Module 3 - Forensic Pathology
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FRSC1030 FRSC pathology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Pathologist:
medical doctor who investigates and studies disease in humans
Forensic pathologist
a pathologist who studies disease and trauma leading to death
What is Forensic Pathology?
branch of medicine for legal purposes and concerned with examining/determiningcause of death, injuries due to crime and negligence, and tissue samples relevant to crimes
Autopsy largely synonymous w/…..
forensic pathology.Term a combination of Greek terms “autos” (self or with one’s own) and “opsomei” = “seeing with eyes” thus “autopsy” means “seeing with one’ s own eyes.
Death Investigative Systems • Differs by….
political jurisdiction
Death Investigative Systems (2 general systems)
Medical Examiner System:, Coroner System:
Medical Examiner System:
physician trained in pathology and forensic pathology (AB, MB, NF, NS)
Coroner System:
investigators of unusual or suspicious deaths (BC, NB, ON, PE, QC); normally, no formal training required (ON: need to be a physician)
Office of the Chief Coroner Ontario Forensic Pathology Service investigate death when:
-appears from unnatural causes -natural deaths if sudden/unexpected -concerns re: care prior to death -mining/construction, police use of force, incarcerated
Office of the Chief Coroner Ontario Forensic Pathology Service determines what
who (identity of deceased) • when (date of death) • where (location of death) • how (medical cause of death) • by what means (natural causes, accident, homicide, suicide or undetermined)
Cause of Death Divided into primary and secondary causes (3)
1. Most recent condition 2. Next oldest condition 3. Oldest (original/initiating) condition
Manner of Death Abbreviation
NASH
Manner of Death (NASH) Five outcomes:
homicide -suicide -accidental -natural -undetermined
Autopsy - Documentation
-photos with/without clothing
-type of clothing -location and type of trauma (e.g., location of bullet wounds; entrance and exit wounds)
-defensive wounds
-collect evidence from external examination and clothing
-note: age, gender, height, weight, physical condition, abnormalities
-rigor-, livor- and algor mortis
Classification of Trauma
Mechanical, Chemical (e.g., acid), Thermal, • Electrical • Radiation • Blast
Classifications of Mechanical Trauma
- Sharp force - Blunt force - Gun shot -Asphyxia
1. Sharp force
-often death by exsanguination
2. Blunt force
-often death by brain damage -commonly creates contusions (accumulation of blood outside normal blood vessels) where impact weapon may leave a distinguishable pattern - extreme contusions are hematomas (bigger pockets of blood) and can help explain context of death
3. Asphyxia – 3 main mechanisms
- suffocation, strangulation, chemical (e.g., CO)
Low-voltage electrical injury; can lead to…
ventricular fibrillation (heart quivers, but does not pump blood).
-High voltage electrical injury heart will become…
defibrillatory (stop beating) and cannot be resuscitated-
Petechiae
Red or purple spot on body, caused by a minor hemorrhage (broken capillary blood vessels)
Petechiae Sometimes associated with…
strangulation if present in eye, but not conclusive as also associated with other conditions (e.g, heart attack)
Pathology can help investigations but…Caution in…
Conclusions!
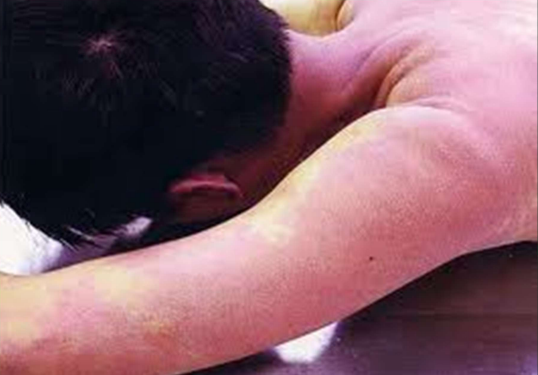
Skin discoloration caused by…
carbon monoxide poisoning
Quantitatively estimating PMI within an accurate time frame is….
crucial (but lots of challenges/assumptions)
Various methods used in field to estimate time since death;
Temperature; Rigor Mortis; Entomology; Decay
Active transport:
mechanism that transports molecules and other substances across membranes
Active transport requires expenditure of….
