Communication | 9618 CS P1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What are the advantages of using a network?
- Users can share files.
- Users can share peripherals: printers and connections to other networks, e.g. The Internet.
- Users can access their files from any computer on the network.
- Servers can control security, software updates, and backup of data.
- Communication with other people, e.g. email and social networking.
What are the disadvantages of using a network?
- expensive to hire workers to maintain it
- you need to by hardware
- susceptible to malware and hacking
What does LAN stand for and what is it?
Local Area Network.
Connects devices within ONE relatively small geographical location, two to several hundred devices (i.e computers in a single building)
What does WAN stand for and what is it?
Wide Area Network.
A network over multiple geographical sites
What are the two different ways a network can be designed?
- client server model
- Peer to peer
What is meant by a client server model of networked computers?
- at least one computer is used to serve
- other computers are referred to as clients
- the server provides services
Downloading a file from a website is an example of a client server application. What is meant by the term client servr?
- file is made available from the web server
- users browser is the client software
- the client/software browser requests the file from the server
- the desired file is returned to the clients computer
A bank has a client server model of network computers. Describe, using the bank as an example, the key features of a client server model.
- Banks server holds the customer account data and performs the requested task
- the computers used by the customers are the clients
- the clients send requests to the server
- results of the request are returned (from server to client)
How does a client-server model enable the employees to access the same files from different computers?
- the other computers are referred to as clients
- the server hosts the shared file
- an employee can request a file from the server from any one of the client computers
What are the benefits of client server?
- centralized backup
- centralized files and rsources
- less expensive as machines don't have to be powerful
- Saving resources on the server reduces the burden on the client
Describe the key features of a peer to peer network.
- all computers are of equal status
- each computer provides access to resources and data
- computers can communicate and share resources
- each computer is responsible for it's own security
List the benefits of peer to peer network
- no possibility of congestion, when more clients are simultaneously requesting to download a file
