Anatomy & Physiology (LAB 2b) - Connective & Epithelial Tissue; repair
1/53
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Connective tissue
the most abundant and widely distributed of primary tissues
- function in binding and support, protecting, insulating, storing reserve fuel, and transporting substances (blood)
- 4 types: connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, & blood
What makes connective tissue different from the others?
- all have common embryonic origin called mesenchyme tissue
- have varying degrees of vascularity
- cells are suspended/embedded in extracellular matrix (ECM) that supports cells so they can bear weight, withstand tension, endure abuse
What are the 3 elements of connective tissue?
- Ground substance
- Fibers
- Cells
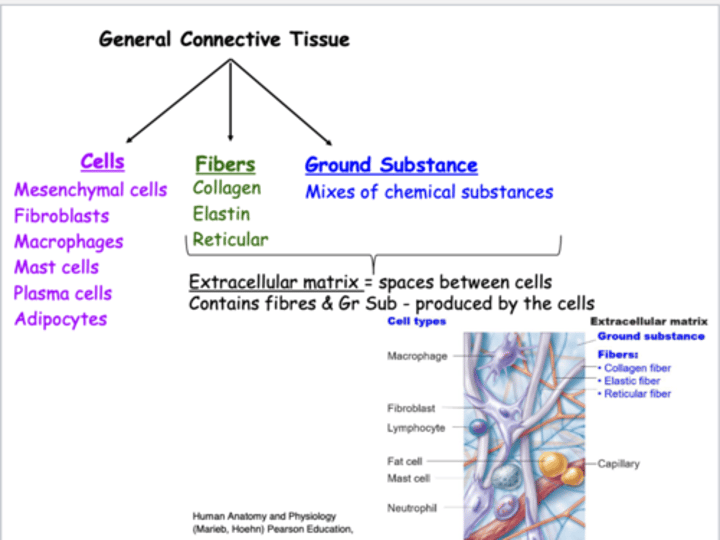
Ground substance
unstructured gel-like material that fills space between cells
- medium thru which solutes diffuse between blood capillaries and cells
Fibers
3 types provide support
- collagen
- elastic
- reticular
Collagen
strongest and most abundant type. tough; provides high tensile strength
Elastic fibers
networks of long, thin, elastin fibers that allow for stretch and recoil
Reticular
short, fine, highly branched collagenous fibers (different chemistry and form from collagen fibers). branching forms networks that offer more "give"
"-blast" cells
immature form of cell that actively secretes ground substance and ECM fibers
- fibroblasts found in connective tissue proper
