8A - Monohybrid crosses
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Monohybrid cross
A genetic cross performed to observe the inheritance of alleles and phenotypes for a single gene
Parental generation = P1
first generation = F1
Autosomal complete dominace
Widows peak = WW
normal = ww
therefore, Ww = Widows peak
Autosomal codominance
happens when two traits are independently and equally expressed
there will be 2 dominant alleles (2 capital letters) and no recessive allele (no lower-case letters).
Autosomal dominance - blood types
Both the A and B blood group alleles are dominant (written as IA and IB, respectively) so they will both be expressed. Meanwhile, the O blood group is recessive and written as i.
I^Ai = type A
I^A I^A = Type A
I^B i = Type B
I^B I^B = type B
ii = type O
I^A I^B= Type AB
Sex-linked alleles
Sex linked traits involve alleles on sex chromosomes
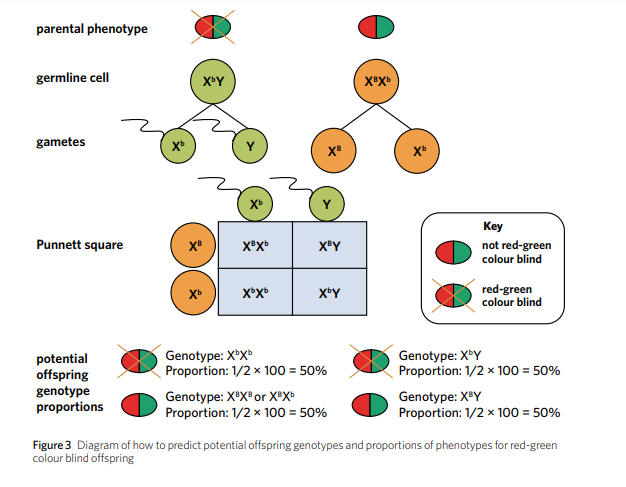
Sex-linked when explaining phenotype
With sex-linked traits, it is important to notice for proportions are calculated with respect to sex. So, in the example shown, we would say 50% of female offspring will be red-green colour blind and 50% of male offspring will be red-green colour blind
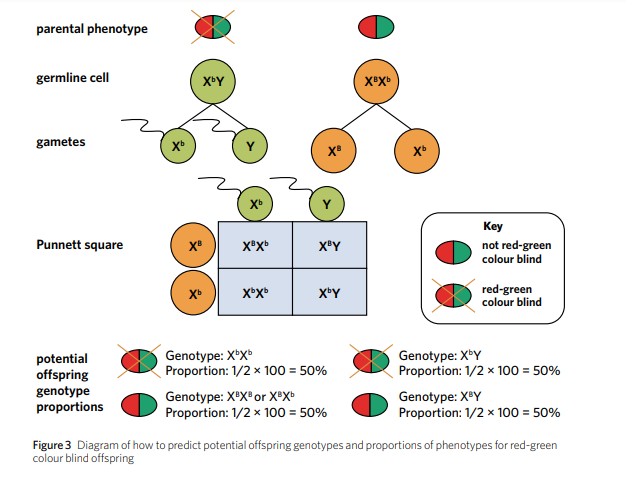
Test cross
when an individual expressing the dominant phenotype but with an unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual. The results indicate whether the individual with the dominant phenotype is homozygous dominant or heterozygous