Unit 2: Cell Transport: Diffusion, Osmosis: Hypertonic, Isotonic & Hypotonic
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
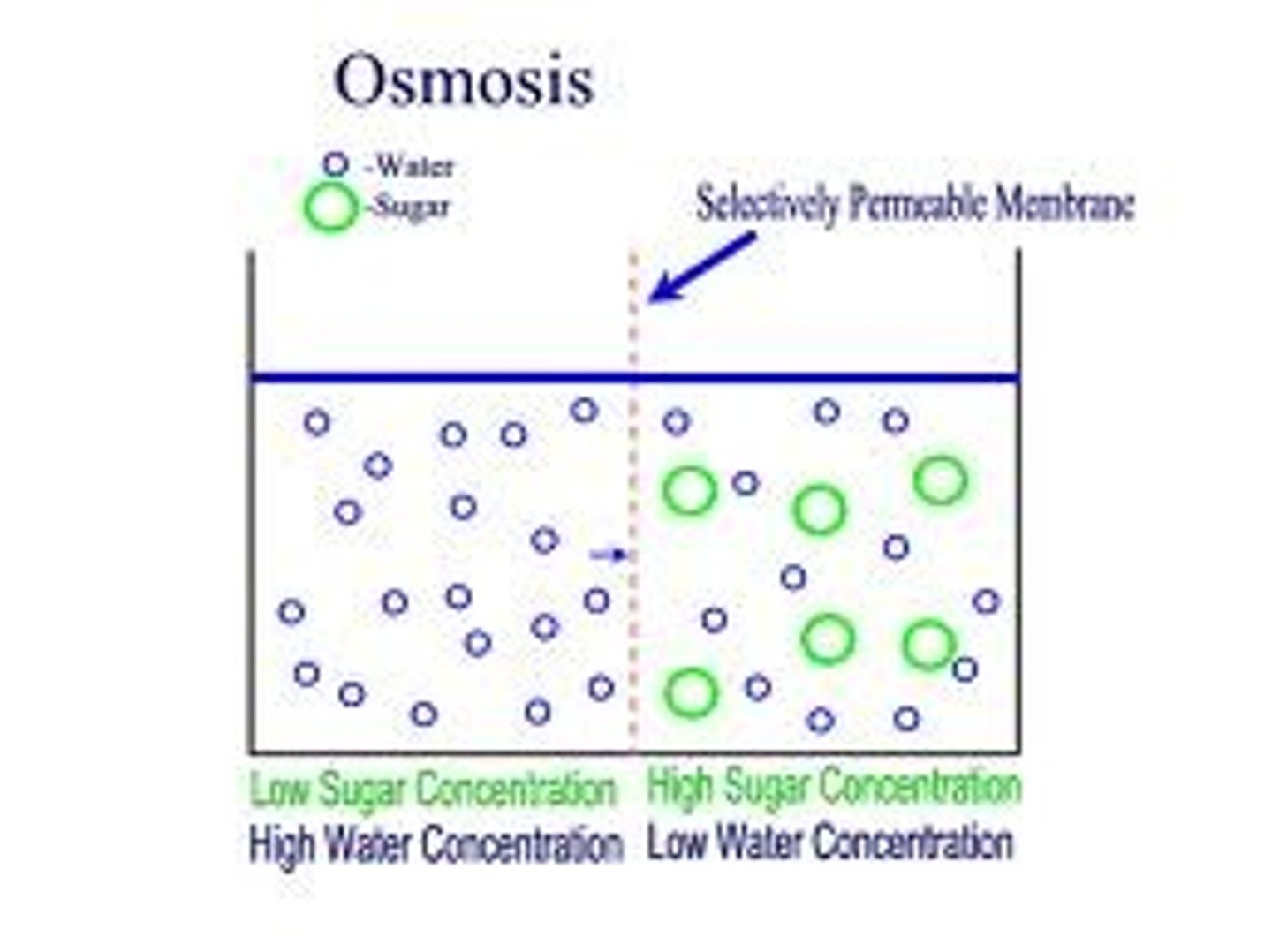
Osmosis
diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane
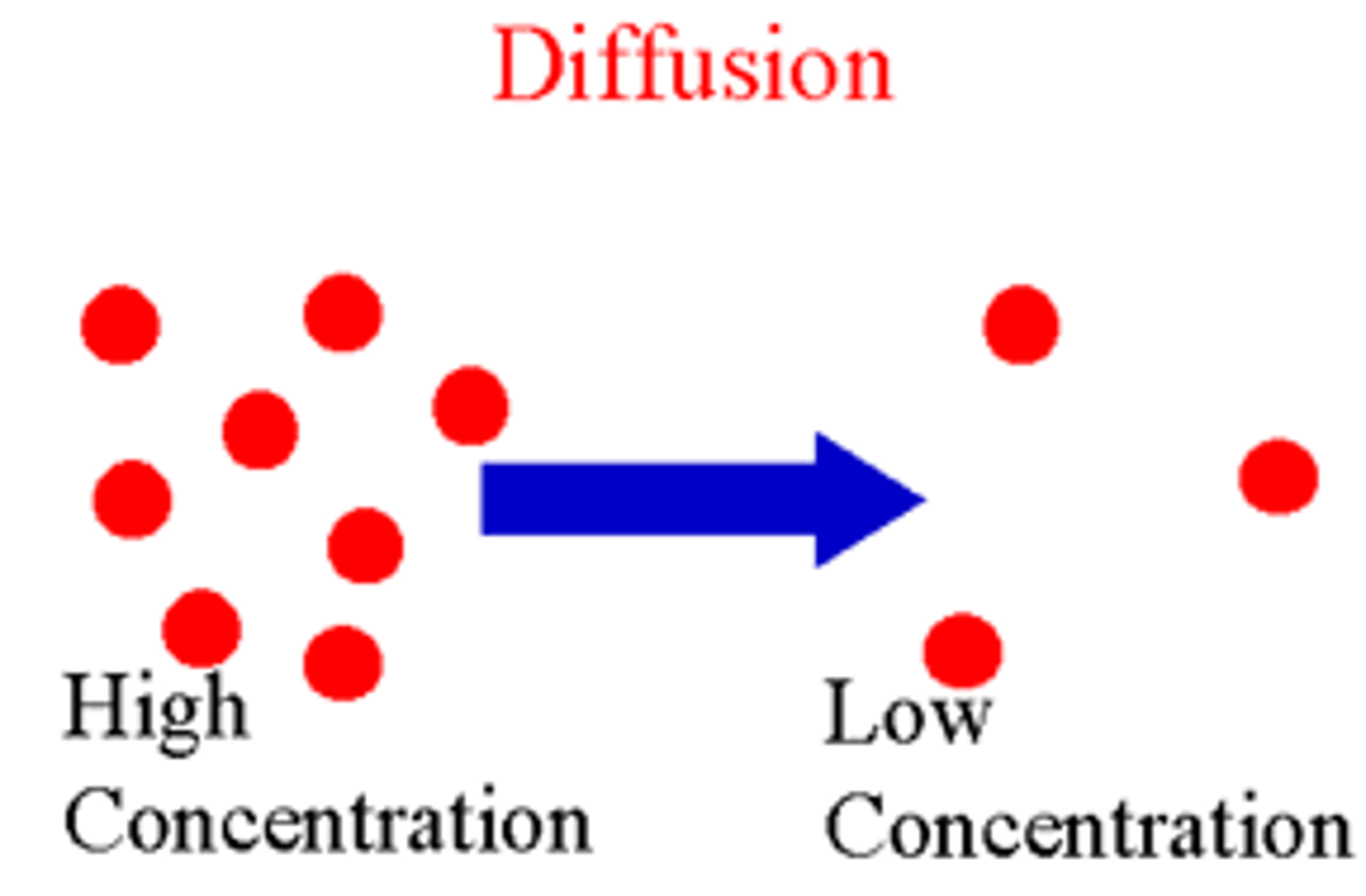
Diffusion
movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
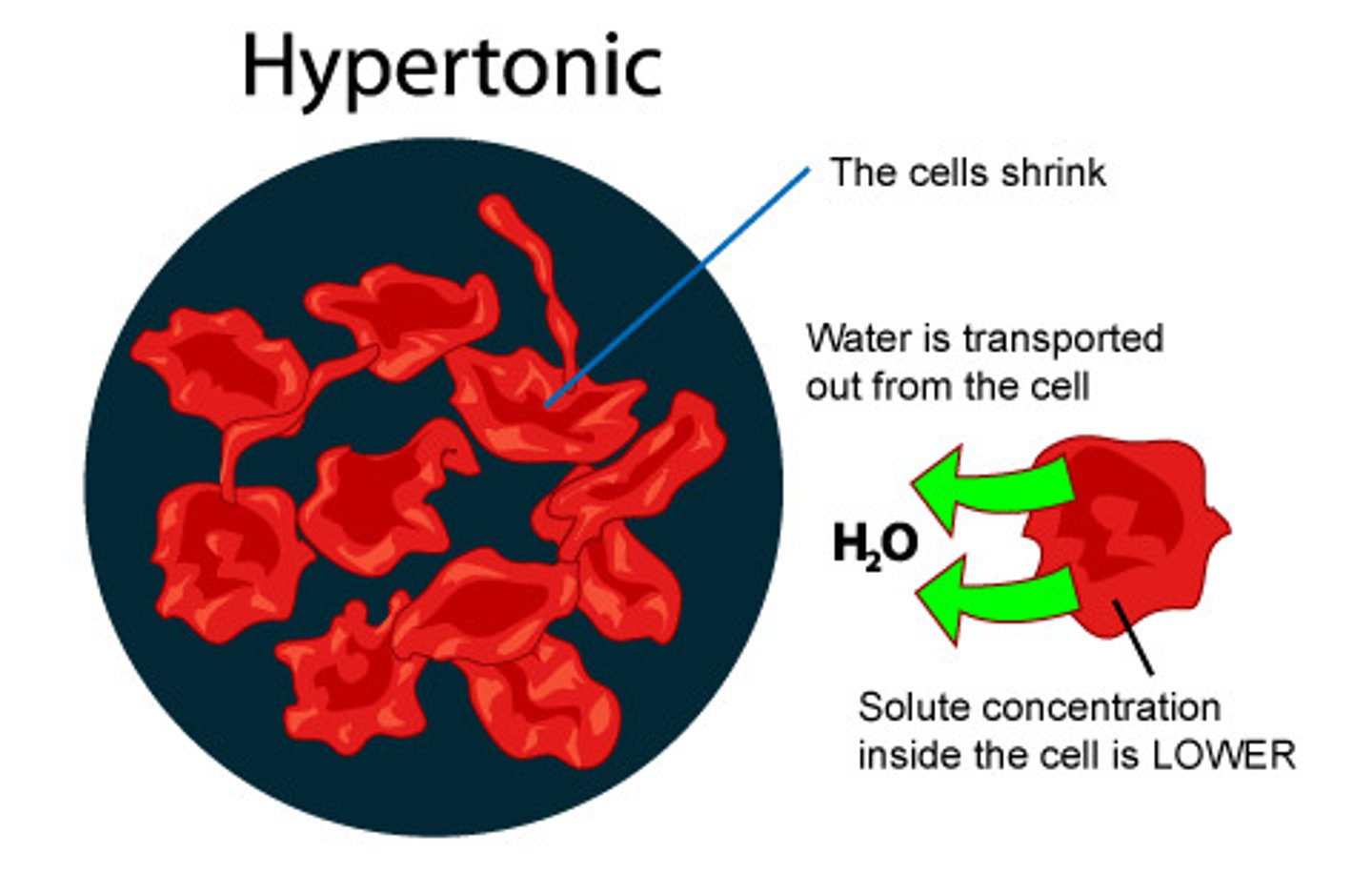
Hypertonic
higher concentration of solutes outside the cell than inside the cell, water flows out of the