what?
Immunity, it helps activate cells that respond to infections (especially respiratory infections)
2 kinds of wound healing processes can occur
Epidermal wound healing or deep wound healing depending on the depth of the injury
Epidermal wound healing
Occurs following a superficial wound that only affects the epidermis then skin returns to normal function
Deep wound healing
Occurs when an injury extends to the dermis and subcutaneous layer which may result in loss of function and/or development of scar tissue
Epidermal wound healing
For abrasions or minor burns, basal cells of the epidermis enlarge and migrate across the would until the would is eventually sealed and the epidermis returns to normal
Phases of deep wound healing (involves bleeding)
Inflammatory phase - clot forms to unite the edges
Migratory phase - clot becomes a scab, fibroblasts migrate to the area and secrete collagen fibers to help bind the edges together
Proleferative phase - wxtensive growth of epithelial cells beneath any scab
Maturation phase - scab falls off once the epidermis has returned to normal thickness
Scar formation
Occurs due to extensive collagen build-up from fiberblasts
Skin burns
Tissue damage caused by excessive heat, electricity, radioactivity, or corrosive chemicals that denature the proteins in the skin; graded according to their severity
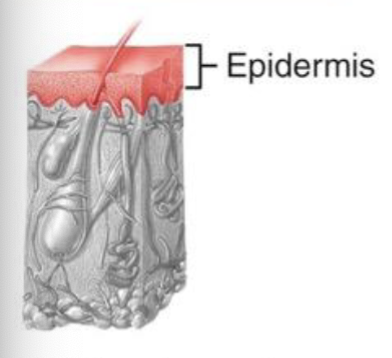
1st degree burns
Involves only the epidermis; Ex/ sunburn
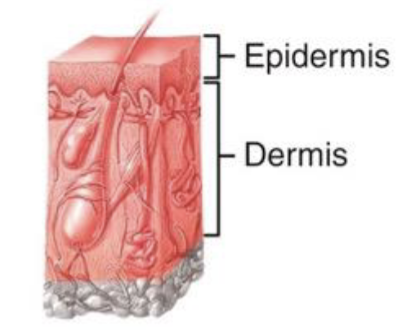
2nd degree burn
Destroys the epidermis and part of the dermis; Ex/ blister
3rd degree burns
Full thickness burn that destroys the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer