04.2G BIO Cell Boundaries (PART G)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

14 Terms
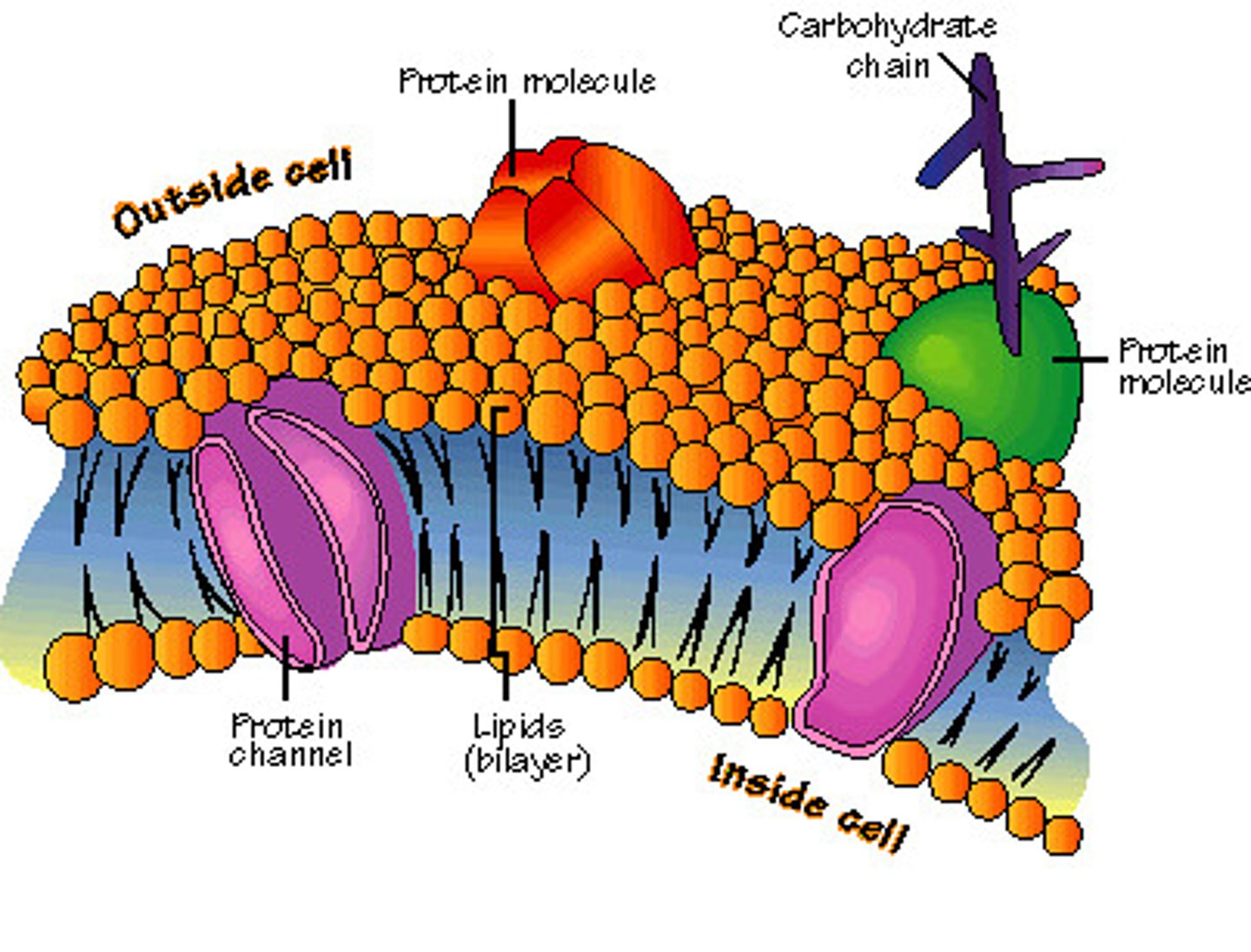
Cell Membrane (Structure)
Very thin two layered boundary that is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, proteins and cholesterol