cell in order to balance the concentration of the solutes
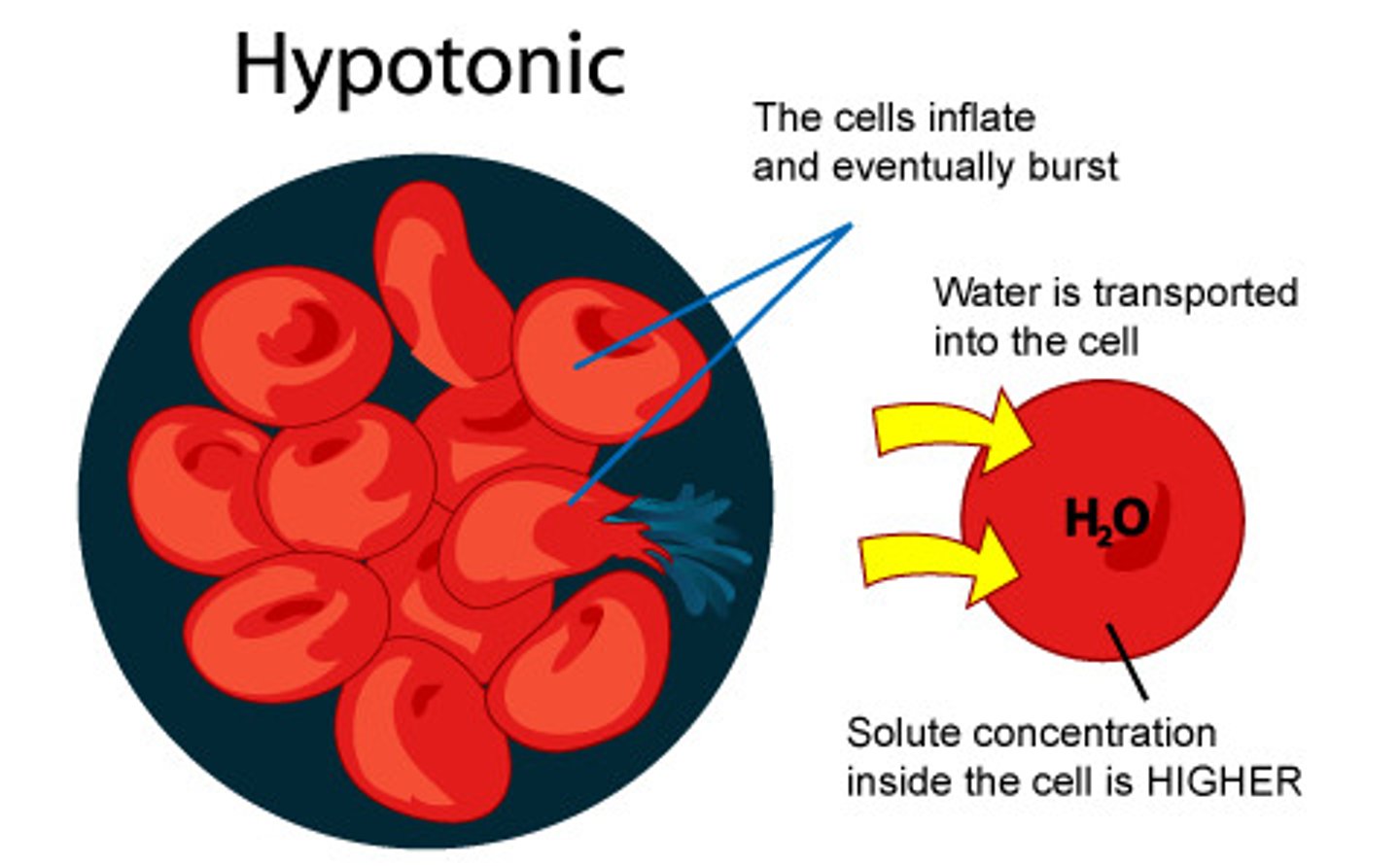
Hypotonic
lower concentration of solutes outside the cell than inside the cell,water will rush into the cell, and an cause it to burst
