A&P II - Quiz 7
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
The extra air you can inhale after a normal breath.
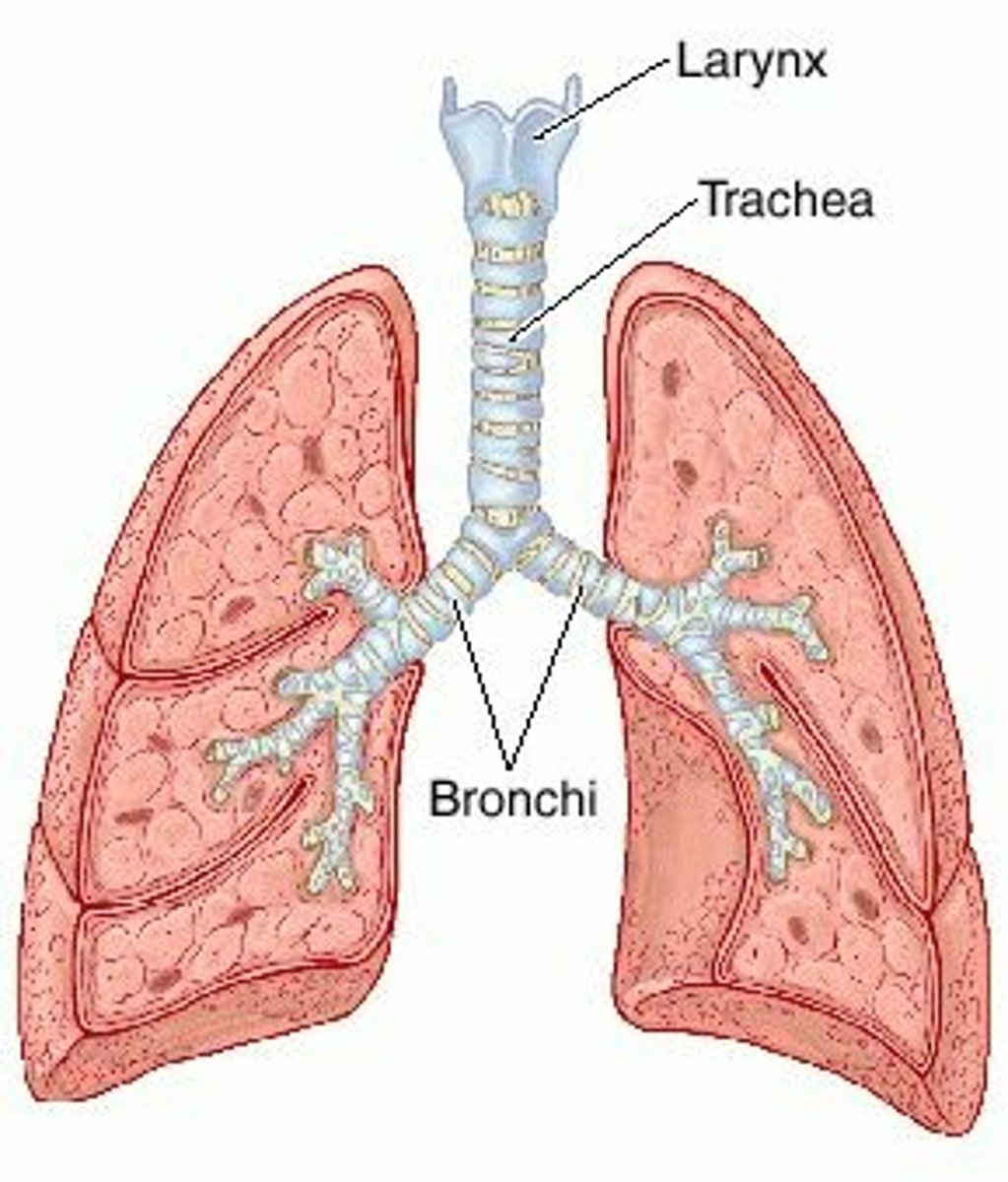
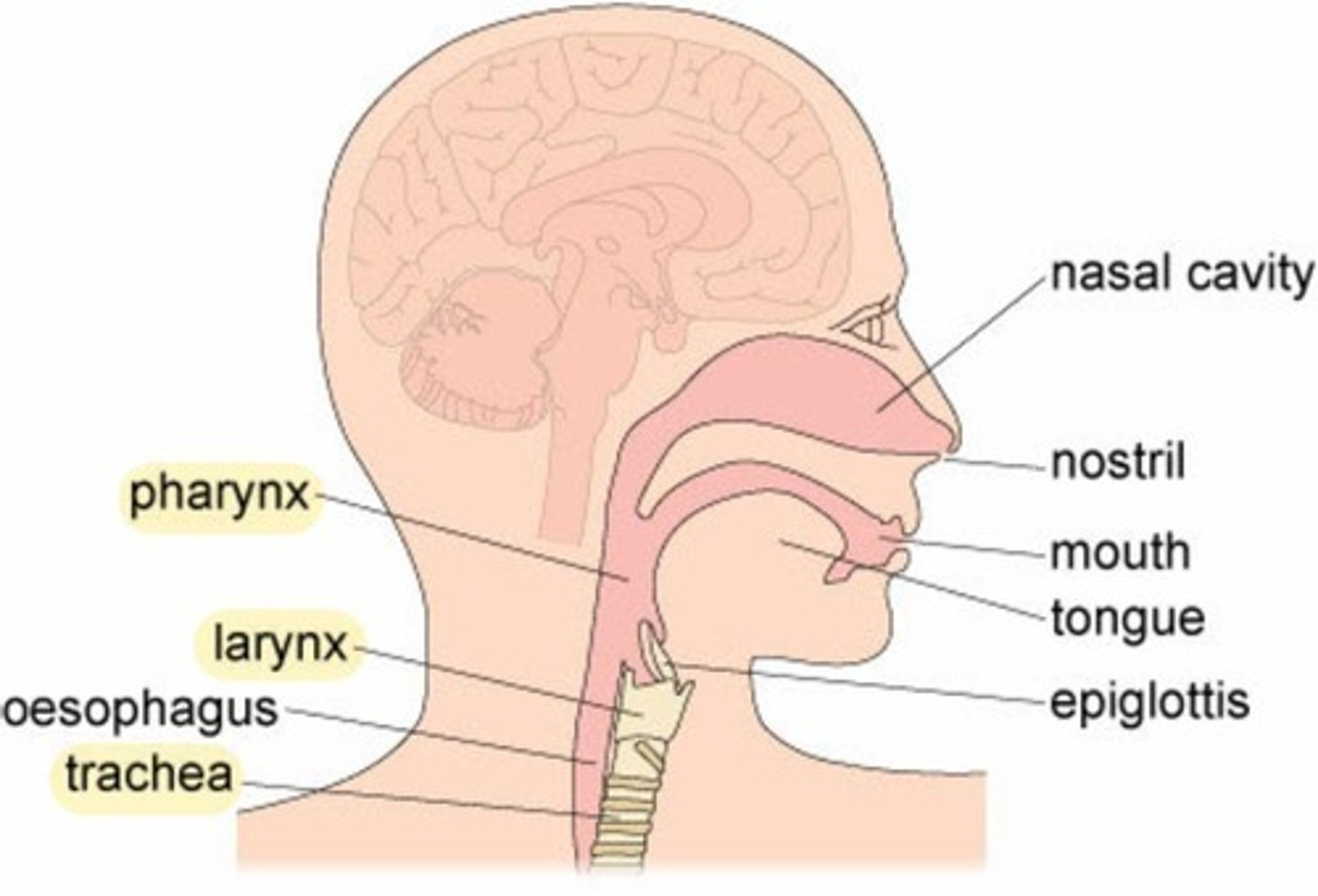
Larynx
The 'voice box'; in the throat, between the pharynx and trachea.
Trachea
The 'windpipe'; a rigid tube in front of the esophagus that carries air to the lungs.
Tidal Volume (TV)
The normal amount of air you breathe in or out during a quiet breath (~500 mL).