Cell Membrane (Function)
Selectively permeable structure that:
- Controls what comes into and out of cells
- Relays messages between cells
- Provides shape and support for cell
Phospholipid (Structure)
Composed of a polar phosphate group, a glycerol and 2 nonpolar fatty acid tails; polar heads face towards water and non-polar fatty acid tails face inward
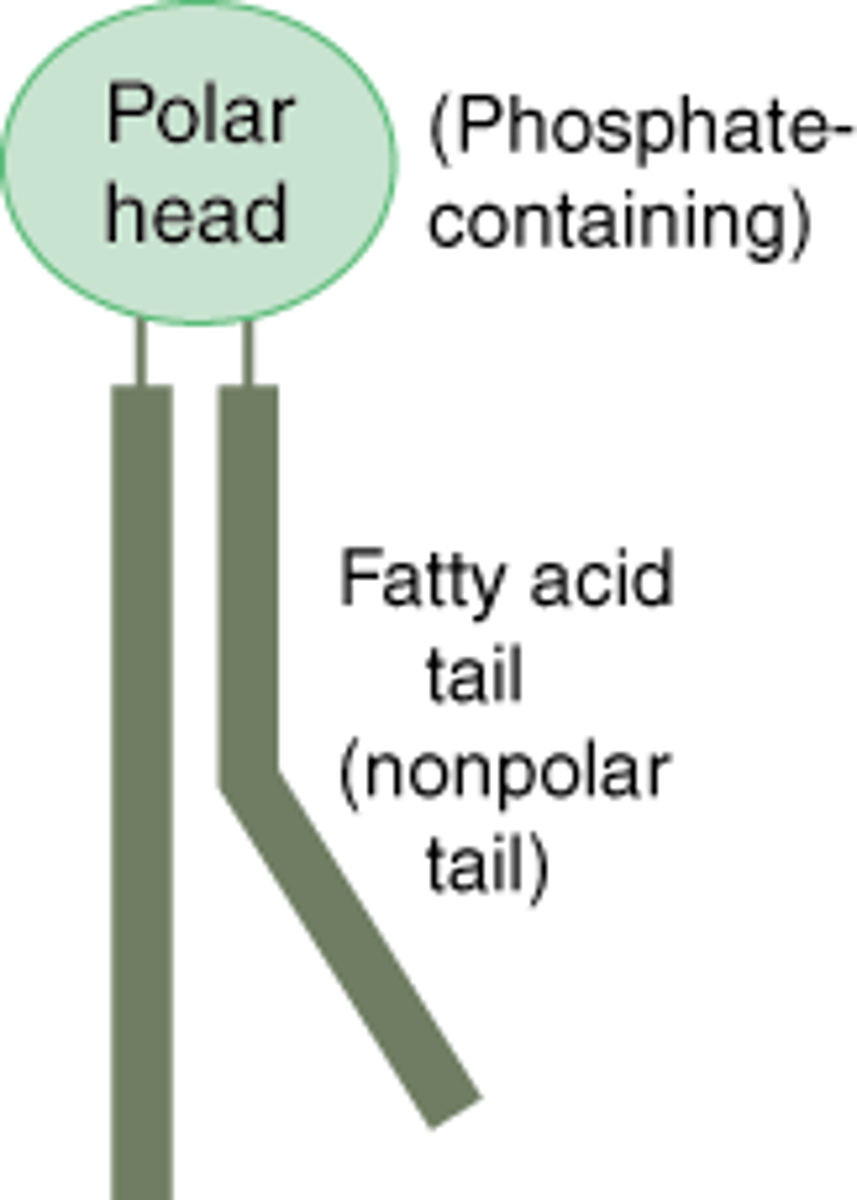
Hydrophilic (Definition)
"Water loving"
Hydrophobic (Definition)
"Water fearing"
Hydrophilic (Structure)
Phosphate head of phospholipid
Hydrophobic (Structure)