- allows user to download different parts of files separately
- the parts are available from more than one host
List the disadvantages of a peer to peer network
- reduced security
- no central management of back up
- if the data from one computer is not backed up, it is lost in all of the other ones
- individual computers may respond slower because they are being accessed by other computers
What is a thin client?
A device or software, which is heavily dependent on having access to a server.
Thin client will not work unless it is connected to the server at all times
What is a thick client?
a computer that can work independently of the network and process and manage its own files.
It is still able to do some processing whether it is connected to a server or not
list the advantages of a thick client
- more robust (device can carry out processing even when not connected to the server)
- reduced server demand
- clients have more control
list the disadvantages of a thick client
- less secure
- data integrity issues
- each client needs to update data and software individually
list the advantages of a thin client
- cost less
- easier to maintain
- last longer
- use less power
- less suseptible to malware (secure)
list the disadvantages of a thin client
- dependent on the server
- more downtime
State the differences between thin clients and thick clients
- thin client relies on server
- thick client can work without server
- thin client relies on faster Internet
- thin client can work on slower network connections
- thin client requires just a few local resources, such as SSD, HDD, ram
- thick client relies heavily on local resources
- Data for thin client is stored on the server
- Data for thick client is stored on the device itself
Define bus topology
Uses a single central cable to which all computers and devices are connected
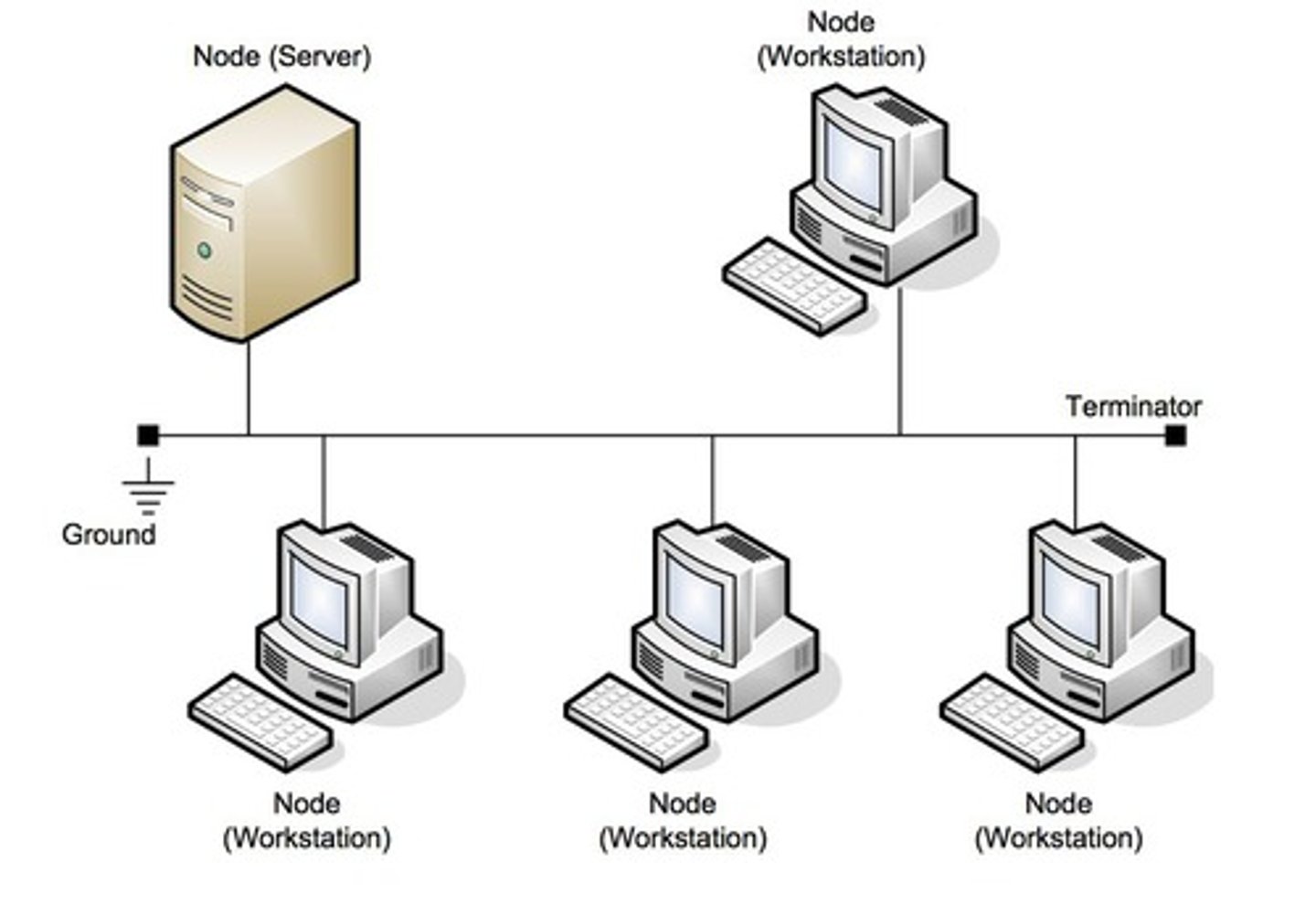
State the advantages of bus topology
- easy to set up and extend
- less cable required
- less expensive
State the disadvantages of bus topology
- if the main cable breaks, network degrades
- difficult to detect and troubleshoot fault at an individual stati
- efficiency reduces as more devices are connected
- less security
- more collisions, and therefore not suitable for heavy traffic
How are packets transmitted between two computers in bus topology?
- packets have the address of the recipient
- sender transmits data through the bus
- bus carries data along the central cable
- as the data arrives at each computer, the system compares the address to see if it matches
Define a star topology.
there is a hub, switch, or router in the center and a collection of clients individually connected to the center device.
