Energy changes in chemical & nuclear reactions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Energy
Defined as the ability to do “work", which is to move an object against an opposing force
Can be classified as Kinetic or potential
It comes in many forms such as heat, electricity, light, sound and chemical energy

Heat
Energy transfer that occurs as a result of a temperature difference
Produces an increase in disorder in how the particles behave
increases the average kinetic energy(temperature) of the molecules
Chemistry Universe
Made up of two parts:Chemical system and surroundings
Chemical system- area of interest/ made up of reactants and products which is classified as open or closed
Surroundings is everything else in the system
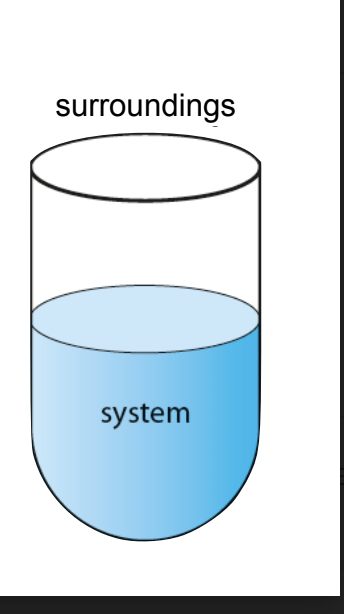
Open vs Closed System
Open- can exchange matter and energy with its surroundings
closed- can only exchange energy and matter cannot go in and out e.g glow sticks
Law of conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but only converted from one form to another
So energy can be exchanged between system and surroundings, but total energy has to stay the same during the process
Energy from the system is gained by surroundings and vice versa
e.g BBQ(Chemical to thermal and light)
Enthalpy
Total Internal Heat content content at constant pressure( sum of kinetic and potential energy)
Examples of energies of enthalpy
This includes the energies of:
• moving electrons within atoms
• vibration of atoms connected by chemical bonds
• rotation and translation of molecules
• nuclear potential energy of protons and neutrons in atomic nuclei