Fatty acid tails of phospholipid
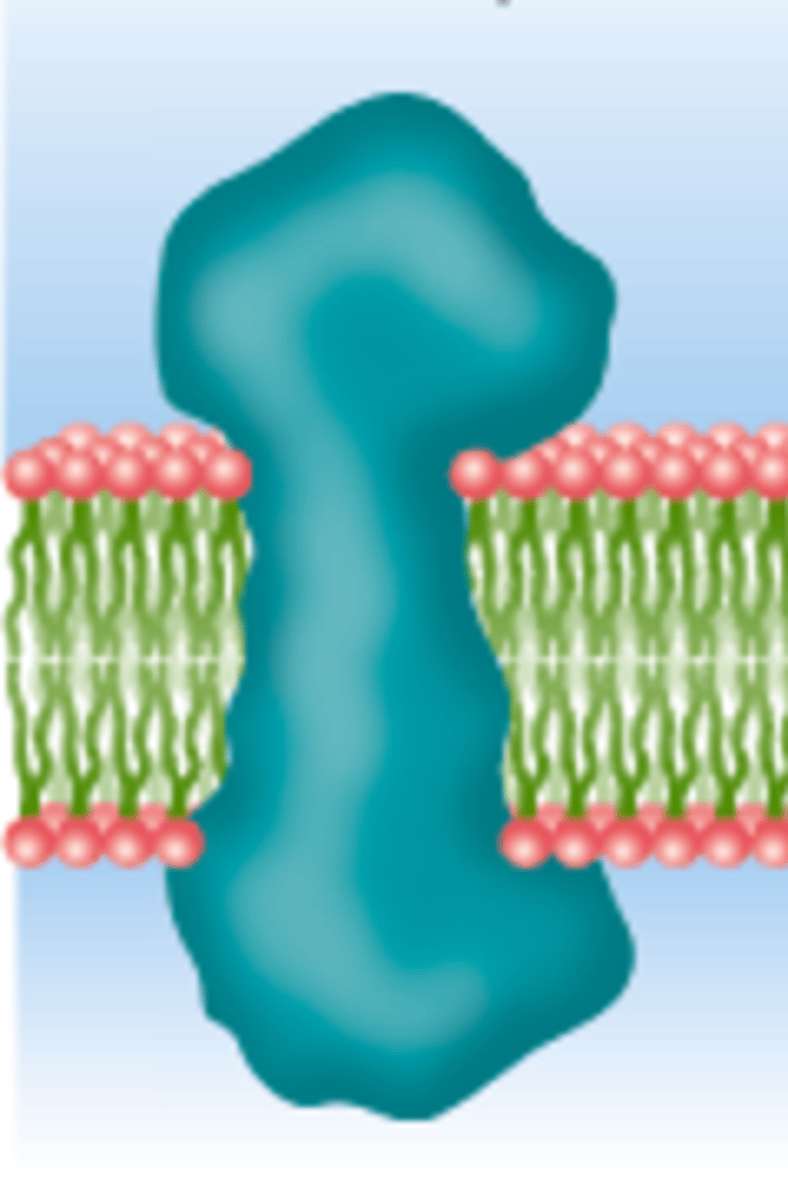
Transmembrane Protein
A protein that spans the entire phospholipid bilayer
Glycoprotein (Definition)
Membrane proteins that acts as a marker protein; contain a carbohydrate (sugar) chain; often