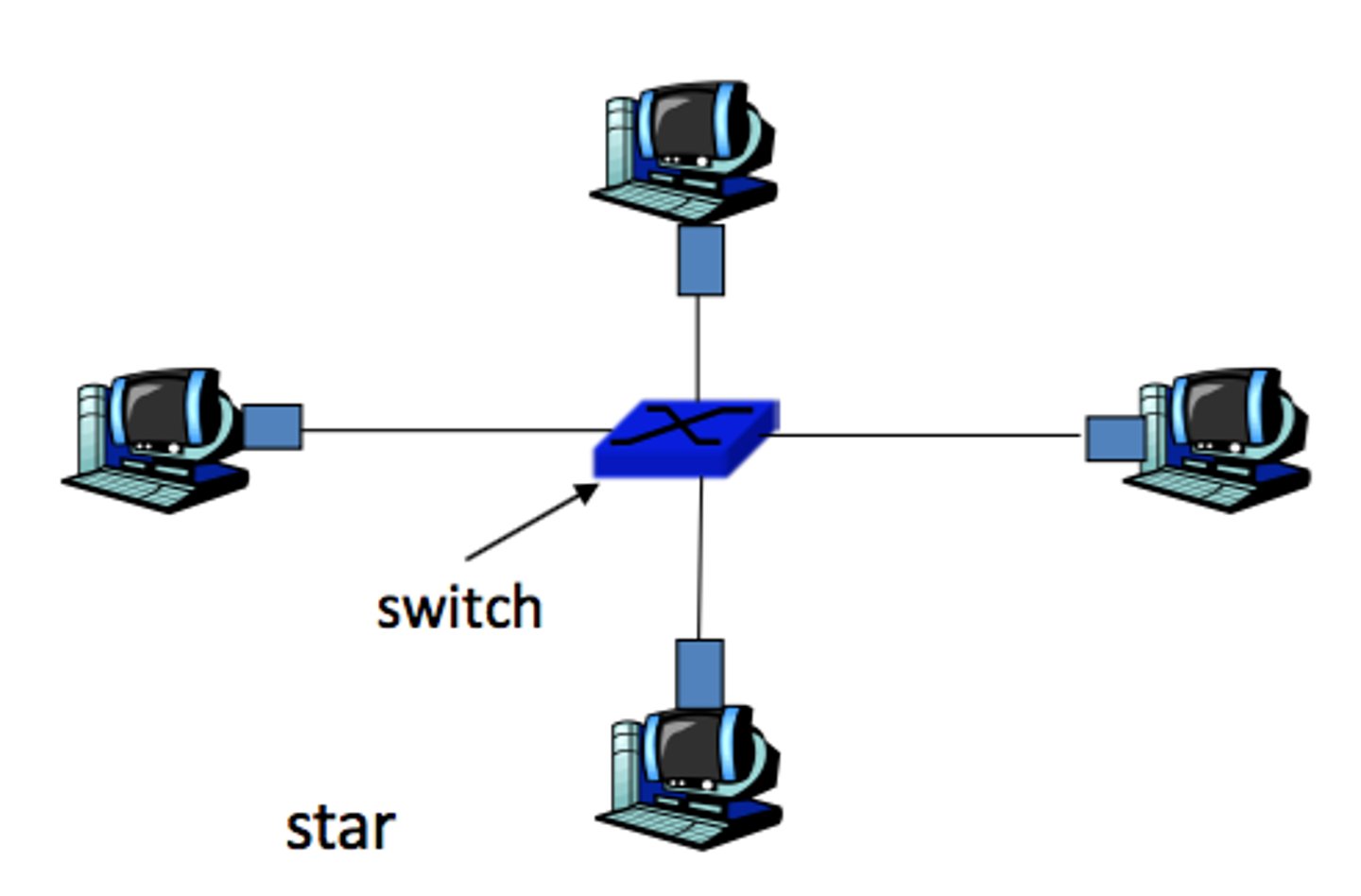
State the advantages of star topology
- signals only go to the destination, therefore it is secure
- easy to connect and remove nodes
- centralized management helps in monitoring the network
- failure of the one node does not affect the rest of the network
State the disadvantages of star topology
- if the central device brakes did the whole network goes down
- performance is dependent on the capacity of the central device
How are packets transmitted between two computers in star topology?
