Genetics - Lecutre 11: Bacterial Genetics and Jacob and Monod and the lac Operon
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What do bacterial colonies lack?
differences in phenotypes
Prototroph
a microorganism that does not require any organic growth factors (E.coli)
Auxotroph
cannot survive on minimal media
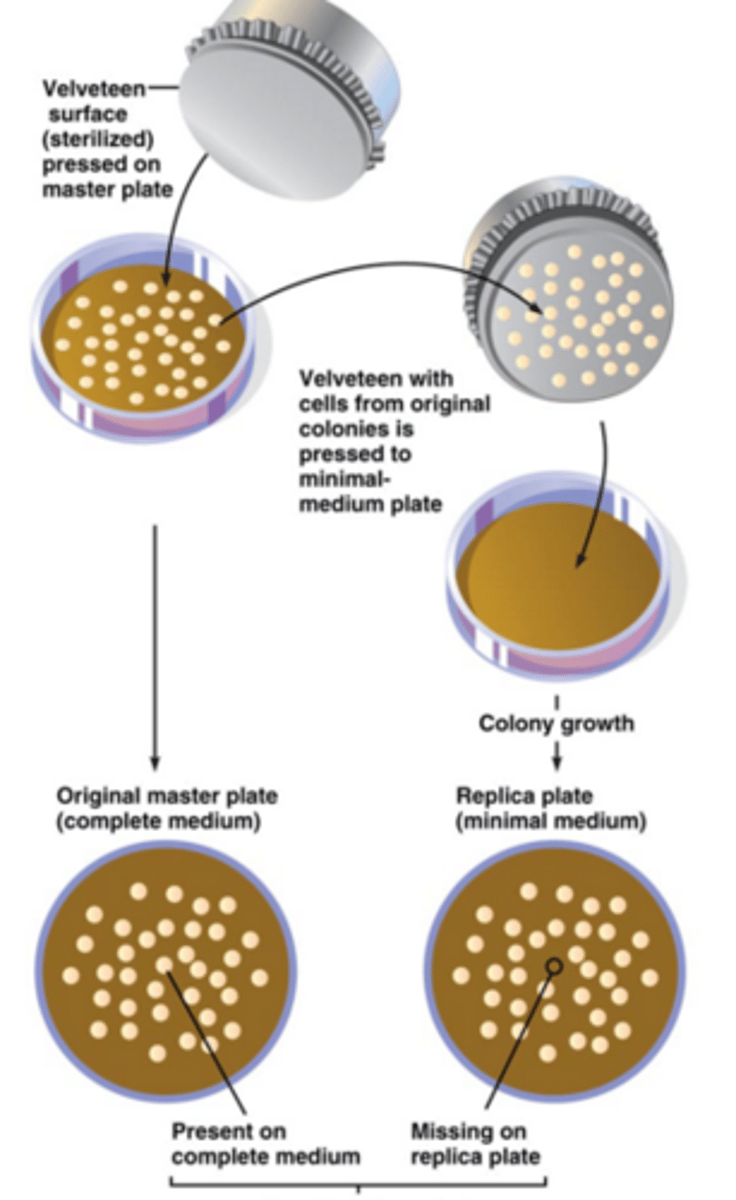
Benefit of replica plating
