AP Biology Unit 7 Review - Natural Selection
==Natural Selection==
}}Key features}}
- ^^Natural selection:^^ The process by which individuals with more favorable traits are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass on their alleles to future generations
- There is @@variation@@ in heritable traits within a population
- Species produce more offspring than the environment can support
- Individuals w/ more favorable traits are more likely to survive + reproduce
@@This will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits over generations@@
}}Evidence of natural selection}}
- ^^Homology^^: Structural similarities resulting from common ancestry. Not always as reliable because of analogous structures + convergent evolution (species independently develop similar structures due to similar environmental pressures)
- ^^Fossil record:^^ Shows extinct species + change over time, but not all organisms can be fossilized so the fossil record is biased
- ^^Embryology^^ can show similarities in structures very early in development
- ^^Molecular data^^: (DNA, amino acids) directly shows differences between the genetics of organisms
==Phylogeny==
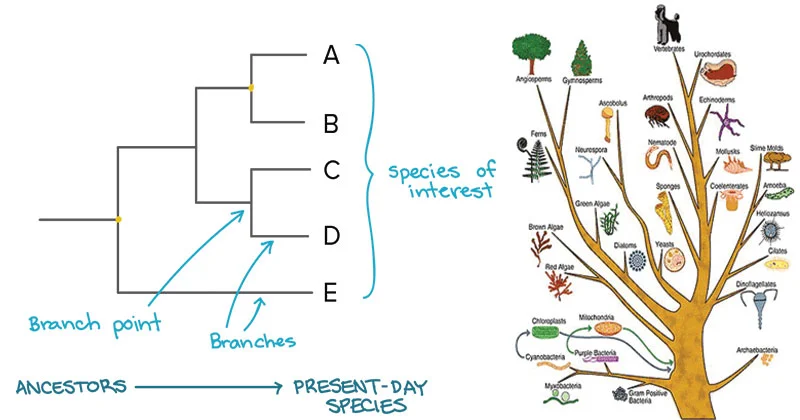
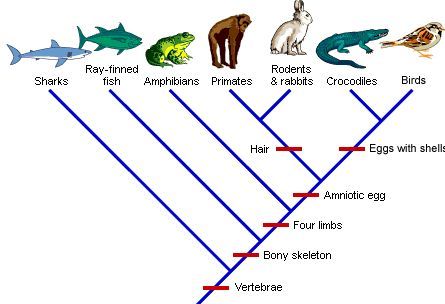
}}Phylogenetic trees}}
@@Represent possible evolutionary relationships@@
^^Sister taxa^^: Share an immediate common ancestor
^^Basal taxon/outgroup:^^ Diverges early in the group’s history, near the whole group´s common ancestor
^^Monopholyetic group:^^ Branch and every subsequent taxon
^^Paraphyletic group:^^ A monophyletic group that leaves out a taxon
^^Polyphyletic group:^^ Group of different taxa with a different common ancestor
==Hardy-Weinberg + Population Genetics==
}}HW Equilibrium}}
^^Population^^: A group of individuals of the same species in the same area that produce viable and fertile offspring
@@HW allele frequency:@@ Dominant allele frequency + recessive allele frequency = 1 (p + q = 1)