serve as markers that help identify the cell and aide in cell-to-cell recognition
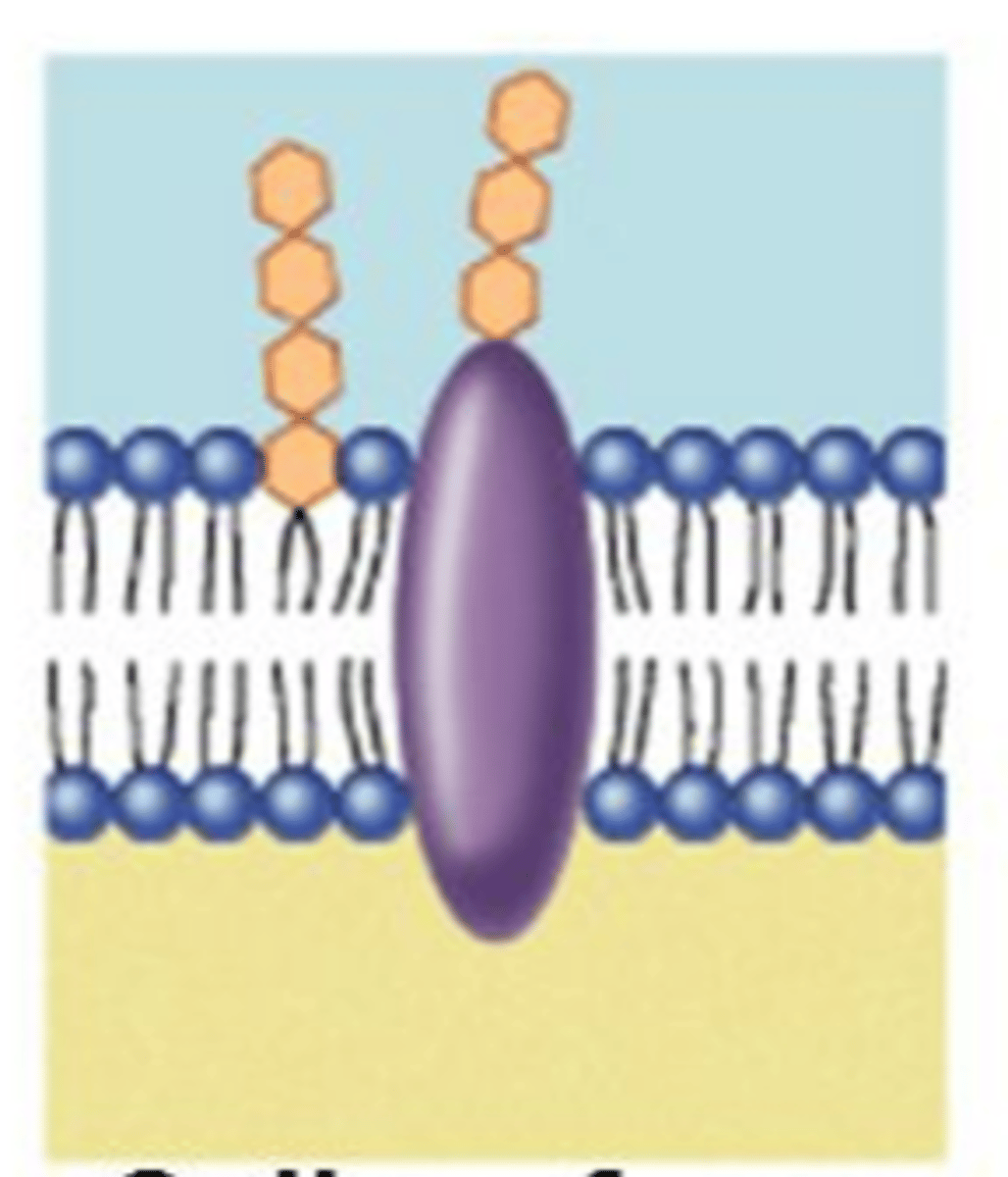
Receptor Proteins (Definition)
Membrane proteins that are involved in intracellular communication and cell-to-cell signalling
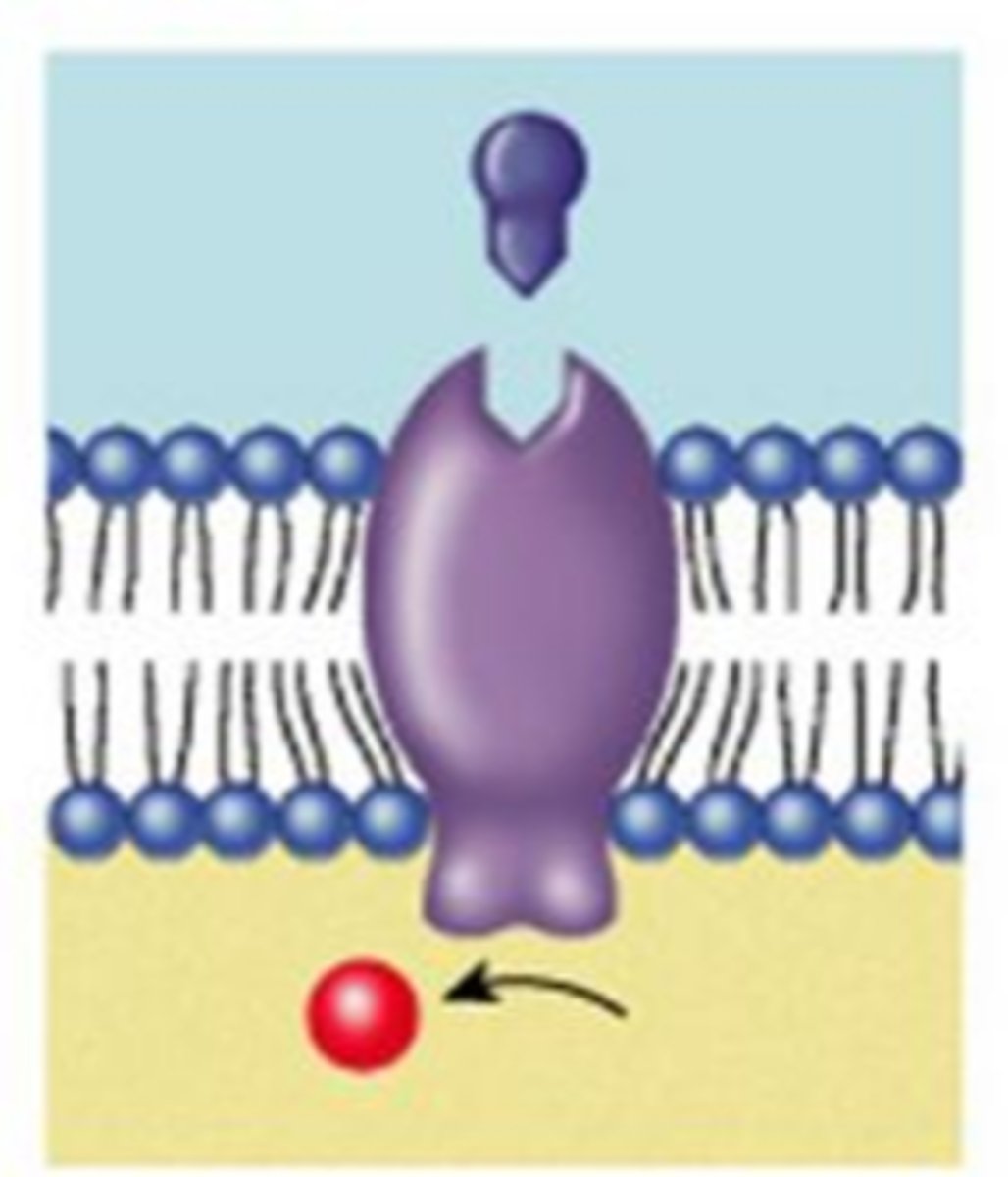
