Chapter 3 Migration Key Terms Flashcards
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Human Geography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Lee’s Law of Migration
Everyone has the opportunity to move, but there are exceptions
Human nature often stops a person from choosing to migrate
A person may not have the economic or physical abilities to do so
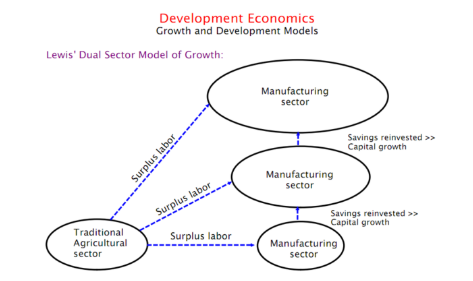
Lewis Model of Surplus Labor
Excess labor on farms was attracted to higher wage earnings in the city
Assumes there is a small urban industrial area surrounded by a large agricultural area which experiences surplus labor situations
Intervening Obstacles
Things that hinder migration
Environmental: Mountains, rivers, deserts, etc…
Political: Restrictive immigration laws, hostility, etc…
Intervening Opportunities
Presence of a nearer opportunity that diminishes the attractiveness of a site further away
Proximity to jobs, countries that offer asylum, etc…
Gravity Model
People are attracted to larger areas, determines the breaking point
Breaking Point: The point where one city becomes more attractive than another
Pop1 x Pop2 / (Distance)2
Harris-Todaro Economic Model
The migrant is rational and calculative in their decision to move to certain city
Zelinsky’s Model of Mobility Transition
Attempts to explain trends of migration as countries individualize
Closely follows the DTM
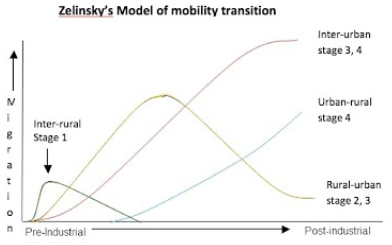
Stage 1 of Zelinsky’s Model
Seasonal migration, little to no permanent migration
Stage 2 of Zelinsky’s Model
Internally: High rate rural → urban migration
Internationally: High rate of emigration
Stage 3 of Zelinsky’s Model
Internally: Urban to urban migration surpasses rural to urban migration
Internationally: Net in-migration > net out-migration
Stage 4 of Zelinsky’s Model
Internally: Rural → urban migration continues at a reduced rate
Internationally: Continued rising levels of net in-migration
Stage 5 of Zelinsky’s Model
Internally: Nearly all migration is inter-urban and intra-urban
Internationally: Continued rising levels of net in-migration
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
19th century geographer E.G. Ravenstein
Made a series of “laws” about the tendencies of migrants
Ravenstein’s 1st Law
Most people migrate for economic reasons
Ravenstein’s 2nd Law
Most relocate a short distance, remain in country
Ravenstein’s 3rd Law
Long-distance migrants that migrate to other countries go to major economic hubs (cities)
Ravenstein’s 4th Law
Most long-distance migrants are male, while women are often short-distance
Ravenstein’s 5th Law
Most long-distance migrants are individuals rather than families with children
Ravenstein’s 6th Law
Most long-distance migrants are young adults seeking work
Absorption
The immediate population surrounding a city moves into it, and gaps left behind are filled by migrants
Step-Migration
Small “steps” to a desired final location
Lee Model
Explains the factors that influence migration decisions by organizing them into push and pull factors
Circular Migration
Short-term with repetitive acts of mobility with intents of moving back home
Seasonal migration
Cohort
A group of people who share a common characteristic(s)
Birthyear, race, eye color, etc…
Push Factor
Centrifugal force, typically negative
Pull Factor
Centripetal force, typically positive
4 Major Types of Push/Pull (ESPN)
Economic
Social
Political
eNvironmental
Chain Migration
Migrating due to a recommendation to move from someone/another migrant
Emigration
From a location
Forced/Involuntary Migration
Migrating against one’s will
Immigration
To a location
Internal Migration Pattern
The regular, predictable movement of people within the borders of a single country
Driven by economic opportunities, environmental changes, or social dynamics
Migration
Permanent move to a new location
Overpopulation
A region’s population exceeds the environments capacity to support it
Population Center (Of Gravity)
The geographical point that represents the average location of a region’s population
Refugee
Forced to migrate to avoid a potential threat to life, cannot return
Must cross the international border
Voluntary Migration
People migrate by choice
Reluctant Migration
Don’t really want to migrate, but have to
Asylum Seeker
Migrated to another country in hope of being recognized as a refugee
Brain Drain
Educated people leaving their home country in search of better opportunities
India
Brain Gain
Educated people entering a new country in search of better opportunities
The US
Counterurbanization
Net migration from urban to rural areas increasing, reversing a trend of urbanization
Suburbanization
Most intraregional migration in developed countries going from cities to surrounding suburbs
Motivated by a desired lifestyle
Floodplain
A low, flat land area that is subject to periodic flooding
Guest Workers
A person who temporarily migrates to another country for labor
Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs)
Similar to refugee but displaced within a country (Did not cross the international border)
Not a citizen anywhere
INTRAregional Migration
Migrating within a region
Kansas to Louisiana
INTERregional Migration
Migrating from one region to another
The US to France
Interregional Migration Trends
Migrate from rural → urban areas
Intraregional Migration Trends
Migrate from cities to surrounding suburbs
Migrant Labor
An individual who moves from one place to another to find employment
Often across borders
Mobility
All types of movement
Net Migration
Difference between the number of immigrants and emigrants
Quotas
Government limit on the amount of immigrants from a certain country
Repatriation
The return of something or someone to their country of origin
Illegal Immigration
Unauthorized immigration, entering the country without legal permission or staying after an expired legal status
United Nations Refugee Agency (UNHCR)
The international organization that provides protection, assistance, and durable solutions for refugees, IDPs, and asylum seekers
Diaspora
The dispersion of people from their original homeland to other locations
Visa
A legal document issued by a country that grants a foreigner permission to enter, stay, or work for a specific period
Green Card
A legal document that proves a foreign national has been granted lawful permanent legal status in the US
Blue Card
Work and residence card for highly skilled non-EU nationals to live and work in a certain EU country
Exaptriate
A skilled worker or professional who lives outside their country
Usually moved for work opportunities