allows us to copy one set of colonies onto multiple different media and determine mutations therein
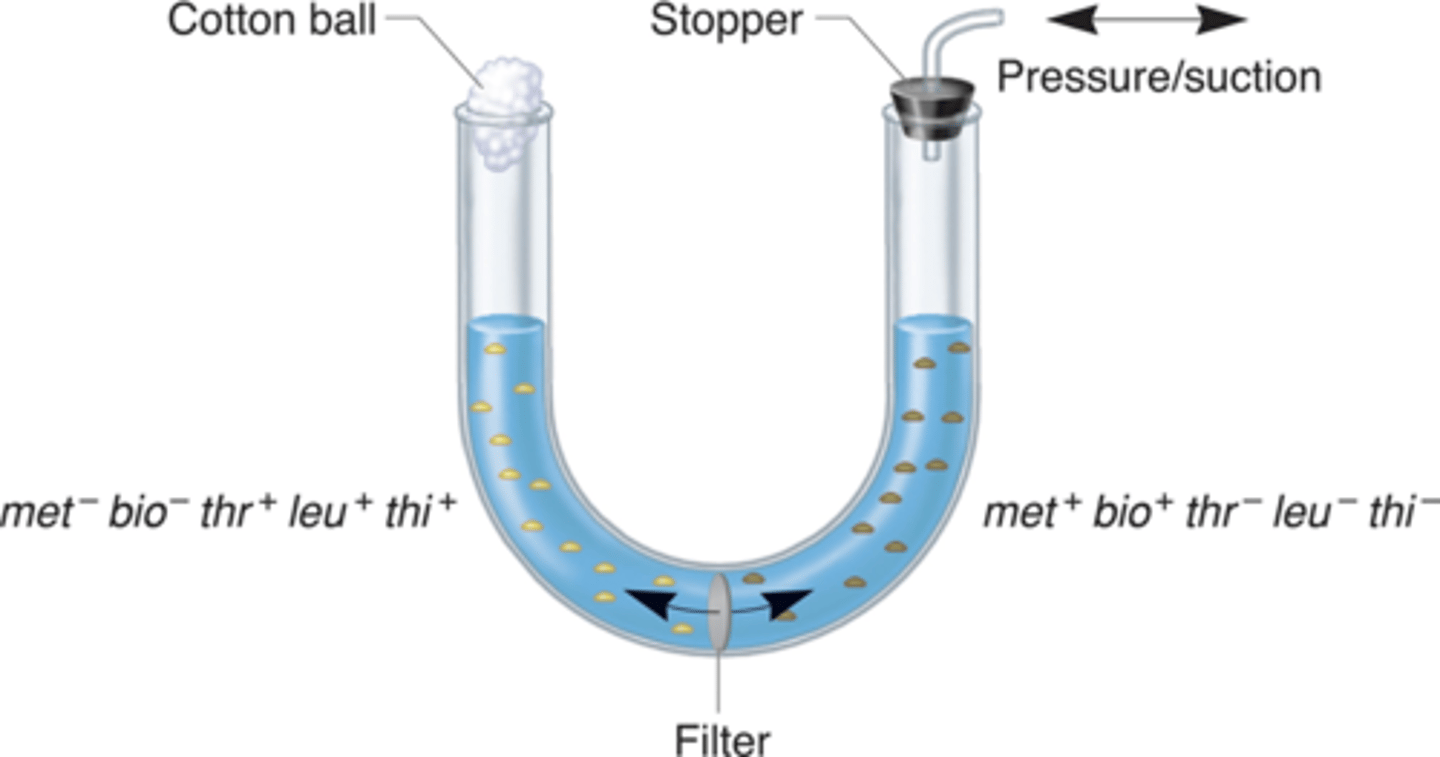
Bernard Davis experiment
Physical contact between the two strains was needed for recombinant cells to form.
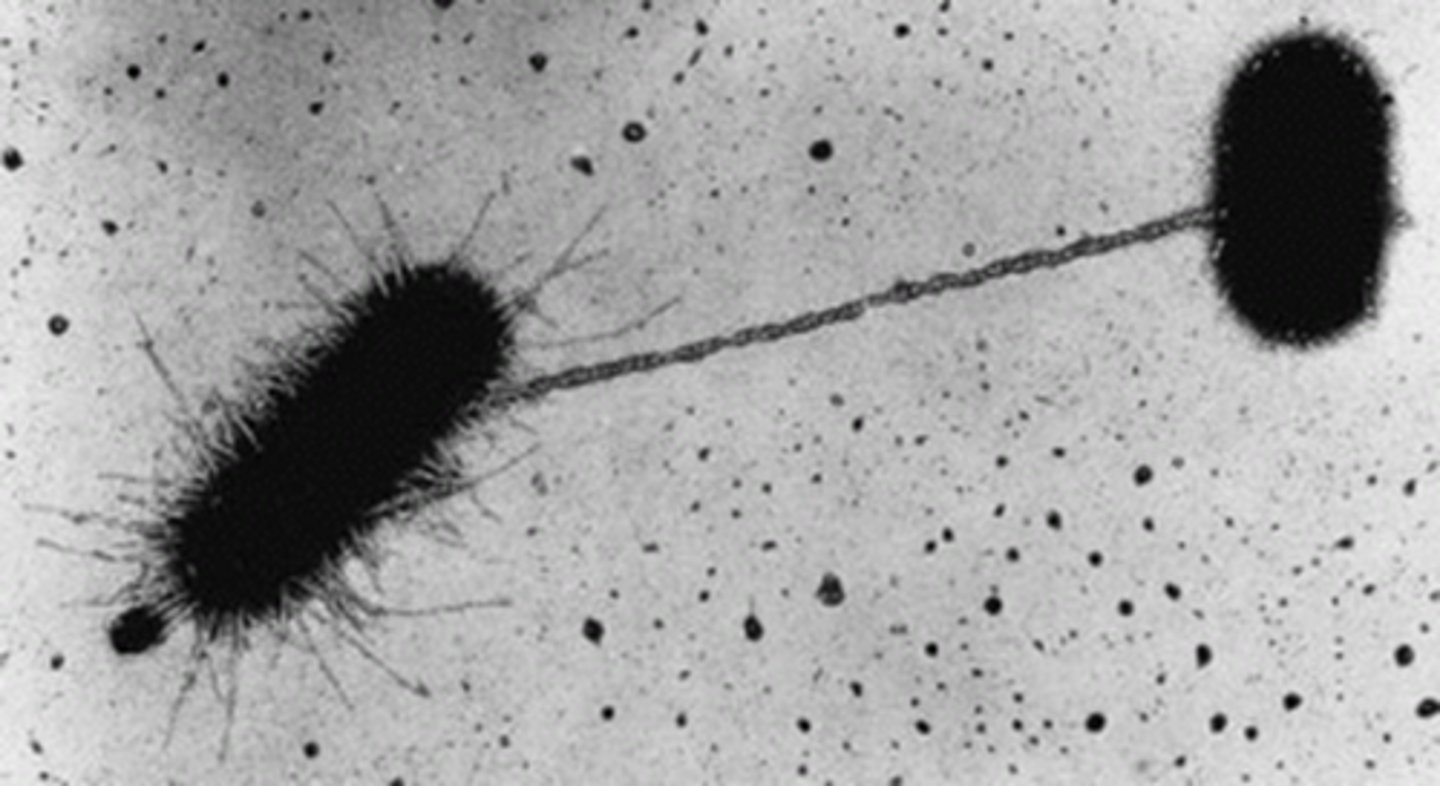
Pilli
Hollow tubes used to move cells or exchange DNA between bacteria by conjunction.
