Electrolysis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:32 PM on 5/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
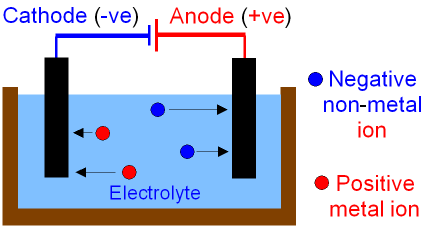
equipment for electrolysis
beaker → containing electrolyte
electrodes → ==cathode== and %%anode%%
electrodes joined with wire
electrodes → ==cathode== and %%anode%%
electrodes joined with wire
2
New cards
what is electrolyte
liquid or solution containing an ionic compound, ions in electrolyte are free to move
3
New cards
what is an electrode
solid conductors, genrally made of metal/ carbon
4
New cards
what is the negative electrode called in electrolysis
cathode
5
New cards
what is the positive electrode called in electrolysis
anode
6
New cards
why are the electrodes joined by wire
so electrons can flow ( there is a power supply such as a battery to drive the flow of electrons)
7
New cards
meaning of the word electrolysis
splitting up with electricity
8
New cards
how does electrolysis work
negative ions attracted to anode and become discharged
positive ions attracted to cathode and become discharged
positive ions attracted to cathode and become discharged
9
New cards
what does it mean to become discharged
go from a charged atom to a neutral atom
10
New cards
in the electrolysis of lead bromide, what happens at the anode
negative ions attracted to anode and are oxidised & become discharged
\
half equation
2Br- → Br2 + 2e-
\
half equation
2Br- → Br2 + 2e-
11
New cards
in the electrolysis of lead bromide, what happens at the cathode
lead ions are combined with two electrons and are reduced to form pure lead
1. ==Pb2+== **+** ==2e-== → Pb
1. ==Pb2+== **+** ==2e-== → Pb
12
New cards
what’s happening in the wire in electrolysis
1. the electrons from the negative ions are being passed to the positive anode
2. and then being transported along the wire around to the cathode (using the power of the battery)
3. these electrons are then given to the positive ion, discharging it
\
*using electricity to convert the ions in a compound back into their pure elemental forms*
13
New cards
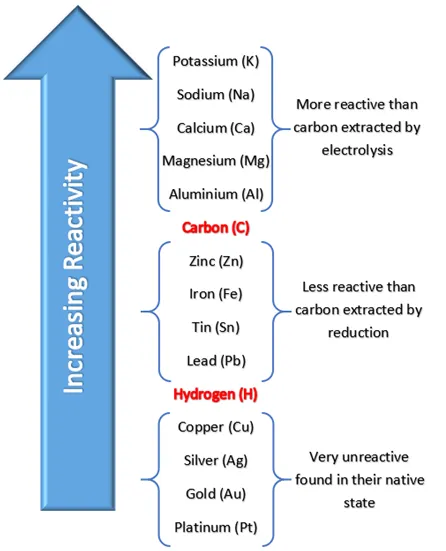
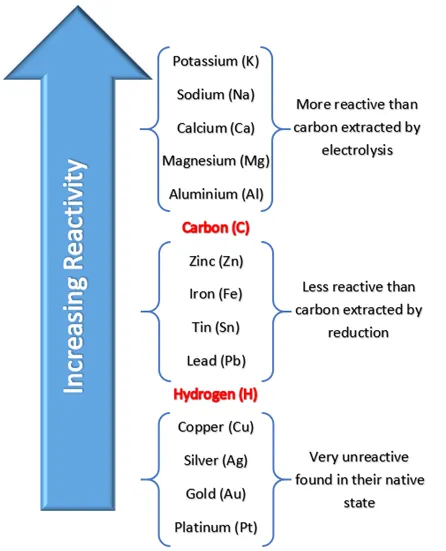
how to reduce a metal
reduction with carbon (only works for metals less reactive than carbon)
electrolysis for those higher than metals
electrolysis for those higher than metals
14
New cards
metals less reactive than carbon
zinc
iron
tin
lead
copper
silver
gold
iron
tin
lead
copper
silver
gold
15
New cards
how to make aluminium oxide into molten mix so it can be electrolysed
purify bauxite
mix it with cryolite to lower MP
melt
mix it with cryolite to lower MP
melt
16
New cards
OIL RIG
oxidation is loss of electrons
reduction is gain of electrons
reduction is gain of electrons
17
New cards
in aqueous solutions, what is the rule for which element is dicharged at the ==CATHODE==
If the metal element formed during electrolysis is **more reactive** than %%hydrogen%%, then hydrogen will be produced at the cathode.
\
If the metal element formed is **less reactive** than hydrogen, then the metal is produced at the cathode.
\
If the metal element formed is **less reactive** than hydrogen, then the metal is produced at the cathode.
18
New cards
metals less reactive than hydrogen
copper
silver
gold
platinum
silver
gold
platinum
19
New cards
which element is carbon in between in reactivity series
aluminium & zinc
20
New cards
which element is hydrogen in between in reactivity series
lead & copper
21
New cards
in aqueous solutions, what is the rule for which element is discharged at the %%__**ANODE**__%%
if a %%***HALIDE***%% is present (aka group 7) it will be discharged
if not, then its %%**ALWAYS**%% the hydroxide which is discharged
if not, then its %%**ALWAYS**%% the hydroxide which is discharged
22
New cards
why is the positive electrode continuously replaced
The positive electrode (anode) is made of carbon, which reacts with the oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and so must be continually replaced.
23
New cards
similarities between ppm and nm
• both have positive charges • both have (negative) electrons • neither has neutrons
24
New cards
why is graphite soft
each (carbon) atom forms three covalent bonds
forming layers (of hexagonal rings) (soft)
(because) layers can slide over each other
forming layers (of hexagonal rings) (soft)
(because) layers can slide over each other
25
New cards
why is buckminister fullerene a good lubricant
molecules are spherical (so molecules) will roll
26
New cards

Explain why the scientist adds excess zinc rather than excess iodine.
to make sure that all the iodine reacts (as) excess iodine would remain in solution (so) iodine could not be filtered off or (so) the zinc iodide would not be pure
27
New cards
Suggest one reason why the percentage yield in this reaction is not 100%
incomplete reactions, in which some of the reactants do not react to form the product.
28
New cards
anything using temp changes, what can you use as a control to improve accuracy
polystryene cup