- packets have the address of the recipient
- sender sends data to the central device
- server reads the address and find where the recipient is
- server directly sends the data to the recipient
- server transmits packets only to the recipient
Where is Star Topology used?
Large organizations such as educational establishments, where high performance is needed.
Also found in homes where the router acts as a server.
What are the features of star topology?
- must have a central device
- each node is connected to the central device
- each node has a dedicated connection
- each connection is bi directional
Define a mesh topology.
all the devices are interconnected with each other
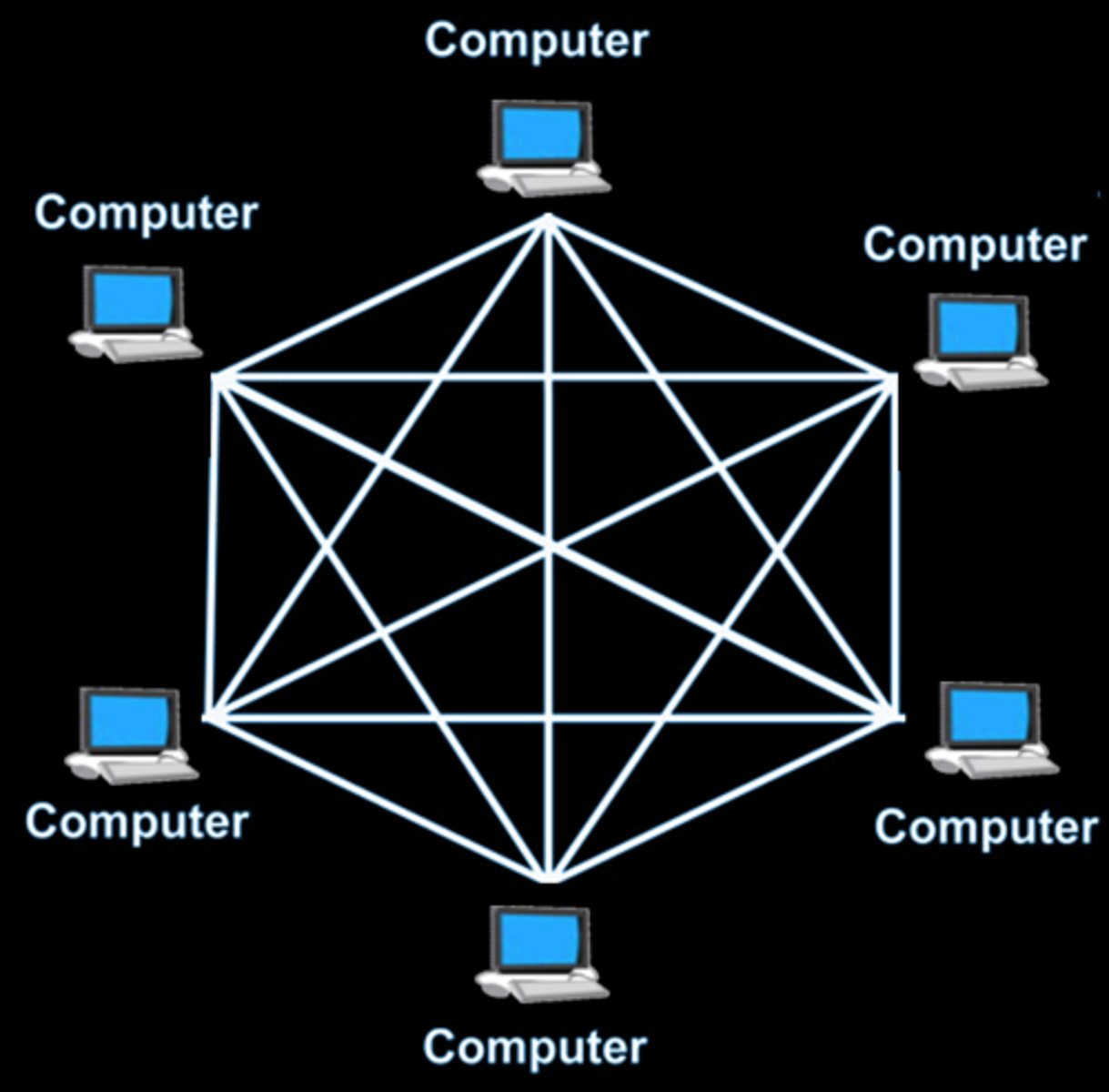
State the advantages of mesh topology
- any broken links in the network do not affect the other nodes
- good privacy and security
State the disadvantages of mesh topology
- a large amount of cabling is needed, which is expensive and time consuming
- set up and maintenance is difficult and complex
How are packets transmitted between two computers in mesh topology?
