4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Last updated 4:43 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Information Systems in organization
Economic theories, Behavioral theories
2
New cards
Economic theories
Transaction cost theory ,Agency Cost theory
3
New cards
Transaction cost theory
By implementing Information Systems the transactions cost function will move more towards the inside which will subsequently lead to cheaper transaction costs.
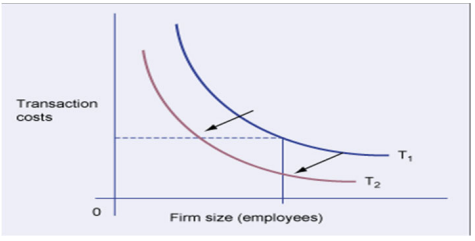
4
New cards
Agency Cost theory
By implementing the use of Information Systems the Agency cost function will move more towards the outside which will lead to cheaper agency costs.
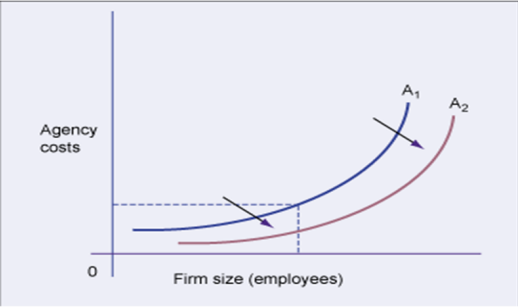
5
New cards
Behavioral theories
IT flattens Organizations, Postindustrial Organizations, Virtual firms
6
New cards
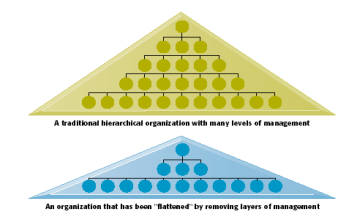
IT flattens Organizations
Structure can be flattened and react faster due to it systems
7
New cards
Virtual firms
• Those firms don’t possess a physical place
• Uses networks to link people, assets and ideas
• Uses networks to link people, assets and ideas
8
New cards
Definition of IT Infrastructure
A set of physical devices and software applications which are service provided by the hardware and software.
9
New cards
Moores law
Every 18 to 24 Months the microprocessing power of IT-devices are doubled
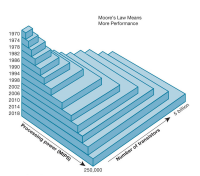
10
New cards
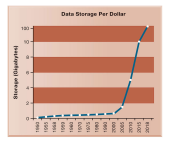
The law of mass digital storage
Throughout the evolution of electronic devices and the eagerness to be more efficient the Amount of storage accessible rose steadily till the 2000 and the increased really fast in the past 20 years to now 100 Gigabyte per dollar.
11
New cards
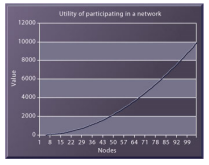
Metcalfe law
The Utility in participating in a network grows exponentially to the amount of nodes connected, The more people join the internet than the more participant grows exponentially
12
New cards
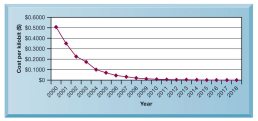
Declining community costs
Because of more efficient devices the cost of Internet speed is decreasing exponentially.
13
New cards
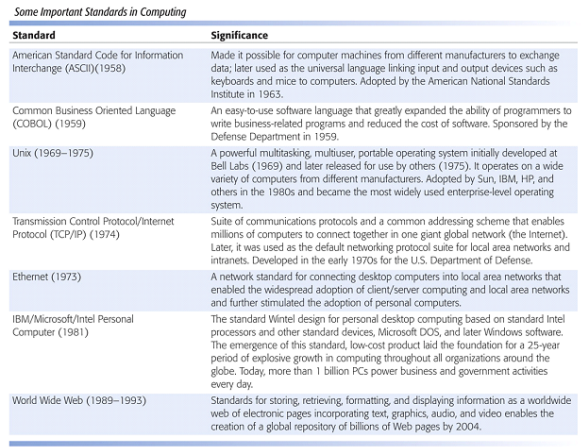
Standards
Standards enabled the world to work simultaneously without fearing to mis communicate between each other.
14
New cards
Electronic Commerce
E-Commerce, E-Business
15
New cards
E-Commerce
Describes the process of buying, selling or exchanging products, services or information via electronic devices such as computers, cellphones or via internet.=Showed that is event stable in recessions
16
New cards
E-Business
Is the same as E-commerce but it includes also the relationships with potential customers, partners, business and processing electronic transactions
17
New cards
Unique features of the Internet-U
Ubiquity
18
New cards
Ubiquity
· Technology is available everywhere (work, home…)
· Effect: Marketplaces removed temporary or geographic locations to become market spaces.
· Strengthen customer convenience & lowering operational costs
· Effect: Marketplaces removed temporary or geographic locations to become market spaces.
· Strengthen customer convenience & lowering operational costs
19
New cards
Unique features of the Internet-G
Global reach & Universal standards
20
New cards
Global reach & Universal standards
· Technology standards is now not limited to geographical boundaries.