- chondroblasts found in cartilage
- osteoblasts found in bone
- hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow
"-cyte" cells
mature, less active form of "-blast" cell that now becomes part of and helps maintain health of matrix
Fat cells
store nutrients
Leukocytes
white blood cells. tissue response to injury
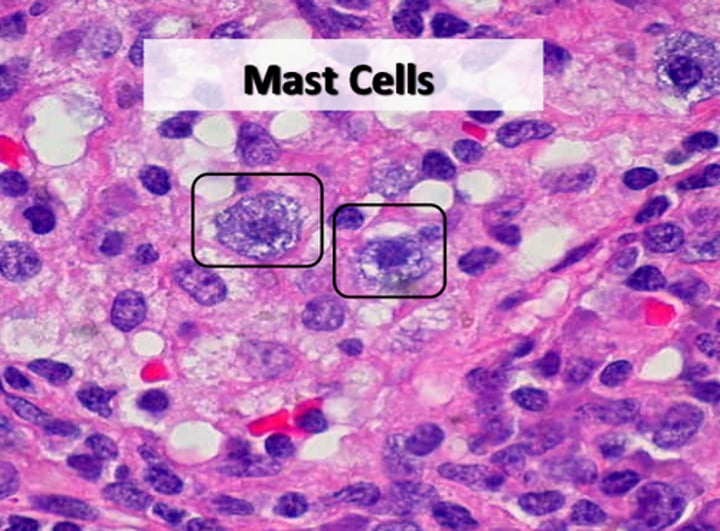
Mast cells
initiate local inflammatory response against foreign microorganisms they detect
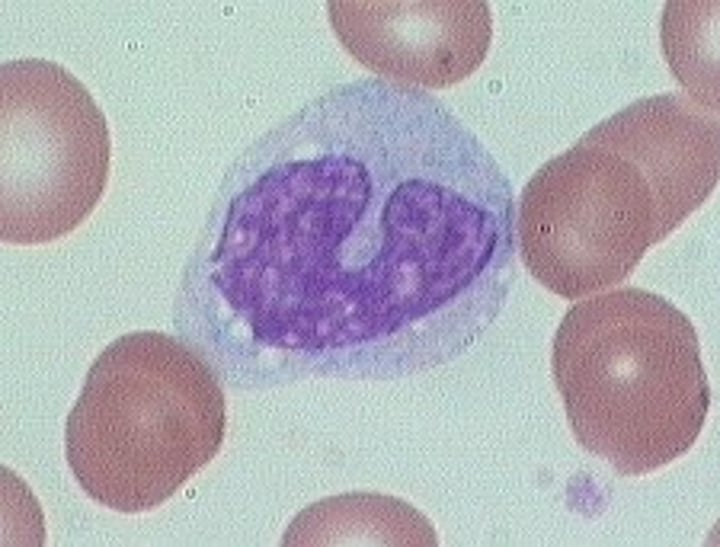
Macrophages
phagocytic cells that "eat" dead cells, microorganisms; function in immune system
Connective tissue proper
the MOST dense; 2 subclasses
- dense CT
- loose CT
Dense CT
regular, irregular, elastic
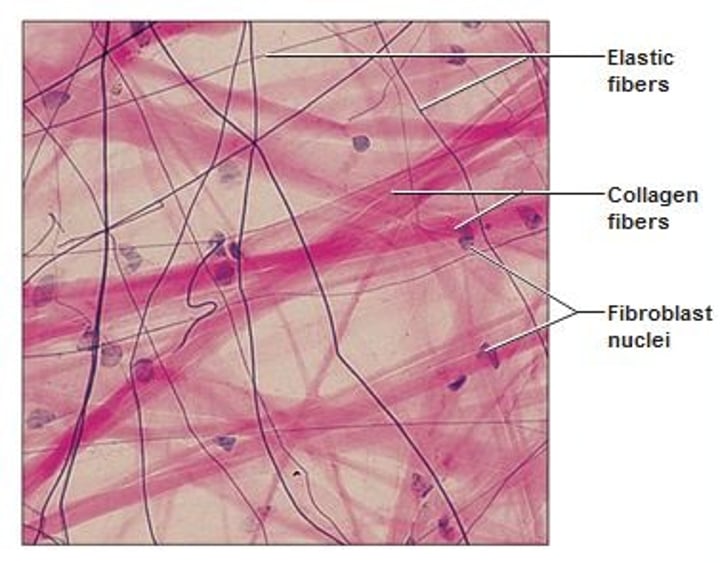
CT Proper - Dense Regular CT
- very high tensile strength
- closely packed bundles of thick collagen fibers run parallel to direction of pull
- poorly vascularized
- very few cells and ground substance, mostly fibers
- location: tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
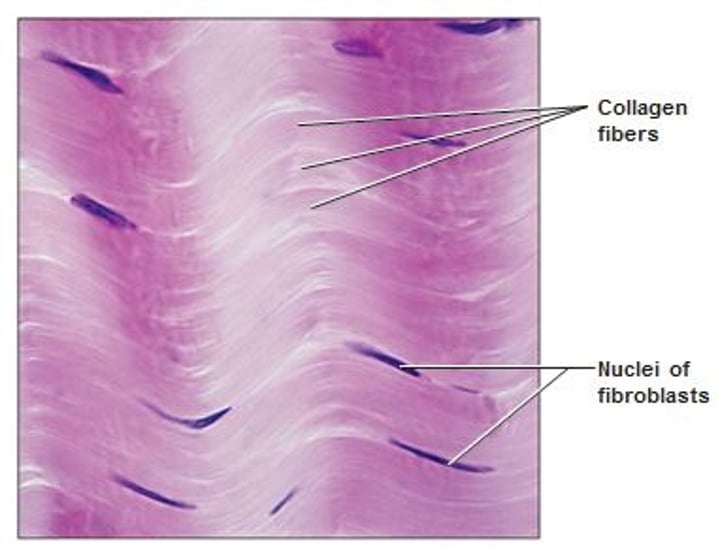
CT Proper - Dense Irregular CT
- resists tension from many directions
- bundles of collagen are thicker and irregularly arranged
- provides structural strength
- location: fibrous capsules of organs & joints, dermis of skin, submucosa of digestive tract
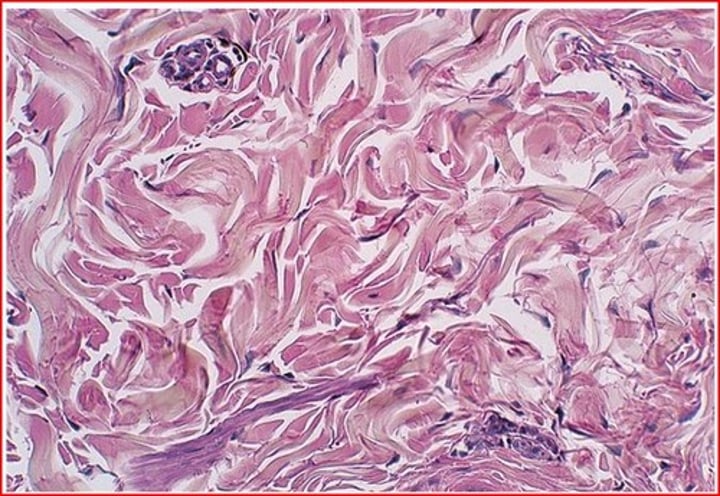
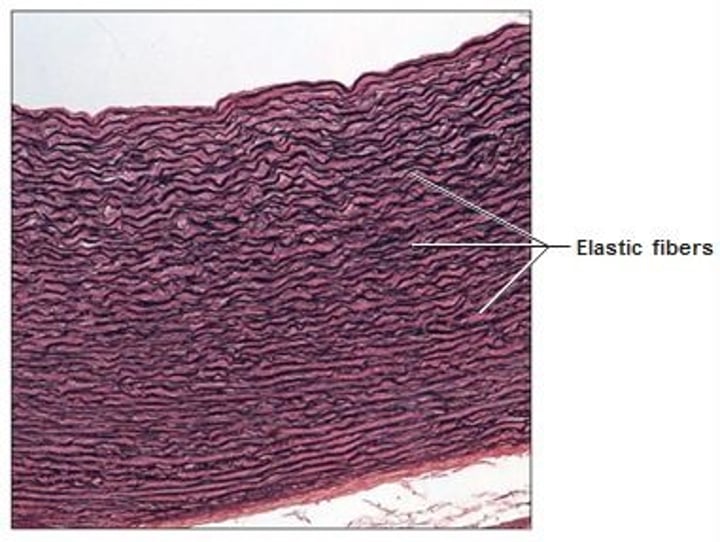
CT Proper - Elastic CT
- contain high portions of elastic fibers
- allows recoil after stretching