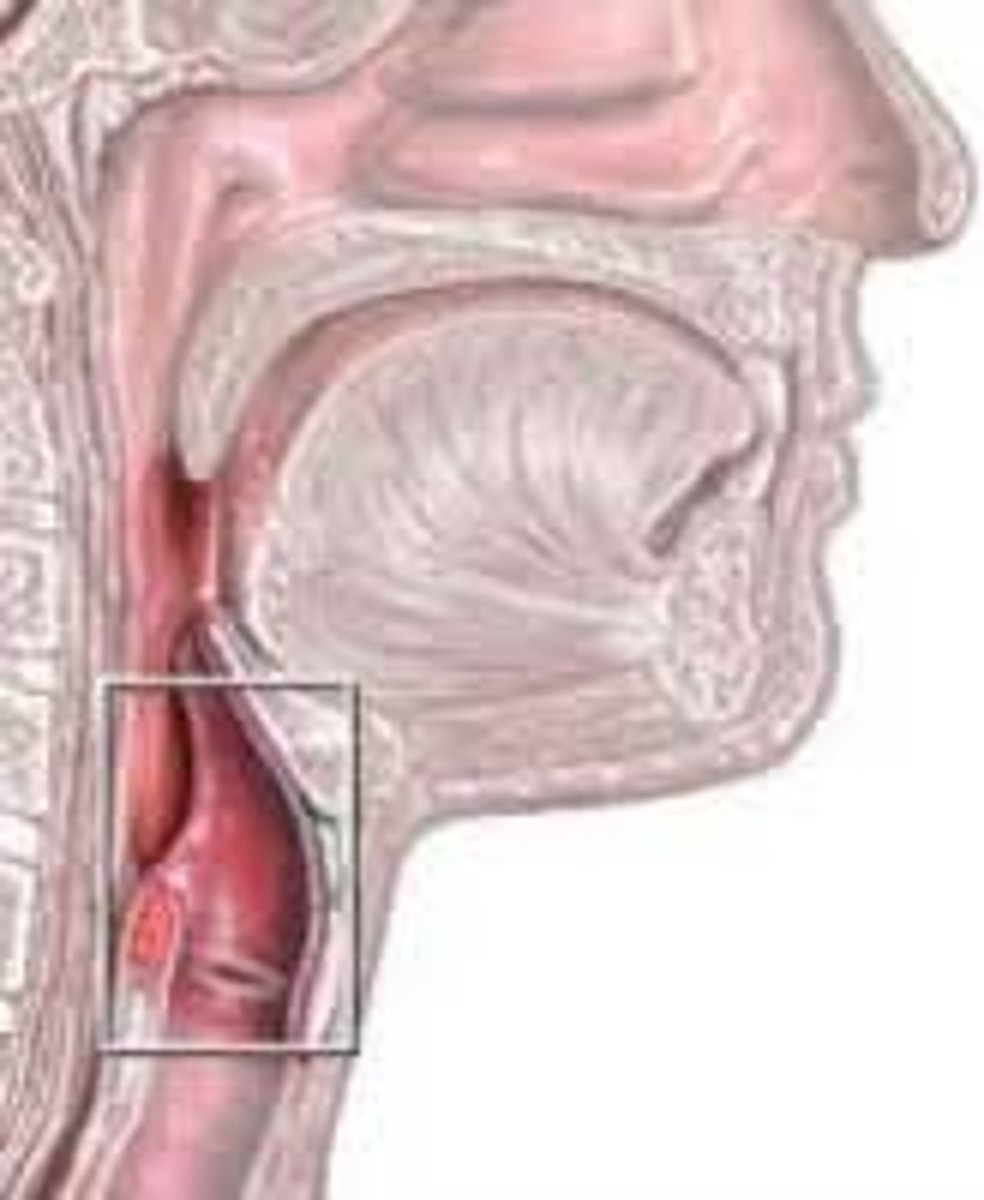
Pharynx
The throat; connects the nose/mouth to the larynx and esophagus.