· Because of this decision billions of people have now access to businesses worldwide
· Loosens cross-cultural boundaries
· Lower market entry cost because of standardization
· Because of this decision billions of people have now access to businesses worldwide
· Loosens cross-cultural boundaries
· Lower market entry cost because of standardization
21
New cards
Interactivity
· Companies have to interact with the user to actively achieve his attention
· Effect: Costumers can have individual and tailored discussions with the service providers.
· Consumer now have the opportunity to become part of the decision. making process.
· Effect: Costumers can have individual and tailored discussions with the service providers.
· Consumer now have the opportunity to become part of the decision. making process.
22
New cards
Information density
· Quality of the information available on the market
· Effect: Greater price transparency, cost transparency and hinders engagement in price discrimination.
· Effect: Greater price transparency, cost transparency and hinders engagement in price discrimination.
23
New cards
Personalization
· Firms allows consumers to modify or change the service or product (messages, goods..)
· Effect: personalized message can be sent to consumers
· Product and services can be customized for various presences
· Effect: personalized message can be sent to consumers
· Product and services can be customized for various presences
24
New cards
Social technology
· It provides a platform for people to share their content and to interact with them.
· Effect: new business-models can emerges through those new platforms.
· Effect: new business-models can emerges through those new platforms.
25
New cards
Forms of Electronic Commerce
Business to customer (B2C), Business to business (B2B), Consumer to consumer (C2C), Government to citizen (G2C), Mobile commerce
26
New cards
Business model
Content provides ,Service provides, Community provider, Portal
27
New cards
Web 2.0
Crowdsourcing and Social networking, Characteristics of things which survived after the Dotcom bubble burst.
28
New cards
E-Commerce marketing
§ Provides new ways to identify and communicate with costumers
§ Long-tail marketing
§ Behavioral targeting
§ Internet advertising formats
§ Long-tail marketing
§ Behavioral targeting
§ Internet advertising formats
29
New cards
§ Long-tail marketing
Big Head, Long Tail
30
New cards
Big Head
Blockbuster strategy Pareto optimum (80/20) Rule
31
New cards
Long Tail
Through internet Companies can offer unpopular products without facing the same economical loss as retail shop
32
New cards
EDI(Electronic Data Interchange)
The transmission of electronic business forms between business partners
33
New cards
M-Commerce
based on the GPS location of the cell-phone, it is used by banks and credit card companies to provide for example an managing app for their customers
34
New cards
Networks and communications Trends
Convergence, Broadband, Broadband wireless
35
New cards
Protocol
defines the format and order in how messages are exchanged between two or more parties.
36
New cards
**business process reengineering(BPR)**
A comprehensive assessment and redesign of business processes
37
New cards
Wireless Standard for Web Access
Bluetooth, Wifi, LTE, WiMax(cover one metropolitan area)
38
New cards
Mobile Wireless Standards for Web Access
4G(long range) and Wifi(short range)
39
New cards
5 Wireless Applications
CRM, SCM, RFID, EMR, WSNs
40
New cards
Enterprise Applications
designed to integrate computer systems that run all phases of an enterprise's operations to facilitate cooperation and coordination of work across the enterprise.
41
New cards
Enterprise Applications cons
Highly expensive to purchase and implement enterprise applications. Need to adopt to Business process changes. Need data standardization, management, cleansing
42
New cards
Next Generation Enterprise Application Pros
o SOA standards
o On-demand solutions
o Cloud-based version
o Social CRM
o Business Intelligence
o On-demand solutions
o Cloud-based version
o Social CRM
o Business Intelligence
43
New cards
Knowledge managements
efficient handling of information and resources within a commercial(통상의) organization.
(Emphasizing on learning)
(Emphasizing on learning)
44
New cards
Theories in Management
Rationalism, Experimentalism
45
New cards
Rationalism
= Scientification (I think therefore it exists)
46
New cards
Experimentalism
=Humanization(Knowledge is experience, We only the truth by experiencing it)
47
New cards
Two dimension of knowledge
Tacit knowledge, Explicit knowledge
48
New cards
Tacit knowledge
Hard to explain to others
49
New cards
Explicit knowledge
Easy to transmit in language and communication
50
New cards
SECI —> Model
Socialization, Externalization, Combination, Internalization
51
New cards
Socialization
Observation is the key in socialization
52
New cards
o Externalization
\-Convert tacit into explicit
\-Quintessential knowledge creating activity
\-Quintessential knowledge creating activity
53
New cards
o Combination
\-Create explicit knowledge from explicit knowledge
\-Exchange and combine
\-Formal education and training
\-Exchange and combine
\-Formal education and training
54
New cards
o Internalization
\-From explicit knowledge to tacit knowledge
\-Learning by doing
\-Documentation
\-Learning by doing
\-Documentation
55
New cards
Enabling condition for Knowledge creation-I
Intention
56
New cards
Intention
· Organization aspiration to meat its goals
· Most important criteria for judging the truthfulness
· Most important criteria for judging the truthfulness
57
New cards
Enabling condition for Knowledge creation-A
Autonomy
58
New cards
Autonomy
· Increase the unexpected opportunities and motivations
· Perform many functions like rugby approach
· Perform many functions like rugby approach
59
New cards
Enabling condition for Knowledge creation-C
Creative Chaos
60
New cards
Creative Chaos
· Stimulate interaction
· Promote greater reflections, increase tension and focused attention
· Promote greater reflections, increase tension and focused attention
61
New cards
Enabling condition for Knowledge creation-Red
Redundancy
62
New cards
Redundancy
· Overlapping approach
· Provide different points of view
· Lead to tacit knowledge and speed knowledge creation
· Provide different points of view
· Lead to tacit knowledge and speed knowledge creation
63
New cards
Enabling condition for Knowledge creation-Req
Requisite Variety
64
New cards
Requisite Variety
· Internal diversity
· Work together
· Flat and flexible structure
· Work together
· Flat and flexible structure
65
New cards
I Shape skill
Someone who has a deep knowledge on a specific domain or area.