- location: walls of large arteries, within some ligaments, within walls of broncial tubes
Loose CT
areolar, adipose, reticular
CT Proper - Areolar CT
- most widely distributed since it supports and binds other tissues
- loose fibers allow for increased ground substance, which can act as water reservoir by holding more interstitial fluid
- gel-like matrix with macrophages, fibroblasts, & mast cells
- wraps & cushions organs, important in inflammation, & holds and conveys tissue fluid
- location: under epithelia, forming lamina propria, surrounds capillaries, packages organs
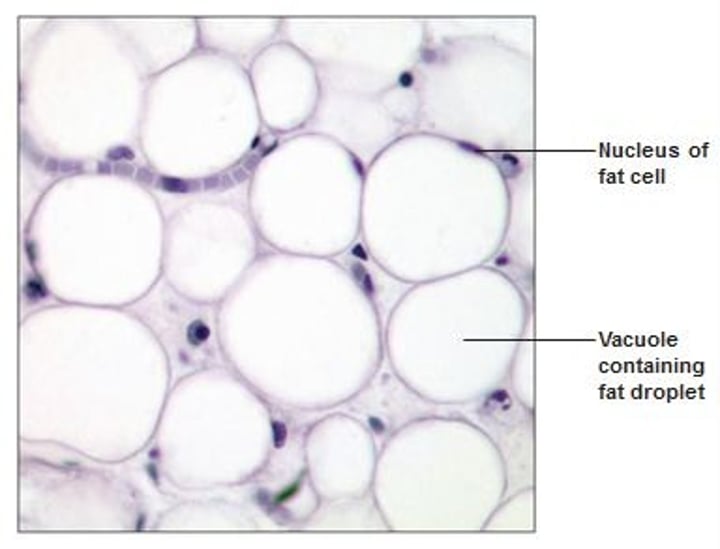
CT Proper - Adipose CT
- closely packed adipocytes, or fat cells, have nucleus pushed to the side by large fat droplet
- richly vascularized & greater nutrient storage
- provides reserve food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
- location: subcutaneous layer, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen, & in breasts
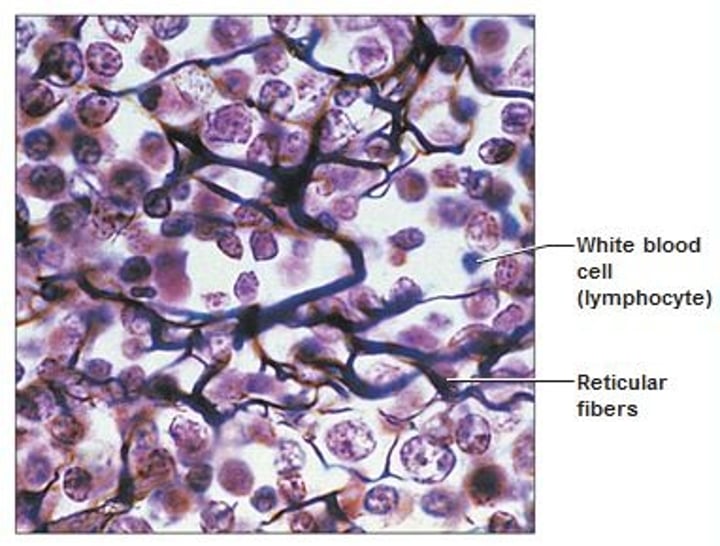
CT Proper - Reticular CT
- resembles areolar tissue, but fibers are thinner reticular fibers
- fibroblast cells called reticular cells secrete reticular fibers made of thin collagen
- fibers form soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types like white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
- location: lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, & spleen)
Cartilage Connective Tissue
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