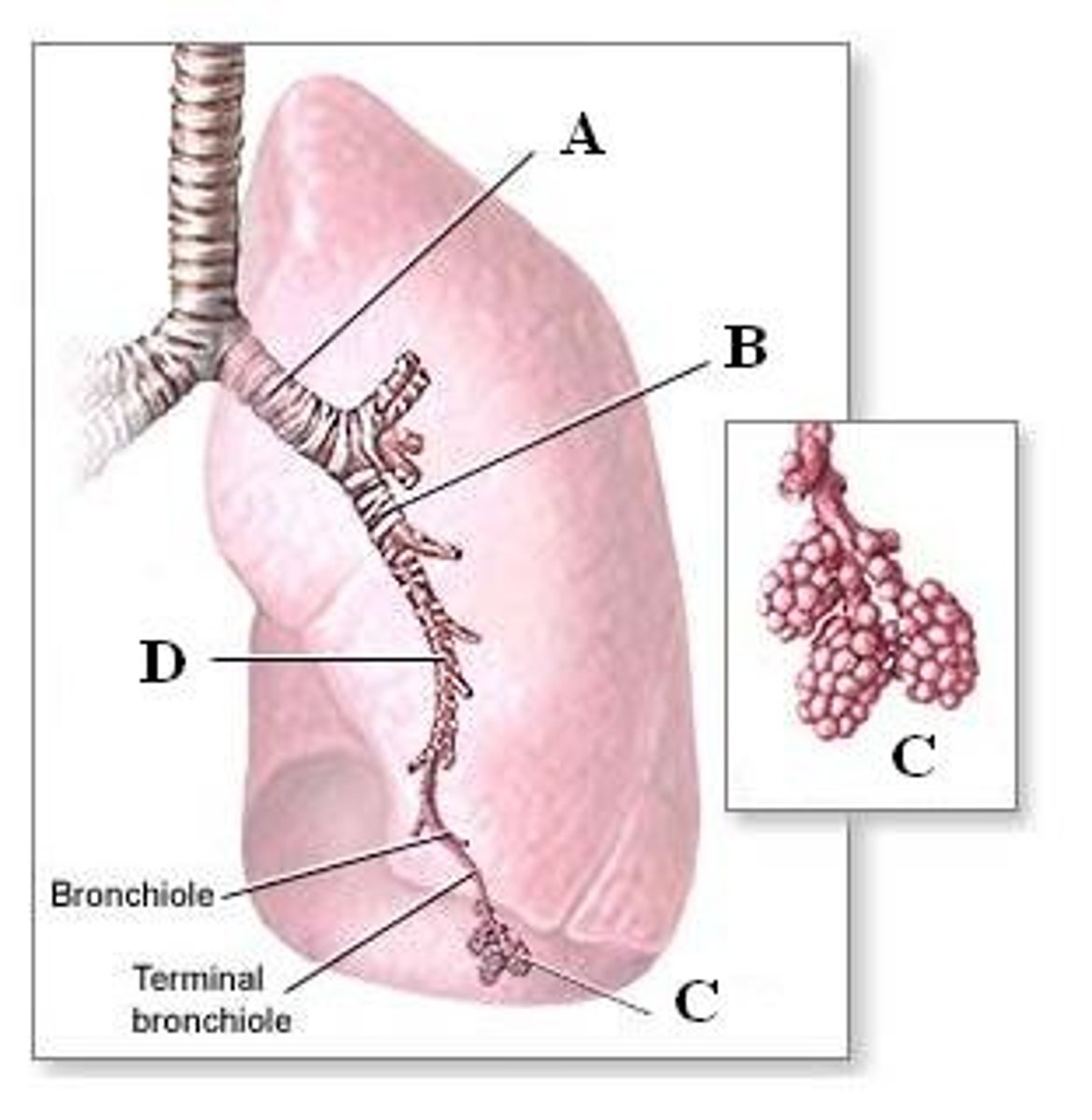
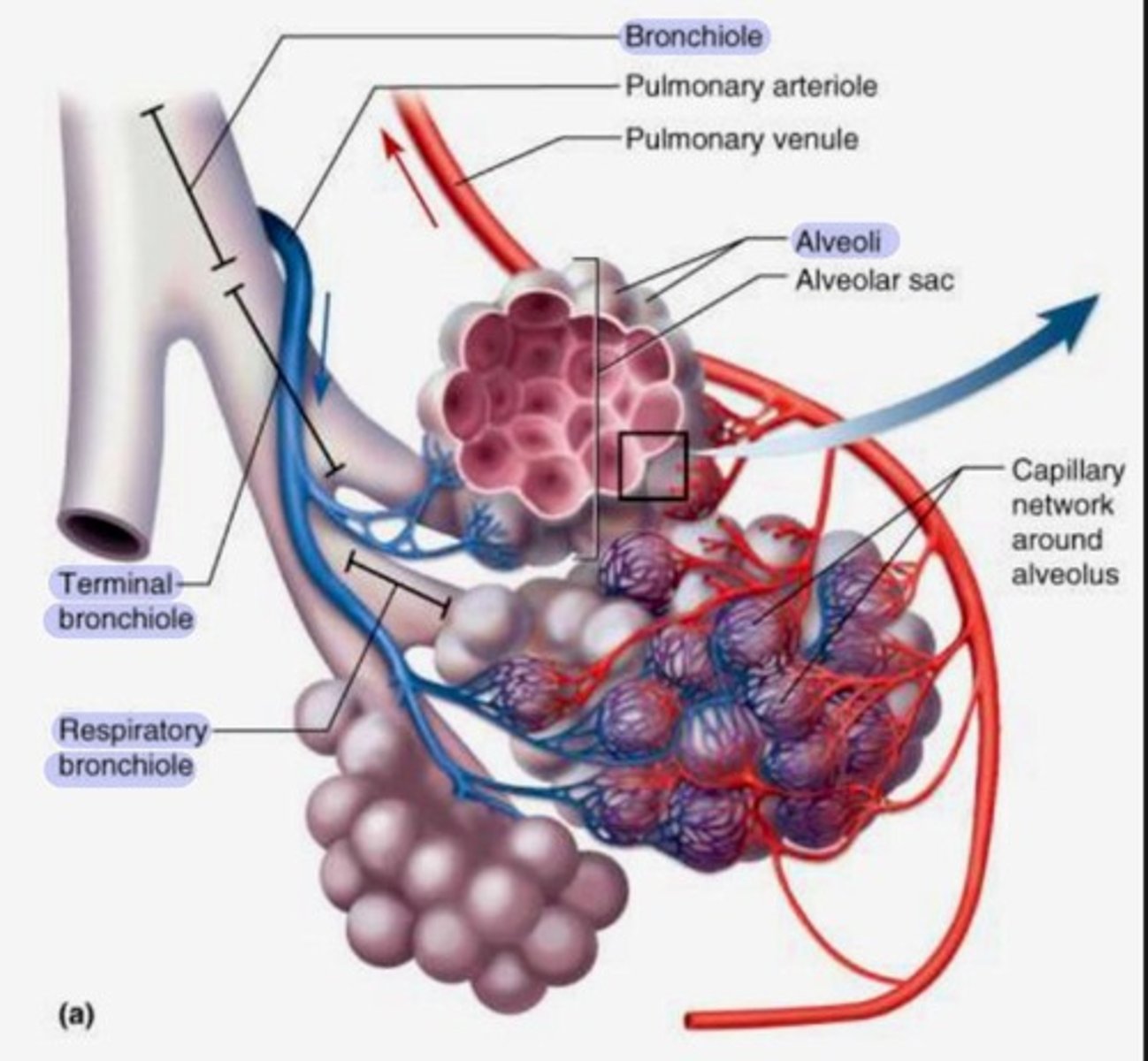
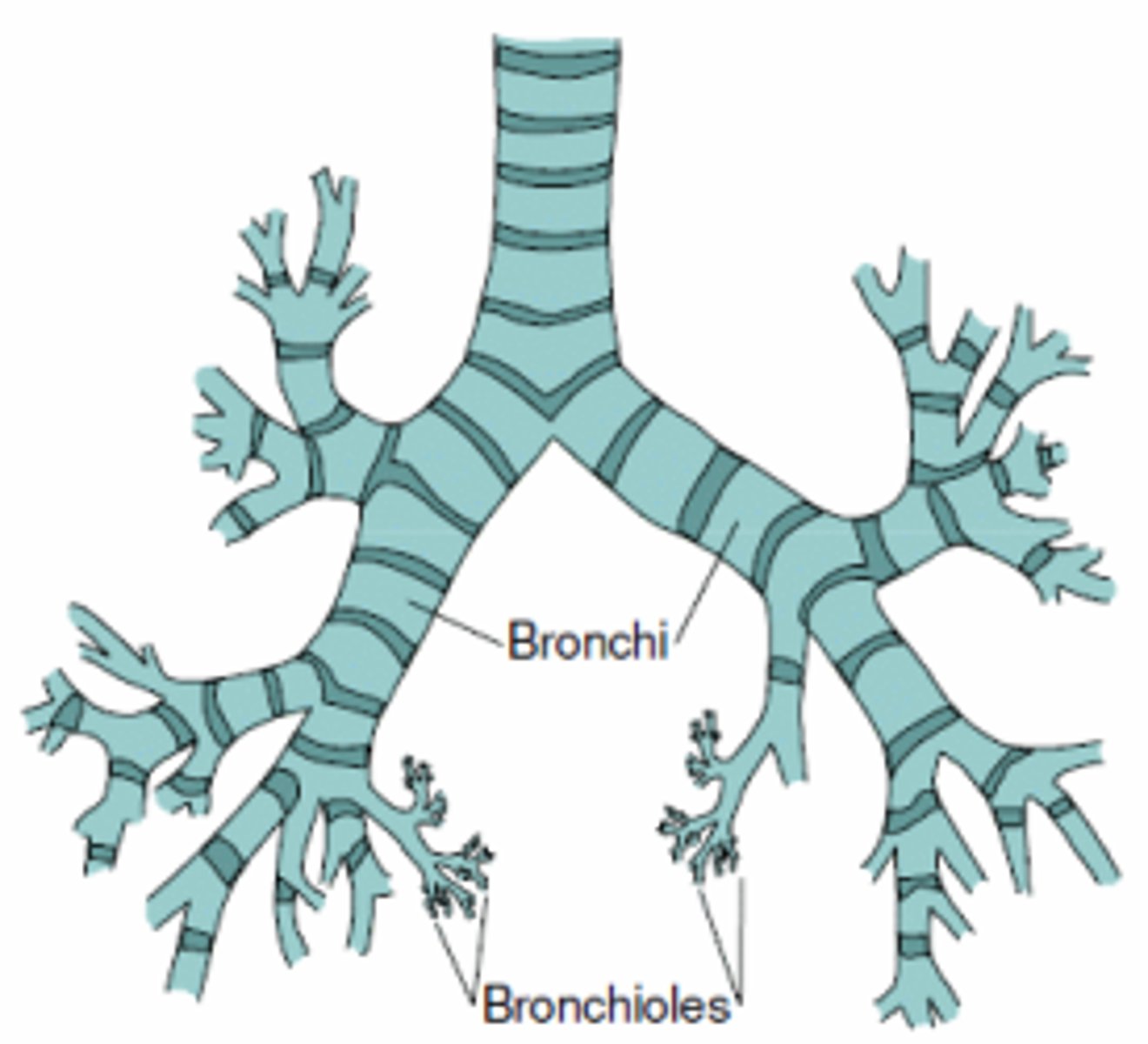
Bronchioles
Small airways in the lungs that come after bronchi and lead to alveolar ducts.
Vital Capacity (VC)
The total amount of air you can breathe in and out (TV + IRV + ERV).
Nasal cavity function
Warms, moistens, filters air, and detects smell.
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs at the end of bronchioles where gas exchange happens.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
The extra air you can breathe out after a normal breath.
Bronchi
Large airways that branch from the trachea into each lung.
Dyspnea
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
Residual Volume (RV)
The air left in the lungs after you exhale as much as you can.
Alveolar ducts
Small ducts that connect bronchioles to alveolar sacs.
Eupnea
Normal, quiet breathing.
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
The total amount of air the lungs can hold (TV + IRV + ERV + RV).