• electronic potential energy of atoms connected by chemical bonds
IT IS IMPOSSIBLE TO MEASURE ENTHALPY OF A CHEMICAL SYSTEM
Enthalpy Change (△H)
CAN be measured in kJ/mol
measure of the amount of heat energy contained in a substance/system.
result from chemical bonds and intermolecular forces in the system being broken and then formed
during reactions, the difference in enthalpy (△H) between reactants and products results in heat change that can be measured
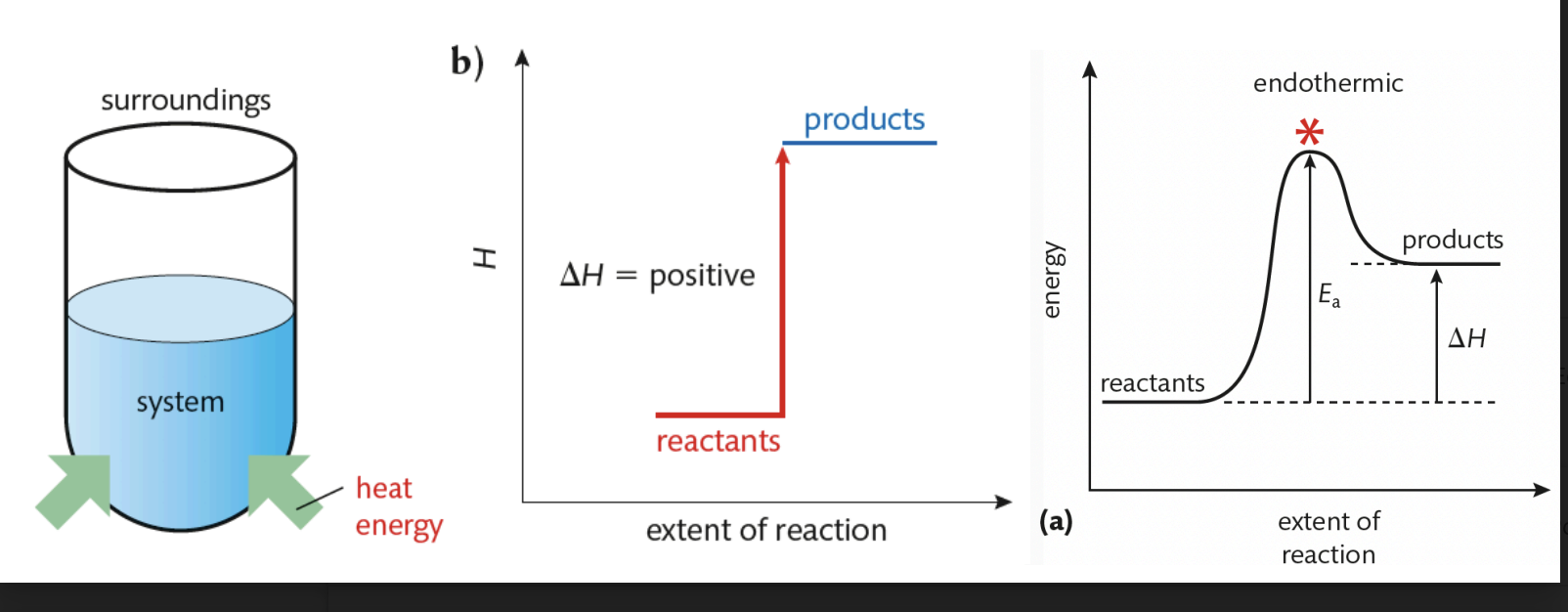
Endothermic Reaction
net absorption of energy from surroundings (energy absorbed to break bonds is GREATER than energy released when products form)
△H is positive
temperature of surroundings decreases
Products have a higher enthalpy than reactants
products are less stable than reactants
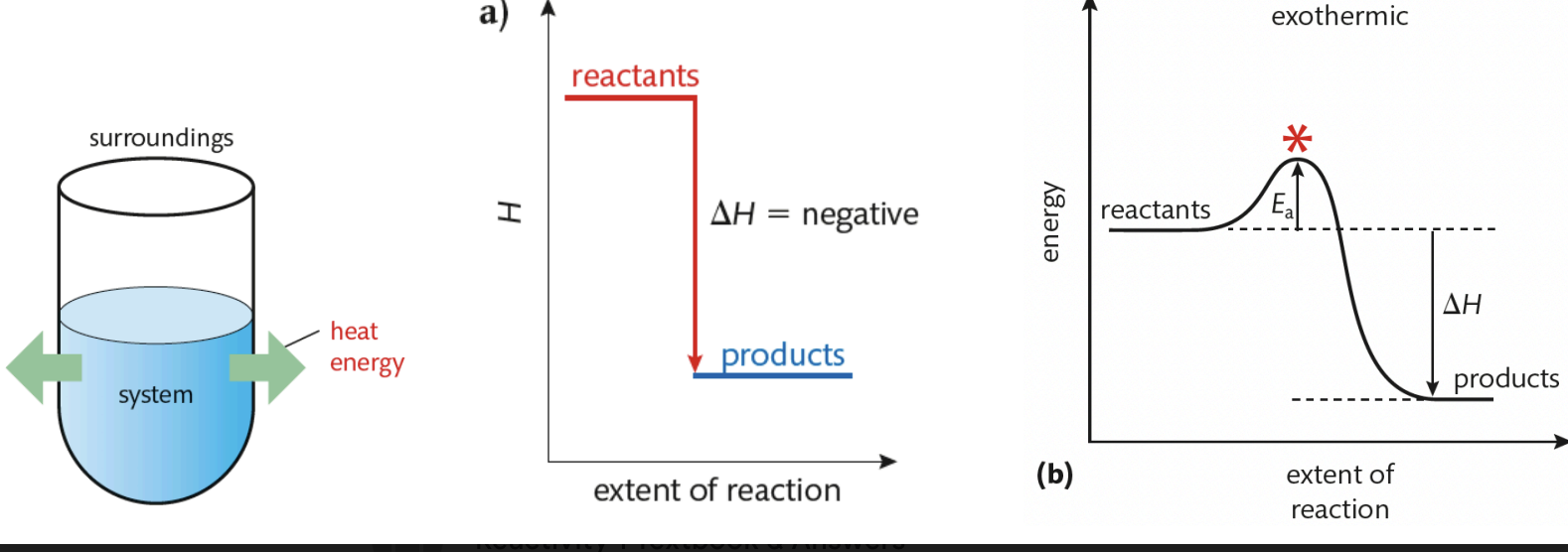
Exothermic Reaction
net release of energy to surroundings (energy absorbed to break bonds is LESS than energy released when products form)
△H is negative
temperature of surroundings increases
What is the heat change calculation formula and what do each variable mean
increases in temperature when an object is heated is
dependent on three things:
1. mass of the object (g)
2. the heat added (K)
3. nature of the substance/specific heat capacity (heat needed to increase the temperature of a unit mass by 1 K. Depends on the number of particles present in a sample. Units: J/gK)
q= mc△T
Relating System and surroundings
when a change occurs in a system (△H), the chemical potential energy change is NUMERICALLY EQUAL to the heat (q) transferred to the surroundings.