Bacterial gene transfer is...
unidirectional
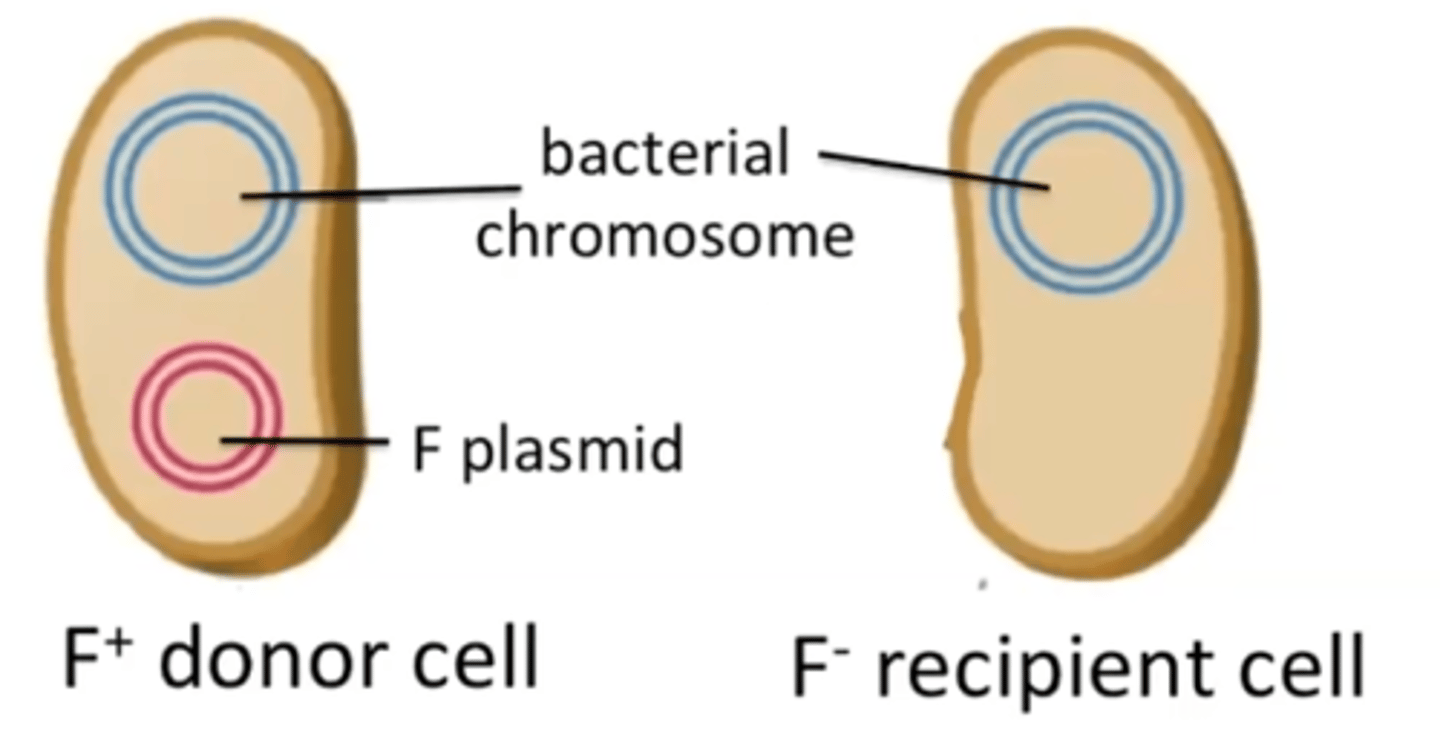
Fertility factor (F factor)
A specific plasmid (transferred by an F+ donor cell) that contains the genes needed for pilus formation and DNA export.
Hfr strains
undergo recombination at high frequency, but recipient cells generally do not become donors
Why can't recipients of Hfr strains become donors?