Glottis
The opening between the vocal cords in the larynx.
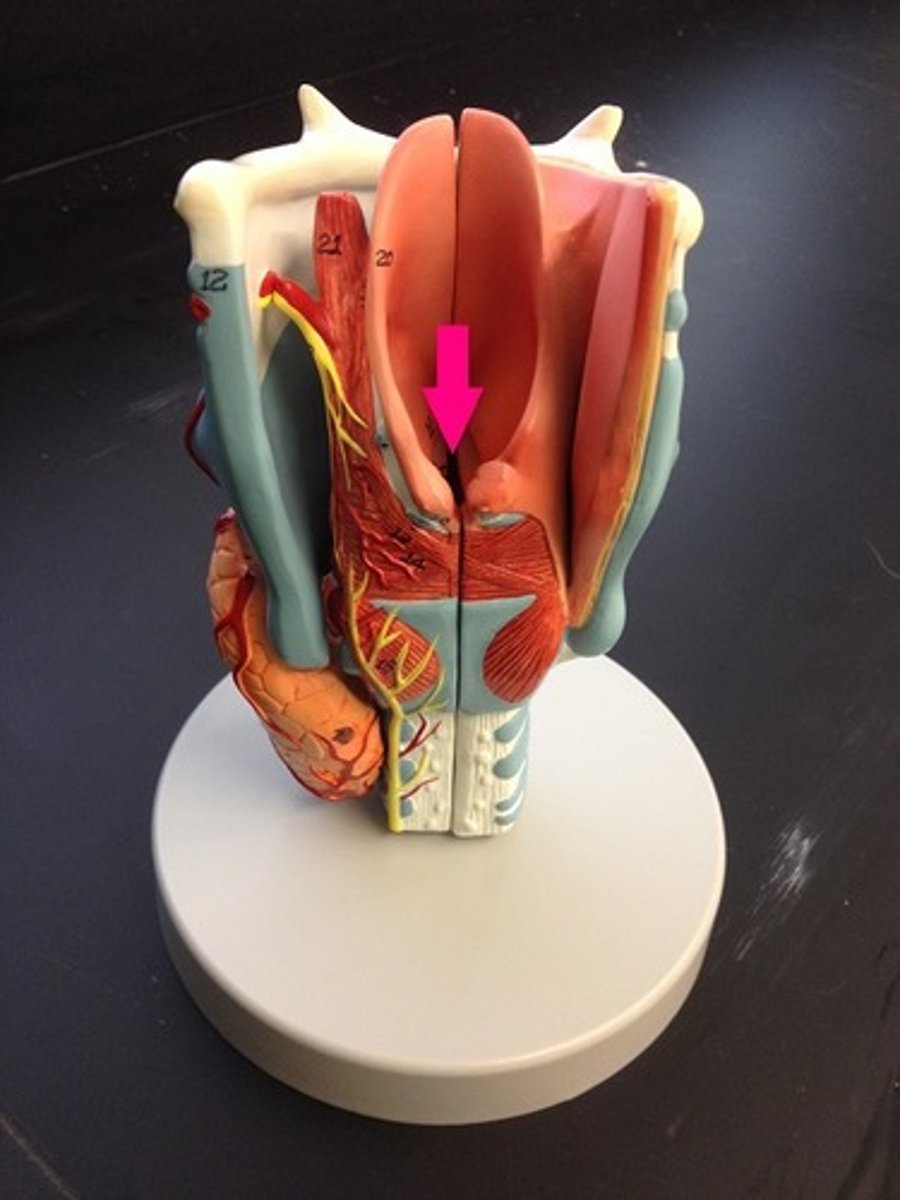
Epiglottis
A flap above the larynx that blocks food from entering the airway during swallowing.
Effects of hyperventilation
Too much CO₂ is lost → blood pH goes up (alkalosis) → may feel dizzy or lightheaded.
Effects of hypoventilation
CO₂ builds up → blood becomes acidic (acidosis) → slow or shallow breathing.
Spirometer
instrument used to measure breathing
Bronchioles
Small tubes branching from bronchi.
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs where gas exchange happens.