Mathematically, this can be shown by:
ΔHsystem = -q surroundings
Standard Enthalpy Changes (△Ho)
the enthalpy changes for a reaction depends on the conditions under which the reaction occurs
Standard enthalpy changes are measured under the following conditions:
pressure= 100 kPa
concentration= 1.0 moldm-3 for all solutions
all substances in their standard states (pure
form of the substance at 298 K and 100 kPa)
REPRESENTING ENTHALPY CHANGE
can use a thermochemical equation (a balanced chemical equation which incorporates the energy change for the system)
potential energy diagram
shows the relative change in energy of reactants/products
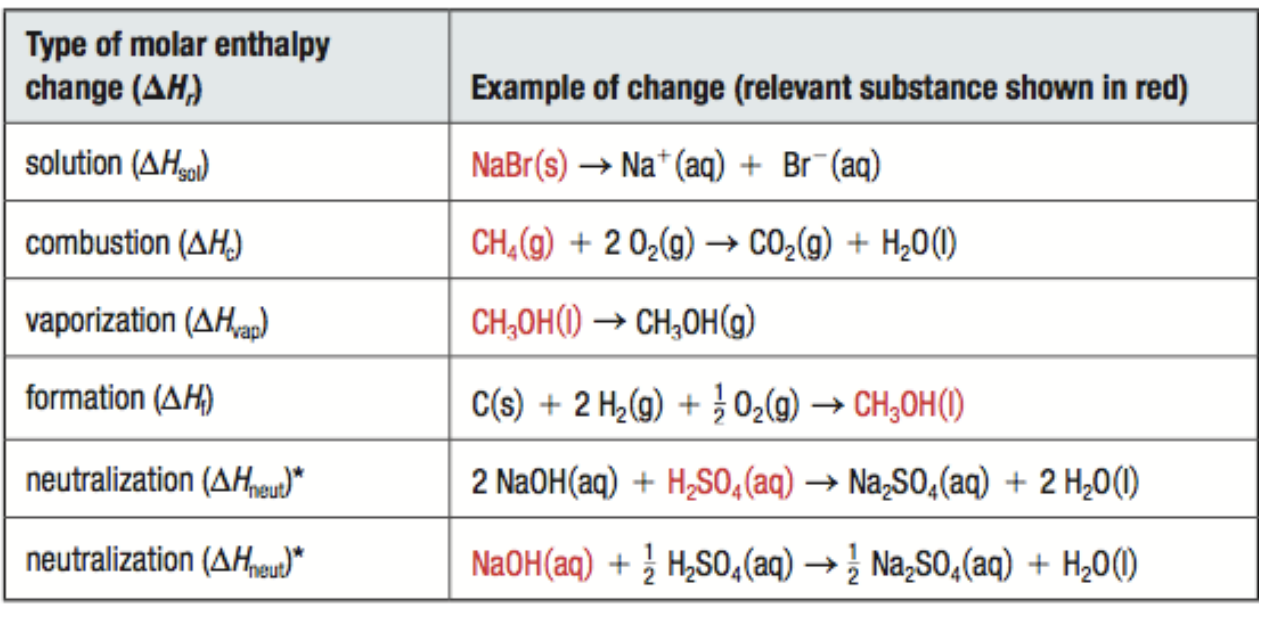
molar enthalpy change
energy change that occurs when 1 mol of a substance undergoes a physical, chemical, or nuclear change
represented by ∆Hr
units are J/mol
*the molecule you are getting the ΔHr MUST have a coefficient of 1
Calorimetry
process of measuring energy changes during a chemical or physical change
use a device called a calorimeter
we assume the calorimeter is a closed system
surroundings is water