Hfr strains have the F-factor integrated onto their main chromosome
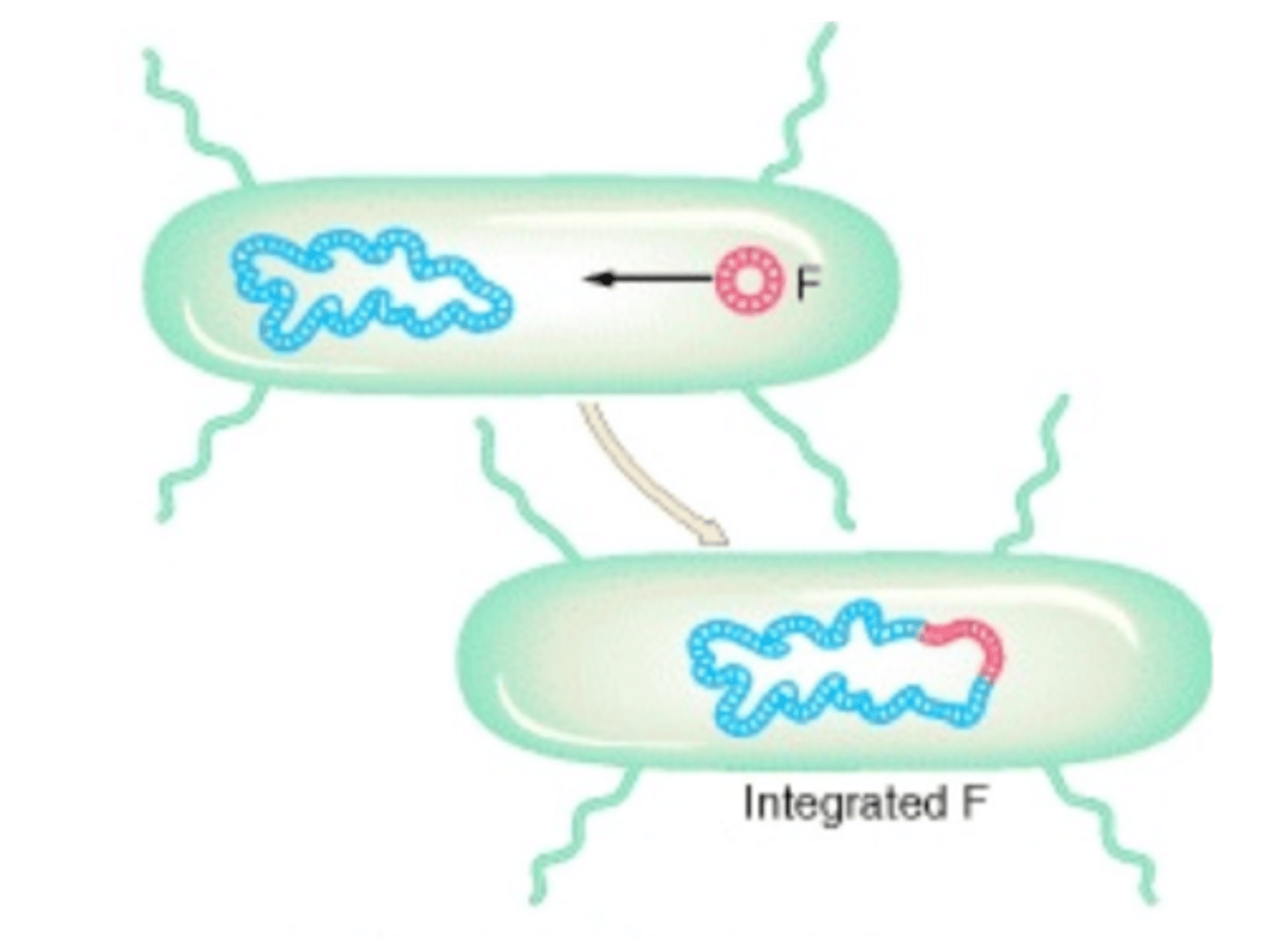
Why does an F-factor integrated onto the main genome prevent recipient cells from becoming donors?
There is no plasmid to be transferred through the pillus, so the entire chromosome is sent through, but the pillus is fragile and often breaks during the transfer, leaving an incomplete, linear piece of DNA in the recipient.
