APES Unit 2: The Living World: Biodiversity
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Species Richness
The number of species in a given area

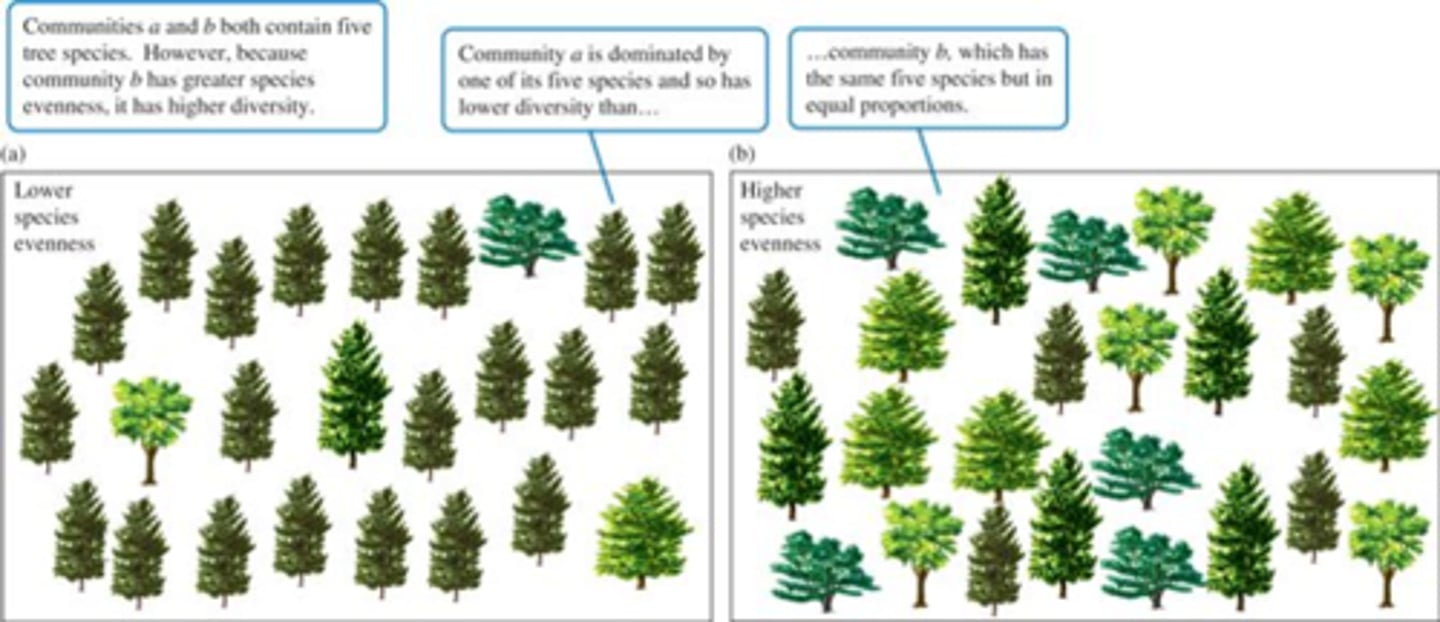
Species Eveness
The relative proportion of individuals within the different species in a given region
Evolution
A change in the genetic composition of a population over time.
Gene
A physical location on the chromosomes within each cell of an organism.
Mutation
A random change in the genetic code produced by a mistake in the copying process.
Recombination
The genetic process by which one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome during reproductive cell division.
Evolution by natural selection
The process in which the environment determines which individuals survive and reproduce.
Fitness
An individual's ablility to survive and reproduce
Adaptation
A trait that improves an individual's fitness
Gene flow
The process by which individuals move from one population to another and thereby alter the genetic composition of both populations.