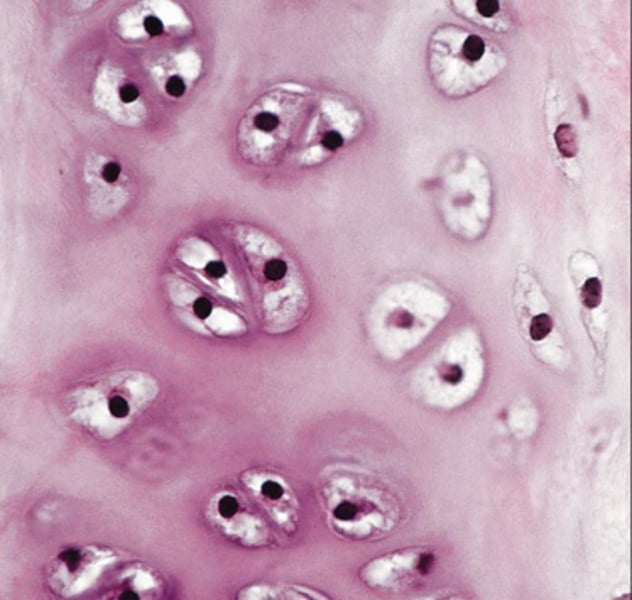
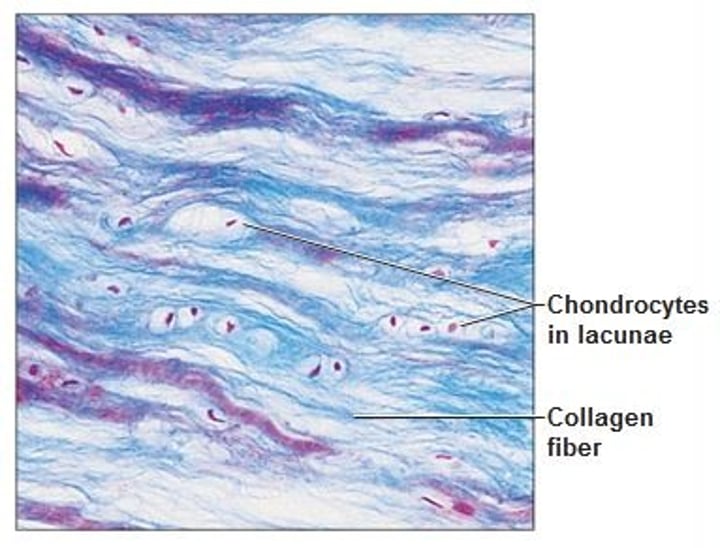
Hyaline Cartilage CT
- most abundant; "gristle"
- chondroblasts produce the matrix and when mature (as chondrocytes) lie in lacunae
- supports & reinforces; serves as resilient cushion; resists compressive stress
- appears as shiny bluish glass
- location: tips of long bones, nose, trachea, larynx, and cartilage of the ribs • Function: cushion and protect
Elastic Cartilage CT
- similar to hyaline but with more elastic fibers
- great tolerance to repetitive bending; stretchable
- maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
- location: ears and epiglottis
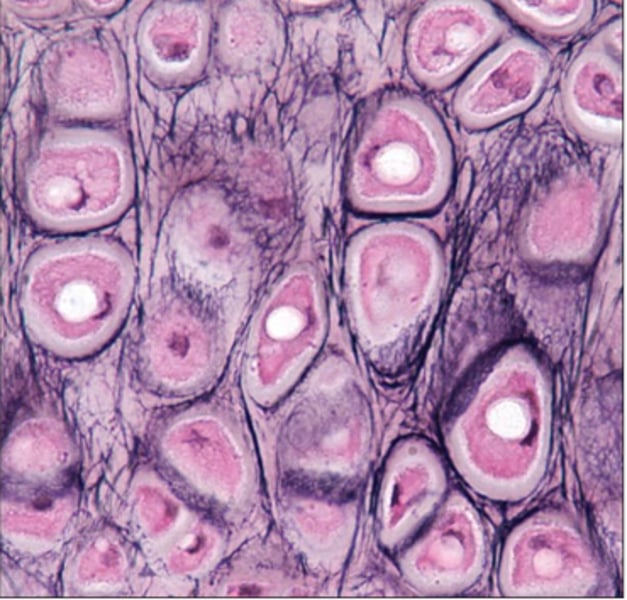
Fibrocartilage CT
- mostly thick collagen fibers
- strongest cartilage; allows it to absorb compressive shock
- withstands heavy pressure
- location: intervertebral disc, knee, symphysis
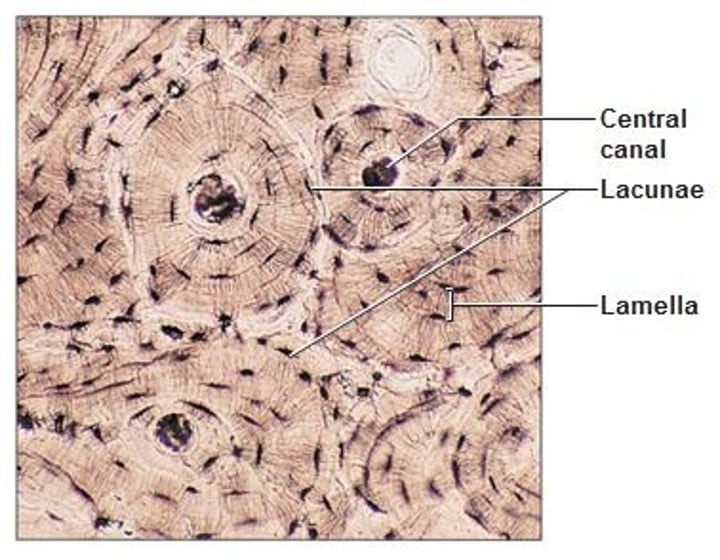
Bone CT
- aka osseous tissue
- supports and protects body structures
- lamella: repeating pattern of collagen fibro architecture
- highly vascularized
- location: bones
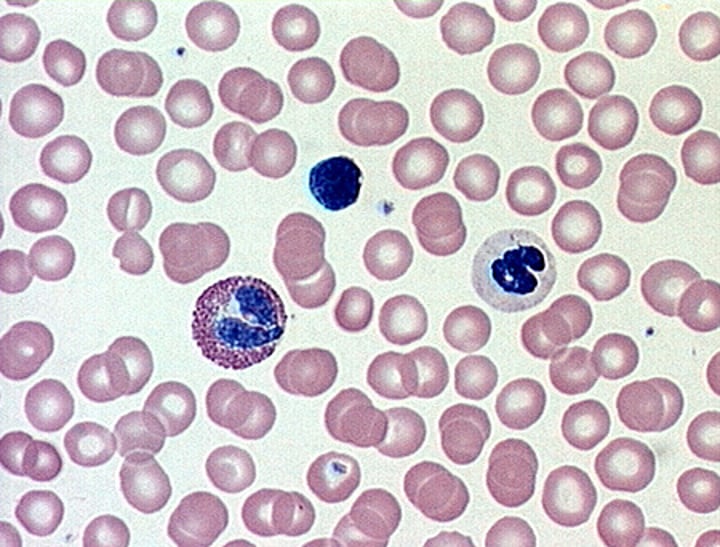
Blood CT
- most atypical connective tissue because it's fluid
- red blood cells are most common cell type also containg white blood cells & platelets
- fibers are soluble proteins that precipitate during blood clotting
- transports respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
- location: contained within blood vessels
Epithelial Tissue
sheet of cells that covers body surfaces or cavities