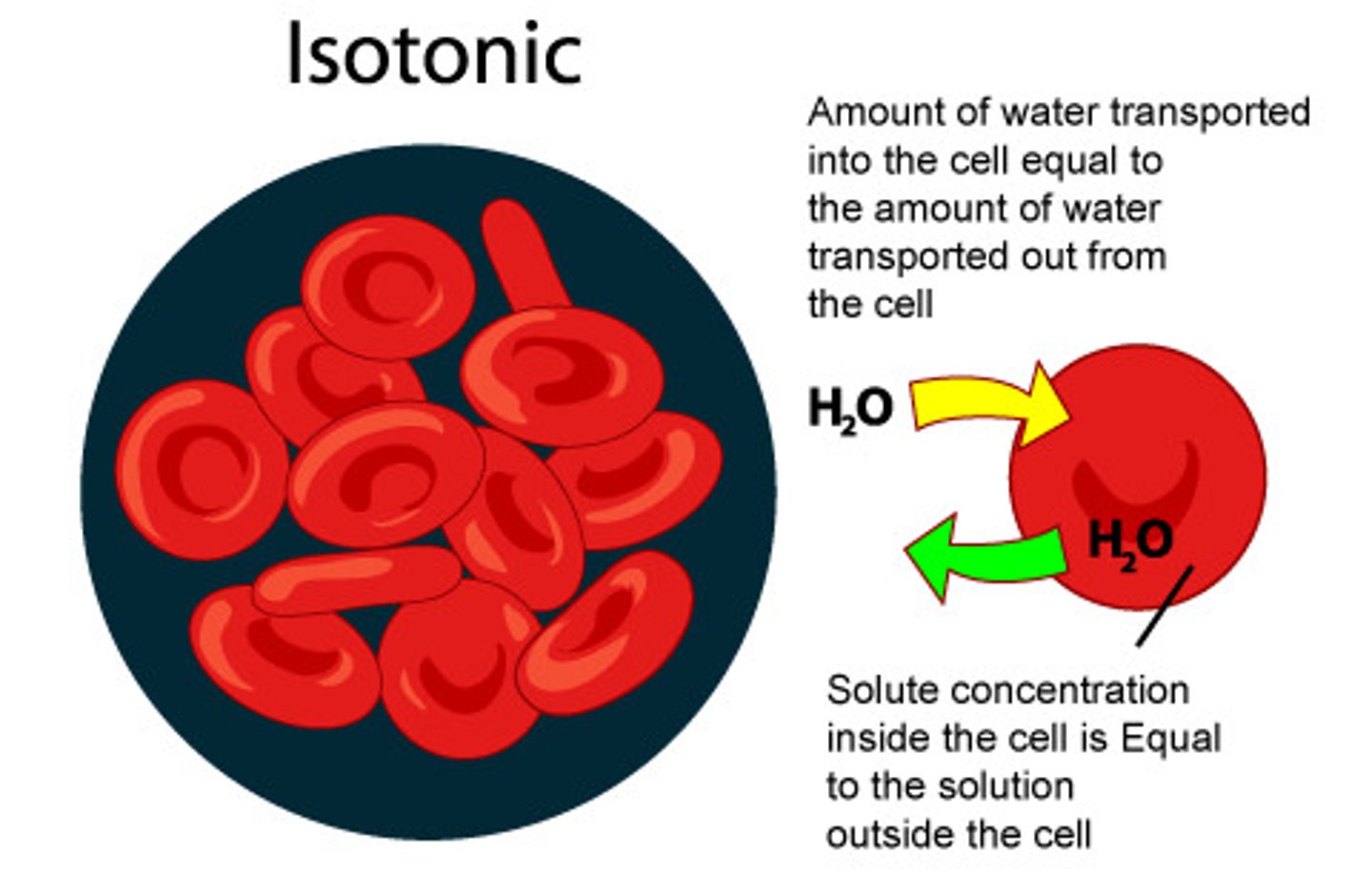
Isotonic
concentration of a solute is equal inside and outside
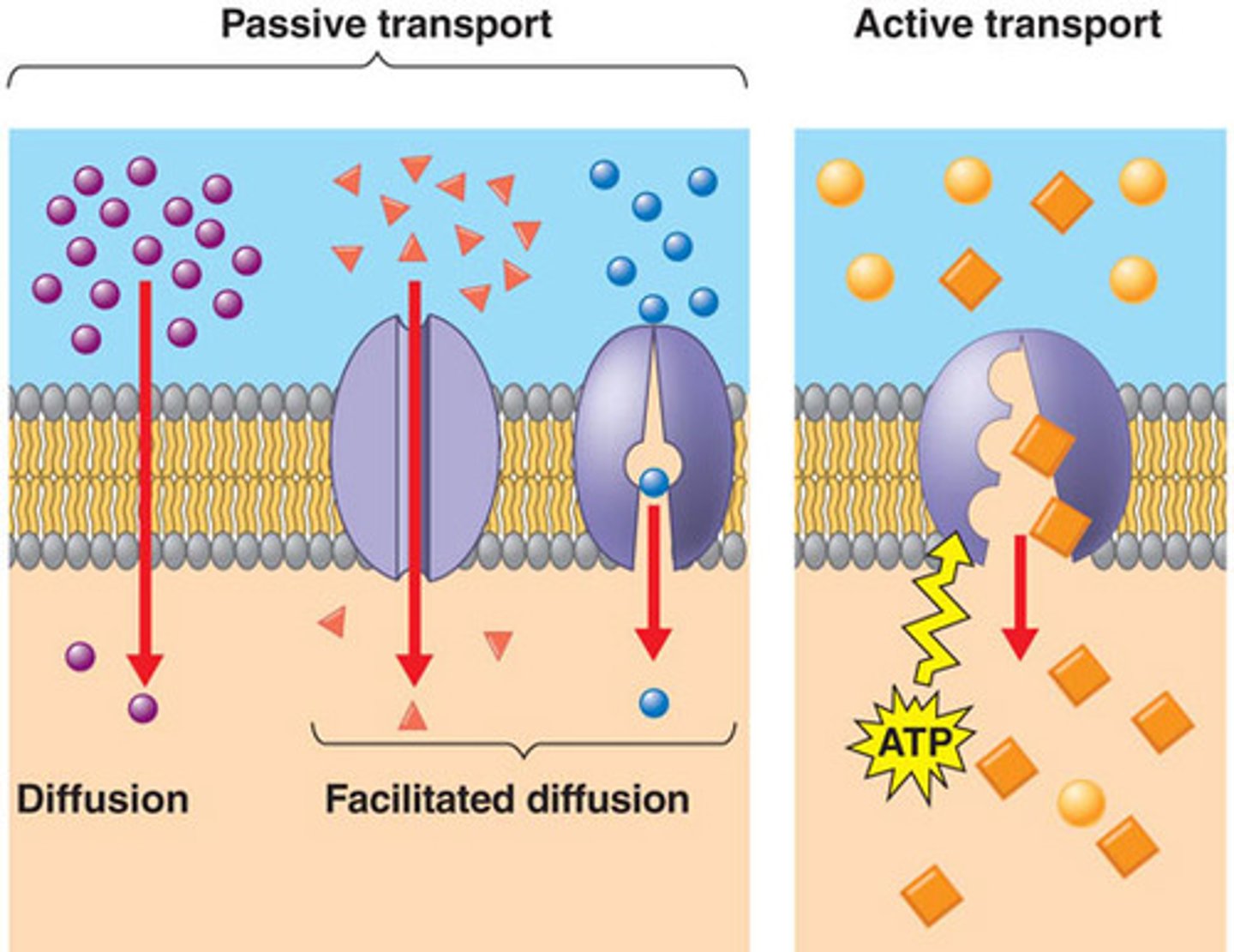
Passive Cell Transport: ex. Diffusion
movement of molecules across a cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration
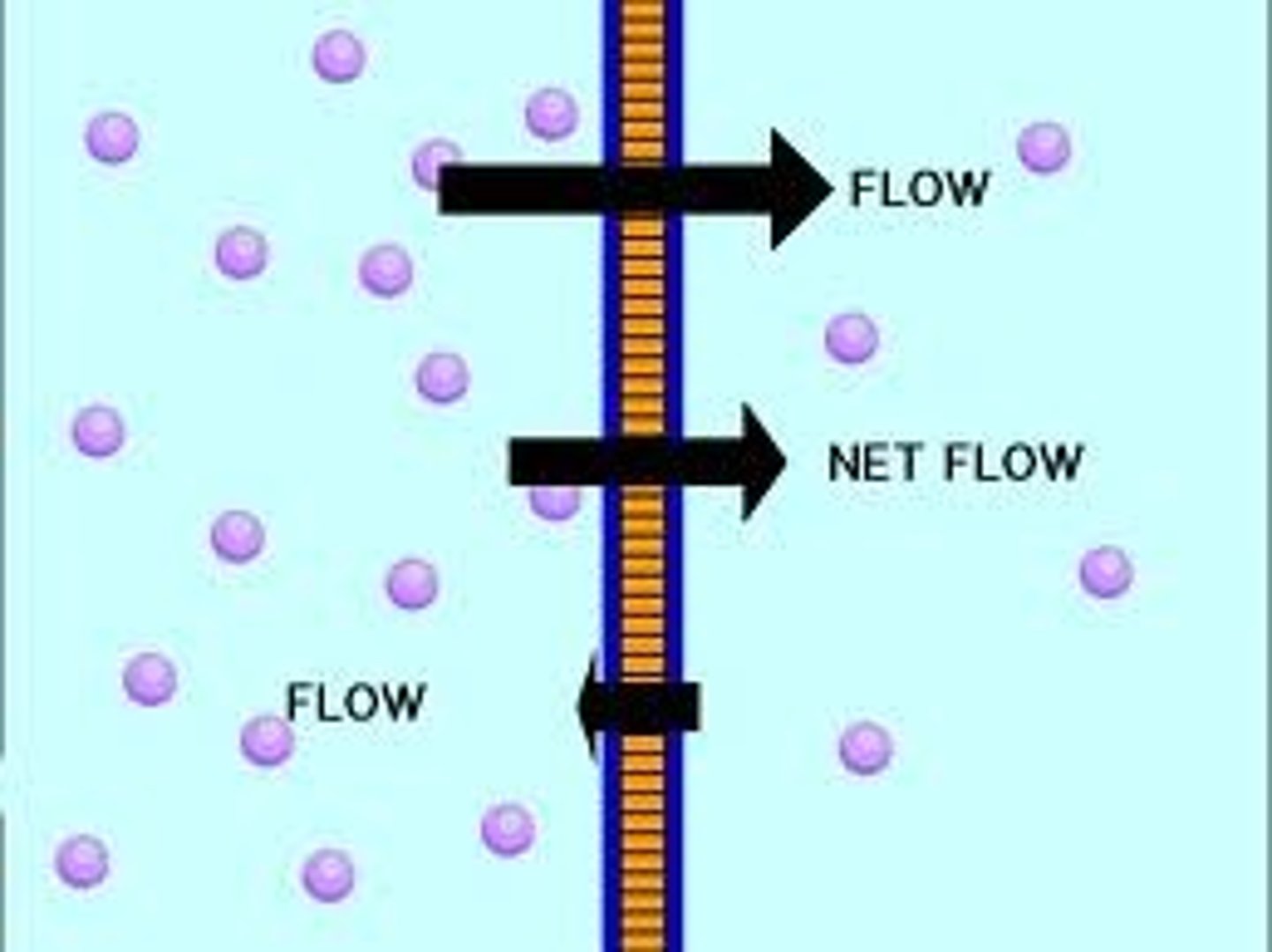
Concentration Gradient
movement of a solution or gas from an area of higher number of particles to an area of lower number of particles, the areas are typically separated by a membrane