66
New cards
T shape Skills
Someone who has a variety of knowledge on a specific domain or area
67
New cards
A shape skills
Someone who has has deep knowledge on various domains and areas and can integrate them together.
68
New cards
Knowledge Spiral
Can transfer one knowledge type through various steps into another knowledge type
69
New cards
KM Strategy
Codification strategy, Personalization strategy
70
New cards
Codification strategy
\-Codifying and storing organizational knowledge
\-Sets of rules about what to do.
\-Sets of rules about what to do.
71
New cards
Personalization strategy
\-Provide creative solution through interpersonal interaction
\-Experiences and skilled people
\-Experiences and skilled people
72
New cards
Comparison strategy-People to document
Knowledge management, Information Technology, Human Resources
73
New cards
Knowledge management
· Develop and electronic document system that codifies, stores etc. and allows reuse of knowledge
74
New cards
Information Technology
· Invest heavily in IT, the goal is to connect people with reusable codified knowledge.
75
New cards
Human Resources
· Hire new people.
· Train people in groups and through computer based distance learning.
· Train people in groups and through computer based distance learning.
76
New cards
Comparison strategy-Person to Person
Knowledge management, Information Technology, Human Resources
77
New cards
Decision making and IS
Structured, Semistructured, Unstructured
78
New cards
Structured
Operational Management
79
New cards
Semistructured
Middle Management
80
New cards
Unstructured
Senior Management
81
New cards
The courts stages of the decision making process
Intelligence→Design→Choice→Implementation
82
New cards
Intelligence
Discovering, indentifying and understanding the problems occurring in the organization
83
New cards
Design
Identifying and exploring solutions to the problem.
84
New cards
Choice
Choosing among solution alternatives
85
New cards
Implementation
Makes chosen alternatives work.
86
New cards
Three reason why information technology don’t always produce positive results
o Information quality
o Management filters
o Organizational inertia and politics
o Management filters
o Organizational inertia and politics
87
New cards
· BI in the enterprise
o Business intelligence
o Business analytics
o Business intelligence vendors
o Business analytics
o Business intelligence vendors
88
New cards
Six Elements in BI environment
o Data from the business environment
o BI Infrastructure
o BI analytics toolset
o Managerial users and methods
o Delivery platform —> MIS, DSS, ESS
o User interface
o BI Infrastructure
o BI analytics toolset
o Managerial users and methods
o Delivery platform —> MIS, DSS, ESS
o User interface
89
New cards
· BIG DATA
o No consensus of the definition.
o We rather concentrate on describing the characteristics of Big data
o Three Characteristics V3
o We rather concentrate on describing the characteristics of Big data
o Three Characteristics V3
90
New cards
o Three Characteristics V3
§ Volume (Scale)
§ Variety (Complexity)
· Various formats, types and structure
· Static data vs streaming data
§ Velocity (Speed)
· Data is begin generated and bleed to be processed fast
· Late decision —> missing opportunities
§ Variety (Complexity)
· Various formats, types and structure
· Static data vs streaming data
§ Velocity (Speed)
· Data is begin generated and bleed to be processed fast
· Late decision —> missing opportunities
91
New cards
· Importance of Big Data
o Pre big data Companies relied on the insight and competencies of the CEO or präsident
o Now post big data everybody has the chance to obtain insight and the information without great effort or expertise.
o Now post big data everybody has the chance to obtain insight and the information without great effort or expertise.
92
New cards
Systems development
Activities that go into producing information systems solution
93
New cards
Systems Analysis
Analysis of problems that organization aims to resolve using information systems
94
New cards
Feasibility study
Determining achievability of solution
95
New cards
Establishing information requirements
Stating information needs that new system must satisfy/Identifying who, when, where and how components of information
96
New cards
System Design
Describes system specifications that will deliver functions identified during systems analysis
97
New cards
Programming
Process of translating system specifications into program code
98
New cards
Testing
Checks whether the system produces desired results under known conditions/Unit testing, system testing, acceptance testing, test plan
99
New cards
Conversion
Process of changing from old system to new system
100
New cards
Production and maintenance
Production is stage after new system is installed and the conversion is complete