@@HW genotype frequenc@@y: Homozygous dominant frequency (p²) + Heterozygous frequency (2pq) + Homozygous recessive frequency (q²) = 1, (p² + 2pq + q² = 1)

@@REQUIREMENTS:@@ No mutations, random mating, no natural selection, very large population, no gene flow
@@Mechanisms of evolution@@ are mutation, gene flow, non-random mating, genetic drift, and natural selection
}}Population genetics}}
^^Genetic drift:^^ Change in allele frequency due to random chance
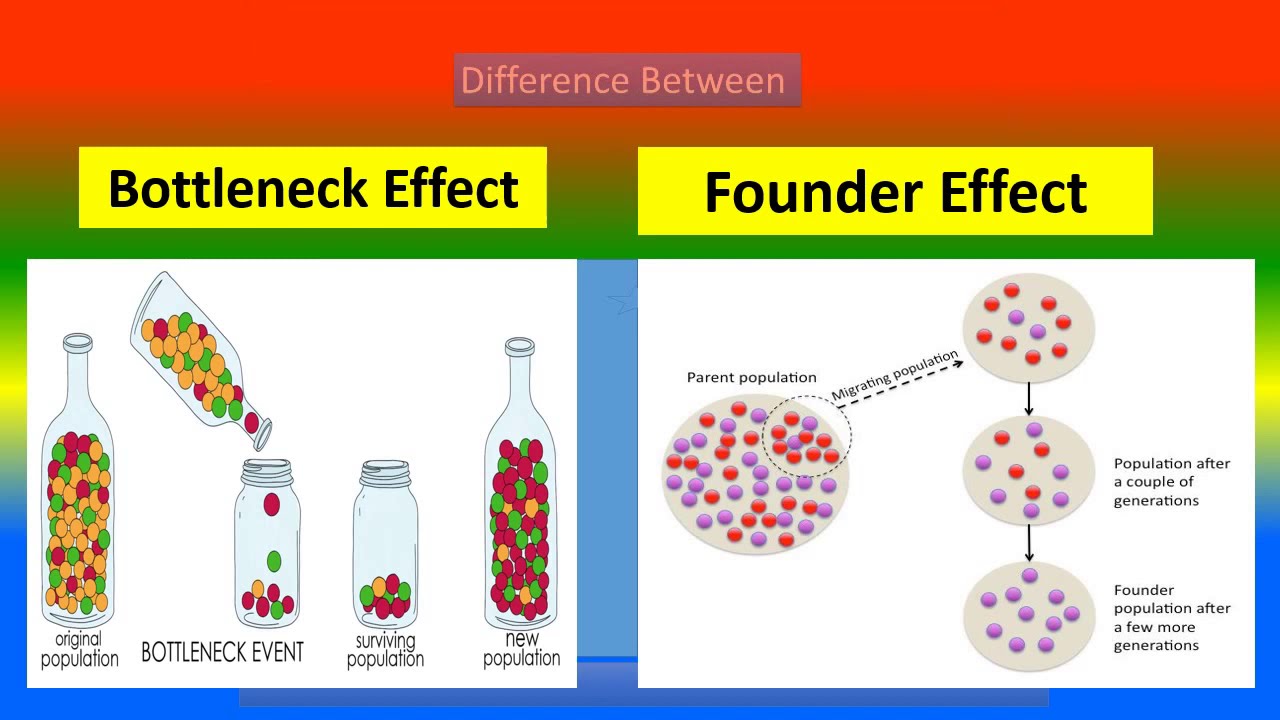
^^Founder effect:^^ Few individuals are isolated from the larger population, creating a new and less genetically varied gene pool (part of genetic drift)
^^Bottleneck effect:^^ Drastic population reduction due to a sudden environmental change, gene pool after the event will be different (part of genetic drift)
^^Gene flow:^^ movement of alleles among populations between gametes
^^Fitness^^: An individual´s reproductive success/how many offspring it´s able to produce
^^Directional selection^^: Conditions favor 1 end of the phenotypic range
^^Disruptive selection:^^ Conditions favor individuals at both ends of the phenotypic range
^^Stabilizing selection:^^ Conditions favor individuals in the middle of the phenotypic range
^^Sexual selection^^: Natural selection for mating success
[[Reproductive Isolation: Existence of biological factors impeding members of 2 species from interbreeding and producing fertile offspring[[
}}Species???!}}
- ^^Biological species concept:^^ A species is a group of populations whose members can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
- @@Other species concepts@@ are morphological (species based on morphology), ecological (classified by ecological niche), and phylogenetic.
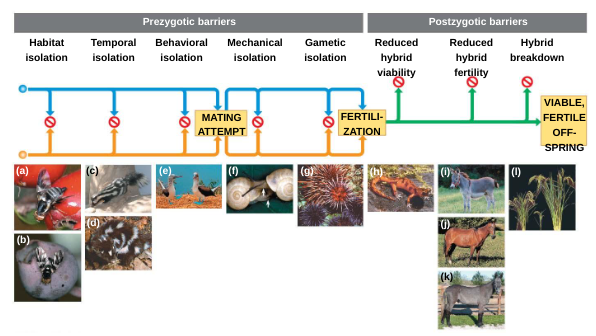
}}Prezygotic Barriers- Block Fertilization}}
- ^^Habitat Isolation:^^ 2 species occupy different habitats and rarely/don’t encounter each other
- ^^Temporal Isolation:^^ Species breed at different times of day, seasons, or years
- ^^Behavioral Isolation:^^ Courtship rituals and other unique mating behaviors make species incompatible
