Female Reproductive System Anatomy
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards with a fill in the blank format to help review the female reproductive system anatomy lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
uterosacral ligament
__ is basically going to attach the uterus to the sacrum.
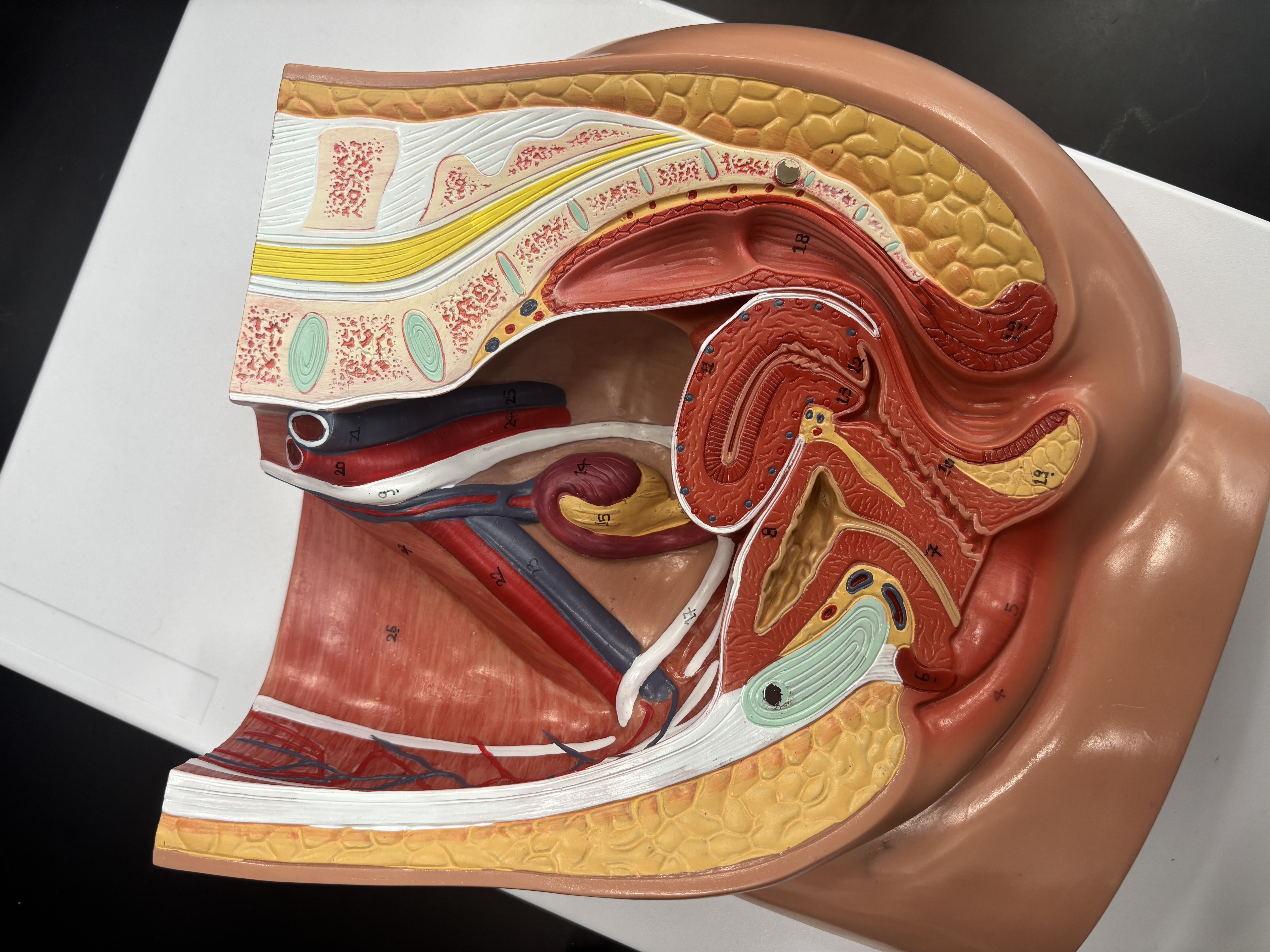
cervix
The round portion at the distal end of the uterus that projects into the vagina or the vaginal canal is called the __.
taken care of
The acidity in the vagina basically is meant to make sure that anything coming into the area is __.
perineal region
The __ actually goes between the legs.
vestibule
The area where the clitoris, the urethra, and the vagina is located is called the __.