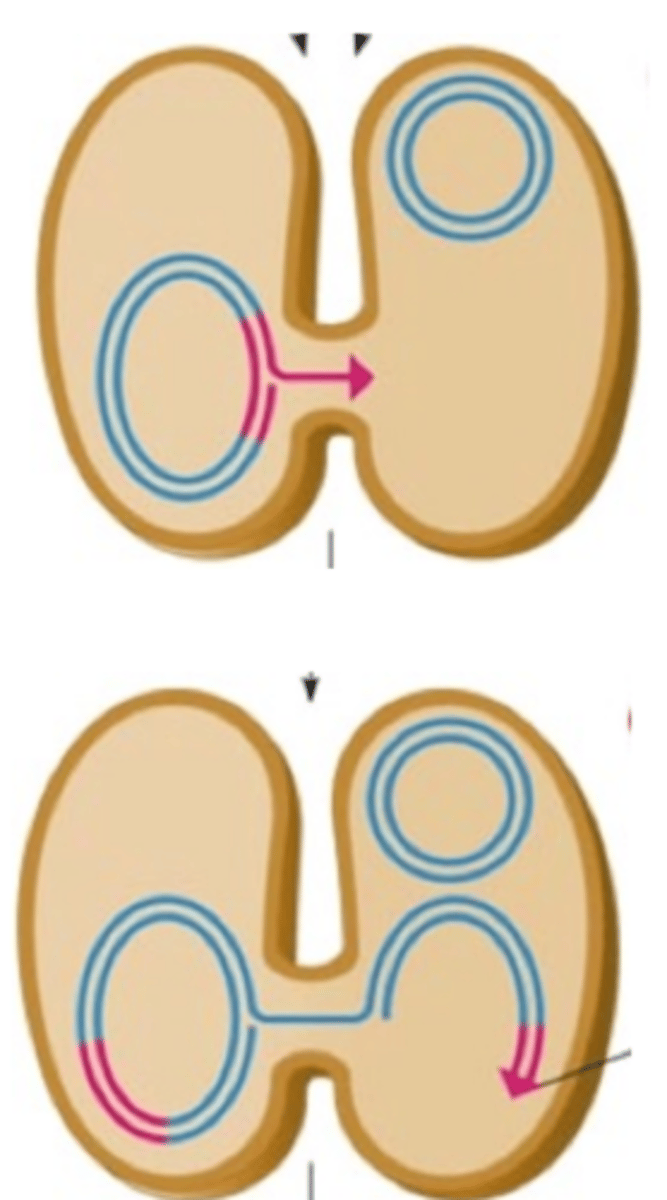
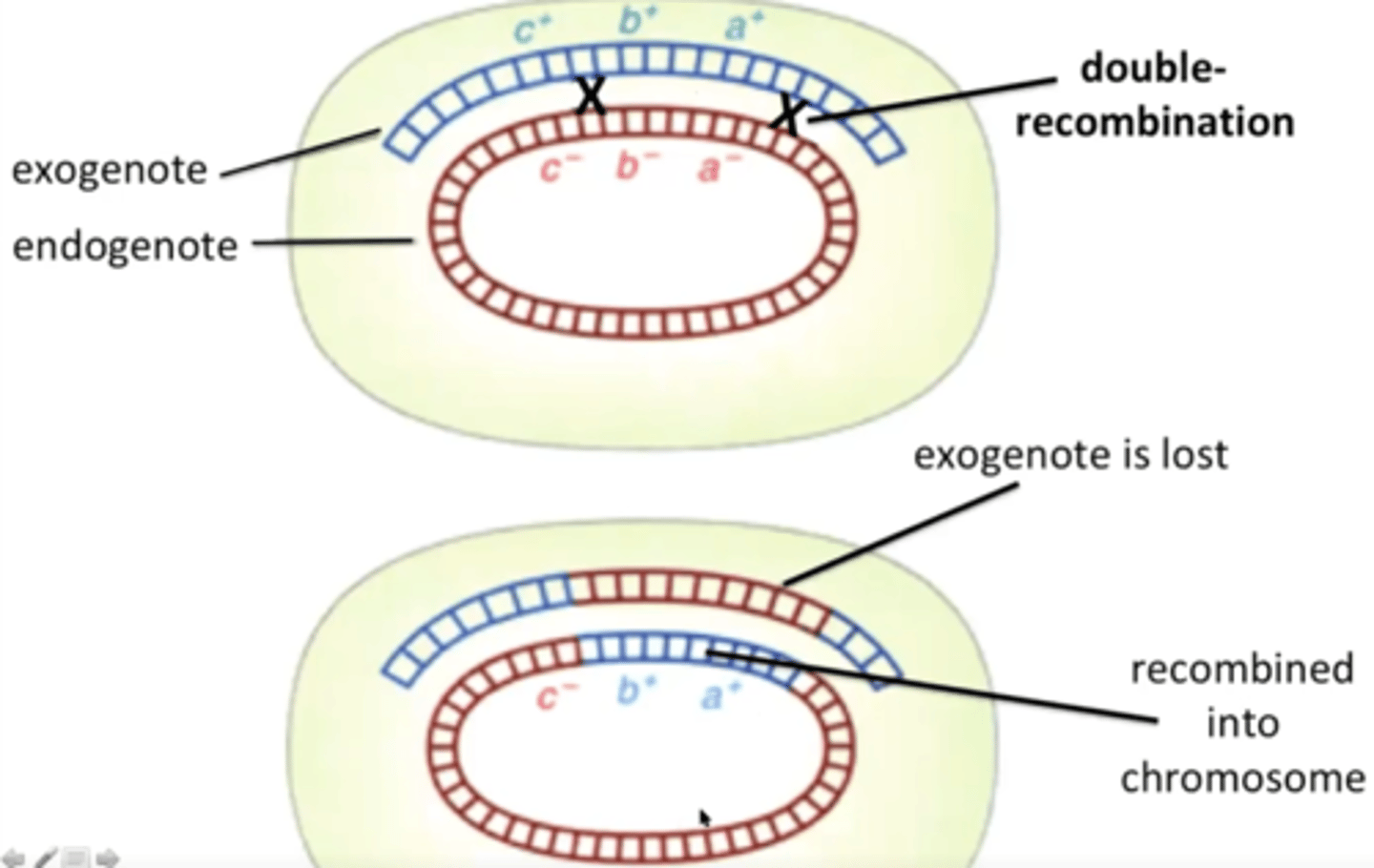
Exogenote
linear piece of chromosome transferred into a bacterial cell from another cell by conjugation
What happens to an exogenote?