- main functions: protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception
Glandular Epithelia
secretory tissue in glands (i.e. salivary glands)
Covering and lining epithelia
on external and internal surfaces (i.e. skin)
Five distinguishing characteristics of epithelial tissue
- polarity
- specialized contacts
- supported by connective tissues
- avascular, but innervated
- regeneration
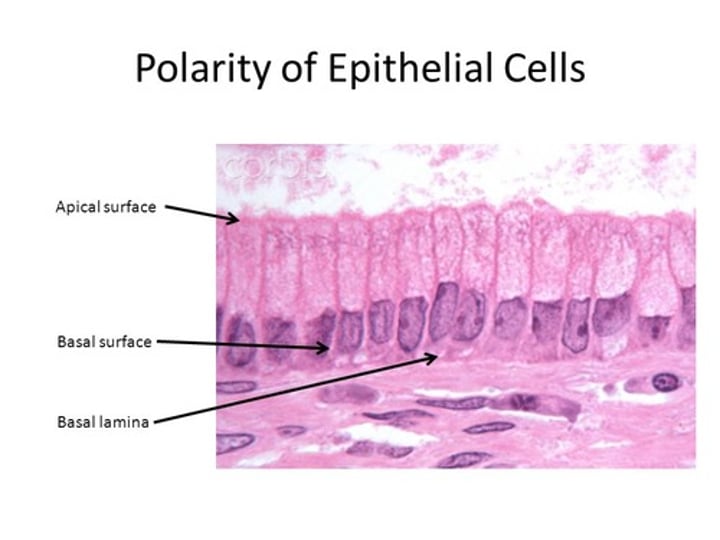
Polarity
top & bottom
- top: apical surface, smooth, but some have specialized fingerlike projections called microvilli
- bottom: basal surface, attaches to basal lamina, an adhesive sheet that holds basal surface of epithelial cells to underlying cells
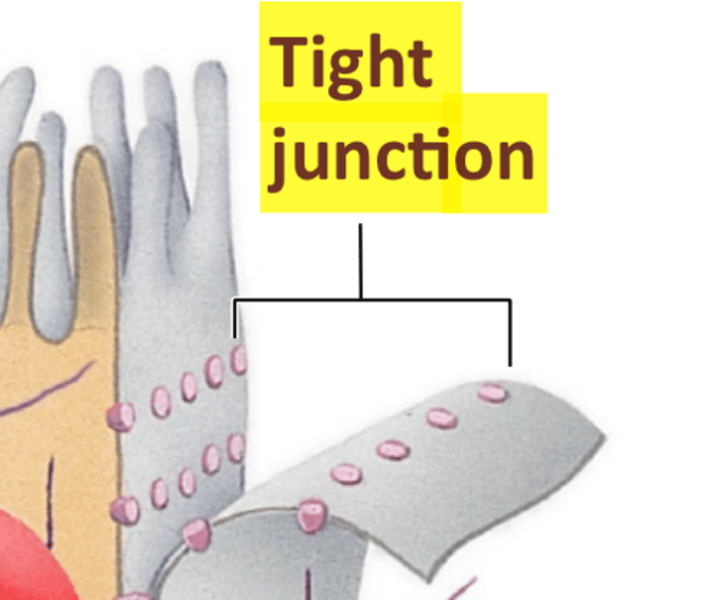
Specialized contacts
epithelial tissues need to fit closely together, so specialized contact points bind adjacent epithelial cells together like tight junctions & desmosomes
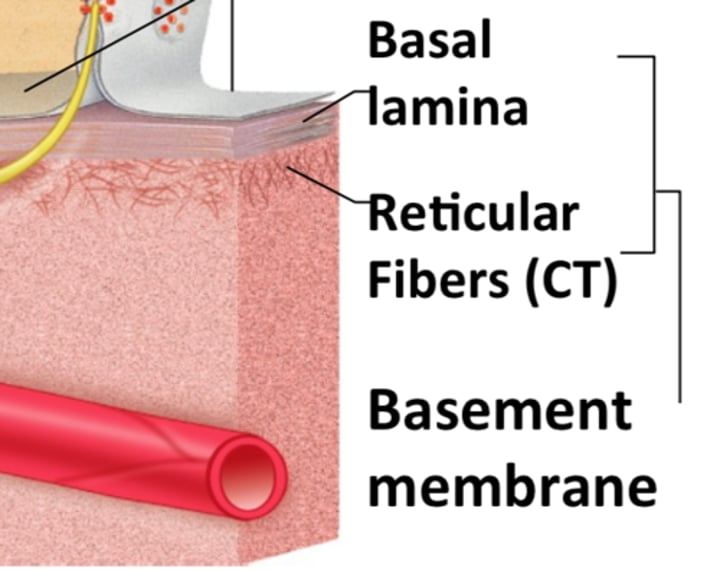
Supported by connective tissues
all epithelial sheets are supported by connective tissue referred to as basement membrane that reinforces epithelial sheet, resists stretching and tearing, & defines epithelial boundary
Avascular, but innervated
no blood vessels are found in epithelial tissue, so must be nourished by diffusion from underlying connective tissues
Regeneration
- high regenerative capacities
- stimulated by loss of apical-basal polarity and broken lateral contacts

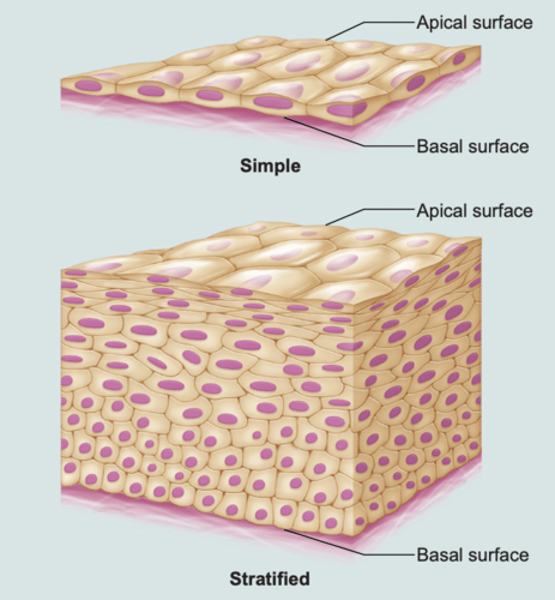