- packets have the address of the recipient
- sender transmits packets directly to the node as each node is connected to at least one other node
Defined hybrid topology
Combination of two or more technologies
State the advantages of hybrid topology
- highly reliable, because in case of failure there are many sub-networks
- easy to troubleshoot and fix issues
State the disadvantages of hybrid topology
- expensive
- difficult to manage
- complex network
Where is hybrid topology used?
Large organizations with different technologies in each building
Define cloud computing
Refers to data and applications, being stored and run on cloud. Less storage is occupied and less processing is done on the local device.
(cloud is a big building which contains servers)
State the advantages of cloud computing
- files stored on cloud can be accessed at any time from any device anywhere in the world with Internet
- no need to carry external storage devices
- can be free
- inbuilt back up
- can easily increase capacity of your device
- Data can be easily shared
What is private cloud?
a cloud that is owned and operated by an organization for its own benefit.
(provide security)
- used by highly regulated industries and govt. agencies
What are the disadvantages of cloud computing?
- Your information is in the hand of a company
- Sensitive data may be vulnerable to hacking
- Generally, have to pay for cloud space
- can only access the cloud with internet
What is public cloud?
Cloud owned by a cloud service provider (for general use)
What are the benefits of wireless networks compared to a wired network?
- Devices can be more mobile as they do not have to be connected to cable
- easier to set up as no cables need to be installed
- additional devices can easily be added
- Many different types of devices can be connected at the same time
What are the drawbacks of wireless networks compared to a wired network?
- easier to hack
- interference
- Signal degrades quickly
What are the drawbacks of copper cables?
- less bandwidth
- needs repeaters to boost signals
- higher interference
State the hardwares used in LAN
- switch:
A connecting device that can send unicast messages
- network interface card (NIC):
Provides a device with a MAC address to uniquely identify it on the network. It allows each individual device to connect to the network.
- wireless network interface card (WNIC):
Same as NIC, except it uses antennas to communicate with networks via microwaves
- cables:
Fiber-optic or copper cables
- bridge:
Has the MAC address of each device. If device1 wants to send data to device2, then data will first go to the bridge and then the bridge identifies if the data should stay on the left or right side.
- WAP, wireless access point:
Allows devices to connect to the LAN instead of using a cable. It makes it easy to move a device to a different location while still being connected to the Internet
- repeater:
Device used to boost signals
What is a wireless network interface card and what does it do?
Provides a device with a MAC address to uniquely identify it on the network. It allows each individual device to connect to the network wirelessly instead of through a cable.
What is a wireless access point (WAP)?
A switch that allows devices to connect wirelessly to the LAN
What is a router?
- Connect two or more networks
- can connect a network to WAN
- receives packets and forwards them toward the destination using the IP address of the destination
- assigns a private IP address
- Connects similar networks
How are videos sent using bit streaming?
- Data is compressed before transmitting
- video is transmitted continuously as a series of bits
- the video is hosted on a media server
- upon download, the server sends data to the buffer on the clients computer
- the buffer stores the data from the server
- the user's streaming software receives the bit stream from the buffer
Define on-demand bit streaming.