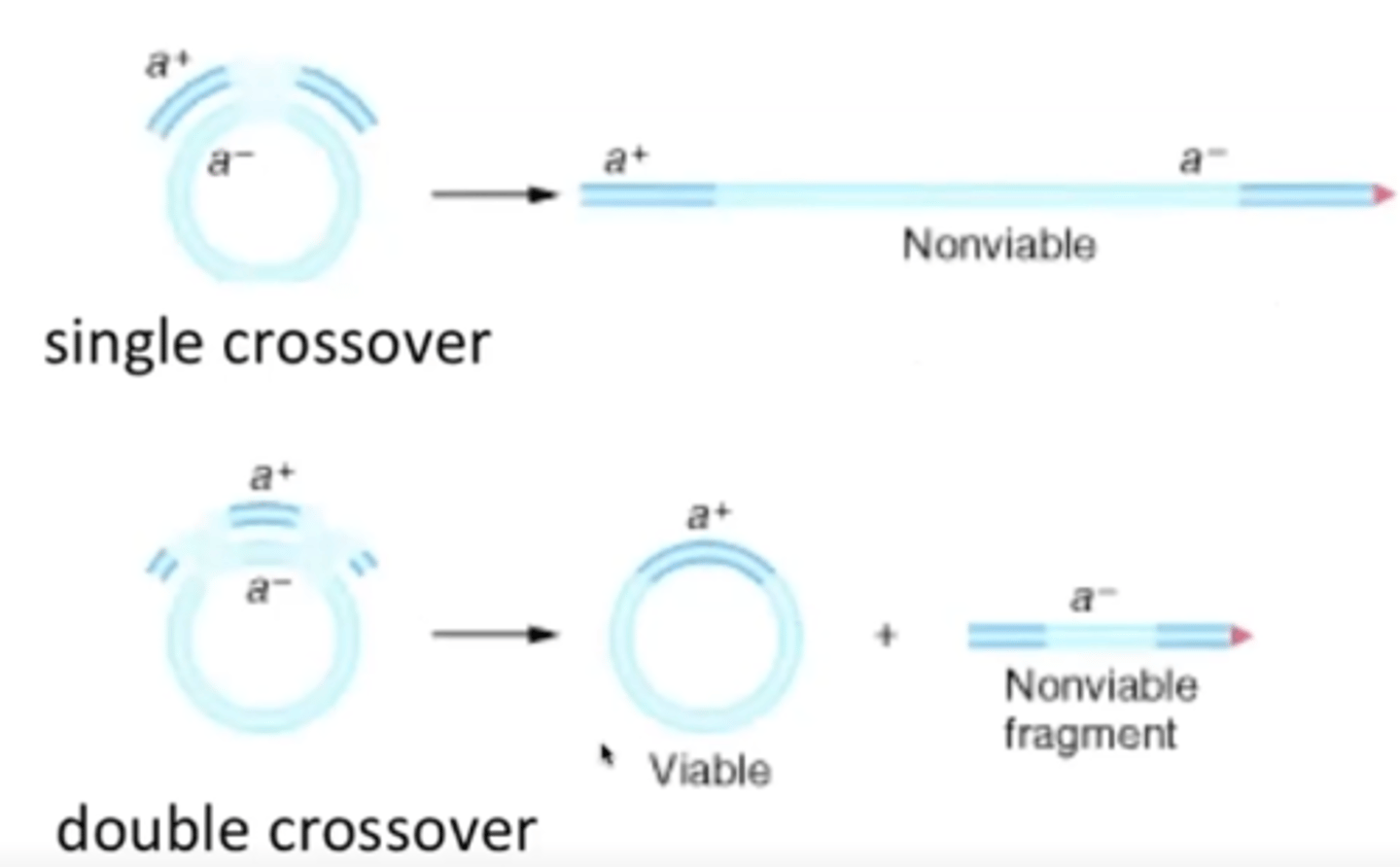
If genes on the exogenote are to persist, they need to be recombined into the existing, circular chromosome. This is done by double recombination.