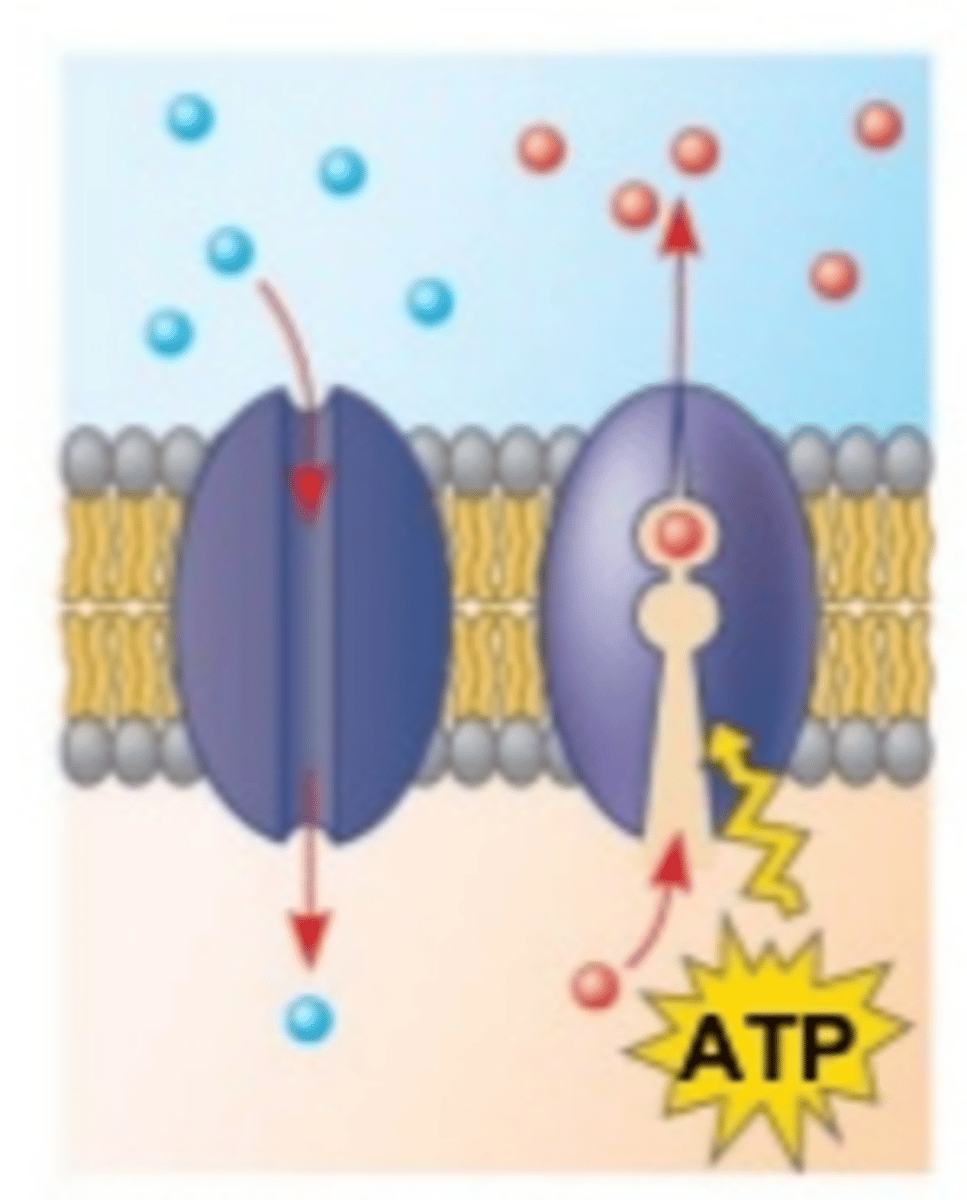
Channel Proteins (Definition)
Membrane protein that allows for the transport of polar and charged substances (usually ions) to diffuse across membranes
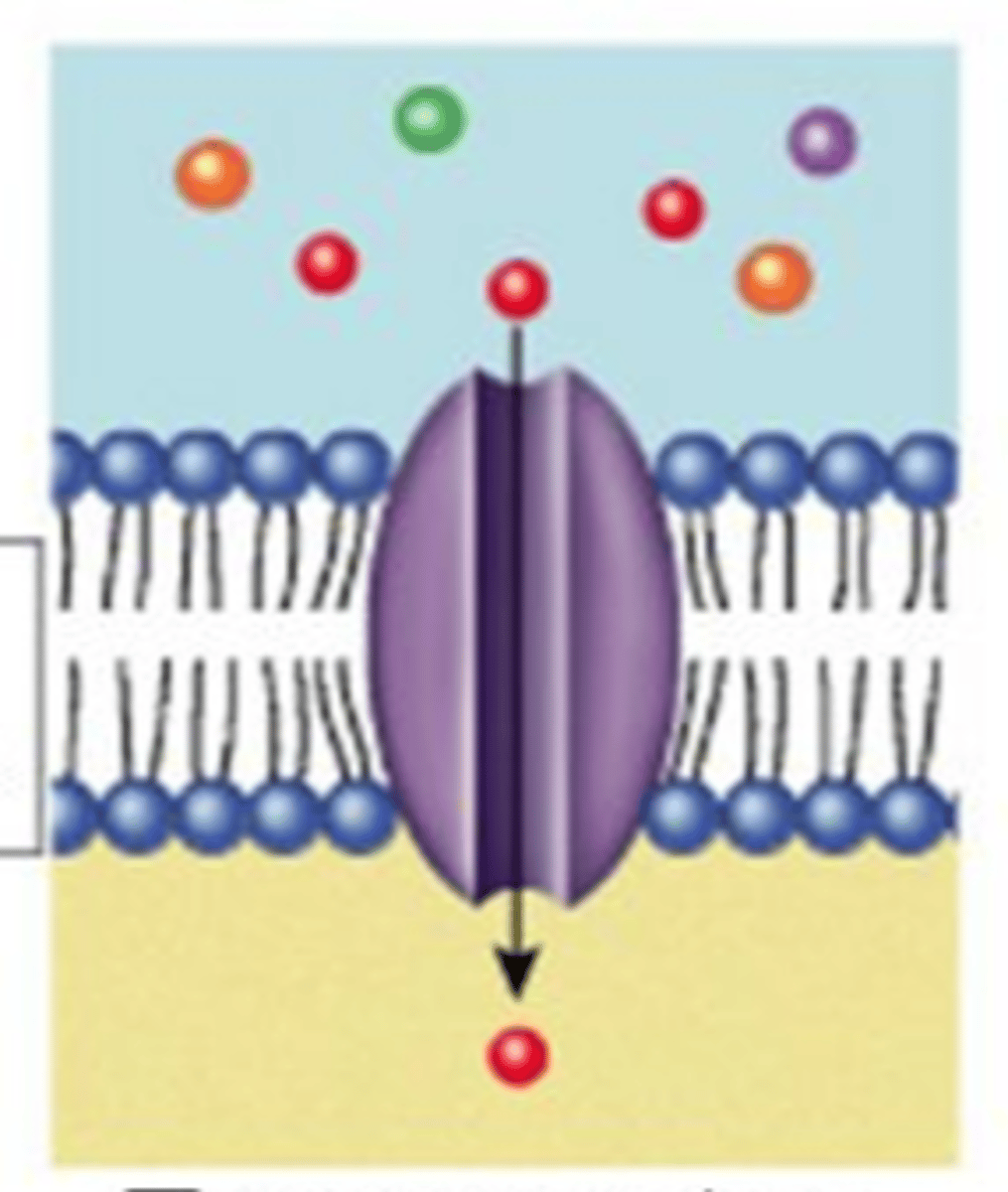
Transport Carrier Protein (Definition)