Classification of Epithelia - first name
indicates # of cell layers
- simple epithelia are a single layer thick & involved in absorption, secretion, or filtration processes
- stratified epithelia are 2+ layers thick & involved in protection
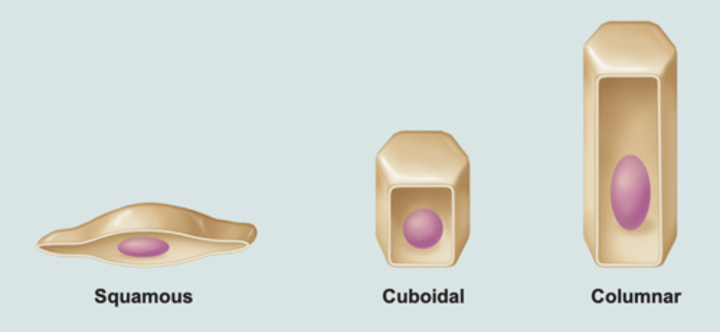
Classification of Epithelia - second name
indicates shape of cells
- squamous: flattened and scale-like
- cuboidal: box-like, cube
- columnar: tall, column-like
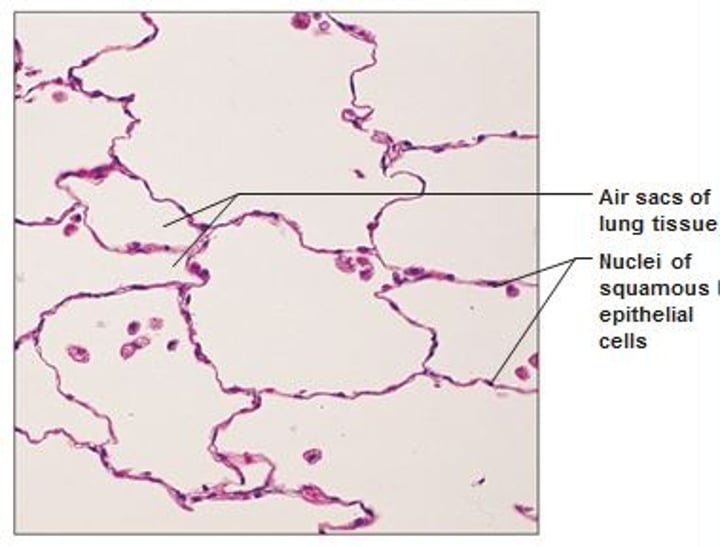
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- cells are flattened laterally, the simplest
- function where rapid diffusion is priority (i.e. kidneys, lungs)
- allows materials to pass by diffusion & filtration in sites where protection isn't important
- secretes lubricating substances in serosae (linings of ventral body cavity)
- location: kidney glomeruli; air sacs of lungs; lining of heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels; serosae
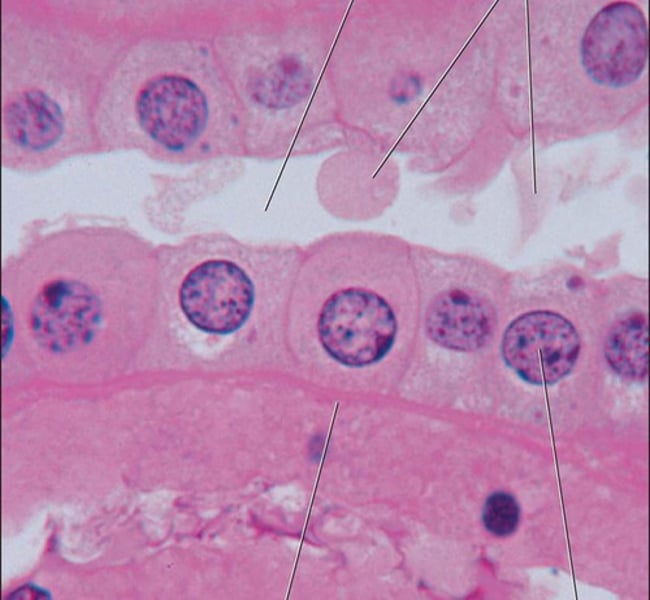
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- single layer of cells
- involved in secretion & absorption
- forms walls of smallest ducts of glands & many kidney tubules
- location: kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface
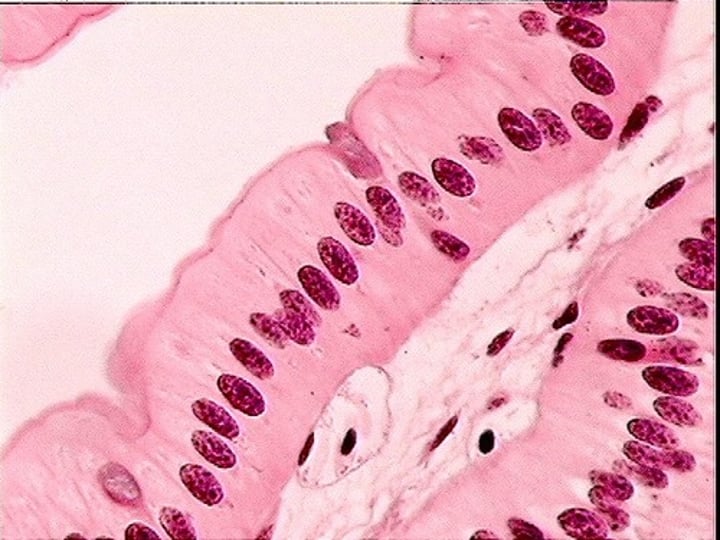
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- single layer of tall, closely packed cells in which some cells have microvilli, & some have cilia (moves mucus) & some layers contain mucus-secreting goblet cells