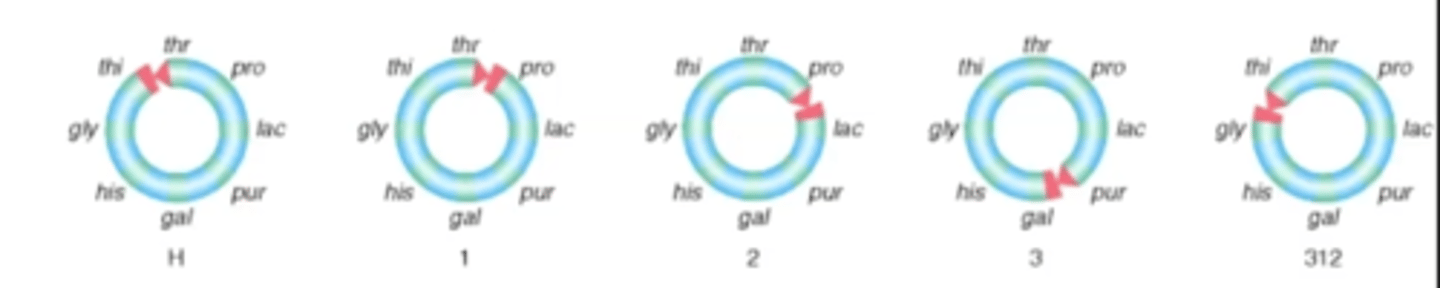
Fragility of pillus and mapping genes:
crossed certain strains of bacteria that were resistant to different antibiotics and found it took around 2 hrs for entire genome to transfer, and for daughter cells to be resistant to all three antibiotics. Then transfer was arrested in different stages using a blender to observe results
Based on pillus mapping data, what conclusion was drawn about the shape of the bacterial chromosome?
It was circular
Why does an exogenote need to undergo double recombination to be viable?
Without double recombination, the chromosome would become linear, which is not viable in bacteria
Messy excision of integrated Hfr:
F' plasmid can have other genes from the chromosome that are not usually donatable
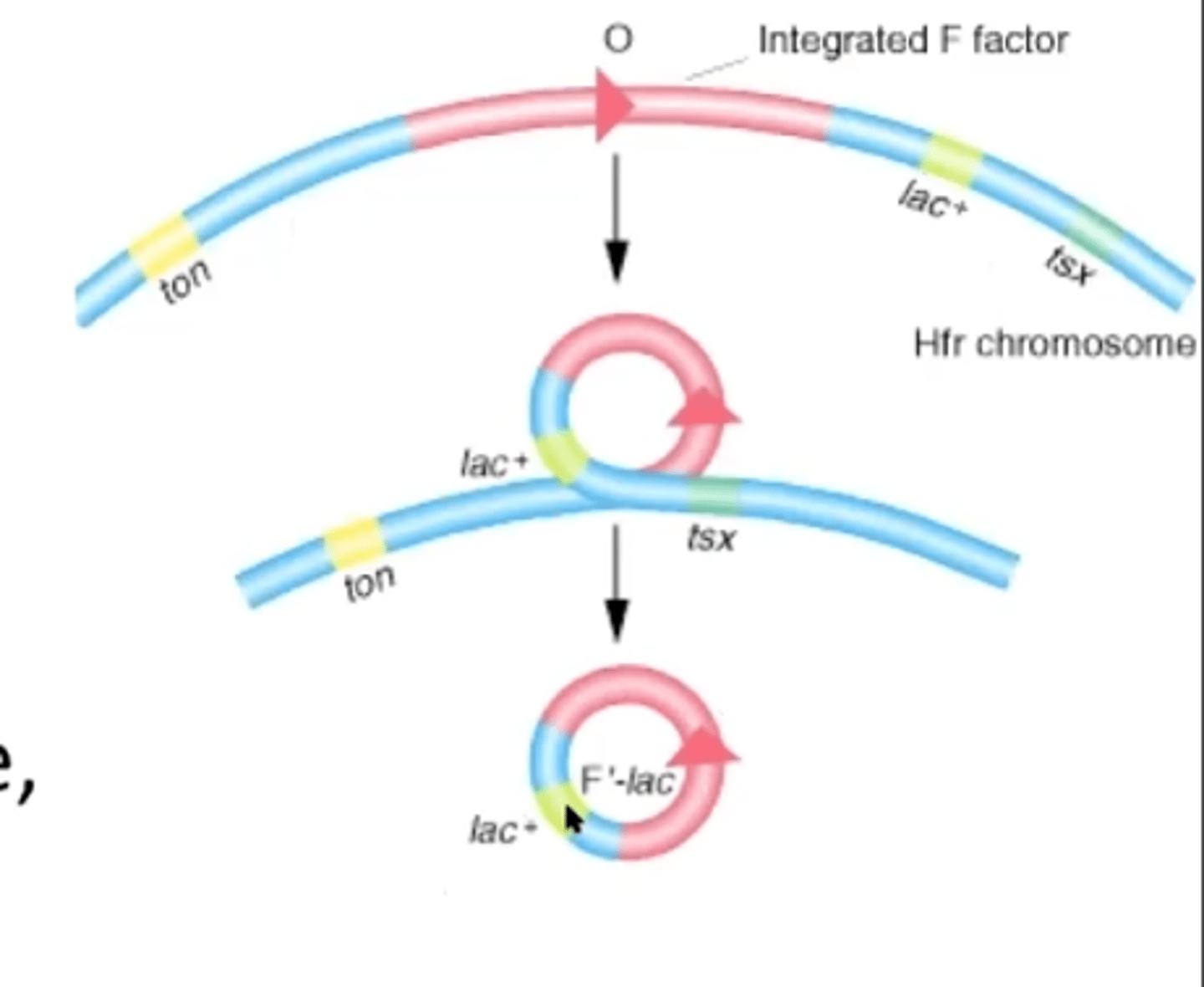
Episome
plasmid that can integrate into bacterial chromosome
Merodiploid
a bacterial cell that is diploid for a portion of its genome
Why is the lac operon a good model system?