Membrane protein that has a binding site for a specific solute like glucose, ions, or amino acids; constantly flip between two states so that the site is alternately open to opposite sides of the membrane
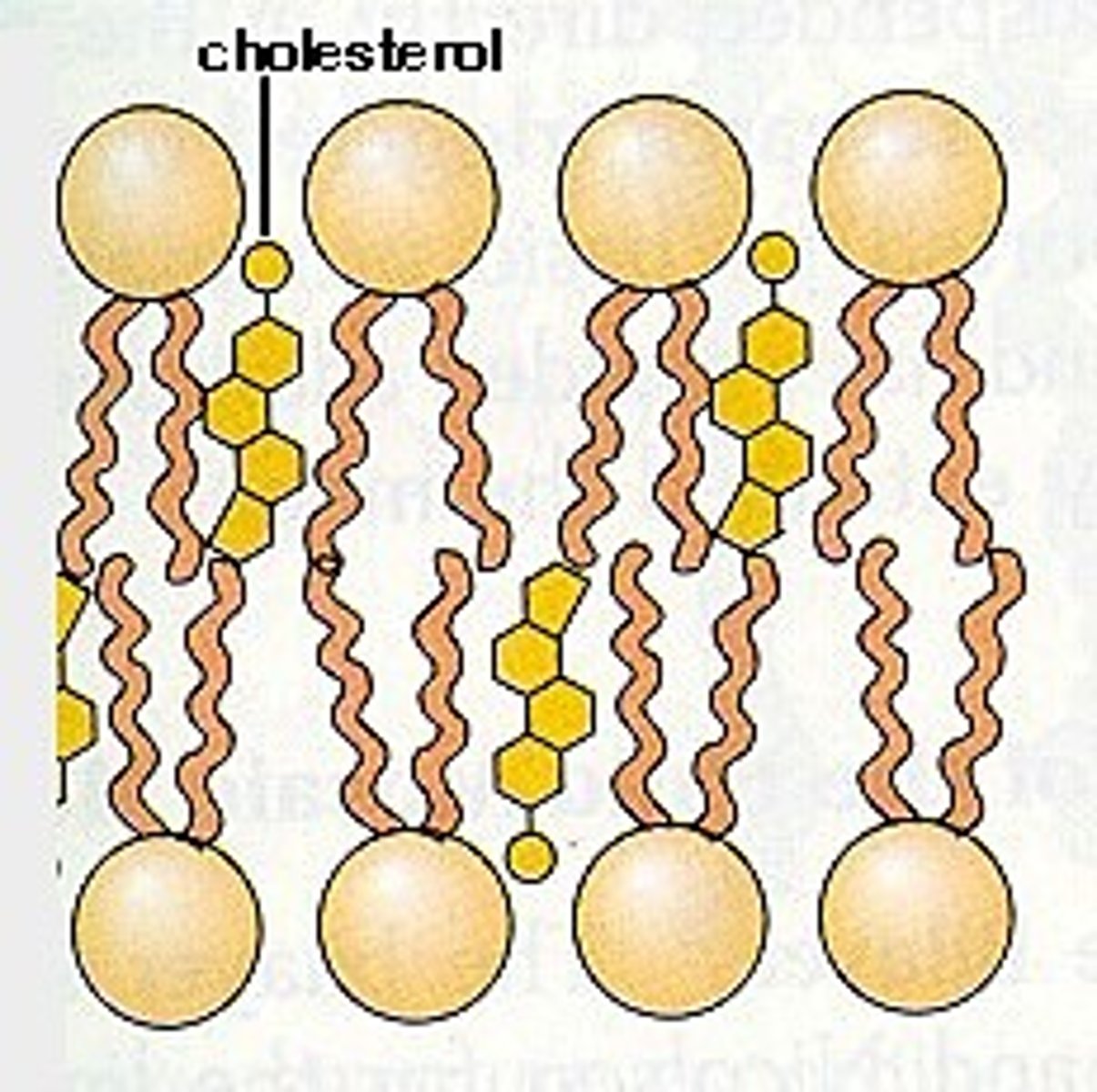
Cholesterol (Structure)
