Unit 3 - Enzymes and Metabolism HL and SL
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Enzymes as catalysts
Enables essential function such energy production, building of molecules, and waste removal to happen fast enough.
Metabolism
Metabolism is the complex network of interdependent and interacting chemical reactions, occurring in living organisms.
Role of enzymes in metabolism
Because enzymes have the ability to catalyze only specific reactions or act on a specific substrate, many different enzymes are required by living organisms, and control over metabolism can be exerted through these enzymes.
Anabolic reactions
Building of larger, more complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy (condensation.)
Catabolic reactions
Breakdown of larger, more complex molecules in to smaller, simpler ones, releases energy (hydrolysis.)
Examples of anabolic reactions
Formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions including proteins synthesis, glycogen formation and photosynthesis.
Examples of catabolic reactions
Includes the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers in digestion a nd oxidation of substrates in oxidation.
Enzymes as globular proteins
Active site is composed of a few amino acids only, but it is the interaction between the amino acids within the overall three dimensional shape of the enzyme ensures that the active site has the necessary properties for catalysis.
Induced fit binding
When substrate binds to the active site, it triggers a change in the three dimensional shape of the enzyme, that allows for a tighter fit. Substrate binding induces a conformational change in the enzyme.
The enzyme also induces the weakening of the bonds within the molecules of the substrate, lowering activation energy, either anabolic or catabolic.
Role of molecular collisions and substrate active collisions in enzyme catalysis:
Enzyme and substrate needs to collide with enough kinetic energy and in the correct orientation. Enzymes or large molecules can be immobilized by being embedded in the membrane, affecting collision mechanics.
Relationship between the structure of the active site, enzyme substrate specificity and denaturation.
Enzyme exhibit specificity, however, level of enzyme specificity can vary. Some can only bind to a single substrate, whereas, others can bind to a range of similar substrates.
Denaturation
This happens where a enzyme experiences a temperature or a pH level outside it’s ideal range. The temperature disrupts the weak hydrogen bonds, causing the unfolding of the enzyme. The pH level can alter the solubility of the enzyme and can also disrupt the ionic bonds. All of this causes the enzyme to lose its biological function.
Effect of pH, temperature and substrate concentration on rate of enzyme activity
Low temperature means that there are fewer collisions, optimal temperature increases the frequency of collisions, but extremely high temperatures causes denaturation, making enzyme lose its function and stopping the reaction.
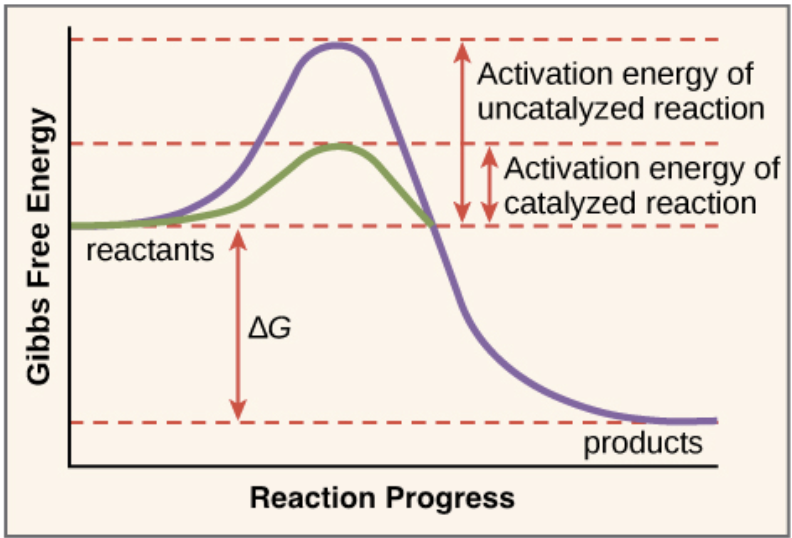
Effect of enzymes on activation energy
Energy is required to break bonds within substrate and there is a energy yield when bonds are made to form the products of an enzyme catalyzed reaction.