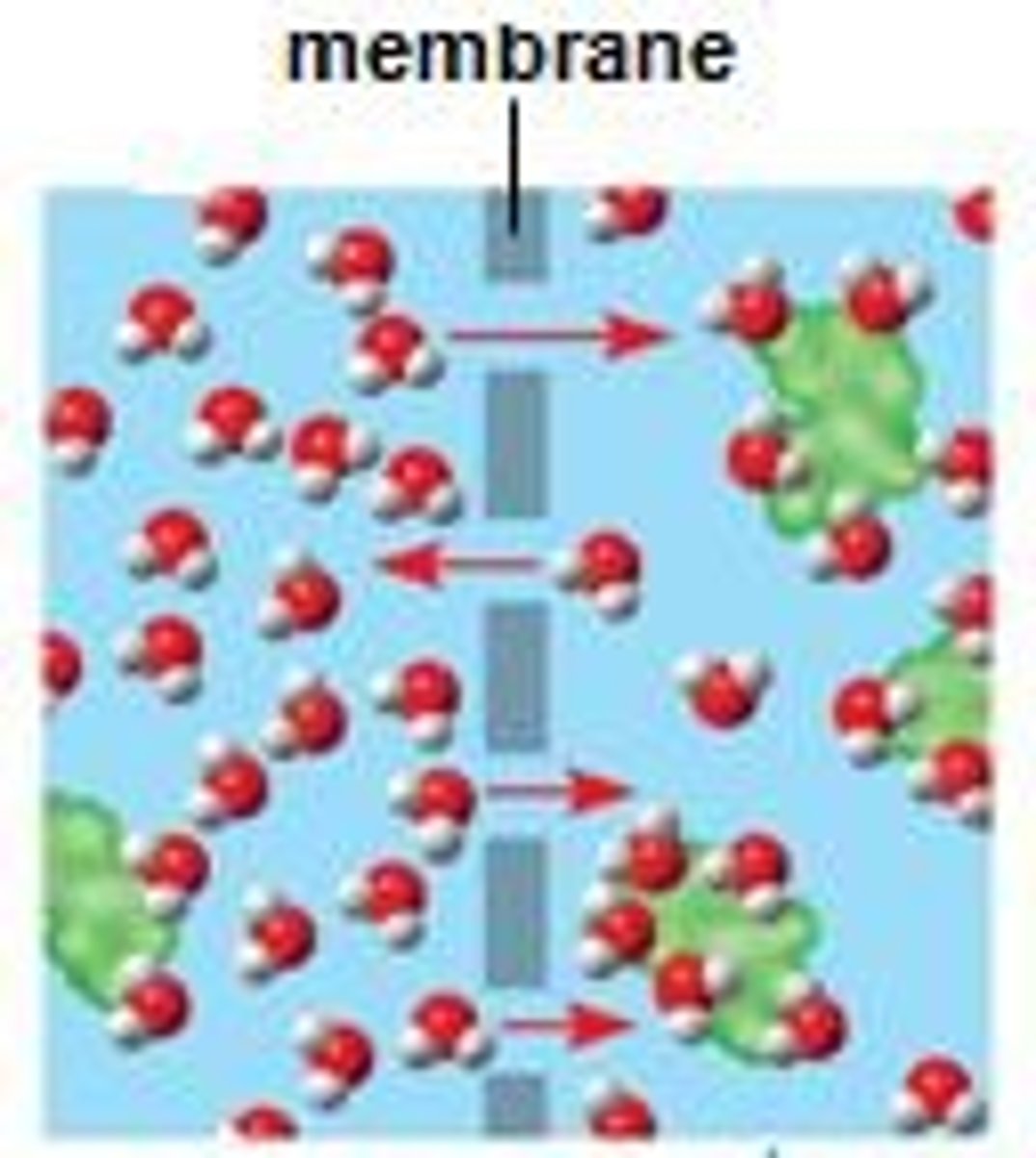
Selectively-Permeable Membrane or Semi-Permeable Membrane
selectively permeable membrane allows small, soluble molecules to pass through it, but prevents large insoluble molecules from passing through.