A lipid made of four fused rings and one fatty acid chain
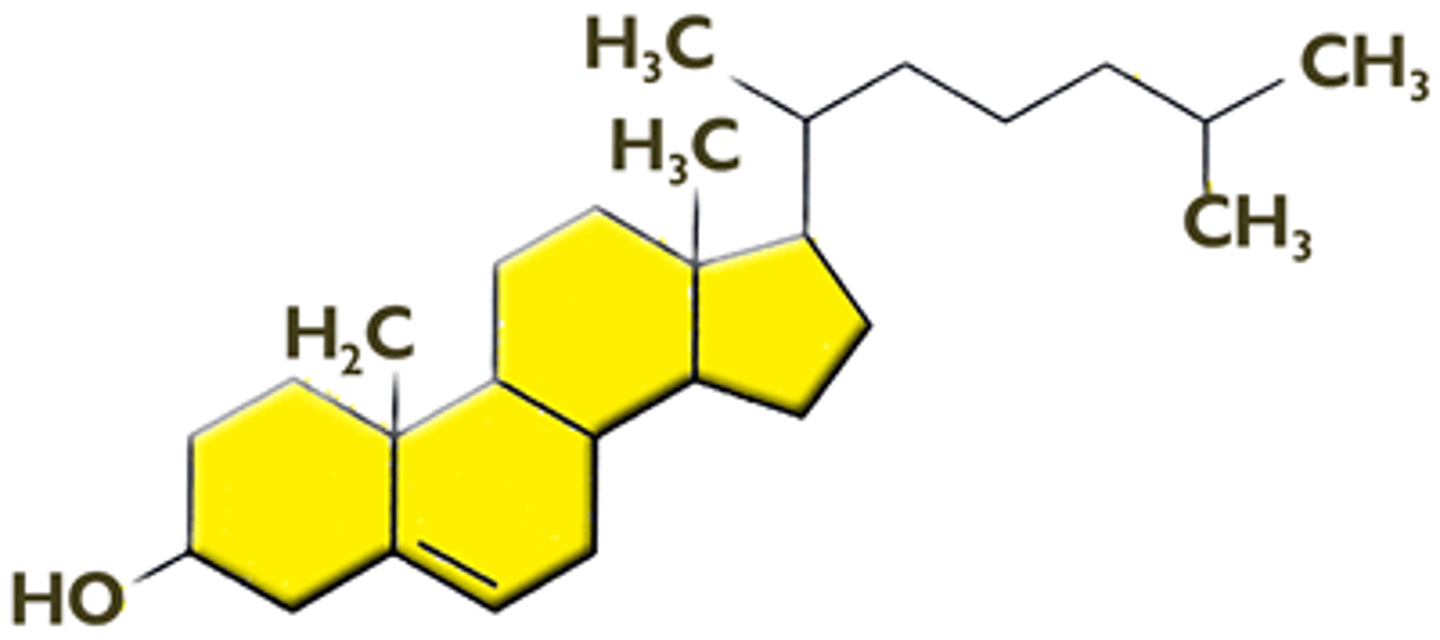
Cholesterol (Function)
A steroid found in the membrane that stabilizes the phospholipids that make up the membrane by preventing the fatty acid chains from sticking together