- ^^Mechanical Isolation:^^ Morphological differences prevent successful mating
- ^^Gametic Isolation:^^ The sperm of one species can’t fertilize the egg of the other species
}}Postzygotic Barriers- Prevent hybrid zygote from developing into fertile/viable adult}}
^^Reduced hybrid viability:^^ The genes of the 2 species interact in a way that impairs the hybrid offspring’s development or survival
^^Reduced hybrid fertility:^^ Hybrid is sterile (unable to reproduce)
^^Hybrid breakdown:^^ The hybrid is able to reproduce, but the hybrid’s offspring are feeble or sterile
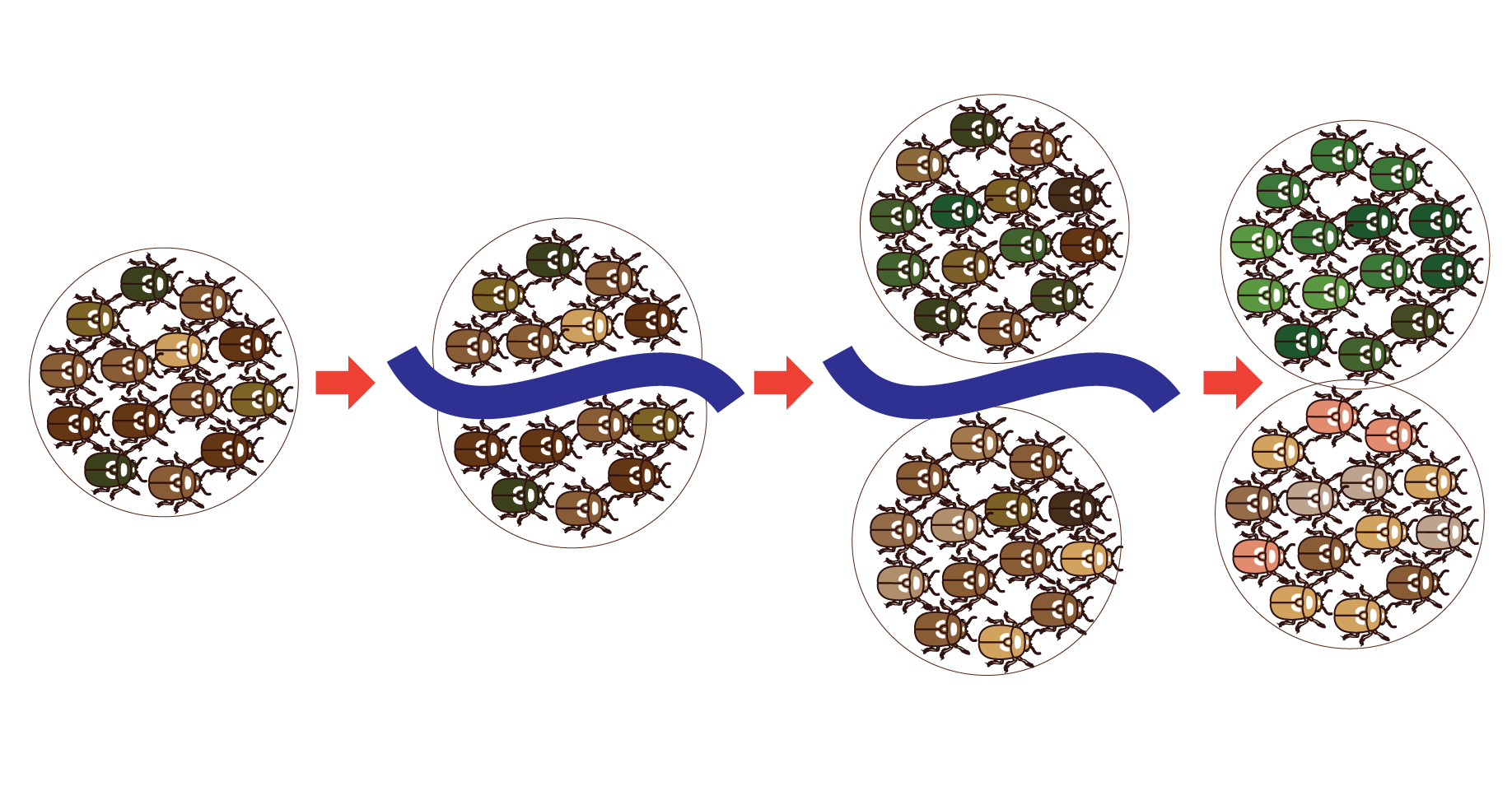
}}Allopatric Speciation- One species splits into 2+ due to a geographical divide that prevents gene flow}}
As @@geo divide@@ interrupts gene flow, @@intrinsic barriers@@ (barriers that make 2 species sexually incompatible) such as genetic differences or sexual selection arise
}}Sympatric Speciation- Speciation in a population that is not geographically separated}}
^^Polyploidy:^^ Offspring receive an extra set(s) of chromosomes due to errors during cell division. Creates a reproductive barrier.
^^Habitat differentiation:^^ Species develop by using different resources in their geographical area and slowly separating from the initial species
^^Sexual selection^^
^^Adaptive Radiation^^: One species diversifies into multiple species to fill empty ecological niches

==Chapters 23-24==
}}23}}
- @@Radiometric dating@@ uses half lives
- @@Mass extinctions@@ pave the way for adaptive radiation because it frees up ecological niches
}}24}}
@@Gram + bacteria@@ has thick simpler walls high in peptidogylcan
@@Gram - bacteria@@ has a thin peptidoglycan wall between possibly toxic outer membrane and inner membrane

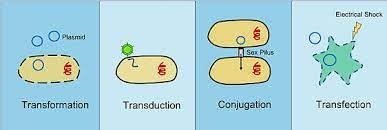
^^Transduction:^^ movement of genes between prokaryotes via phages (viruses that infect bacteria)
^^Conjugation^^: Genetic material transferred directly between prokaryotes
^^Transformation^^: A bacteria takes up a piece of DNA in its environment