PROkaryote (pronounce pro-carry-oat)
Cells with NO nucleus & NO membrane-bound organelles (ex. bacteria) PRO = NO
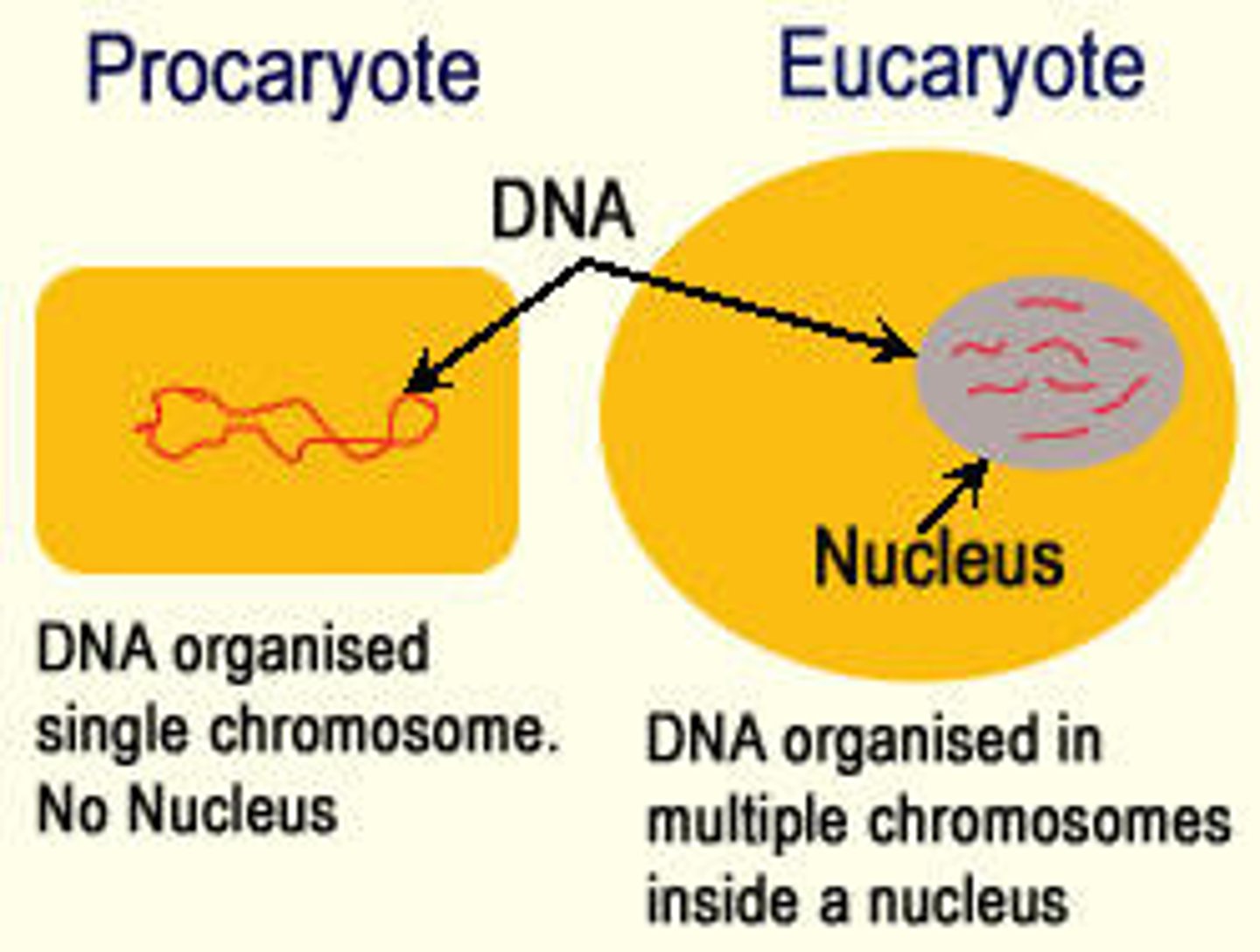
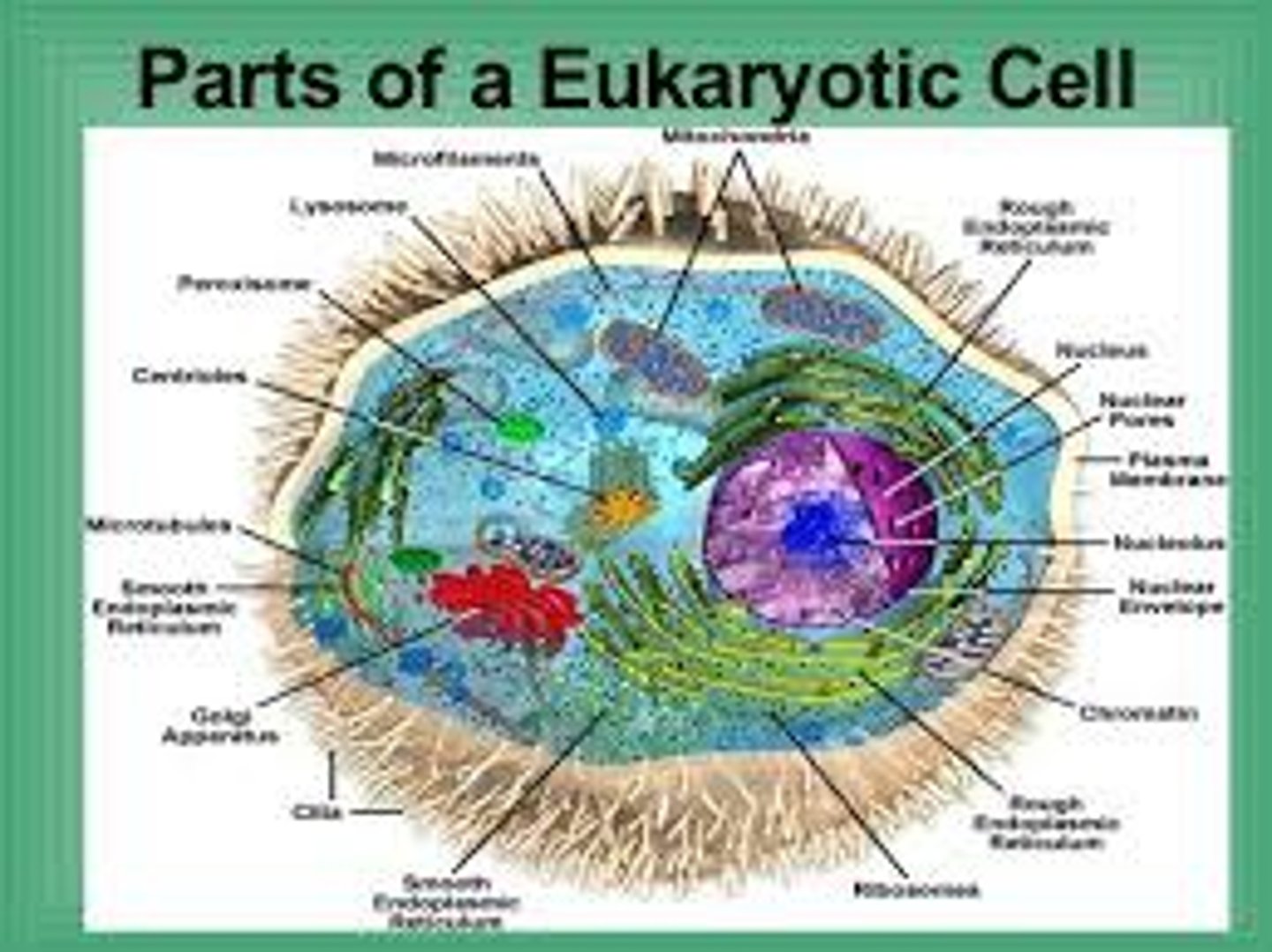
EUkaryote (pronounced you-carry-oat)
Cells with a nucleus and organized membrane-bound organelles EUkaryotes have a TRUE nucleus
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.

Solvent
In a solution, the substance in which the solute dissolves.

Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