- involved in absorption and secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances
- location: digestive tract, gallbladder, ducts of some glands, bronchi, and uterine tubes
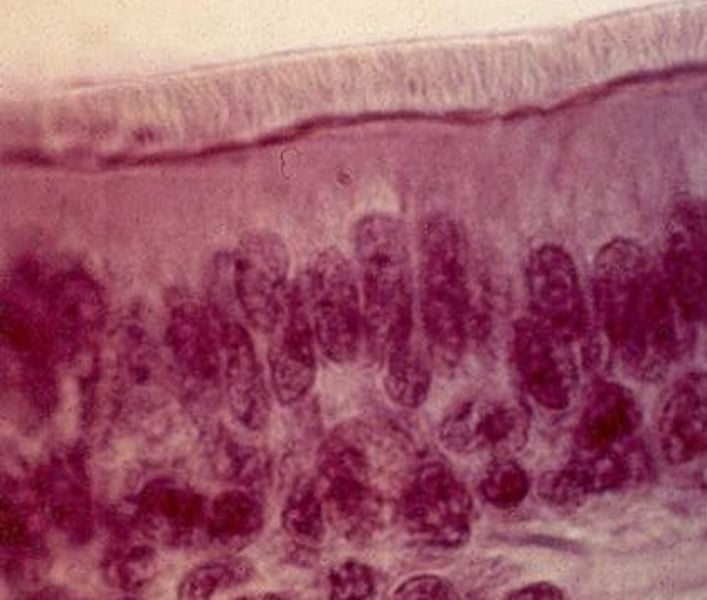
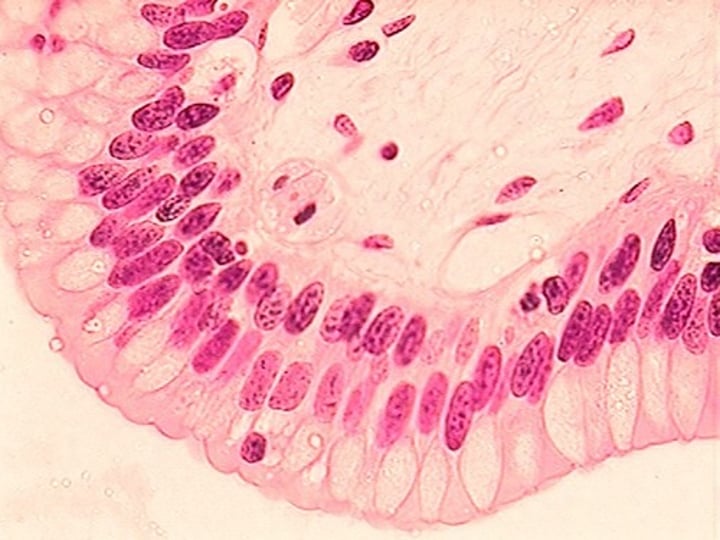
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- cells vary in height & appear to be multi-layered & stratified, but tissue is in fact single-layered simple epithelium
- many cells are ciliated
- secretion, particularly of mucus, & also in movement of mucus via ciliary sweeping action
- location: upper respiratory tract, ducts of large glands, and tubules in testes
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- more durable than simple epithelia because protection is the major role
- two or more layers of cells
- new cells regenerate from below
- location: areas of high wear & tear, keratinized cells found in skin; nonkeratinized cells are found in moist linings
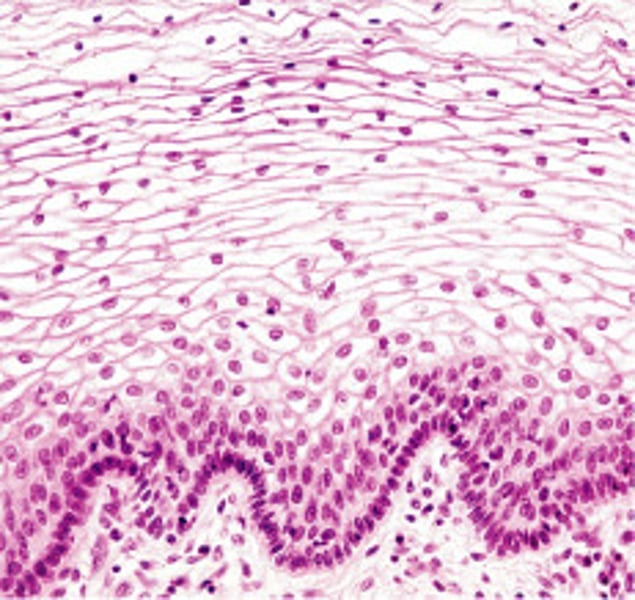
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
- quite rare
- form ducts of large glands
- location: sweat, mammary glands and esophageal glands
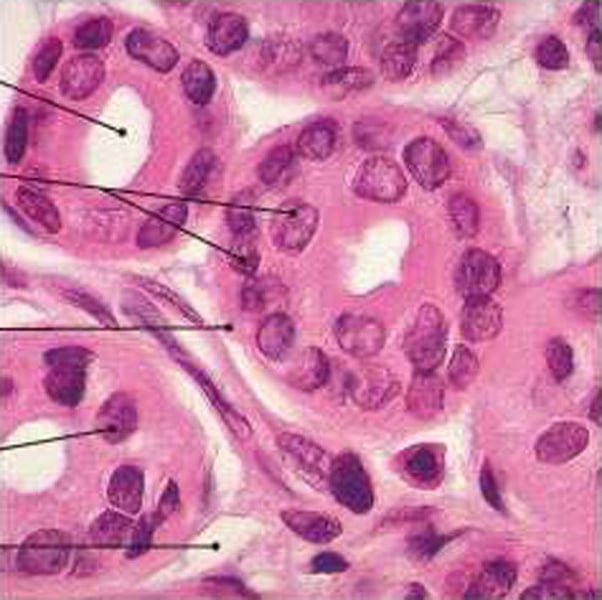
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
- quite rare
- location: pharynx, in male urethra, and lining some glandular ducts
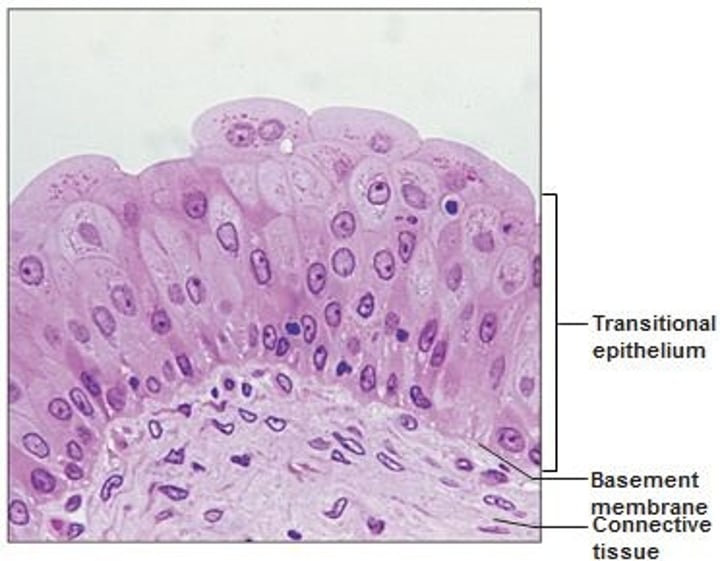
Transitional Epithelium
- resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal
- forms lining of hollow urinary organs