cellular energy (ATP) to move molecules against a concentration gradient
When an organism dies active transport ceases due to…
loss of cellular energy that is required for the process
When selective membrane permeability is lost, analyte concentrations across barriers approach….
equilibrium values
Rigor Mortis:
Stiffening of body after death muscle membranes become more permeable to Ca2+ (muscles contract)
Rigor Mortis: -Begins _____ after death, remains…
2-6 hours, 2-3 days
Livor Mortis:
(lividity)settling of blood no longer circulating, gravity (purple)
Livor Mortis: Begins about _____ after death (unless ______)
1 hr, poisoned by CO
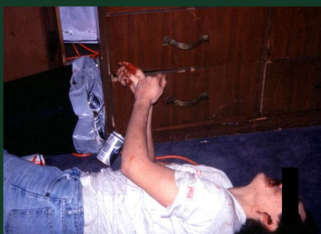
What is this an example of …
rigor mortis
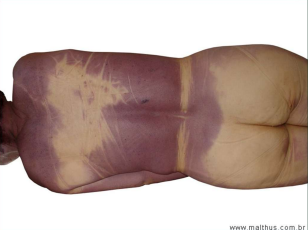
What is this an example of …
Livor Mortis:
Algor Mortis:
decrease in body temperature after death
Glaister equation:
linear relationship of anal temp/time -1.5 C/hr (2C during 1st hr, 1C per hr nearing ambient T)
Pallor mortis:
change in tone of skin occurs within 15–25 min after death
Pallor mortis: little to no use in….
TOD, occurs too quickly from lack of circulation of blood
Algor, Rigor and Livor Mortis what can impact these ?
Disease Drugs/Poison (CO) Weight\ Surface Area Ambient temp Environmental Conditions Conductivity of medium body on
Vitreous Humour : Estimate PMI using….
analyte concentration in vitreous humor
Vitreous Humour
gelatinous fluid between lens and retina of eye
Vitreous Humour: Through diffusion from retina the potassium ion (K+ ) concentration…..
increases predictably with time after death
Several factors have been shown to decrease strength of correlation between [K+] and PMI (3)
– Environmental and ambient temperature – Antemortem conditions – Cause of death
What also impacts K+ concentration
• Death from drug overdoses/chronic illness = extremely variable K+•
Individuals with burn injuries - higher K+ levels than expected.
K+ concentration alone to estimate PMI yields……
wide interval
K+ ions analyzed simultaneously with other analytes found in vitreous humor to increase accuracy of….
PMI estimate (e.g., Sodium (Na+ ), ammonium (NH4 + ) and barium (Ba2+))
Internal Examinations and Dissection
Remove, weigh and examine internal organs
• Look for signs of disease -coarse visual and histology
• Stomach contents examined • Small intestines (undigested portions) examined
• PMI (temp of body and organs)
• MANY OTHER ASPECTS LIKE TOX in next section….
Traditional postmortem examination can be traced back….
700 years to its beginnings in Italy
Traditional autopsy begins with a…
deep Y-shaped incision in chest. Next, skin is peeled back to expose rib cage, must be sawed open with bone cutter so various organs can be removed and examined.
Characteristics of Autopsy:
• Usually invasive/destructive.
• Time consuming.
• Can be subjective (see Gouge Inquiry!)
• May lead to loss of evidence.
Virtopsy
non-invasive imaging, scans entire body and captures 2D and 3D images; generates same conclusions as hours of classical autopsy
term virtopsy created from terms….
virtual and autopsy: “virtual” in ancient Latin means “useful”.
Virtopsy Provides objective documentation to analyze….
process of physical features and evidence.
Virtopsy: combination of…
C.T. (Computed Tomography), M.R.I. (magnetic resonance imaging) and 3-D surface- scanning technology.
MSCT stands for…
Multi-Sliced Computed Tomography derived from the traditional CT scan (Computed tomography) or CAT (computed axial tomography) scan
MSCT consists of……
a rotating X-ray supply that spins around a patient at an extremely high speed. Directly opposite to this X-ray is an array of the X-ray detectors that also rotate at exactly the same rate. As ring rotates around patient, X-rays are emitted, and detectors capture images.