Extinction
The death of the last member of a species

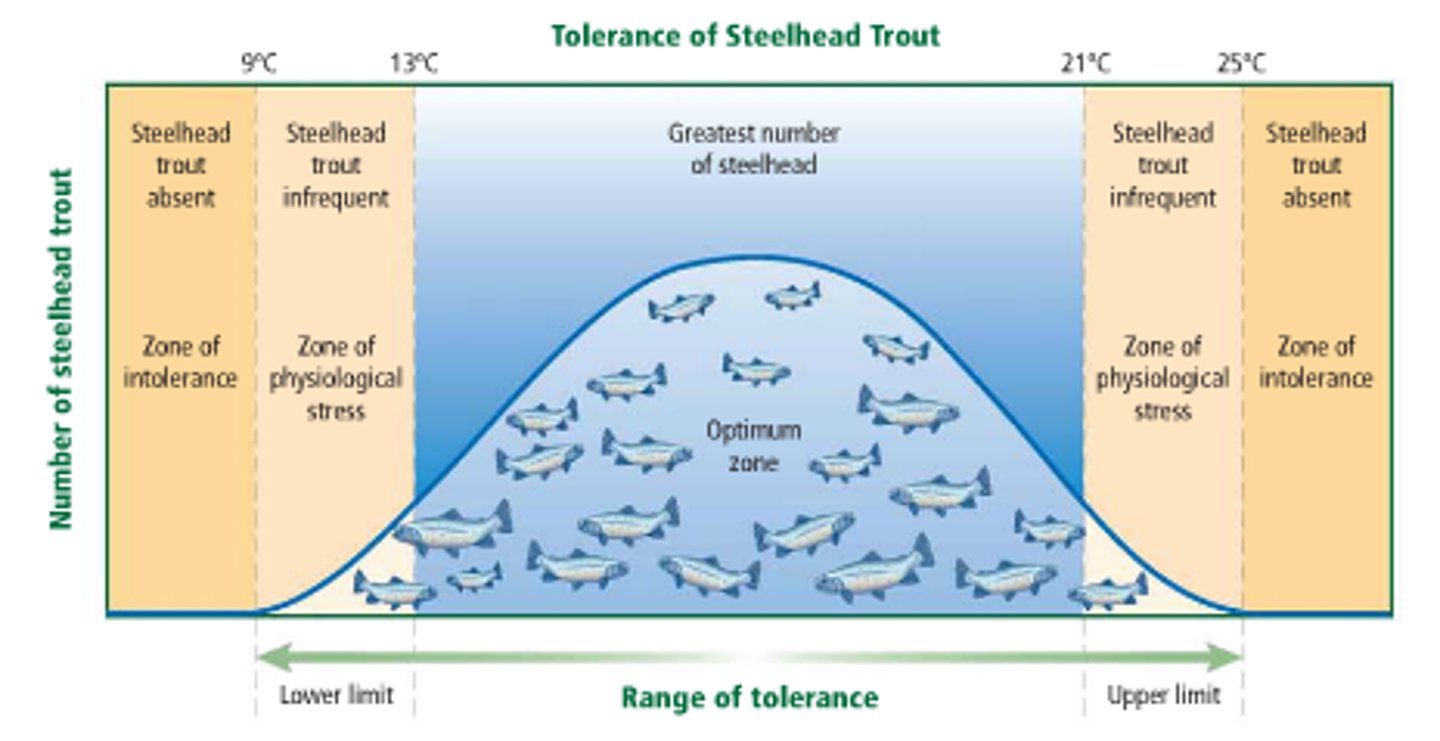
Range of tolerance
The limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate
Fundamental niche
The suite of abiotic conditions under which a species can survive, grow, and reproduce
Realized niche
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives
endemic species
Species that is found in only one area. Such species are especially vulnerable to extinction.
ecological succession
series of gradual changes that occur in a community following a disturbance
primary succession
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
secondary succession
reestablishment of a damaged ecosystem in an area where the soil was left intact
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
climax community
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species over time
cultural services
the spiritual and recreational benefits that ecosystems provide
regulating services
the ways that ecosystems control important conditions and processes, such as climate, the flow of water, and the absorption of pollutants
supporting services
basic ecosystem processes (nutrient cycles, soil formation)
provisioning services
products obtained from ecosystems
keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded.
island biogeography theory
explains how species come to be distributed among oceanic islands
bottleneck effect
A change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population
founder effect
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population
selective pressure
environmental conditions that select for certain characteristics of individuals and select against other characteristics
zone of intolerance
A region that is so far removed from an organism's optimal range for an environmental variable that the organism cannot survive.
Examples of primary succession
Glacier retreat, lava flow, recently exposed sand dune; topsoil is not present
Examples of Secondary Succession
Hurricane
Flooding
Forest fire
Clear-cut forest
Avalanche
Landslide
examples of keystone species
sea stars, sea otters, beavers
examples of indicator species
lichens, Northern spotted owls, amphibians
examples of supporting services
nutrient cycling, soil formation, primary productivity
examples of provisioning services
Food, fuel, raw materials, freshwater & medicines.
Examples of regulating services
Air quality, climate, erosion control, pollination & natural disaster mitigation.
Examples of cultural services
Recreation and mental and physical health
Tourism
Aesthetic appreciation and inspiration for culture, art, and design
Spiritual experience and sense of place
Biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
species diversity
The number and relative abundance of species in a biological community.
genetic diversity
The range of genetic material present in a gene pool or population of a species.
ecosystem diversity
variety of habitats, living communities, and ecological processes in the living world
zone of physiological stress
range where organisms survive, but experience some stress such as infertility, lack of growth, decreased activity, etc.
optimal range of tolerance
range where organisms survive, grow, and reproduce