- Digital video tapes are converted to bit streaming format for broadcasting on the net (encoding)
- these encoded streaming videos are then uploaded to a dedicated server
- a link for the encoded video is placed on a website
- a user clicks on the link to download the encoded streaming video
- Streamed video is broadcasted to the user
Define real time bit-streaming
- event is captured live with a video camera
- the video camera is connected to a computer
- the video signal is converted to streaming media files encoded on the computer
- the encoded feed is then uploaded from the computer to a dedicated streaming service via cable or high-speed Internet connection
- server sends the live images to all users
- cannot be paused
State the differences between the world wide web and the Internet
INTERNET:
- massive network
- Internet stands for interconnected networks
- uses TCP/IP protocol
WORLD WIDE WEB:
- Collection of multimedia, webpages, and documents
- Stored on a website
- hTTp:// protocols are used to transmit data
- uRLs specify the location of webpages
What are the benefits of bit streaming?
- no need to wait for a whole file to be downloaded
- no need to store large files on a device
- allows on-demand playback
- no special software is required for playback in browser
What are the drawbacks of bit streaming?
- video hangs if you have slow Internet
- may require specific software
- viruses could be downloaded
What is CSMA/CD?
carrier sense multiple access with collision detection.
It is the method for multiple hosts to communicate on a Ethernet.
How does CSMA/CD work?
- before transferring the data, a device checks if the channel is busy
- if the channel is free, the data is sent
- when transmission begins, it listens to the other device
- if there is a collision transmission is stopped
- both devices wait a different random time then try again
detects collisions by change in voltage
What are the functions of a CSMA/CD?
- Monitor traffic
- only allows data to be sent when the line is available
- detects collisions on the network
- calculates random wait time
What is a modem?
Device that connects router to the Internet.
Connect a device to the Internet over a telephone line
Describe the transmission of data using the public switched telephone network (PSTN)
- PSTN consists of many different types of communication lines
- Data is transmitted in both directions at the same time
- the communication passes through different switching centers
What are the benefits and drawbacks of dedicated lines?
BENEFITS:
- faster transmission of data
- improved security
- more consistent transmission speed
DRAWBACKS:
- expensive to set up and maintain
- disruption to the dedicated line would leave no alternative
What is the purpose of an IP address?
- used to locate a device on a network
- each address is unique within the network
- allows a device to send data to the correct destinations
What is a public IP address?
- public IP addresses are registered on the Internet
- it gives access to the Internet
- unique
- assigned by ISP
What is a private IP address?
- not publicly registered on the Internet
- cannot access the Internet just by private IP
- assigned by router
Explain the difference between public and private IP
- public address can be reached across the Internet
- private address can only be reached internally
- NAT (network address translation) is necessary for a private IP to access the Internet
- public IP does not need NAT
- private addresses are more secure
- public IP addresses are provided by ISP, whereas private IP addresses are assigned by a router
- public addresses are unique
- private addresses are unique within their network, but can be duplicated within other networks
What is a static IP address
A permanent IP address. When a computer disconnects and rejoins a network, the address does not change.
- Address is assigned by ISP
What is a dynamic IP address
Every time the computer re-join the network, the address changes.
- Address is assigned by the network OS
What is the purpose of subnetting?
- split a large network into a grouping of smaller networks
- helps minimize traffic
- improvies speed and network performance
- a subnet mask ensures that traffic remains within its designated subnet
What is the format of an IPv4?
- each IP address should contain 4 numbers
- should be in range 0-255
- seperated by full stops
- the address should not be more than 32 bits
- 4 groups
i.e 192.168.0.1
What is the format of an IPv6?
- valid hexadecimal number
- only one double colon is allowed
- 8 groups
- seperated by colons
i.e
2001 : 0800 : 0000 : 0000: 0000 : 0000 : 0000 : 0000
Explain why there is a need for IPv6
The number of IP addresses needed will exceed the number available if we only use IPv4
What is a DNS (domain name service) server?
- resolves domain names to numbers
- looks for the IP address of a particular domain name
(domain name is the identifier of a website i.e youtube.com)
How is a URL converted to a matching IP?
- url is parsed to obtain the domain name
- domain name is sent to the nearest DNS server
- DNS holds a list of domain names and matching IPs
- Domain name resolver searches its database for the domain name
- If DNS does not find the domain name, the request is forwarded to higher level DNS
- If domain name is found, the IP address is returned
- If not found, error message appears