Anterior
The opening to the urethra is __ toThe opening to the vagina.
vulva
The whole thing for the external genitalia is called the __.
mons pubis
The __ is the the most anterior part of the female genitalia.
prepuce
The __ in women is also a little bit of foreskin that basically goes over the body of the clitoris.
labia majora
Any structures that would have become the scrotum actually becomes the __.
skin
The labia minora does not include any __ covering and does not include any pubic hair.
The vestibule
__ is basically this nice, like, internal portion in the female external genitalia that goes from the body of the excuse me. The glands clitoris includes the urethra and also includes the vaginal opening.
bulb of the vestibule
The __is actually also erectile tissue and is essentially equivalent to the corpus spongiosum erectile tissue in men.
greater vestibular glands
The __ basically are going to secrete a lubricating fluid during arousal.
urethral glands
The male equivalent of the greater vestibular gland is the __.
perirethral gland
The __ actually has openings right here that are near the urethral opening, and is also known as the g spot.
cavernosis
Ishcial Cavernosus runs along the ischium, and then the __ tissue is where the clitoris is.
penis
For women, ischio cavernosus and bulbospongiosis muscles essentially grip onto the __.
Pelvic Prolapse
A __ is when the pelvic organs push out of the body.
Kegel
__ exercises require you basically to contract the muscles of your pelvic floor.
erection
In women, the only process they have in the female sexual response is actually the __ process.
orgasms
Women can have multiple __ because, actually, we don't have to go through the resolution phase.
Oocytes
__ are what you produce in the ovary, which is an immature egg.
Oocytes
Oogenesis is going to be the creation of the __ or creation of eggs.
ooagonia
During fetal development period, essentially, what's going to happen is you have this __, this stem cell that's gonna go through mitosis.
primordial follicles
Right before birth, you're gonna start to create these __ , which is essentially going to be your now what we consider to be a primary oocyte because it has 46 chromosomes.
meiosis
The oocyte inside of that primordial follicle is gonna start to go through __.
mitosis
During fetal development, as you start to create these primordial follicles, most of them, actually all of them, will be selected to go through the beginning part of __.
arrested
Primary oocyte essentially is going to go through prophase I right here, and then it's going to be __ and stop development in prophase one.
ovarian
The __ cycle is what is happening to the oocytes in the ovaries.
uterine
The __ cycle is showing you the endometrium layer, what's happening to this layer over time.
follicular
During the __ phase, you basically build the follicle cells around the oocyte and continue to go through meiosis.
luteal
The __ phase happens after ovulation.
pro phase one
At the beginning of menstruation, what's going to happen is you're gonna now take these primordial follicles, which remember have a primary oocyte arrested in __.
ovulated
A graphene or a vesicular follicle that is actually going to have the oocyte that gets __ out.
luteinizing hormone
You see how meiosis one is going to end right here, And then what's gonna happen is you're gonna have a __ surge.
fertilization
The rest of meiosis two is gonna happen only after __.
Down syndrome
One of the genetic chromosome errors mentioned was __, where you end up with a third chromosome for chromosome twenty one.
one egg
Genetic abnormalities in sperm are really truly affecting genetic abnormalities in your embryo or fetus less likely, however, it is more important for women because they are only creating __ a month.
corpus luitum
Once the egg or, really, I should say the secondary oocyte gets ovulated out, those follicle cells are now going to develop into a new structure called the __.
implantation
Then if you don't have __, menstruation will occur.
anterior pituitary
What happens here is the hypothalamus is going to secrete an outotropin releasing hormone, It hits the __ gland releasing FSH and LH, this is no different than men.
ovulation
As more and more LH is produced, you're gonna see this spike in LH, which is gonna cause __ right here, and it also causes the development of the corpus luteum, essentially.
corpus luteum
Once the corpus luteum develops, we're gonna be in the luteal phase, and the luteal phase is when our __ secretes progesterone and estrogen.