beta-gal is ONLY made in the presence of lactose - postive and negative regulation
How can beta-gal activity be monitored?
Processing known substrates into colorful derivatives that act as indicators
Inducers
Compounds that stimulate the transcription of specific genes
IPTG
inducer of lac operon: inactivates repressor but is not broken down by β-galactosidase
lacZ
encodes B-galactosidase
lacY
encodes lactose permease
Describe the relationship between lacZ and lacY
co-regulated
lacI
encodes the lac repressor
lacI-
mutation that causes cells to produce enzymes all the time (constitutively)

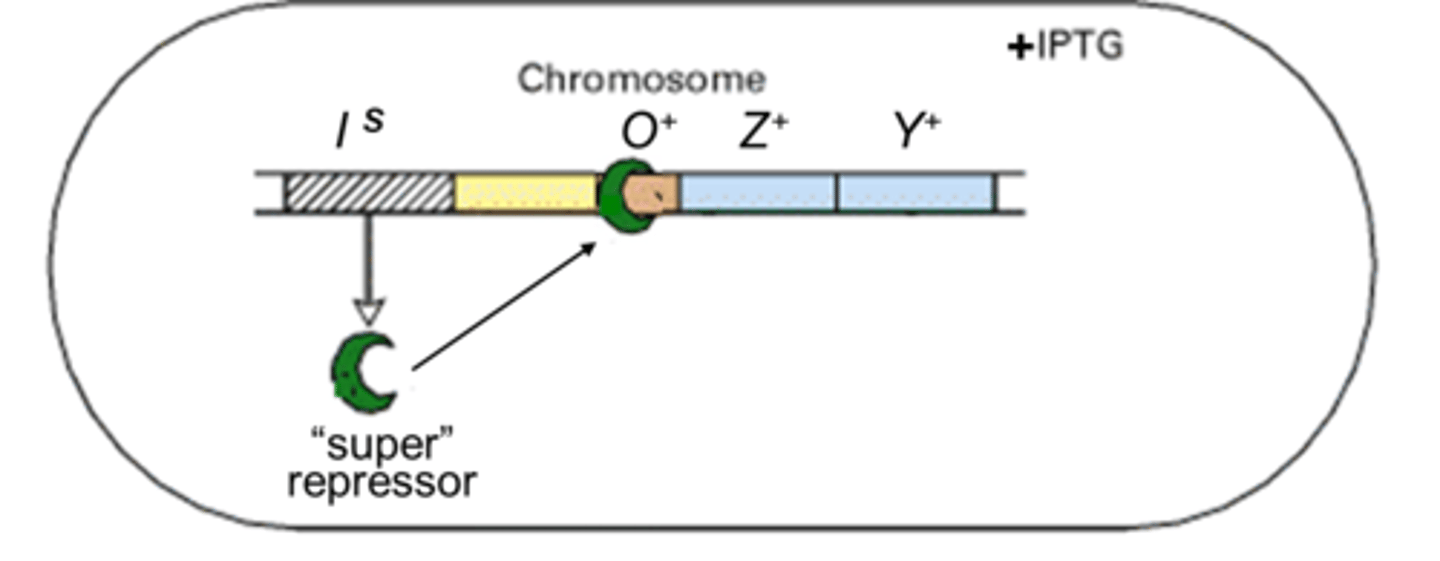
lacI^S mutation
super repressor. cannot bind lactose or IPTG and therefore cannot leave operator so the system is always shut off.
lacO
operator where the repressor binds
2 classes of lacO mutations:
sometimes they were constitutive (O^c)
sometimes they genes following were permanently turned off

lacP
lac promoter
Mutation in lacP (lacP-)
genes will never be expressed
Structural genes of lac operon
lacZ, lacY, lacA
Which part of the lac operon is cis-dominant?
lacO
Which part of the lac operon is trans-dominant?
lacI