- ability of cells to change shape when stretched allows for increased flow of urine &, for bladder, more storage space
- lines the ureters, bladder, and part of the urethra
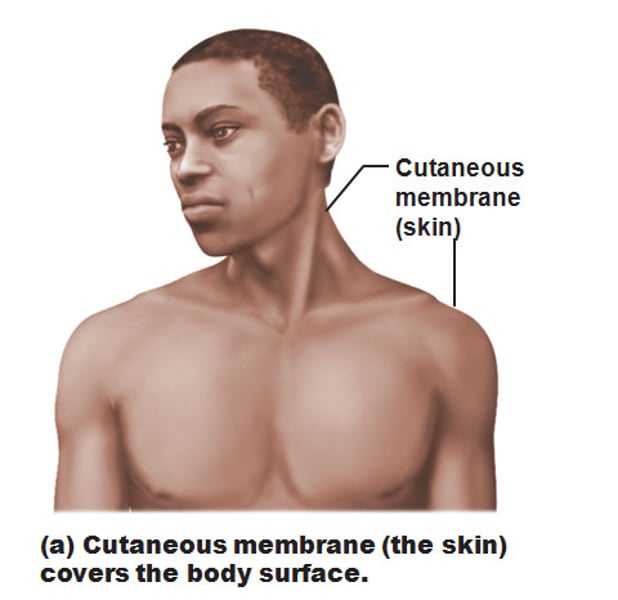
Cutaneous Membranes
- another name for skin
- keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) attached to a thick layer of connective tissue (dermis)
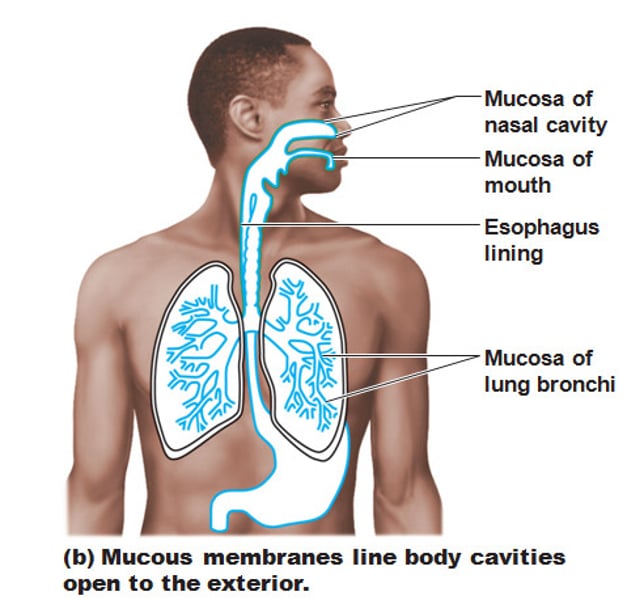
Mucous Membranes
- line body cavities that're open to exterior (i.e. digestive, respiratory, urogenital tracts)
- moist membranes bathed by secretions
- may secrete mucus
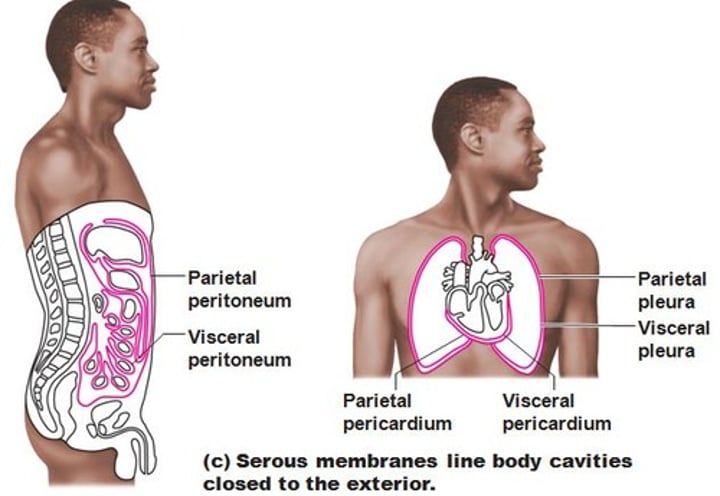
Serous Membranes (aka serosae)
constructed from simple squamous epithelium (called mesothelium) resting on thin areolar connective tissue
Tissue Repair Step 1
Inflammation sets stage
- release of inflammatory chemicals causes dilation of blood vessels & increase in blood vessel permeability
- clotting of blood occurs
Tissue Repair Step 2
Organization restores blood supply
- begins as the blood clot is replaced with granulation tissue (new capillary-enriched tissue)
- epithelium begins to regenerate
- fibroblasts produce collagen fibers to bridge the gap until regeneration is complete
- any debris in area is phagocytized
Tissue Repair Step 3
Regeneration and fibrosis effect permanent repair
- scab detaches
- fibrous tissue matures
- epithelium thickens and begins to resemble adjacent tissue
- results in a fully regenerated epithelium with underlying scar tissue, which may or may not be visible